Analys
SIP Nordic – Råvaruguiden – juni 2013

 Silver – gulds vilda lillebror
Silver – gulds vilda lillebror
Silver är med största sannolikhet en av de mest volatila av världens populära marknader. När silver rör sig, rör sig silver snabbt. Både stora vinster och förluster kan ske under loppet av några veckor, vilket kan vara spännande eller skräckinjagande beroende på vilken sida du sitter på.
Silver har haft en tuff start på året med en nedgång på drygt 25 %. Samtidigt har guld tappat runt 17 %. En skillnad på 8 procentenheter. Silver en guldprodukt med hävstång
Att silver tappat mer än guld är ingen slump. Silver omnämns inte så ofta i medier. Däremot skrivs det och analyseras det kring gulds vara och inte vara och här finns det gott om information att hämta. För att följa silvers utveckling räcker det att kolla på guld.
Silver kan beskrivas som gulds vilda lillebror som gärna gör som storebror men lite yvigare. Med andra ord brukar silver följa guldets dagliga utveckling men med större rörelser.
Om man kollar på hur den dagliga utvecklingen för guld och silver varit sedan januari 2012 styrks ovanstående teori.
Av de totalt 369 handelsdagarna rörde sig guld och silver åt samma håll i 289 dagar av dessa. Nästan 80 % av dagarna.
Kollar man sedan vidare på de dagar då guld och silver rörde sig åt samma håll överpresterade silver guld 222 dagar av dessa eller 80 % av dagarna.
Värt att notera är att de dagar som guld och silver rör sig åt samma håll rör sig silver 3,3 gånger kraftigare i snitt. Således är silver en guldprodukt med hävstång.
Egentligen är det inte så konstigt att detta fenomen finns. I vår Tradingklubb på tisdagar pratar vi ofta om att man inte ska gå emot marknadsklimatet. Med det menas att man inte ska ta en position i en aktie i motsatt riktning som OMXS30 trendar. Så gäller nog även silver och guld. Frågan är hur många stora investerare som vågar gå lång i silver samtidigt som guld går ned och vice versa.
Alexander Frick
Råvaror – Energi
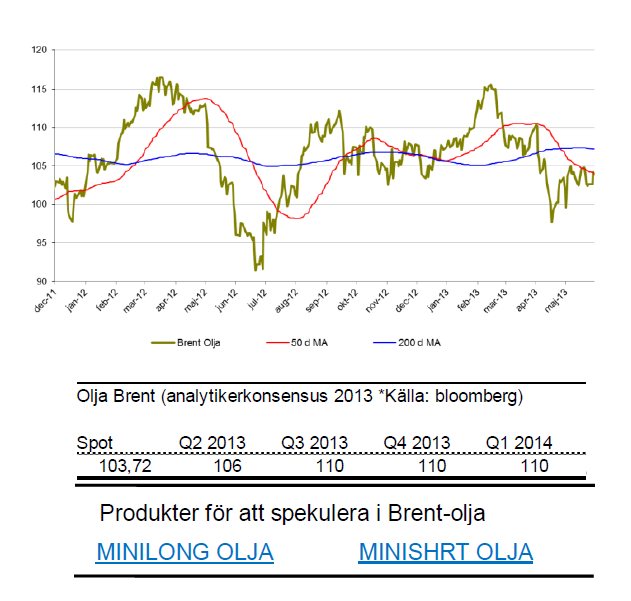
Brent olja
- Berg och dalbanan fortsätter. Under maj har brent ökat med 2,2 %. För året är dock brent ned knappa 6 %.
- Oljan kämpar mot rapporter från OECD och IMF om att Kinas tillväxt ser sämre ut.
- Vidare så håller ökade lager priset nere.
- Ökad oro för åtstramningar på tillgångssidan till följd av oroligheter i mellanöstern motarbetar de negativa nyheterna.
- Utvecklingen för USD och huruvida FED kommer fortsätta med sitt QE kommer styra mycket för oljans fortsatta utveckling.
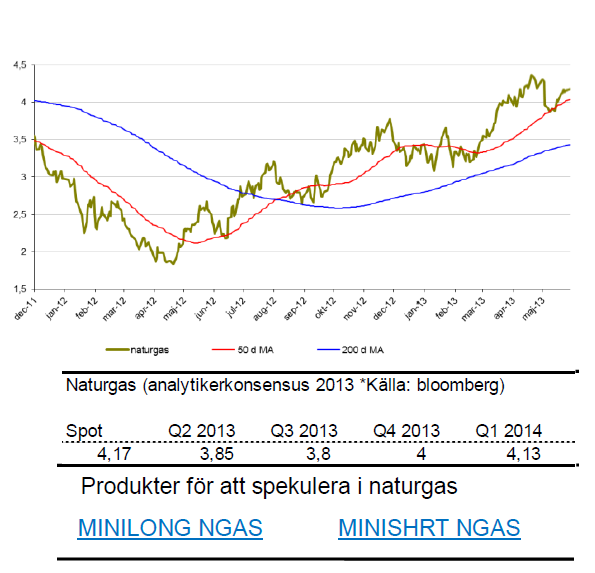
Naturgas
- Naturgas starka trend fortsätter. Trots en rekyl under maj månad är trenden fortsatt uppåt.
- Naturgas tappade ca 3.5 % under maj men är för året ändå upp nästan 30 %.
- Rekylen under maj månad kan mycket väl ha varit hälsosam och skapat en ny högre botten.
- Ökningen av lagrad naturgas är nu på mycket låga nivåer. De lägsta på fem år.
- Återigen är det vädret i USA som till stor del driver uppgången. En vinter som var kallare än normalt har nu skiftet till en varmare vår vilket gör att bränsle krävs för kylsystem.
Råvaror – Metaller
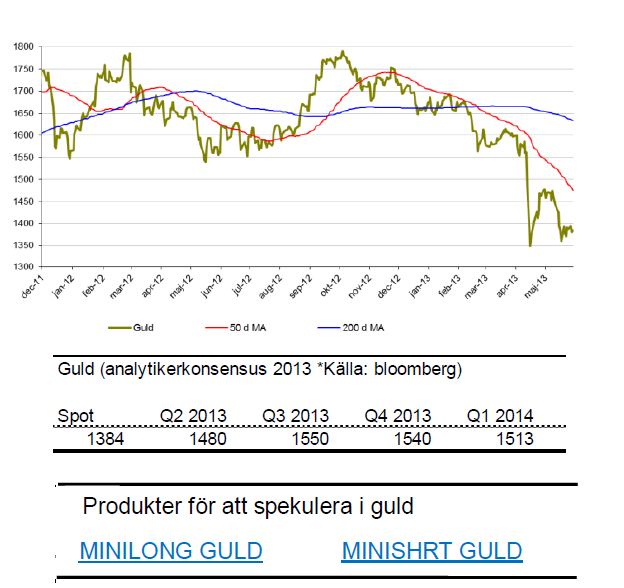
Guld
- Dödskorset (50D- korsar 200D-medelvärde uppifrån) i februari visade sig ge ordentligt med bränsle åt nedgången.
- Under maj fortsatte nedgången och guld gick ned 4,7 %. För året är guld ned 15 %.
- Viktig nivå kring $1350. Återstår att se om denna nivå skapat en dubbelbotten.
- Medierapportering om att FED skulle ge upp sitt stödköpsprogram har inte hjälpt guldkursen. FED fortsätter att pumpa in smått otroliga $85 miljarder USD och håller räntan låg.
- Riskaptiten är fortsatt hög varför mycket guld säljs av för inslussning i aktiemarknaden.
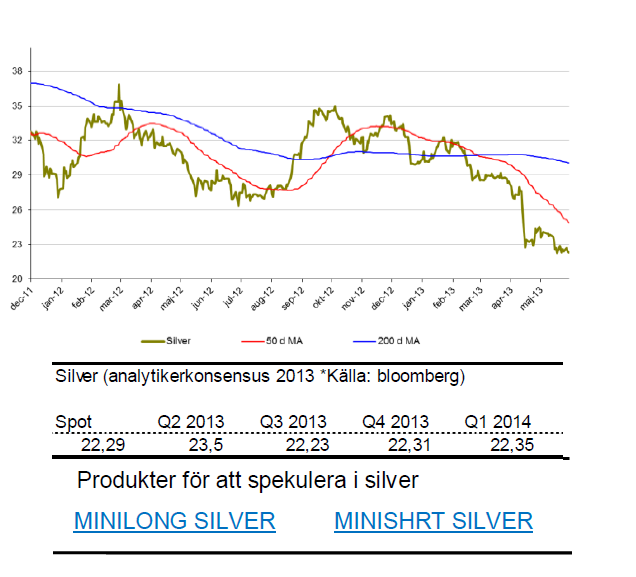
Silver
- Som jag skrev i min krönika följer silver guld slaviskt.
- För maj månad är silver ned dryga 8 % och för året är silver ned 25 %.
- Likt guld tar silver stryk av att riskaptiten fortsatt är hög och behovet av en ”säker hamn” är svalt.
- Silver har den senaste tiden testat stödet vid $22. Intressant nivå att bevaka den närmsta tiden.
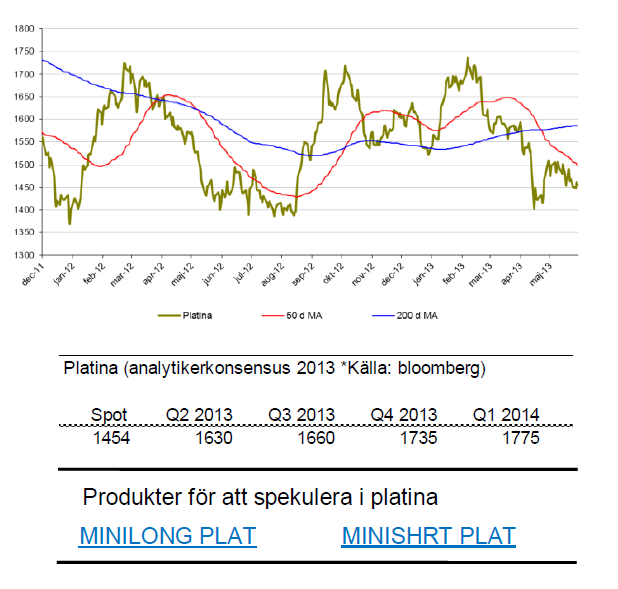
Platina
- Platina fortsätter att prisa högre än guld. Under maj är priset på platina ned knappa 3 %.
- För året är platina ned knappa 4 %.
- Till skillnad från guld och silver drivs platina till största del av industriell efterfrågan. Bilindustrin (autokatalysatorer) går knackigt vilket trycker ner platina.
- Spekulanter ligger i övervikt i korta positioner vilket kan tala för en fortsatt nedgång.
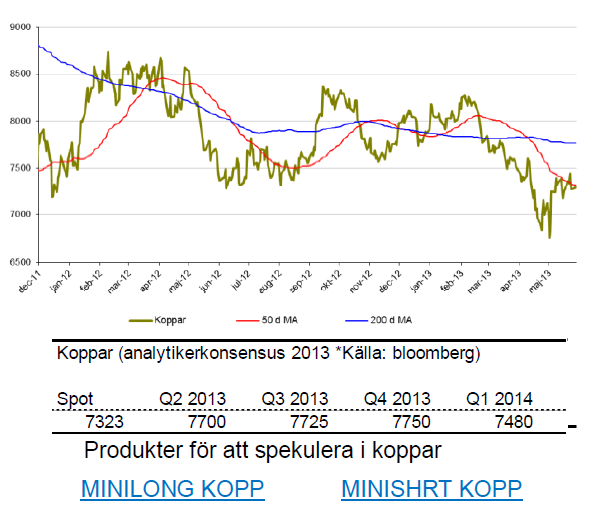
Koppar
- Under maj ökade koppar med 4 %. För året är dock koppar ned dryga 8 %.
- Rapporter om sämre kinesisk tillväxt pressar priset nedåt.
- Under maj månad kan vi dock ha sett ett trendskifte.
- FED flaggar för att ekonomin återhämtar sig vilket kan hjälpa kopparn. Dessutom har två ras i stora gruvor skapat ett litet stopp i produktionsledet vilket drar ned tillgången.
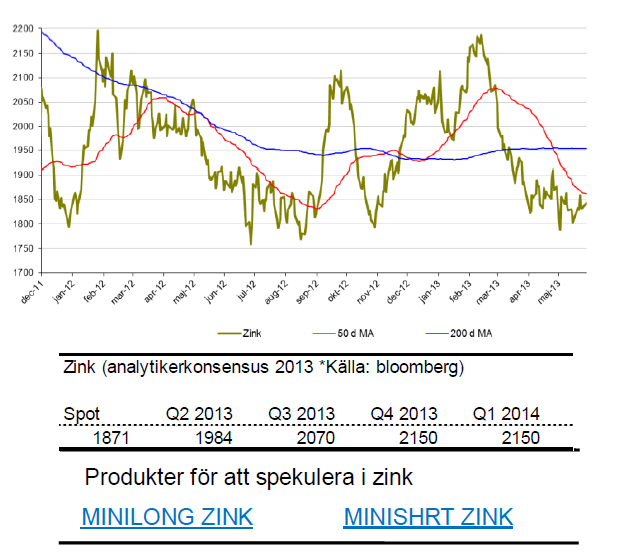
Zink
- Utsikten för basmetaller har ljusnat något. Under maj är zink oförändrat vilket är bra med tanke på att zink tappat 9 %.
- Motståndet kring $1800 har visat sig hålla och likt koppar kan ett trendskifte var på gång. Rekyler värda att bevaka.
- Ytterligare fakta som talar för en vändning är att lagren av zink nu är de lägsta på tre år.
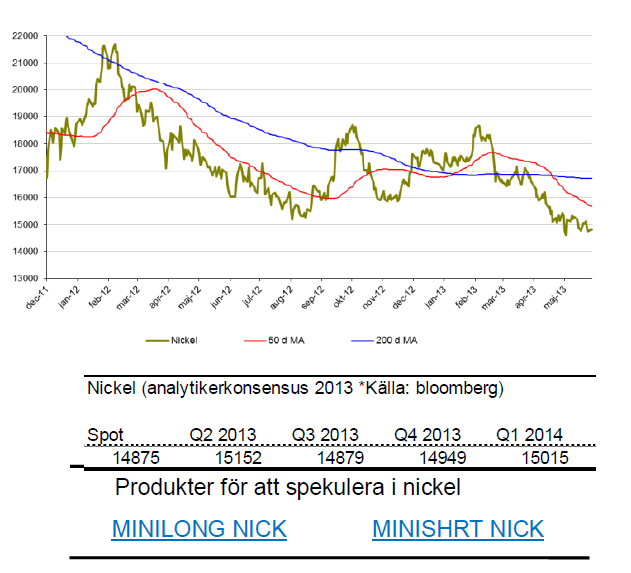
Nickel
- För nickel går det tyngre. Ett dödskors i april kan mycket väl vara starten på fortsatt nedgång.
- Nickel är för året ned drygt 14 %.
- Under maj tappade nickel nästan 3 %.
- Nickel presterade sämst av alla basmetaller under 2012. Slutsiffran blev -8 % för 2012.
- Nickelmarknaden är fortsatt mättad med ökande lager.
- Många stora projekt inom nickelproduktion är redan finansierade och irreversibla vilket kommer att öka tillgången av nickel ytterligare.
Råvaror – Jordbruk
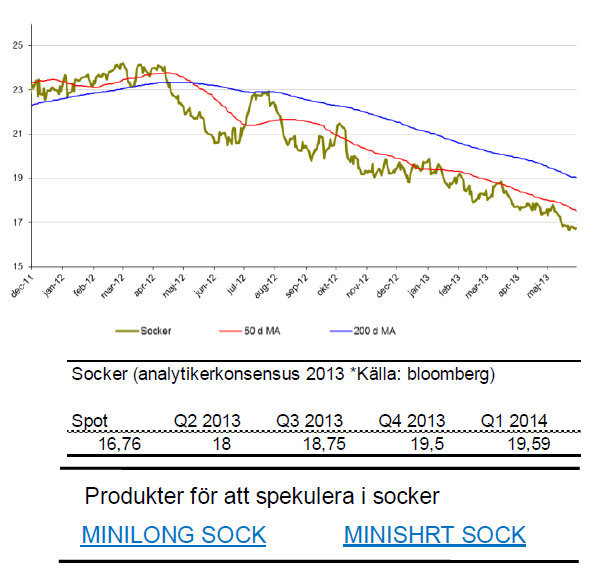
Socker
- Sockers kräftgång fortsätter. Sedan oktober förra året är sockerpriset ned 23 %.
- För året är sockerpriset ned drygt 14 % och maj var inte bättre. Ned 5 %.
- En anledning till det fortsatta prisfallet är att nuvarande nivåer inte motiverar sockerproduktion. Andra grödor eller etanol ses som mer attraktiva.
- Socker har befunnit sig i en negativ trend i snart 2 år. Det är fortfarande långt ned till bottennivåerna där det återigen blir attraktivt för ett köp.
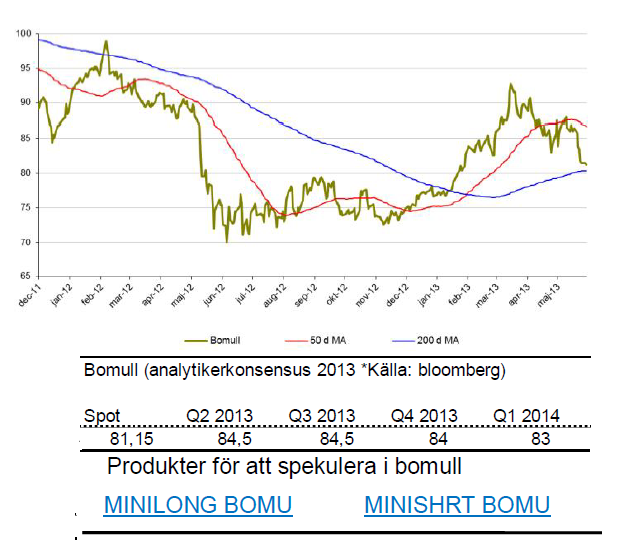
Bomull
- Bomullspriset utvecklades starkt under början av 2013. Nu har dock priset fallit sedan i mars och trenden börjar så smått peka nedåt.
- För året är priset på bomull upp 7,8 %.
- Sedan toppen i mars är dock bomull ned med 12 % vilket visar att säljarna återigen kopplat greppet. Även i maj har de haft kontrollen. Bomull tappade i maj 5 %.
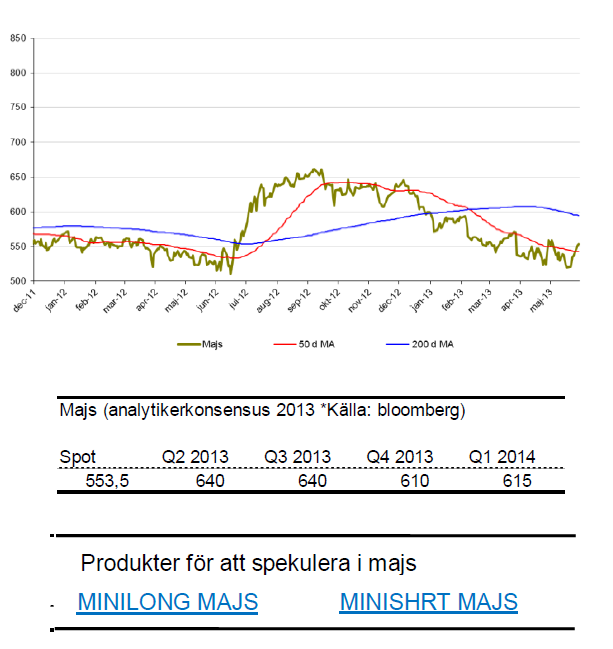
Majs
- Sedan förra sommarens kraftiga uppgång till följd av dålig skörd har majs befunnit sig i en negativ trend.
- För året har majs tappat 4 %.
- Under maj månad tappade majs knappa 3 %.
- För många spannmål väntas goda eller mycket goda skördar vilket kan trycka ned priset ytterligare.
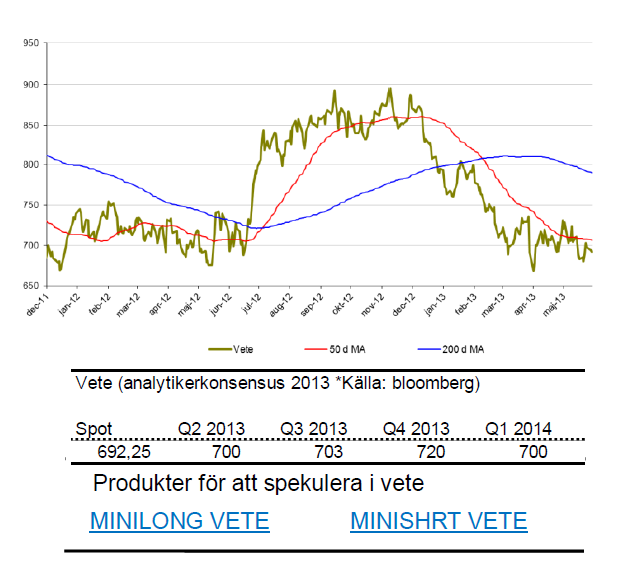
Vete
- För vete gäller samma sak. Sedan förra sommarens topp är trenden negativ.
- God skörd väntas även här så försiktighet gäller.
- För året är vete ned 11 %.
- Under maj är priset på vete ned något.
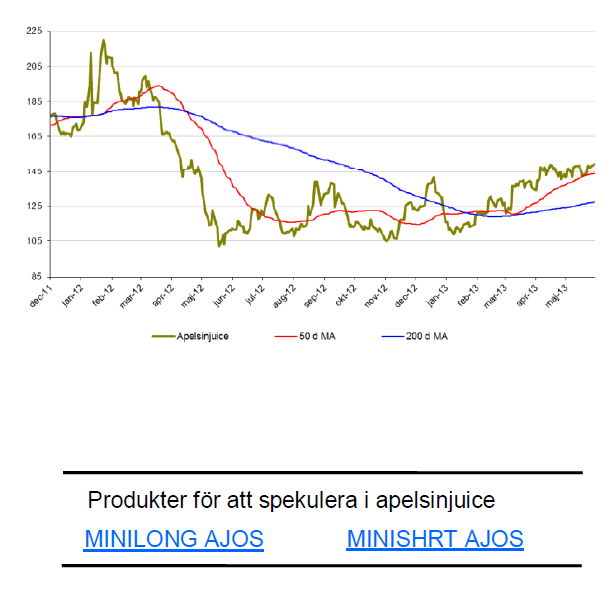
Apelsinjuice
- Vi har länge bevakat apelsinjuice i Tradingklubben.
- För året är apelsinjuice upp 20 %.
- I maj är priset upp 5 %.
- Floridas citrusodlare brottas just nu med det allvarligaste hotet det någonsin stått inför, en bakteriell sjukdom utan botemedel som har smittat samtliga de 31 länen i vilka det odlas apelsiner och citroner.
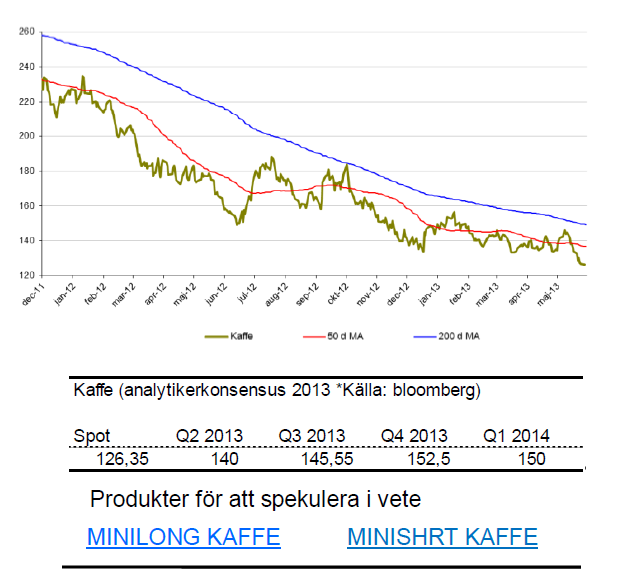
Kaffe
- Kaffe ligger fortfarande i en långsiktigt nedåtgående trend.
- För året är kaffe ned 13 %. I maj stannade nedgången på hela 11 %
- Likt apelsinjuice kämpar dock odlare med sjukdomar. Något som kanske kan vända trenden.
- Växtsjukdomen Roya, också känt som kafferost eller kaffebladssvamp, är en liten orangefärgad svamp som nu har nått Centralamerika.
[box]Denna uppdatering är producerat av SIP Nordic och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Ansvarsbegränsning
Detta produktblad utgör endast marknadsföring och har sammanställts av SIP Nordic Fondkommission AB.
Innehållet ger inte fullständig information avseende det finansiella instrumentet. Investerare uppmanas att del av prospekt och slutliga villkor, vilka finns tillgängliga på: www.rbsbank.se/markets, innan ett investeringsbeslut tas.
Förekommande exempel är simulerade och baseras på SIP Nordics egna beräkningar och antaganden, en person som använder andra data eller antaganden kan nå andra resultat. Administrativa avgifter och transaktionsavgifter påverkar den faktiska avkastningen.
Analys
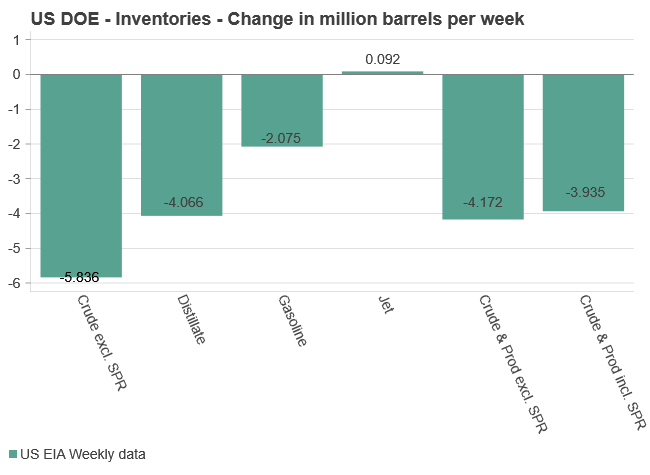
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

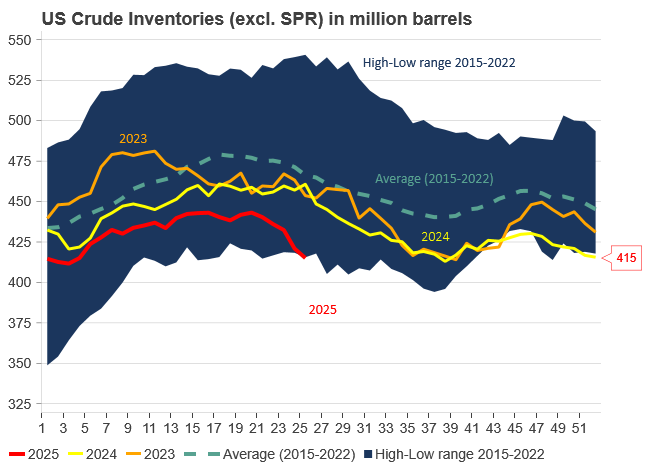
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanA muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanJonas Lindvall är tillbaka med ett nytt oljebolag, Perthro, som ska börsnoteras
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanOljan, guldet och marknadens oroande tystnad
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanDomstolen ger klartecken till Lappland Guldprospektering