Analys
LME Week 2014 på tre minuter

![]() LME veckan är dagarna då industrin för basmetaller samlas i London och försöker bilda sig en uppfattning om var priserna på metallerna ska ta vägen nästa år. Upptakten till årets konferens var allt annat än positivt när basmetallerna kommit ner i pris och investmentbankerna sänkt utsikterna inför nästa år. Hemma efter årets LME-vecka sammanfattar vi diskussioner, teman och frågor.
LME veckan är dagarna då industrin för basmetaller samlas i London och försöker bilda sig en uppfattning om var priserna på metallerna ska ta vägen nästa år. Upptakten till årets konferens var allt annat än positivt när basmetallerna kommit ner i pris och investmentbankerna sänkt utsikterna inför nästa år. Hemma efter årets LME-vecka sammanfattar vi diskussioner, teman och frågor.
Förväntningar
Inför årets tillställning reste vi till London med förväntansbilden av att Indonesiens exportförbud skulle föra nickel till årets snackis, tätt följt av de fysiska premierna för aluminium och LME:s aktion att införa en börshandlad fysisk premie efter att ha misslyckats lösa situationen med de långa köerna för att få ut aluminium ur LME-lagerhusen. I vår förväntansbild fanns inte det generellt negativa sentimentet kring makroutsikterna och metallmarknaderna inför 2015. Att Kina bromsar in har vi haft i korten i flera år och borde inte vara en överraskning för någon i branschen.
LME-seminariet
LME:s Vd, Gary Jones adresserade problemet med köer till lagerhusen redan i öppningsanförandet. Stora ord krävdes för att klä arbetet med att ta bort köerna men de maskerade inte LME:s misslyckande och kvittot kom när LME lanserade ett kontrakt för den fysiska premien. På så vis kan metallhandlare handla risken för att köerna och därmed premierna ska gå upp eller ner. En häpnadsväckande raffinerad lösning på ett problem med att få ut metalltackor ur ett plåthus med en gaffeltruck.
Generella teman
- Utbudet är viktigare än efterfrågan för priserna 2015
- Ökad nationalisering av naturtillgångar (Indonesien, nickel)
- Metallerna divergerar med allt mer åtskiljd fundamenta
- Lägre energipriser sänker metallprisgolvet genom lägre produktionskostnad
- Kinas husmarknad största orosmolnet på makrosidan
- Ökad volatilitet efter lanseringen av minikontrakt för retailmarknaden i Kina via LME:s kommande Hong Kong-kontrakt
- Lagerstatistik har blivit svårtolkad då stora lager finns utanför LME-husen
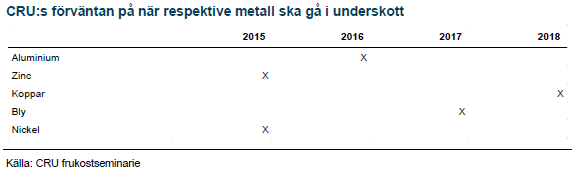
- Konsensus förväntan på när underskott ska uppstå per metall:
LME Week metall för metall
Nedan sammanfattar vi intrycken från diskussionerna per metall. Av de tre, zink, aluminium och koppar, som avhandlades på det officiella LME-seminariet trodde åhörarna att risken för prisuppgång var störst för Zn 43 % följt av Al 42% och sist koppar med 15%.
Koppar
Alla metaller pressas av ökat utbud utom koppar som pressas av förväntan om ökat utbud. Utbudstoppen har flyttats från 2014 till 2015 efter flera förseningar bland de stora projekten och Grasbergs minskade export under 2014 under Indonesiens exportförbud. Riskerna för utbudstoppen nästa år är mycket mindre då 30% av den kommer från normalisering i produktionen i vissa stora gruvor (bland annat Grasberg), 35% infasning av nya gruvor som börjat producera (de är förbi det mest kritiska stadiet) och 35% från nya greenfield- eller brownfieldprojekt. Kinas årliga tillväxt i kopparimport väntas falla till den lägsta på 6 år och kombinationen gör att priserna väntas ner under 2015 men sedan åter upp 2016 då pipelinen för kopparprojekt är tunn längre fram. Viktigaste produktionsfaktorerna under 2015 är Sierra Goroda, Sisha, Oyu Tolgoi, Caserones, Toromocho och Mine minestro Hales. Vi håller kvar vårt scenario med en koppardipp till 5500 USD/ton 2015 men där medelpriset blir mellan 5750 USD/ton.
Aluminium
Första halvan av 2014 dominerades av uppskruvade förväntningar på efterfrågan från Amerikansk bilindustri. I kombination med mycket trendföljande spekulation steg priset snabbt. Utsikterna för aluminium i bilindustrin har sedan dess delvis grusats när nästa generations bilar verkar gå från aluminium till höghållfasta supertunna stål. Indonesiens exportförbud har inte drivit upp priset på råvaran bauxit och avställd smältverkskapacitet finns hela tiden i bilden, redo att kliva in och dämpa långsiktiga prisrallyn. Det finns ingen brist på aluminium globalt men en del vittnar om brist i statistiken med oväntade poster på 850 Kt i Mexico ämnad för amerikanska marknaden. Kina och resten av världen är delvis separerade men om ex Kina går i underskott kommer Kinas export av halvfabrikat täcka upp. Vi behåller vårt scenario för 2015 med aluminium mellan 1800-2000 och 1900 USD/ton i medelpris.
Zink
Annalkande gruvstängningar börjar etablera sig som tema och zink är nu nästa nickel i mångas sinne. Tesen fick dock visst motstånd där man menar att det visserligen ska stängas några få riktigt stora gruvor men det finns å andra sidan ett stort antal små gruvor som kommer expandera med strategin att ta marknadsandelar i bakvattnet av de utbrutna. Svårt att bedöma sannolikheten med många små expansioner men vi står kvar i relativt positiv syn på zink med 2250 USD/ton som medelpris 2015
Nickel
Tveklöst den metall där deltagarna har störst tro på högre priser inför 2015. Underliggande fundamenta har förvärrats under året och kunskapen kring Filipinernas säsongsmönster i exporten som har täckt upp för Indonesiens exportförbud så här lång börjar sprida sig. Filipinerna går nu in i monsunperioden då regnfall minskar möjligheterna att exportera malm radikalt. Deltagarna räknar med att nickelmarknaden hamnar i underskott nästa år och att lagernivåer kommer konsumeras för att balansera marknaden. Högre prisestimat är ett tema och vårt scenario med snittpris på 23 000 USD/ton är visserligen en stor rörelse men finner relativt god acceptans. Nickel är i våra ögon den enda basmetall som har risk för prisuppgång på mer än 50 % under 2015 från dagens nivåer.
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

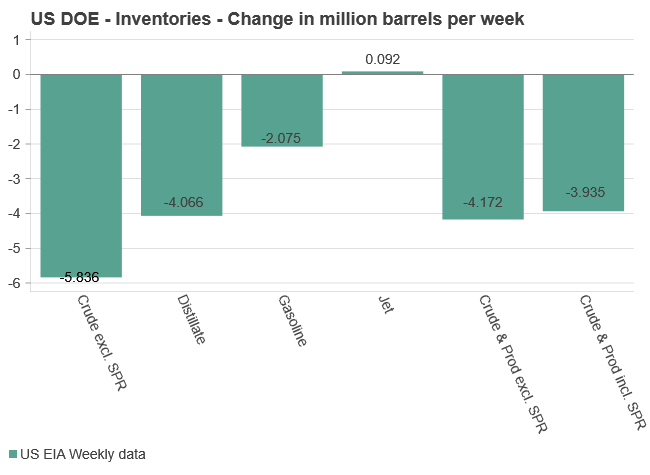
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

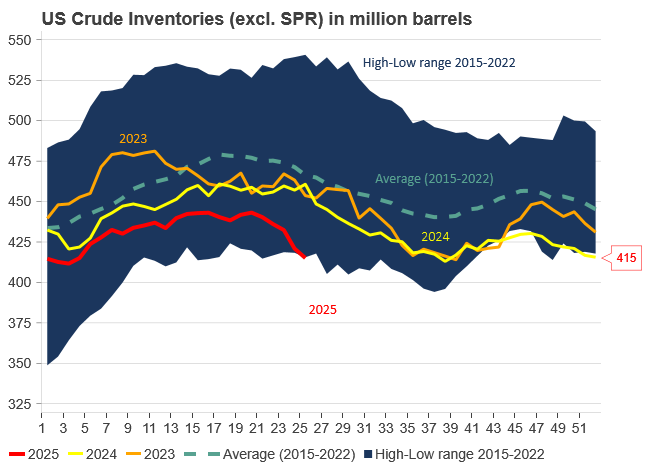
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanOljan, guldet och marknadens oroande tystnad
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanJonas Lindvall är tillbaka med ett nytt oljebolag, Perthro, som ska börsnoteras