Analys
SIP Nordic – Råvaruguiden – juni 2012
 Råvaror och Grexit
Råvaror och Grexit
Det spekuleras vilt i medierna om ett potentiellt Grekiskt utträde ur EU, även kallat Grexit. Det debatteras fram och tillbaka om hur troligt detta scenario är. Frågan jag ställer mig är hur detta kommer påverka råvaror och i synnerhet ädelmetallen guld.
De senaste veckorna har debatten kring den grekiska krisen eskalerat igen. Valet för några veckor sedan, där politikerna misslyckades att sätta ihop en regering, ökade oroligheten för att Grekland inte kommer att kunna fullfölja de budgetåtaganden som den förra regeringen klubbat igenom. Nyvalet i mitten av juni kommer att vara mycket viktigt, inte enbart för den europeiska ekonomin utan också för den framtida utvecklingen för råvaror.
 Man kan lugnt säga att ECB har en tuff sommar framför sig med en potentiell Grexit men också sämre utsikter för bland annat Spanien och Italien.
Man kan lugnt säga att ECB har en tuff sommar framför sig med en potentiell Grexit men också sämre utsikter för bland annat Spanien och Italien.
‘Att ECB måste trycka nya pengar är nog inte en dålig gissning, något som kommer att kunna straffa euron och som i sin tur kommer att påverka råvarorna.
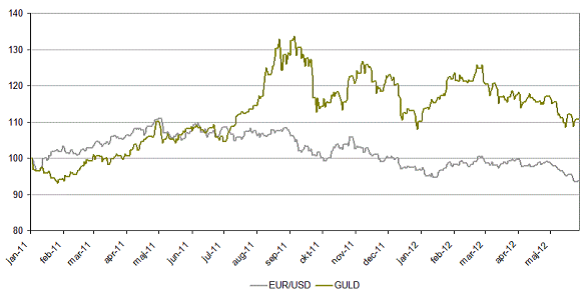
En svagare euro kontra dollarna har historiskt sett en negativ påverkan på bland annat ädelmetallerna guld och silver. Många kommer säkert ihåg förra årets skriverier om USAs dåliga ekonomi som fick dollarna att falla och guldet att klättra upp till nivåer kring 1900$/oz. Nu ser vi det omvända.
Den europeiska krisen har till och med fått de allra mest pessimistiska att tro på en EUR/USD kurs kring 1.00 (nu kring 1.25). Det är alltså ingen dålig gissning att guld kan falla om EUR/USD också faller. Som bilden nedan visar har Guld haft en stark koppling till EUR/USD den senaste tiden.
Detta grundar sig i att om dollarn blir starkare jämfört med andra valutor blir guld dyrt att investera i för utländska investerare. Självklart är det så att är många fler faktorer än dollarkursen som styr guldpriset men jag kommer i alla fall hålla koll på kursen den närmaste tiden.
Råvaror – Energi
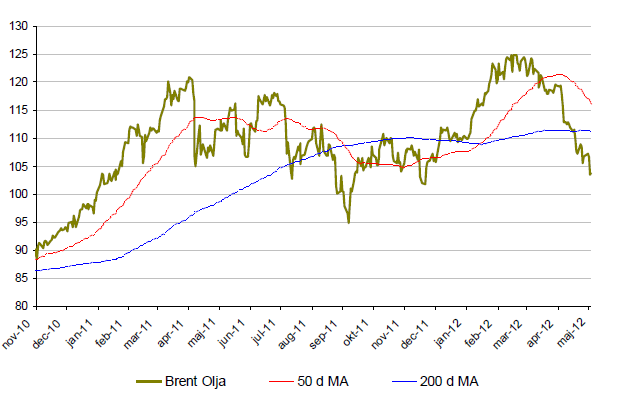
Brent olja
- Brentoljan är nu för första gången i år nere på negativa siffror. Drygt 3% ned för året.
- Under maj månad har Brent-oljan tappat nästan 13%.
- En viktig faktor är den stärkta dollarn kontra andra valutor vilket pressar priset på oljan.
- Rekordhöga lagernivåer driver ned priset. Oroligheterna i mellanöstern som drev upp oljepriset i början av året verkar nu vara utraderade.
- Säljare av olja blir fler och fler vilket i kombination av en stärkt dollar och höga lagernivåer kan tala för ett fortsatt fall i oljepriset. $100 är en viktig nivå.
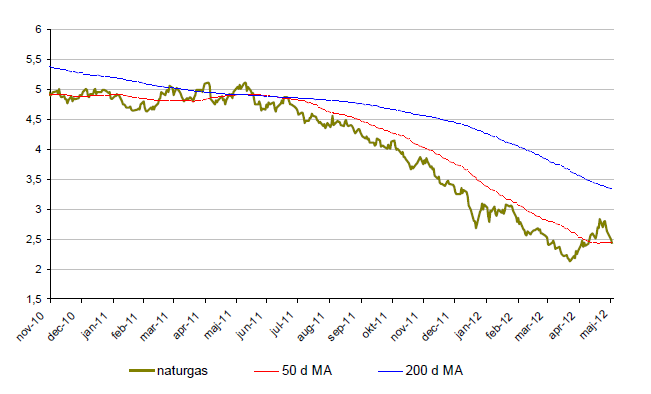
Naturgas
- Naturgas fortsätter att stiga. Under maj månad har naturgas stigit ytterligare 5%.
- Under april-maj har priset på naturgas ökat med nästan 14%.
- För året är dock naturgas ned drygt 20%.
- Lagren av naturgas väntas öka under 2012 med 26 %.
- Trots stora naturgaslager ökar priset på naturgas vilket dels kan förklaras av att temperaturen i USA spås ligga under det normala i juni och juli.
Råvaror – Metaller
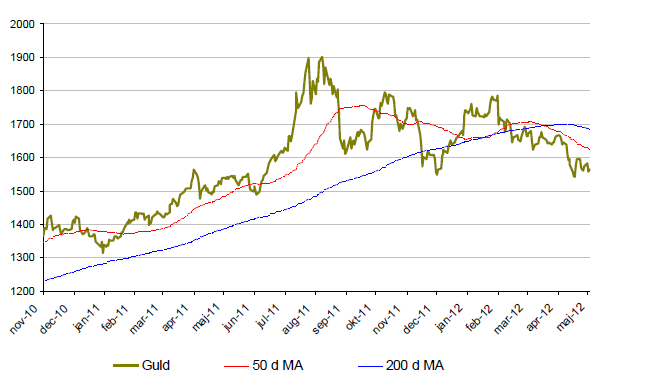
Guld
- Guld fortsätter att tappa under maj. Under maj månad är guld ned ca. 6%.
- Sedan i slutet av februari har guld tappat drygt 12% och ligger nu +-0 för året.
- Reuters publicerade i april sin guldundersökning. Där förutspås en guldkurs som fluktuerar i ett stort spann men som ligger något över dagens nivåer vid årets slut.
- En starkare dollar kontra andra valutor, med euron i spetsen, bidrar till kräftgången i guldpriset.
- Olika centralbanker med Mexiko, Ryssland och Sydkorea i spetsen köpte under 2011/2012 455 ton guld. Det största inköpet sedan 1964.
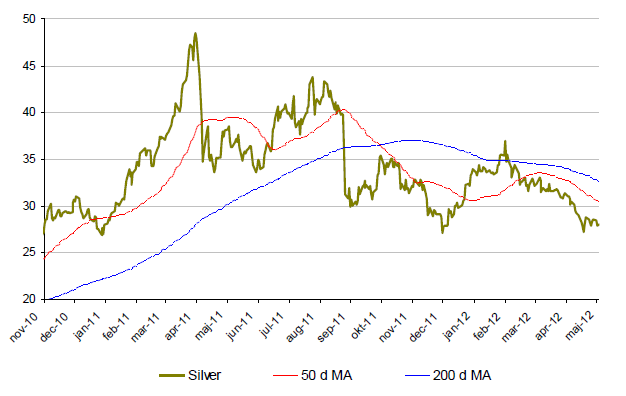
Silver
- Silvers kraftiga uppgång under jan-feb raderades under maj månad.
- Efter en nedgång på över 10% i maj är nu silver +-0 för året.
- Silverproduktionen väntas öka 4% under 2012.
- Överskottet av silver väntas i slutet av 2012 bli smått otroliga 5060 ton.
- Den europiska kreditkrisen i kombination med rädsla för minskad kinesisk tillväxt bidrar till de negativa sentimenten i silver.
- Att dollarn stärkts mot euron bidrar även till den fallande trenden.
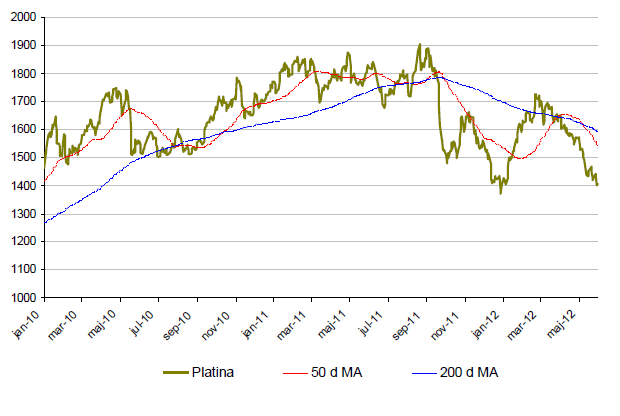
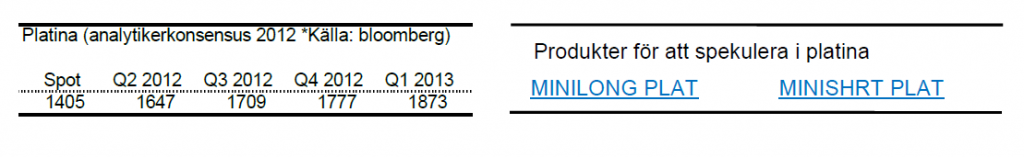
Platina
- Likt de andra ädelmetallerna är platina ned under maj månad. Nedgången stannade vid knappa 11%.
- För året är platina upp knappa 2%.
- Platina fortsätter at handlas till en billigare kurs än guld. Analytikerna spår dock att platina kommer vara den dyrare av de två vid slutet av året.
- Den starka dollarn sätter även här käpparna i hjulet på platinapriset.
- Efter strejken vid Rustenburggruvan i Sydafrika ökar nu lagren av platina samtidigt som efterfrågan minskar.
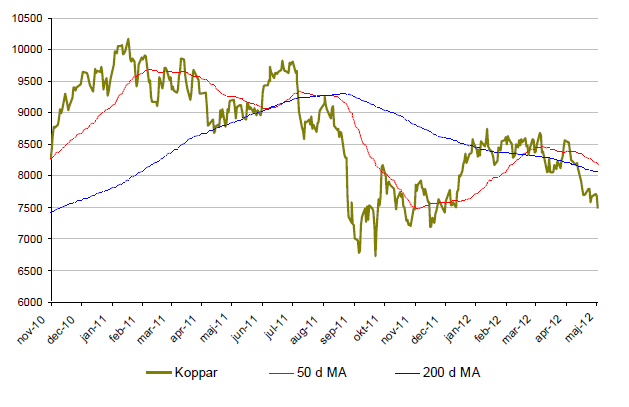
Koppar
- Kan tyckas tjatigt men även koppar tappade under maj månad. Nedgången med nästan 14% raderar ut hela årets uppgång.
- Kopparinventarierna ligger på låga nivåer och lagren av koppar räcker endast i tre veckor.
- Samma siffra väntas sjunka till 2.8 under 2013 vilket kan trycka upp kopparpriset ytterligare.
- Den största risken ligger i att Kina, med 40% av världskonsumtionen, står inför en minskande tillväxt.
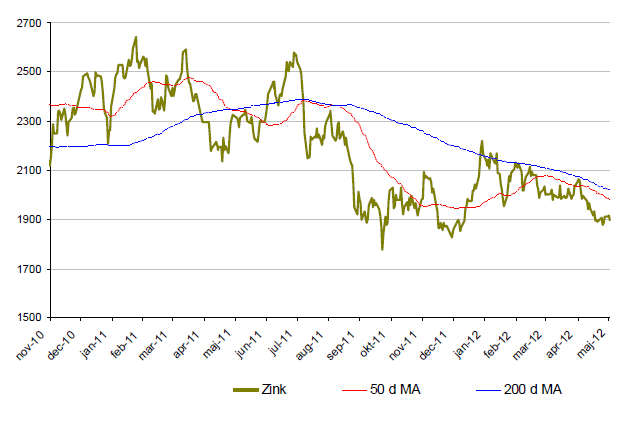
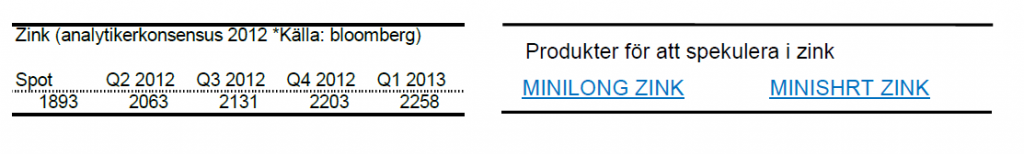
Zink
- Den tunga månaden för metaller gäller även för zink. Zink är under maj månad ned ca. 8%. För året är zink upp drygt 3,5%.
- Zinklagrena är mer än fulla vilket kan komma att pressa priset ytterligare.
- Kina är återigen en viktig bricka i spelet. En minskad tillväxt i Kina kommer troligtvis ha en betydande effekt på zinkpriset. Kina står för 43% av världens konsumtion.
- Det uppskattas att nuvarande zinktillgång skulle räcka 9,1 veckor, 2,6 veckor längre än 2011.
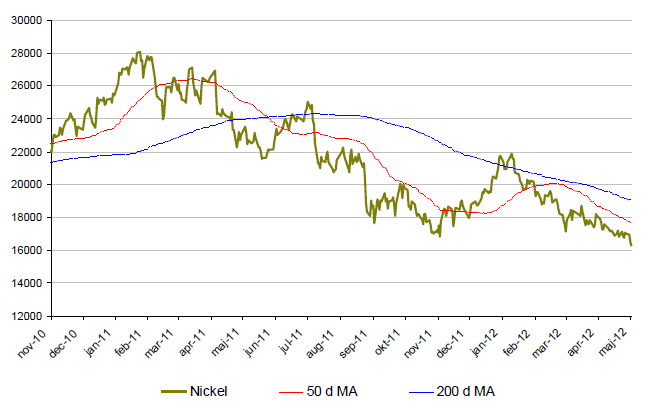
Nickel
- Nickel presterade sämst av alla basmetaller under 2011.
- Nickel fortsätter sin kräftgång under 2012. I maj backade nickel över 8% och är för året ned nästan 9%.
- Nickelmarknaden är mättad med ökande lager.
- Produktionen väntas överstiga konsumtionen under 2012. Mängden tillgänglig nickel väntas dock minska under 2013 och i kombination med ett bättre marknadsläge spår analytikerna ett högre nickelpris under 2013.
- Nuvarande nickelnivåer räcker för 9,1 veckors konsumtion. Ca en vecka högre än 2011.
Råvaror – Jordbruk
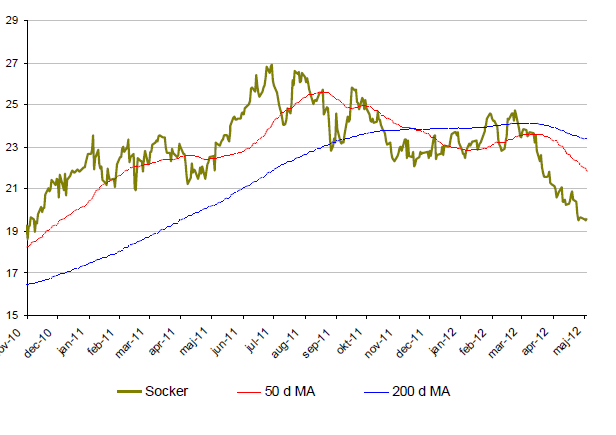
Socker
- Socker startade året starkt, till följd av dåliga och torra väderförhållandena i världens största sockerproducerande land, Brasilien.
- Sedan mars faller dock socker kraftigt. Indien producerar och exporterar socker i hög fart vilket resulterat i att socker under mars-maj tappat nästan 24%.
- I Indien, som öppnat för obegränsad export, spås rekordskördar.
- Genomsnittspositionen är fortsatt lång men säljarna börjar nu bli fler och fler.
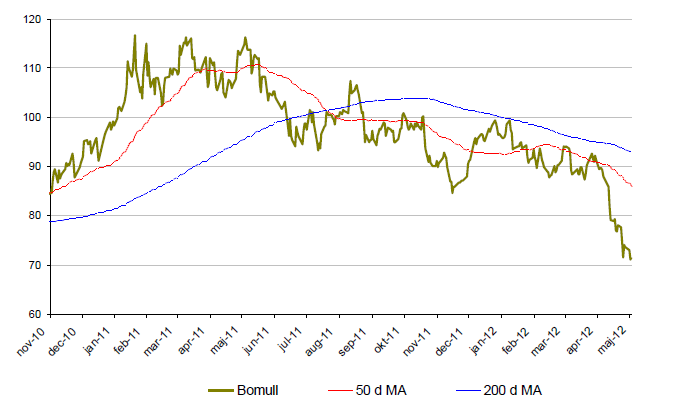
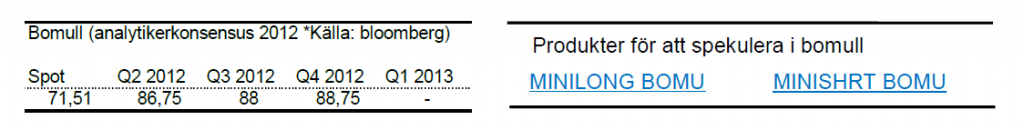
Bomull
- Bomull är för året ned ca 26% där merparten av nedgången kom i maj. I maj föll bomullspriset med närmare 20%.
- Rekordexport av bomull från Indien pressar priset.
- Trots att bomullspriset fallit kraftigt under 2012 är det fortfarande nästan dubbelt så högt som priset för några år sedan. Fallhöjden är således stor.
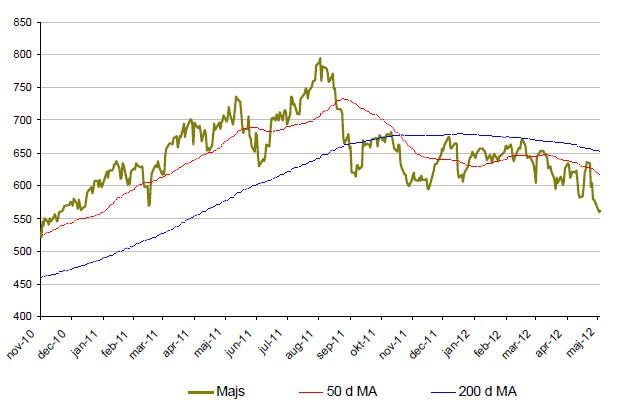
Majs
- Majspriset är under maj månad ned över 14% vilket också motsvarar årsnedgpngen i majs.
- Den kommande skörden vänats vara av mycket god kvalitet.
- För att den negativa trenden i majs ska brytas krävs fortsatt torka i USA. Regnväder är dock att vänta under sommamånaderna.
- Statistik som visar USA-exporten av majs ökar kraftigt. Kina importerar nu rekordstora mängder majs.
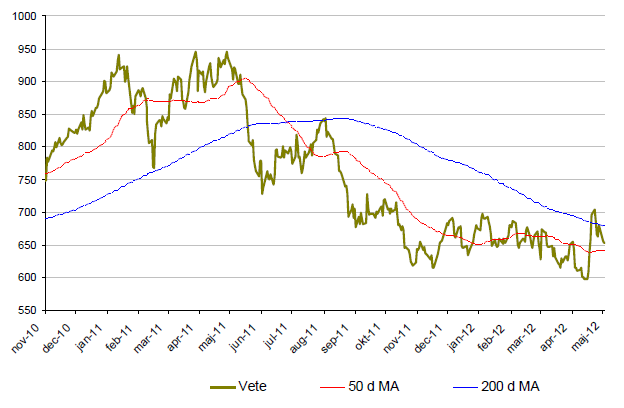
Vete
- Vetepriset är under maj månad upp nästan 7% till följd av torra väderförhållanden i USA, Kina och Europa.
- För året är dock vete ned dryga 1%.
- Spekulanterna har under maj månad skiftat tro. Antalet korta positioner har minskat kraftigt.
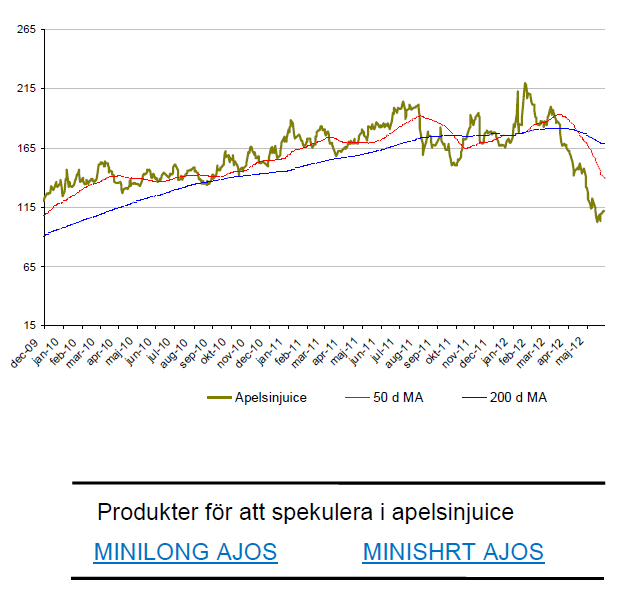
Apelsinjuice
- Priset på apelsinjuice fortsätter att falla som en sten. Under maj månad är priset apelsinjuice ned 26%.
- Det finns fortfarande fallhöjd i kursen då apelsinjuice har stigit med nästan 70 % sedan 2009.
- Skörden I Florida är mycket god till följd av frostfria väderförhållanden. Samtidigt visar rapporter att efterfrågan på apelsinjuice minskar vilken kyler av priset.
[box]Denna uppdatering är producerat av SIP Nordic och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Ansvarsbegränsning
Detta produktblad utgör endast marknadsföring och har sammanställts av SIP Nordic Fondkommission AB.
Innehållet ger inte fullständig information avseende det finansiella instrumentet. Investerare uppmanas att del av prospekt och slutliga villkor, vilka finns tillgängliga på: www.rbsbank.se/markets, innan ett investeringsbeslut tas.
Förekommande exempel är simulerade och baseras på SIP Nordics egna beräkningar och antaganden, en person som använder andra data eller antaganden kan nå andra resultat. Administrativa avgifter och transaktionsavgifter påverkar den faktiska avkastningen.
Analys
Also OPEC+ wants to get compensation for inflation

Brent crude has fallen USD 3/b since the peak of Iran-Israel concerns last week. Still lots of talk about significant Mid-East risk premium in the current oil price. But OPEC+ is in no way anywhere close to loosing control of the oil market. Thus what will really matter is what OPEC+ decides to do in June with respect to production in Q3-24 and the market knows this very well. Saudi Arabia’s social cost-break-even is estimated at USD 100/b today. Also Saudi Arabia’s purse is hurt by 21% US inflation since Jan 2020. Saudi needs more money to make ends meet. Why shouldn’t they get a higher nominal pay as everyone else. Saudi will ask for it

Brent is down USD 3/b vs. last week as the immediate risk for Iran-Israel has faded. But risk is far from over says experts. The Brent crude oil price has fallen 3% to now USD 87.3/b since it became clear that Israel was willing to restrain itself with only a muted counter attack versus Israel while Iran at the same time totally played down the counterattack by Israel. The hope now is of course that that was the end of it. The real fear has now receded for the scenario where Israeli and Iranian exchanges of rockets and drones would escalate to a point where also the US is dragged into it with Mid East oil supply being hurt in the end. Not everyone are as optimistic. Professor Meir Javedanfar who teaches Iranian-Israeli studies in Israel instead judges that ”this is just the beginning” and that they sooner or later will confront each other again according to NYT. While the the tension between Iran and Israel has faded significantly, the pain and anger spiraling out of destruction of Gaza will however close to guarantee that bombs and military strifes will take place left, right and center in the Middle East going forward.
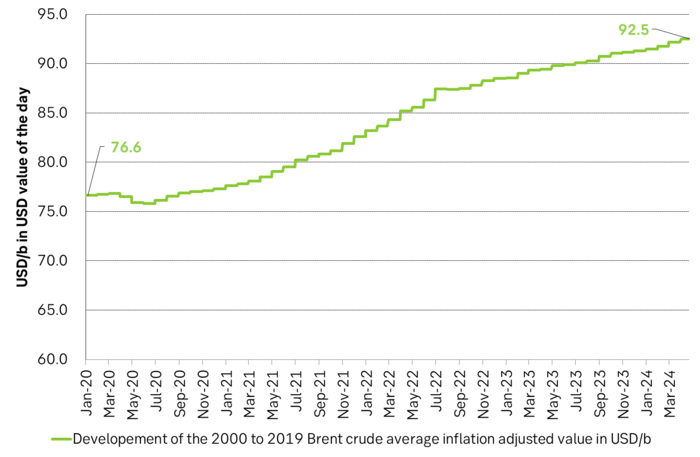
Also OPEC+ wants to get paid. At the start of 2020 the 20 year inflation adjusted average Brent crude price stood at USD 76.6/b. If we keep the averaging period fixed and move forward till today that inflation adjusted average has risen to USD 92.5/b. So when OPEC looks in its purse and income stream it today needs a 21% higher oil price than in January 2020 in order to make ends meet and OPEC(+) is working hard to get it.
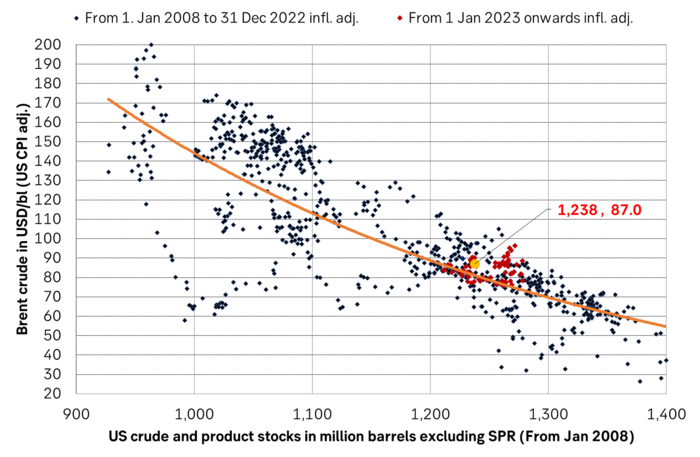
Much talk about Mid-East risk premium of USD 5-10-25/b. But OPEC+ is in control so why does it matter. There is much talk these days that there is a significant risk premium in Brent crude these days and that it could evaporate if the erratic state of the Middle East as well as Ukraine/Russia settles down. With the latest gains in US oil inventories one could maybe argue that there is a USD 5/b risk premium versus total US commercial crude and product inventories in the Brent crude oil price today. But what really matters for the oil price is what OPEC+ decides to do in June with respect to Q3-24 production. We are in no doubt that the group will steer this market to where they want it also in Q3-24. If there is a little bit too much oil in the market versus demand then they will trim supply accordingly.
Also OPEC+ wants to make ends meet. The 20-year real average Brent price from 2000 to 2019 stood at USD 76.6/b in Jan 2020. That same averaging period is today at USD 92.5/b in today’s money value. OPEC+ needs a higher nominal price to make ends meet and they will work hard to get it.
Inflation adjusted Brent crude price versus total US commercial crude and product stocks. A bit above the regression line. Maybe USD 5/b risk premium. But type of inventories matter. Latest big gains were in Propane and Other oils and not so much in crude and products
Total US commercial crude and product stocks usually rise by 4-5 m b per week this time of year. Gains have been very strong lately, but mostly in Propane and Other oils
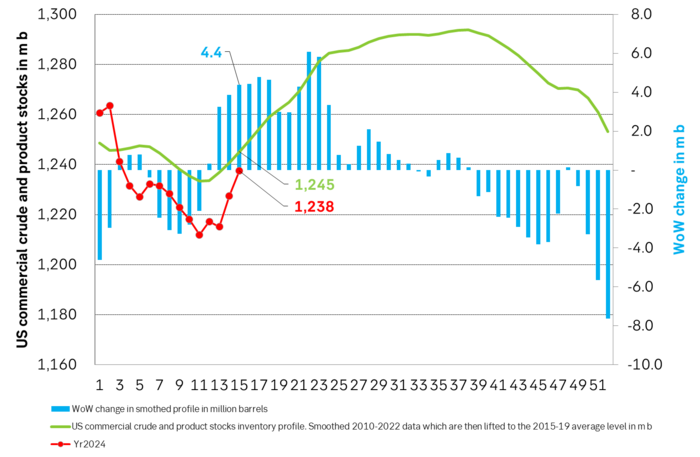
Last week’s US inventory data. Big rise of 10 m b in commercial inventories. What really stands out is the big gains in Propane and Other oils
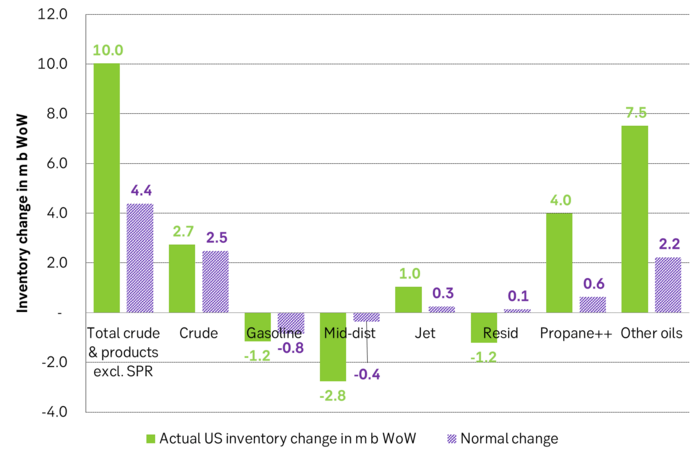
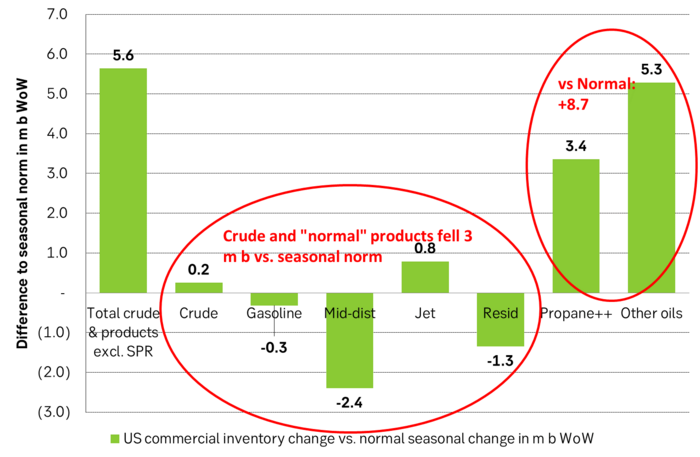
Take actual changes minus normal seasonal changes we find that US commercial crude and regular products like diesel, gasoline, jet and bunker oil actually fell 3 m b versus normal change.
Analys
Nat gas to EUA correlation will likely switch to negative in 2026/27 onward

Historically positive Nat gas to EUA correlation will likely switch to negative in 2026/27 onward

Historically there has been a strong, positive correlation between EUAs and nat gas prices. That correlation is still fully intact and possibly even stronger than ever as traders increasingly takes this correlation as a given with possible amplification through trading action.
The correlation broke down in 2022 as nat gas prices went ballistic but overall the relationship has been very strong for quite a few years.
The correlation between nat gas and EUAs should be positive as long as there is a dynamical mix of coal and gas in EU power sector and the EUA market is neither too tight nor too weak:
Nat gas price UP => ”you go black” by using more coal => higher emissions => EUA price UP
But in the future we’ll go beyond the dynamically capacity to flex between nat gas and coal. As the EUA price moves yet higher along with a tightening carbon market the dynamical coal to gas flex will max out. The EUA price will then trade significantly above where this flex technically will occur. There will still be quite a few coal fired power plants running since they are needed for grid stability and supply amid constrained local grids.
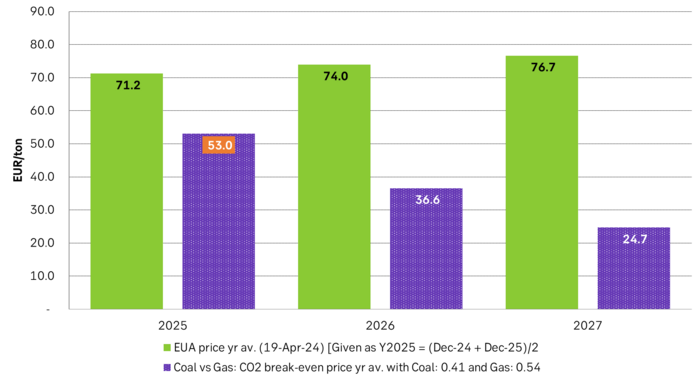
As it looks now we still have such overall coal to gas flex in 2024 and partially in 2025, but come 2026 it could be all maxed out. At least if we look at implied pricing on the forward curves where the forward EUA price for 2026 and 2027 are trading way above technical coal to gas differentials. The current forward pricing implications matches well with what we theoretically expect to see as the EUA market gets tighter and marginal abatement moves from the power sector to the industrial sector. The EUA price should then trade up and way above the technical coal to gas differentials. That is also what we see in current forward prices for 2026 and 2027.
The correlation between nat gas and EUAs should then (2026/27 onward) switch from positive to negative. What is left of coal in the power mix will then no longer be dynamically involved versus nat gas and EUAs. The overall power price will then be ruled by EUA prices, nat gas prices and renewable penetration. There will be pockets with high cost power in the geographical points where there are no other alternatives than coal.
The EUA price is an added cost of energy as long as we consume fossil energy. Thus both today and in future years we’ll have the following as long as we consume fossil energy:
EUA price UP => Pain for consumers of energy => lower energy consumption, faster implementation of energy efficiency and renewable energy => lower emissions
The whole idea with the EUA price is after all that emissions goes down when the EUA price goes up. Either due to reduced energy consumption directly, accelerated energy efficiency measures or faster switch to renewable energy etc.
Let’s say that the coal to gas flex is maxed out with an EUA price way above the technical coal to gas differentials in 2026/27 and later. If the nat gas price then goes up it will no longer be an option to ”go black” and use more coal as the distance to that is too far away price vise due to a tight carbon market and a high EUA price. We’ll then instead have that:
Nat gas higher => higher energy costs with pain for consumers => weaker nat gas / energy demand & stronger drive for energy efficiency implementation & stronger drive for more non-fossil energy => lower emissions => EUA price lower
And if nat gas prices goes down it will give an incentive to consume more nat gas and thus emit more CO2:
Cheaper nat gas => Cheaper energy costs altogether, higher energy and nat gas consumption, less energy efficiency implementations in the broader economy => emissions either goes up or falls slower than before => EUA price UP
Historical and current positive correlation between nat gas and EUA prices should thus not at all be taken for granted for ever and we do expect this correlation to switch to negative some time in 2026/27.
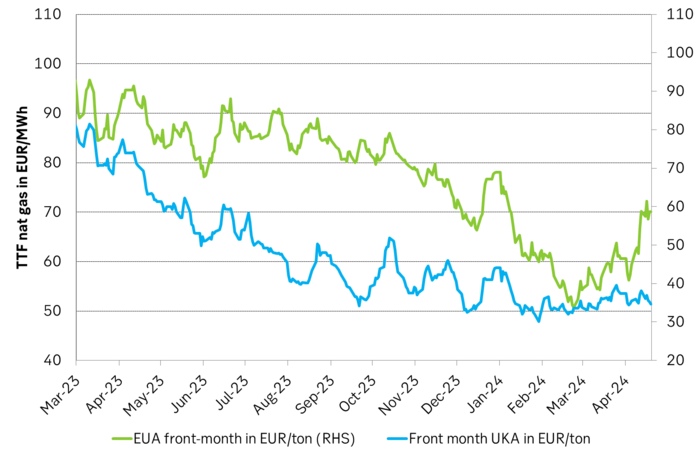
In the UK there is hardly any coal left at all in the power mix. There is thus no option to ”go black” and burn more coal if the nat gas price goes up. A higher nat gas price will instead inflict pain on consumers of energy and lead to lower energy consumption, lower nat gas consumption and lower emissions on the margin. There is still some positive correlation left between nat gas and UKAs but it is very weak and it could relate to correlations between power prices in the UK and the continent as well as some correlations between UKAs and EUAs.
Correlation of daily changes in front month EUA prices and front-year TTF nat gas prices, 250dma correlation.
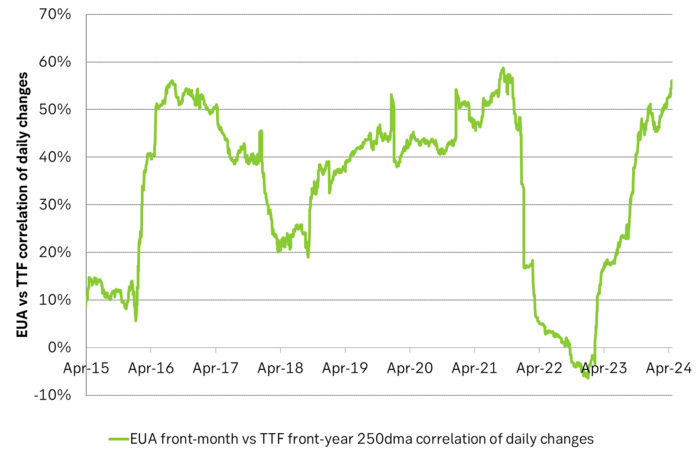
EUA price vs front-year TTF nat gas price since March 2023
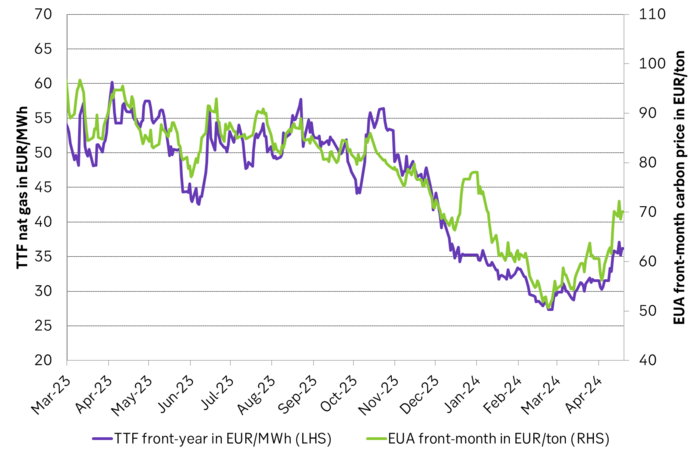
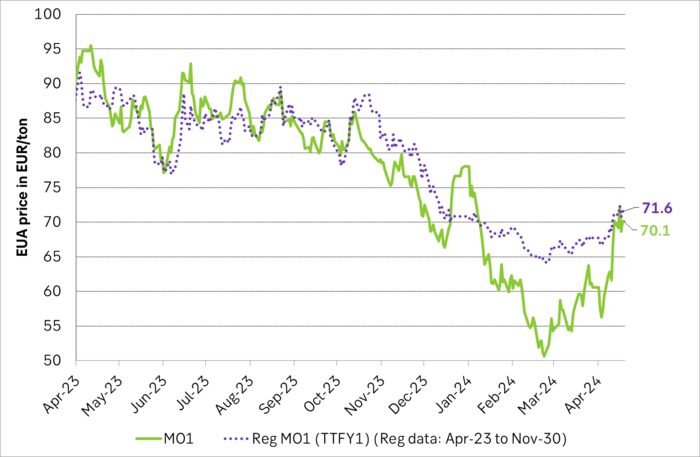
Front-month EUA price vs regression function of EUA price vs. nat gas derived from data from Apr to Nov last year.
The EUA price vs the UKA price. Correlations previously, but not much any more.
Forward German power prices versus clean cost of coal and clean cost of gas power. Coal is totally priced out vs power and nat gas on a forward 2026/27 basis.
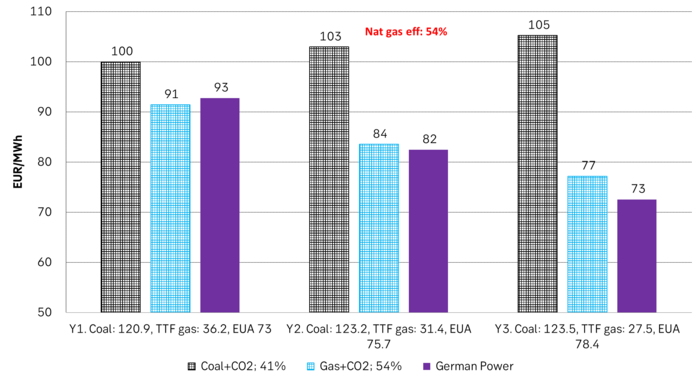
Forward price of EUAs versus technical level where dynamical coal to gas flex typically takes place. EUA price for 2026/27 is at a level where there is no longer any price dynamical interaction or flex between coal and nat gas. The EUA price should/could then start to be negatively correlated to nat gas.
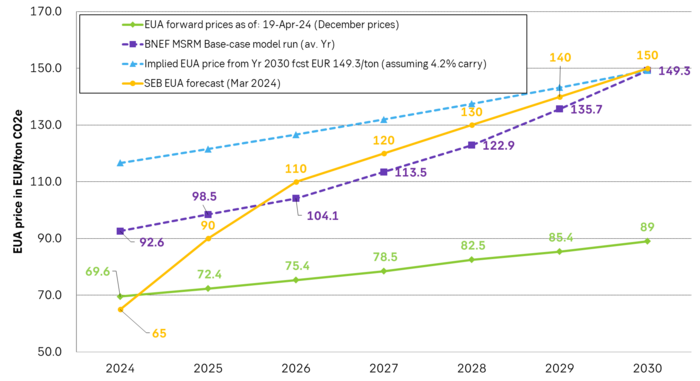
Forward EAU price vs. BNEF base model run (look for new update will come in late April), SEB’s EUA price forecast.
Analys
Fear that retaliations will escalate but hopes that they are fading in magnitude

Brent crude spikes to USD 90.75/b before falling back as Iran plays it down. Brent crude fell sharply on Wednesday following fairly bearish US oil inventory data and yesterday it fell all the way to USD 86.09/b before a close of USD 87.11/b. Quite close to where Brent traded before the 1 April attack. This morning Brent spiked back up to USD 90.75/b (+4%) on news of Israeli retaliatory attack on Iran. Since then it has quickly fallen back to USD 88.2/b, up only 1.3% vs. ydy close.

The fear is that we are on an escalating tit-for-tat retaliatory path. Following explosions in Iran this morning the immediate fear was that we now are on a tit-for-tat escalating retaliatory path which in the could end up in an uncontrollable war where the US unwillingly is pulled into an armed conflict with Iran. Iran has however largely diffused this fear as it has played down the whole thing thus signalling that the risk for yet another leg higher in retaliatory strikes from Iran towards Israel appears low.
The hope is that the retaliatory strikes will be fading in magnitude and then fizzle out. What we can hope for is that the current tit-for-tat retaliatory strikes are fading in magnitude rather than rising in magnitude. Yes, Iran may retaliate to what Israel did this morning, but the hope if it does is that it is of fading magnitude rather than escalating magnitude.
Israel is playing with ”US house money”. What is very clear is that neither the US nor Iran want to end up in an armed conflict with each other. The US concern is that it involuntary is dragged backwards into such a conflict if Israel cannot control itself. As one US official put it: ”Israel is playing with (US) house money”. One can only imagine how US diplomatic phone lines currently are running red-hot with frenetic diplomatic efforts to try to defuse the situation.
It will likely go well as neither the US nor Iran wants to end up in a military conflict with each other. The underlying position is that both the US and Iran seems to detest the though of getting involved in a direct military conflict with each other and that the US is doing its utmost to hold back Israel. This is probably going a long way to convince the market that this situation is not going to fully blow up.
The oil market is nonetheless concerned as there is too much oil supply at stake. The oil market is however still naturally concerned and uncomfortable about the whole situation as there is so much oil supply at stake if the situation actually did blow up. Reports of traders buying far out of the money call options is a witness of that.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGuldpriset når nytt all time high och bryter igenom 2300 USD
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLundin Mining får köprekommendation av BMO
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanCentralbanker fortsatte att köpa guld under februari
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanUSAs stigande konsumtion av naturgas
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanKakaomarknaden är extrem för tillfället
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanHur mår den svenska skogsbraschen? Två favoritaktier
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBoliden på 20 minuter
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanBetydande underskott i utbudet av olja kan få priset att blossa upp