Analys
SIP Nordic – Råvaruguiden – mars 2013

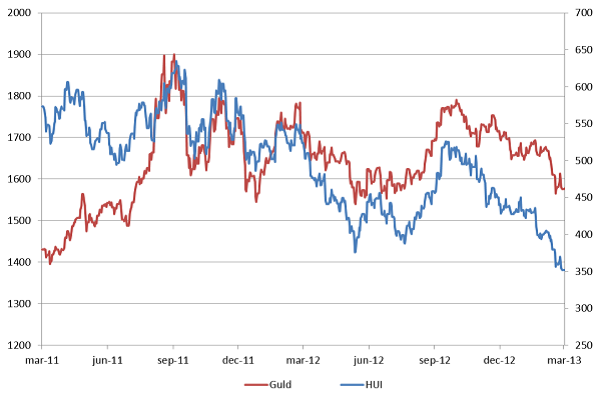
![]() Under mars månad kan Avanzas kunder handla RBS Mini Futures, som följer index, utan courtage. Därför tänkte jag skriva lite om ett index som kanske är lite okänt för det flesta. NYSE Arca Gold Bugs eller HUI-index.
Under mars månad kan Avanzas kunder handla RBS Mini Futures, som följer index, utan courtage. Därför tänkte jag skriva lite om ett index som kanske är lite okänt för det flesta. NYSE Arca Gold Bugs eller HUI-index.
Gold Bugs index eller HUI är ett aktieindex bestående av 16 guldbolag. BUGS står för ”Basket of Unhedged Gold Stocks”. Vilket betyder att indexet enbart inkluderar bolag som inte försäkrar sin guldproduktion längre än ett och ett halvt år fram i tiden. Indexets ingående bolag sägs därför återspegla den framtida tron om guldpriset väl.
Den senaste tiden har guldpriset fallit och HUI Index har inte varit något undantag. Sedan slutet av september förra året har guldpriset tappat ca. 11 %. HUI index har under samma tid tappat 34 %.
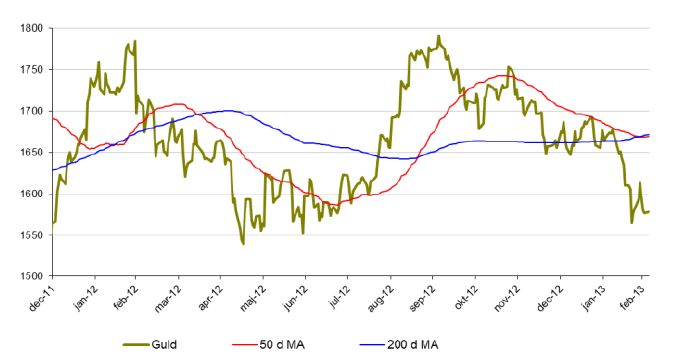
Utveckling för guld och HUI indexars 2011 – mars 2013. (Höger axel för guldpriset och vänster för HUI)
Den senaste veckan har medierna kantats av att guldpriset gått in i en negativ trend och att fler investerare söker sig bort från den säkra hamn som guld symboliserat i lite skakigare tider. Guldets fortsatta utveckling ser fortsatt spännande ut och ett viktigt stöd kring $1550 närmar sig. Om guld faller igenom kan detta mycket väl betyda en fortsatt nedgång för HUI Index.
Vid ett sådant scenario kan man utnyttja en nedåtgående rörelse genom att köpa MINISHRT GBUG
Vill man istället gå mot strömmen och har en fortsatt tro på att guldbolagen ska öka sin årliga tillväxt samt att guldpriset kommer att återhämta sig kan man köpa MINILONG GBUG
Alexander Frick
Råvaror – Energi
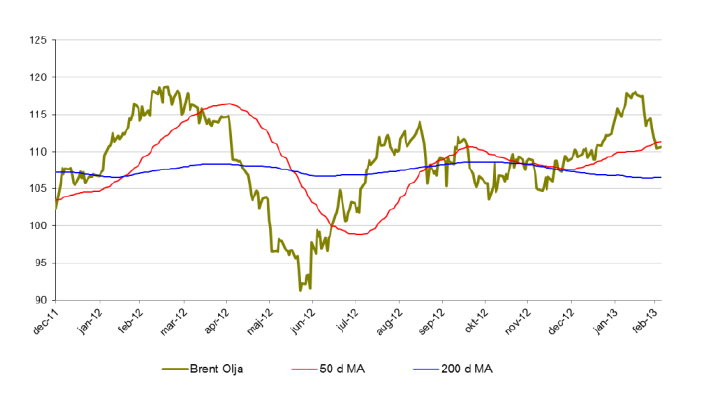
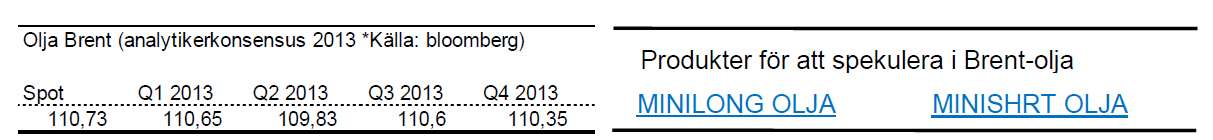
Brent olja
- Efter en stark start på året har brentoljan återigen vänt ned. För året är brentoljan på +-0 %.
- Minskad import från USA samt ökade lager bidrar till brentoljans nedgång.
- Uttalande från Ben Bernanke (FED) om en paus i stimulanspaket påverkar även priset på olja negativt.
- Bland spekulanter (bland annat fonder) ökas de långa positionerna vilket kan indikera att en vändning uppåt är på väg.
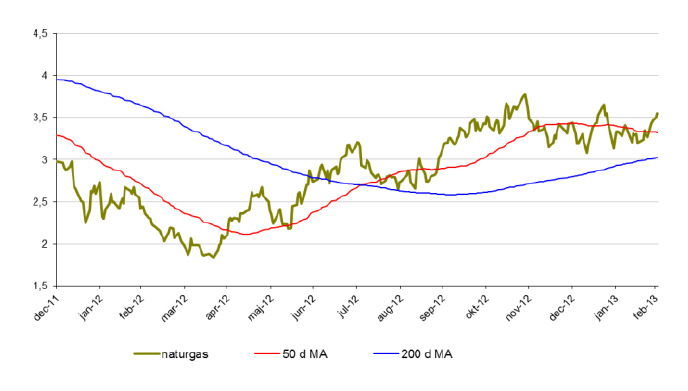
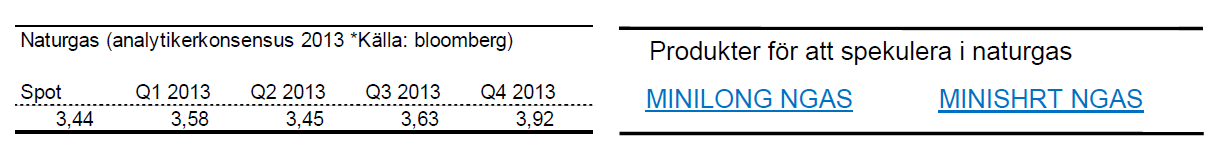
Naturgas
- Från i mitten av april hade Naturgas en mycket stark period under 2012. Sedan botten i april klättrade priset på naturgas med nästan 84 % och avslutade året på cirka 10 % upp.
- För året är priset på naturgas upp drygt 13 %.
- Naturgas handlas nu över 50 dagarsmedelvärde och den långa trenden pekar uppåt.
Råvaror – Metaller
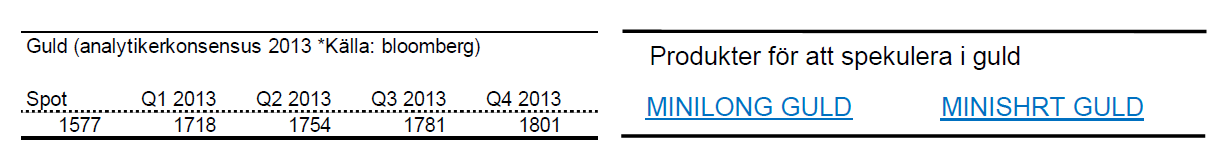
Guld
- Guld befinner sig i ett otroligt spännande läge. Sedan årets början är guld ned nära 5 %.
- Guld närmar sig nu ett stödområde kring $1550 som är väl värt att bevaka. Om stödet håller kan en lång position vara intressant. Om guld bryter under denna nivå är en kort position lika intressant.
- Vi har även sett ett s.k. dödskors i guld den senaste veckan vilket betyder att 50 dagars medelvärde skär 200 dagars uppifrån. Detta brukar kunna tolkas som en signal om nedgång.
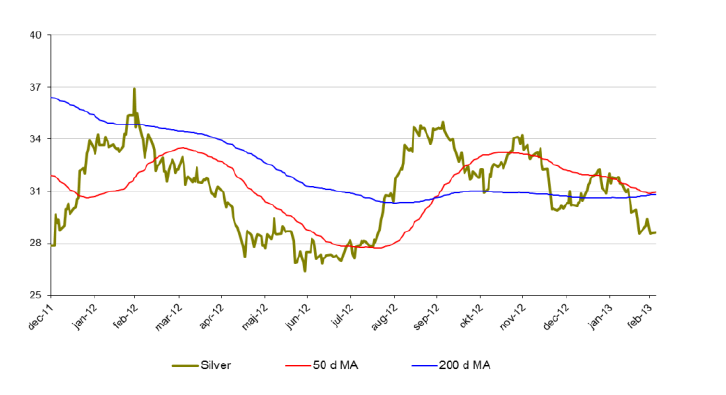
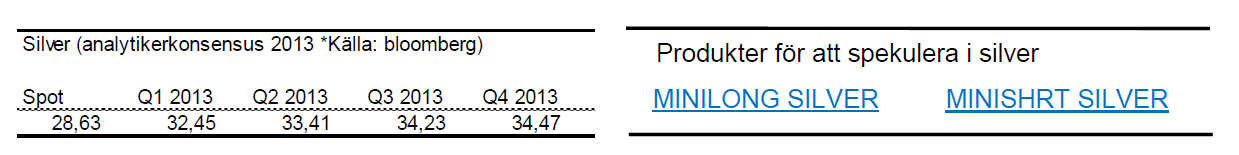
Silver
- Silver följer med guld nedåt.
- Tecken på framförallt en starkare amerikansk ekonomi driver priset på silver nedåt.
- För året är priset på silver ned knappa 7 %.
- Viktiga stödområden kring $27.
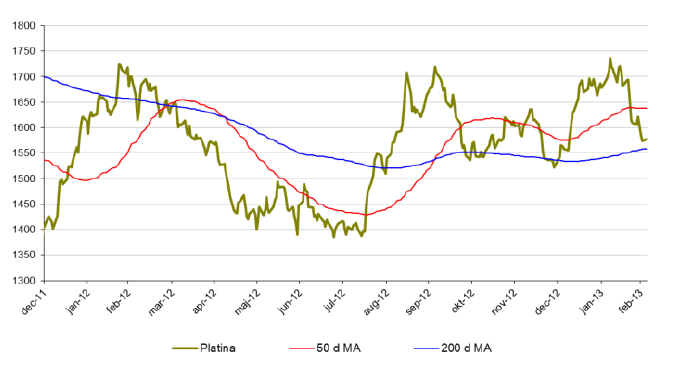
Platina
- Platina har likt silver och guld åkt berg och dalbana. För året är dock platina upp 3,5 % men föl under februari 11 %.
- Platina handlas nu till samma nivå som guld.
- Likt guld finns det intressanta motståndszoner kring $1550 att bevaka.
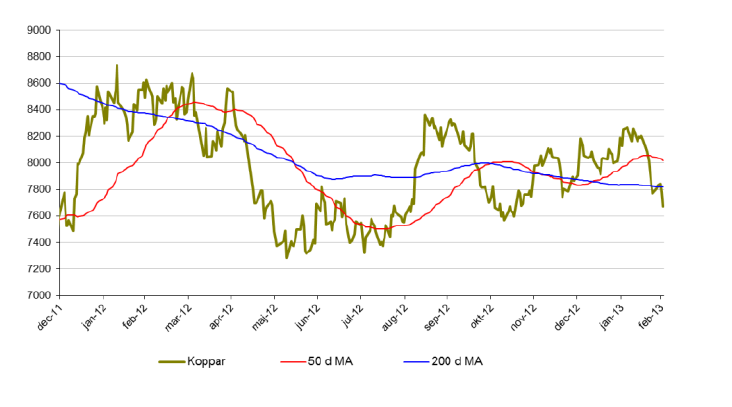
Koppar
- Med risk att bli för tjatig så är koppar inget undantag. En stark start på året har växlat till en negativ trend.
- Koppar är för året ned 7% från att ha varit plus 5 % i början av februari.
- Koppar handlas just nu över
- Tillväxtländernas förbrukning kommer styra mycket under 2013.
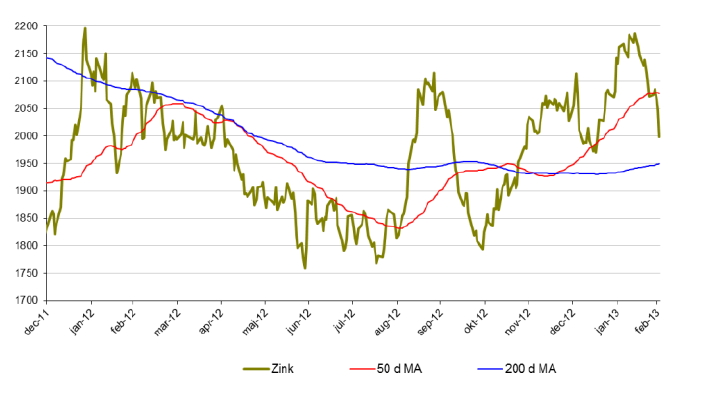
Zink
- Zink är för året ned 2,5 %.
- Sedan mitten av februari har zinkpriset fallit med 8 %.
- Zink handlas snart i regionen kring golvet i den stigande trendkanalen. Rekyler där kan vara intressanta att bevaka.
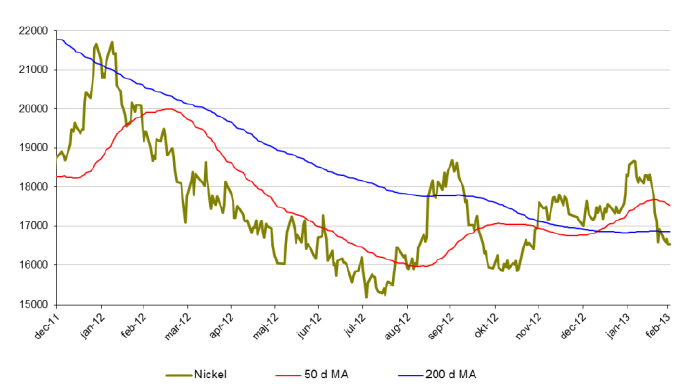
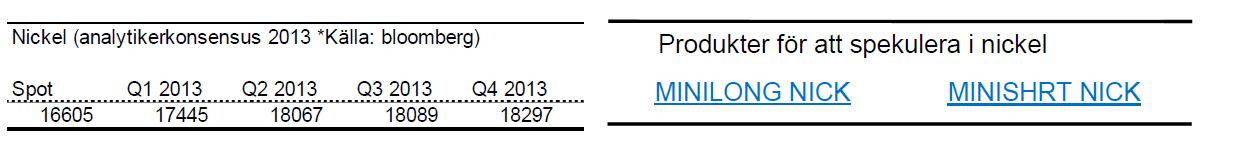
Nickel
- Nickel är för året ned drygt 3 %.
- Under februari tappade nickel nästan 11 %.
- Nickel presterade sämst av alla basmetaller under 2012. Slutsiffran blev -8 % för 2012.
- Nickelmarknaden är fortsatt mättad med ökande lager.
- Många stora projekt inom nickelproduktion är redan finansierade och irreversibla vilket kommer att öka tillgången av nickel ytterligare.
Råvaror – Jordbruk
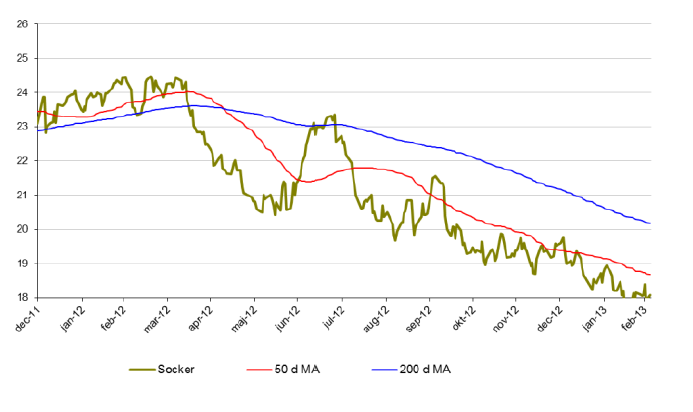
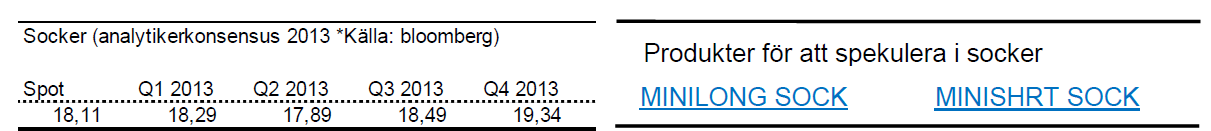
Socker
- Sockers kräftgång fortsätter. Sedan oktober förra året är sockerpriset ned 17 %.
- För året är sockerpriset ned knappt 8 %.
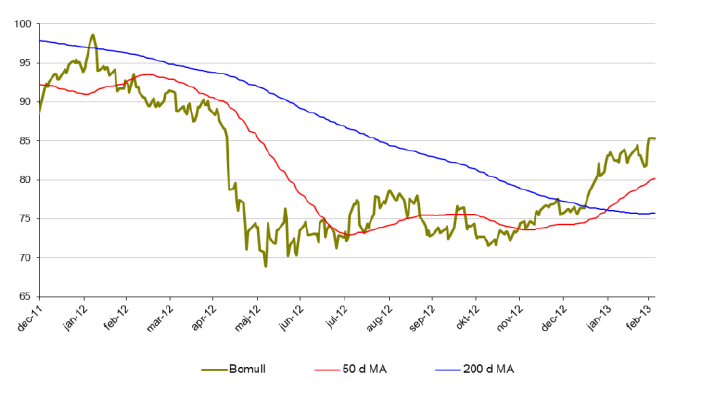
Bomull
- Bomullspriset utvecklas starkt under början av 2013.
- För året är priset på bomull upp 13,7 %.
- Under februari månad är bomull upp 1,2 %.
- Sedan november 2012 är priset på bomull upp 22 %.
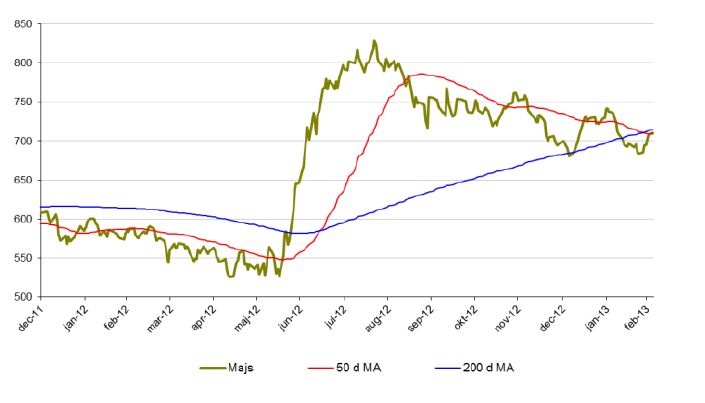
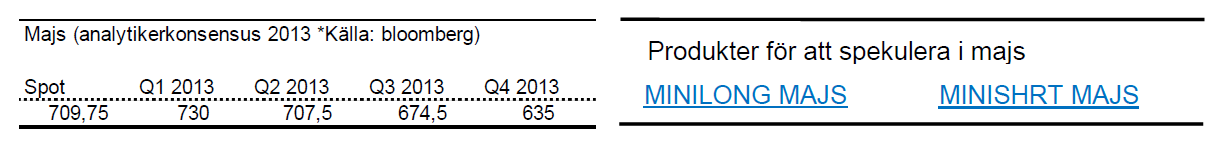
Majs
- Rekordstora skördar väntas i USA vilket kan pressa priset på majs.
- För året är dock majs upp 5 %.
- Under februari föll priset på majs med 1,7 % men köparna kom i slutet på månaden tillbaka.
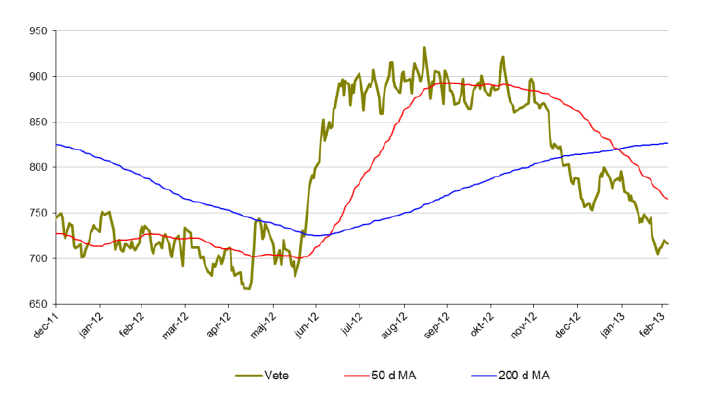
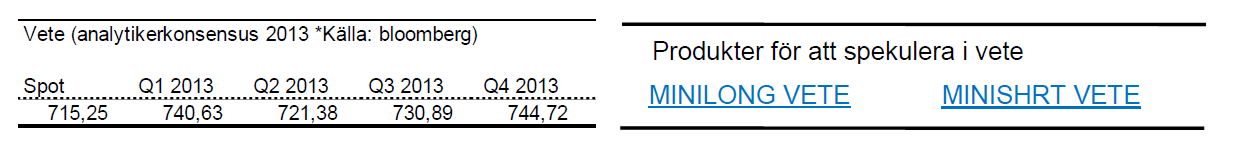
Vete
- Vete befinner sig i en negativ trend. Sedan i mitten av november 2012 har priset på vete backat med drygt 20 %.
- För året är vete ned 10 %.
- Under februari månad tappade vete 9 %.
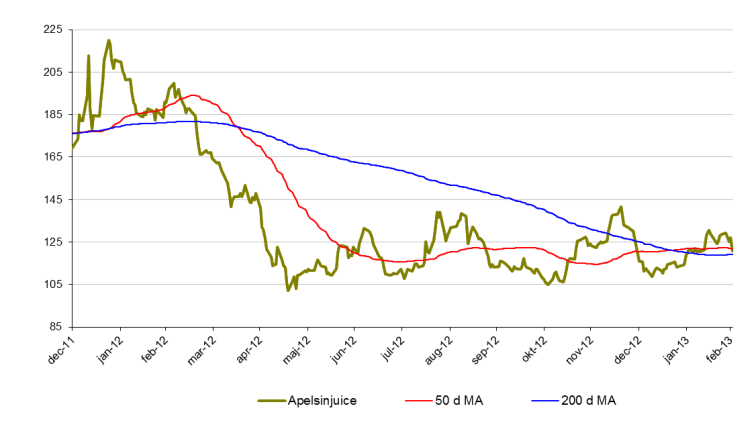
Apelsinjuice
- Vi har länge bevakat apelsinjuice i Tradingklubben.
- Apelsinjuice konsoliderar nu och känns svårtippad.
- För året är apelsinjuice upp 4 %.
- Priset på apelsinjuice är fortfarande 70 % högre än botten 2009. Fallhöjden är således hög. Mycket hög.
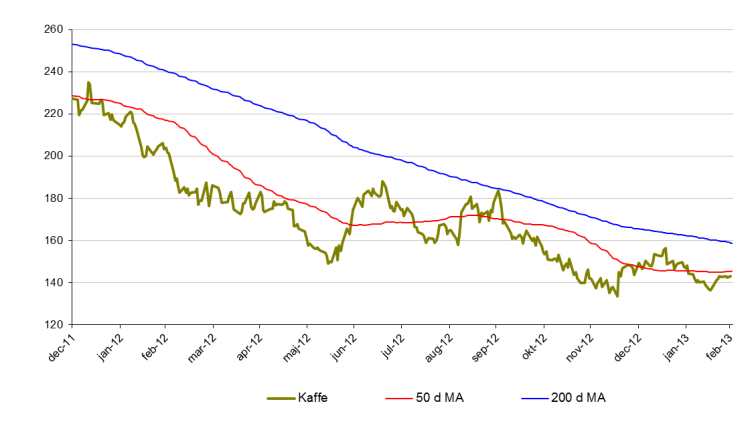
Kaffe
- Kaffe ligger fortfarande i en långsiktigt nedåtgående trend.
- För året är kaffe ned 2%.
- Viktigt stödområde kring 135$.
[box]Denna uppdatering är producerat av SIP Nordic och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Ansvarsbegränsning
Detta produktblad utgör endast marknadsföring och har sammanställts av SIP Nordic Fondkommission AB.
Innehållet ger inte fullständig information avseende det finansiella instrumentet. Investerare uppmanas att del av prospekt och slutliga villkor, vilka finns tillgängliga på: www.rbsbank.se/markets, innan ett investeringsbeslut tas.
Förekommande exempel är simulerade och baseras på SIP Nordics egna beräkningar och antaganden, en person som använder andra data eller antaganden kan nå andra resultat. Administrativa avgifter och transaktionsavgifter påverkar den faktiska avkastningen.
Analys
OPEC+ in a process of retaking market share

Oil prices are likely to fall for a fourth straight year as OPEC+ unwinds cuts and retakes market share. We expect Brent crude to average USD 55/b in Q4/25 before OPEC+ steps in to stabilise the market into 2026. Surplus, stock building, oil prices are under pressure with OPEC+ calling the shots as to how rough it wants to play it. We see natural gas prices following parity with oil (except for seasonality) until LNG surplus arrives in late 2026/early 2027.

Oil market: Q4/25 and 2026 will be all about how OPEC+ chooses to play it
OPEC+ is in a process of unwinding voluntary cuts by a sub-group of the members and taking back market share. But the process looks set to be different from 2014-16, as the group doesn’t look likely to blindly lift production to take back market share. The group has stated very explicitly that it can just as well cut production as increase it ahead. While the oil price is unlikely to drop as violently and lasting as in 2014-16, it will likely fall further before the group steps in with fresh cuts to stabilise the price. We expect Brent to fall to USD 55/b in Q4/25 before the group steps in with fresh cuts at the end of the year.

Natural gas market: Winter risk ahead, yet LNG balance to loosen from 2026
The global gas market entered 2025 in a fragile state of balance. European reliance on LNG remains high, with Russian pipeline flows limited to Turkey and Russian LNG constrained by sanctions. Planned NCS maintenance in late summer could trim exports by up to 1.3 TWh/day, pressuring EU storage ahead of winter. Meanwhile, NE Asia accounts for more than 50% of global LNG demand, with China alone nearing a 20% share (~80 mt in 2024). US shale gas production has likely peaked after reaching 104.8 bcf/d, even as LNG export capacity expands rapidly, tightening the US balance. Global supply additions are limited until late 2026, when major US, Qatari and Canadian projects are due to start up. Until then, we expect TTF to average EUR 38/MWh through 2025, before easing as the new supply wave likely arrives in late 2026 and then in 2027.
Analys
Manufacturing PMIs ticking higher lends support to both copper and oil

Price action contained withing USD 2/b last week. Likely muted today as well with US closed. The Brent November contract is the new front-month contract as of today. It traded in a range of USD 66.37-68.49/b and closed the week up a mere 0.4% at USD 67.48/b. US oil inventory data didn’t make much of an impact on the Brent price last week as it is totally normal for US crude stocks to decline 2.4 mb/d this time of year as data showed. This morning Brent is up a meager 0.5% to USD 67.8/b. It is US Labor day today with US markets closed. Today’s price action is likely going to be muted due to that.

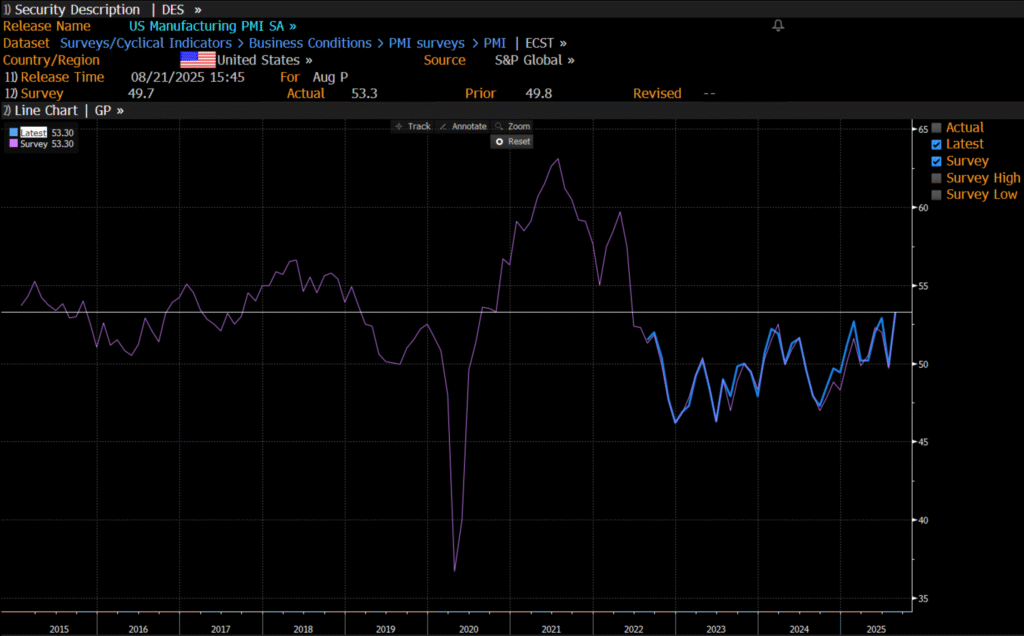
Improving manufacturing readings. China’s manufacturing PMI for August came in at 49.4 versus 49.3 for July. A marginal improvement. The total PMI index ticked up to 50.5 from 50.2 with non-manufacturing also helping it higher. The HCOB Eurozone manufacturing PMI was a disastrous 45.1 last December, but has since then been on a one-way street upwards to its current 50.5 for August. The S&P US manufacturing index jumped to 53.3 in August which was the highest since 2022 (US ISM manufacturing tomorrow). India manufacturing PMI rose further and to 59.3 for August which is the highest since at least 2022.
Are we in for global manufacturing expansion? Would help to explain copper at 10k and resilient oil. JPMorgan global manufacturing index for August is due tomorrow. It was 49.7 in July and has been below the 50-line since February. Looking at the above it looks like a good chance for moving into positive territory for global manufacturing. A copper price of USD 9935/ton, sniffing at the 10k line could be a reflection of that. An oil price holding up fairly well at close to USD 68/b despite the fact that oil balances for Q4-25 and 2026 looks bloated could be another reflection that global manufacturing may be accelerating.
US manufacturing PMI by S&P rose to 53.3 in August. It was published on 21 August, so not at all newly released. But the US ISM manufacturing PMI is due tomorrow and has the potential to follow suite with a strong manufacturing reading.
Analys
Crude stocks fall again – diesel tightness persists

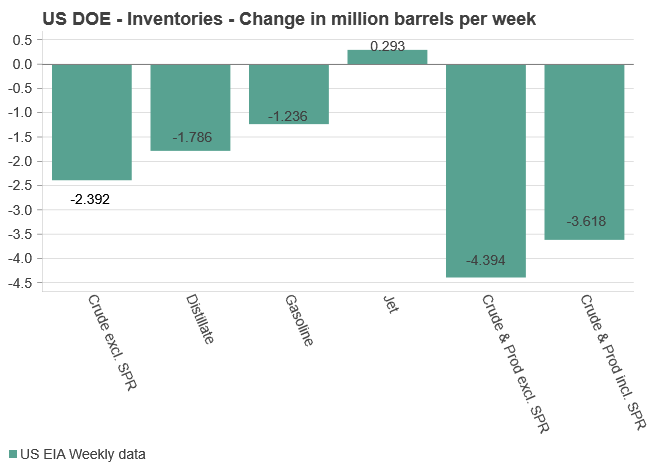
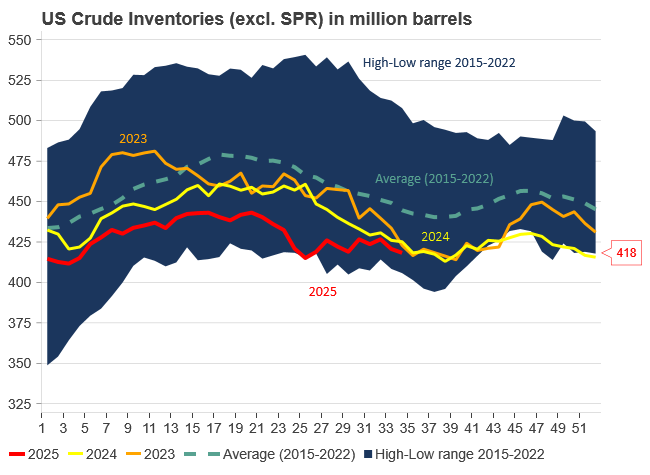
U.S. commercial crude inventories posted another draw last week, falling by 2.4 million barrels to 418.3 million barrels, according to the latest DOE report. Inventories are now 6% below the five-year seasonal average, underlining a persistently tight supply picture as we move into the post-peak demand season.

While the draw was smaller than last week’s 6 million barrel decline, the trend remains consistent with seasonal patterns. Current inventories are still well below the 2015–2022 average of around 449 million barrels.
Gasoline inventories dropped by 1.2 million barrels and are now close to the five-year average. The breakdown showed a modest increase in finished gasoline offset by a decline in blending components – hinting at steady end-user demand.
Diesel inventories saw yet another sharp move, falling by 1.8 million barrels. Stocks are now 15% below the five-year average, pointing to sustained tightness in middle distillates. In fact, diesel remains the most undersupplied segment, with current inventory levels at the very low end of the historical range (see page 3 attached).
Total commercial petroleum inventories – including crude and products but excluding the SPR – fell by 4.4 million barrels on the week, bringing total inventories to approximately 1,259 million barrels. Despite rising refinery utilization at 94.6%, the broader inventory complex remains structurally tight.
On the demand side, the DOE’s ‘products supplied’ metric – a proxy for implied consumption – stayed strong. Total product demand averaged 21.2 million barrels per day over the last four weeks, up 2.5% YoY. Diesel and jet fuel were the standouts, up 7.7% and 1.7%, respectively, while gasoline demand softened slightly, down 1.1% YoY. The figures reflect a still-solid late-summer demand environment, particularly in industrial and freight-related sectors.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanOmgående mångmiljardfiasko för Equinors satsning på Ørsted och vindkraft
-
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLundin Gold hittar ny koppar-guld-fyndighet vid Fruta del Norte-gruvan
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuld stiger till över 3500 USD på osäkerhet i världen
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanWhat OPEC+ is doing, what it is saying and what we are hearing
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAlkane Resources och Mandalay Resources har gått samman, aktör inom guld och antimon
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLyten, tillverkare av litium-svavelbatterier, tar över Northvolts tillgångar i Sverige och Tyskland