Analys
SHB Råvarubrevet 27 juli 2012
 Olja
Olja
Brentoljan har gått upp i pris varje dag under veckan. I skrivande stund ligger priset på 105.90 USD/fat vilket motsvarar en uppgång på 2.5%. Detta är den tredje veckan i rad med uppgångar. En del av uppgången kan förklaras av det förbättrade risksentimentet vilket i sin tur har försvagat dollarn. Risksentimentet fick ytterligare stöd under fredagen då ECB:s Mario Draghi indikerade att centralbanken kan tänka sig att stödköpa obligationer utgivna av krisdrabbade länder. ECB har använt sig av stödköp tidigare men avslutade köpprogrammet i mars.
Koppar
Kopparpriset har stigit med knappt 2 % under veckan, framförallt drivet av positivare framtidsutsikter. Priset på koppar har stigit något mer än de andra basmetallerna (exempelvis aluminium). En anledning kan vara den något anstränga utbudssituationen. Den volym som finns lagrad för omedelbar användning befinner sig 20 % under genomsnittet för de 10 senaste åren. Något som talar emot en kraftig prisuppgång för koppar är att Kinas valuta yuanen försvagats mot US-dollarn. (Kina är världens största kopparkonsument). Yuanen handlas nu till 6.38, vilken är en försvagning från 20-års lägsta på 6.28 (som nåddes under maj). Å andra sidan kommer de kinesiska exportföretagen nu få kostnadsfördelar gentemot sina utländska konkurrenter.
Guld
Paradoxalt nog har även guldet gynnats av den förbättrade riskaptiten. Under veckan har priset gått upp 2.7% för att just nu handlas på 1627 USD/ounce. Prisutvecklingen på guld börjar mer och mer likna utvecklingen för metaller såsom koppar och aluminium. För tillfället verkar guldet ha tappat sina ”positiva portföljegenskaper”, det vill säga ha en negativ korrelation med marknaden. I det längre perspektivet kan det vara intressant att se vad som händer i de stora guldköpande länderna (Indien och Kina). De senaste siffrorna från Indien visar på en nedgång med upp till 35 % jämfört med månaden innan. De indiska köparna (främst landsbygdsbefolkning och urban medelklass) pressas av en svag börs samt som den indiska rupien har tappat mycket mot US-dollarn. Om trenden håller i sig så skulle detta vara andra året i följd som importen till Indien minskar.
Socker
Det regn i Brasilien som sedan några veckor tillbaka har försenat sockerskörden avsevärt har avtagit. Torrt väder är gynnsamt för skörden och det stora antal fartyg som väntat på last i de brasilianska hamnarna minskar till antal. Marknaden håller även ögonen på monsunperioden i Indien vilken står för ca 70% av landets årliga nederbörd. Monsunperioden har hittills medfört betydligt mindre regn än estimerat vilket kan komma att påverka den kommande skörden negativt. Torkan i USA som medfört stora skador på majs skördarna har lett till spekulationer om ett eventuellt ökat intresse för socker som substitut till majs sirap.
Kaffe
Stora mängder regn i Brasilien i juni har fördröjt skörden av kaffe samt även delvis försämrat bönornas kvalitet. Regnet har avtagit och enligt prognosen ska det torrare vädret hålla i sig till början av augusti vilket är positivt för kaffeproducenterna. Spekulationer kring en minskad efterfrågan av kaffe till följd av de ekonomiska oroligheterna i Europa fortsätter påverka priset och producenterna verkar invänta ett något mer gynnsamt prisläge.
Apelsinjuice
Den rådande orkansäsongen i Florida har hittills inte orsakat någon skada på skörden och kvaliteten samt utbudet av apelsiner är god. Orkansäsongen har fått en mild start men något ökad risk för tilltagande storm över Atlanten i början av veckan fick priset att klättra marginellt.
Vete
Terminspriser på vete har i veckan gått ned i både Chicago och Paris påverkat bland annat av lägre priser på majs i USA och förbättrat väder i stora delar av Europa. Oron ökar dock i Ryssland, där avkastningsnivån hittills ligger långt under det normala för vetet, tidigare i veckan rapporterade det ryska jordbruksministeriet att skörden var till 22 procent avklarad och att avkastningsnivån ligger nästan 30 procent under förra årets nivå – vilket skulle innebära en total produktionsnivå på under 40 miljoner ton, att jämföra med drygt 56 miljoner ton förra året. Exporttakten vad gäller ryskt vete har varit ganska hög den senaste tiden och fler och fler börjar nu tro att någon form av exportbegränsningar kommer införas någon gång på säsongen, även om regeringen fortsätter hävda att det inte är aktuellt.
Marknaden är nu ganska nervös och väldigt mycket negativt är redan inräknat i dagens höga prisnivå, det kanske blir svårt för priserna att gå så mycket högre nu men skicket på den amerikanska majsen (som till stor del drivit prisuppgången) kan mycket väl förvärras ytterligare och situationen i Ryssland är som sagt klart osäker. Någon större nedgång är svår att se inom en snar framtid, på lite längre sikt är risken dock som vanligt stor och fallhöjden är såklart väldigt stor från dagens nivåer.
Majs
Majsen i Chicago har gått ned något i pris under veckan, delvis som följd av att en del regn har fallit i delar av USA samt att en del prognoser lovar lite ytterligare lite regn i helgen – frågan är om det verkligen kommer göra någon nytta, förmodligen inte. Torrt och varmt väder beräknas dessutom återkomma i nästa vecka och grödans skick lär försämras än mer. Flera amerikanska analytiker har nu justerat ned sina förväntningar på den amerikanska majsens avkastningsnivå till runt 130 bushels per acre, en del även en bra bit under det – att jämföra med 146 bushels per acre i USDA:s WASDE-rapport för juli månad. Inte mycket talar för en nedgång för majspriserna den närmaste tiden, efterfrågan från inte minst etanolindustrin har gått ned som följd av prisuppgången men förväntad produktionsnivå går ner ännu mer. Samtidigt ökar oron även för majsen i EU och inte minst i Ukraina, även det orsakat av torr och varm väderlek.
Soja
Sojapriserna i Chicago har gått ned i pris under veckan likt de andra stora jordbruksprodukterna. Viss nederbörd har fallit där det behövs i USA men inte tillräckligt för att ha gjort någon större nytta. I helgen väntas ytterligare lite regn men i nästa vecka beräknas det torra och varma vädret vara tillbaka. Avkastningspotentialen fortsätter att falla i takt med att grödans skick försämras kontinuerligt; kommande två veckor är en klart kritisk period för plantorna och även om väderprognoserna är ganska varierande ser det inte särskilt ljust ut. Sojan ser fortsatt stark ut och efterfrågan håller i sig trots den historiskt sett väldigt höga prisnivå.
[box]SHB Råvarubrevet är producerat av Handelsbanken och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Ansvarsbegränsning
Detta material är producerat av Svenska Handelsbanken AB (publ) i fortsättningen kallad Handelsbanken. De som arbetar med innehållet är inte analytiker och materialet är inte oberoende investeringsanalys. Innehållet är uteslutande avsett för kunder i Sverige. Syftet är att ge en allmän information till Handelsbankens kunder och utgör inte ett personligt investeringsråd eller en personlig rekommendation. Informationen ska inte ensamt utgöra underlag för investeringsbeslut. Kunder bör inhämta råd från sina rådgivare och basera sina investeringsbeslut utifrån egen erfarenhet.
Informationen i materialet kan ändras och också avvika från de åsikter som uttrycks i oberoende investeringsanalyser från Handelsbanken. Informationen grundar sig på allmänt tillgänglig information och är hämtad från källor som bedöms som tillförlitliga, men riktigheten kan inte garanteras och informationen kan vara ofullständig eller nedkortad. Ingen del av förslaget får reproduceras eller distribueras till någon annan person utan att Handelsbanken dessförinnan lämnat sitt skriftliga medgivande. Handelsbanken ansvarar inte för att materialet används på ett sätt som strider mot förbudet mot vidarebefordran eller offentliggörs i strid med bankens regler.
Analys
Sell the rally. Trump has become predictable in his unpredictability

Hesitant today. Brent jumped to an intraday high of $66.36/b yesterday after having touched an intraday low of $60.07/b on Monday as Indian and Chinese buyers cancelled some Russian oil purchases and instead redirected their purchases towards the Middle East due to the news US sanctions. Brent is falling back 0.4% this morning to $65.8/b.

It’s our strong view that the only sensible thing is to sell this rally. In all Trump’s unpredictability he has become increasingly predictable. Again and again he has rumbled about how he is going to be tough on Putin. Punish Putin if he won’t agree to peace in Ukraine. Recent rumbling was about the Tomahawk rockets which Trump threatened on 10 October and 12 October to sell/send to Ukraine. Then on 17 October he said that ”the U.S. didn’t want to give away weapons (Tomahawks) it needs”.
All of Trump’s threats towards Putin have been hot air. So far Trump’s threats have been all hot air and threats which later have evaporated after ”great talks with Putin”. After all these repetitions it is very hard to believe that this time will be any different. The new sanctions won’t take effect before 21. November. Trump has already said that: ”he was hoping that these new sanctions would be very short-lived in any case”. Come 21. November these new sanctions will either evaporate like all the other threats Trump has thrown at Putin before fading them. Or the sanctions will be postponed by another 4 weeks or 8 weeks with the appearance that Trump is even more angry with Putin. But so far Trump has done nothing that hurt Putin/Russia. We can’t imagine that this will be different. The only way forward in our view for a propre lasting peace in Ukraine is to turn Ukraine into defensive porcupine equipped with a stinging tail if need be.
China will likely stand up to Trump if new sanctions really materialize on 21 Nov. Just one country has really stood up to Trump in his tariff trade war this year: China. China has come of age and strength. I will no longer be bullied. Trump upped tariffs. China responded in kind. Trump cut China off from high-end computer chips. China put on the breaks on rare earth metals. China won’t be bullied any more and it has the power to stand up. Some Chinese state-owned companies like Sinopec have cancelled some of their Russian purchases. But China’s Foreign Ministry spokesperson Guo Jiakun has stated that China “oppose unilateral sanctions which lack a basis in international law and authorization of the UN Security Council”. Thus no one, not even the US shall unilaterally dictate China from whom they can buy oil or not. This is yet another opportunity for China to show its new strength and stand up to Trump in a show of force. Exactly how China choses to play this remains to be seen. But China won’t be bullied by over something as important as its oil purchases. So best guess here is that China will defy Trump on this. But probably China won’t need to make a bid deal over this. Firstly because these new sanctions will either evaporate as all the other threats or be postponed once we get to 21 November. Secondly because the sanctions are explicit towards US persons and companies but only ”may” be enforced versus non-US entities.
Sanctions is not a reduction in global supply of oil. Just some added layer of friction. Anyhow, the new sanctions won’t reduce the supply of Russian crude oil to the market. It will only increase the friction in the market with yet more need for the shadow fleet and ship to ship transfer of Russian oil to dodge the sanctions. If they materialize at all.
The jump in crude oil prices is probably due to redirections of crude purchases to the Mid-East and not because all speculators are now turned bullish. Has oil rallied because all speculators now suddenly have turned bullish? We don’t think so. Brent crude has probably jumped because some Indian and Chinese oil purchasers of have redirected their purchases from Russia towards the Mid-East just in case the sanctions really materializes on 21 November.
Analys
Brent crude set to dip its feet into the high $50ies/b this week

Parts of the Brent crude curve dipping into the high $50ies/b. Brent crude fell 2.3% over the week to Friday. It closed the week at $61.29/b, a slight gain on the day, but also traded to a low of $60.14/b that same day and just barely avoided trading into the $50ies/b. This morning it is risk-on in equities which seems to help industrial metals a little higher. But no such luck for oil. It is down 0.8% at $60.8/b. This week looks set for Brent crude to dip its feet in the $50ies/b. The Brent 3mth contract actually traded into the high $50ies/b on Friday.

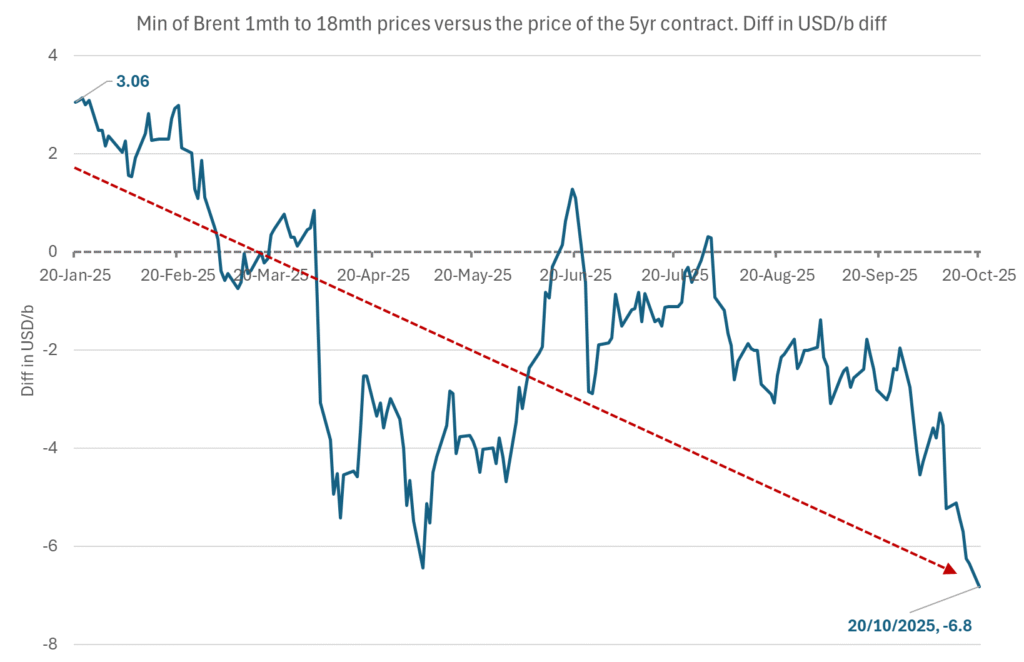
The front-end backwardation has been on a weakening foot and is now about to fully disappear. The lowest point of the crude oil curve has also moved steadily lower and lower and its discount to the 5yr contract is now $6.8/b. A solid contango. The Brent 3mth contract did actually dip into the $50ies/b intraday on Friday when it traded to a low point of $59.93/b.
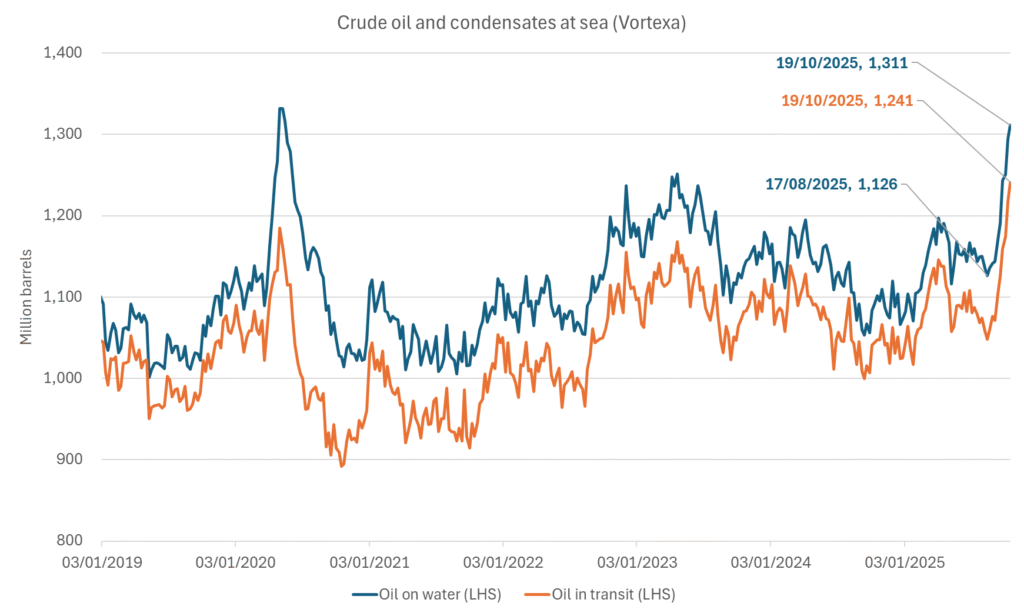
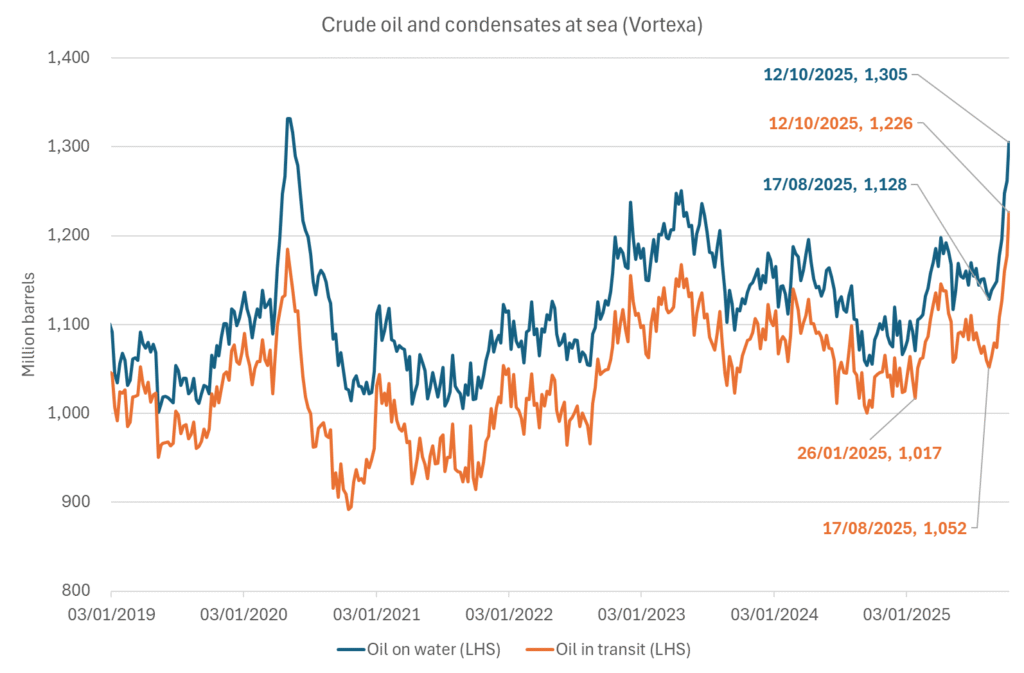
More weakness to come as lots of oil at sea comes to ports. Mid-East OPEC countries have boosted exports along with lower post summer consumption and higher production. The result is highly visibly in oil at sea which increased by 17 mb to 1,311 mb over the week to Sunday. Up 185 mb since mid-August. On its way to discharge at a port somewhere over the coming month or two.
Don’t forget that the oil market path ahead is all down to OPEC+. Remember that what is playing out in the oil market now is all by design by OPEC+. The group has decided that the unwind of the voluntary cuts is what it wants to do. In a combination of meeting demand from consumers as well as taking back market share. But we need to remember that how this plays out going forward is all at the mercy of what OPEC+ decides to do. It will halt the unwinding at some point. It will revert to cuts instead of unwind at some point.
A few months with Brent at $55/b and 40-50 US shale oil rigs kicked out may be what is needed. We think OPEC+ needs to see the exit of another 40-50 drilling rigs in the US shale oil patches to set US shale oil production on a path to of a 1 mb/d year on year decline Dec-25 to Dec-26. We are not there yet. But a 2-3 months period with Brent crude averaging $55/b would probably do it.
Oil on water increased 17 mb over the week to Sunday while oil in transit increased by 23 mb. So less oil was standing still. More was moving.
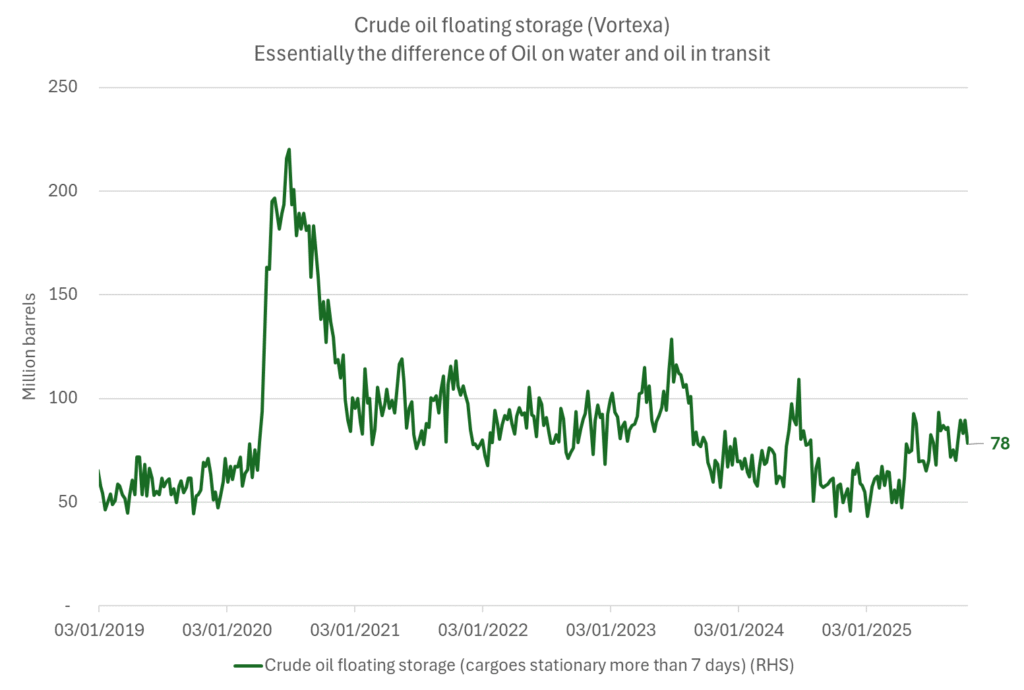
Crude oil floating storage (stationary more than 7 days). Down 11 mb over week to Sunday
The lowest point of the Brent crude oil curve versus the 5yr contract. Weakest so far this year.
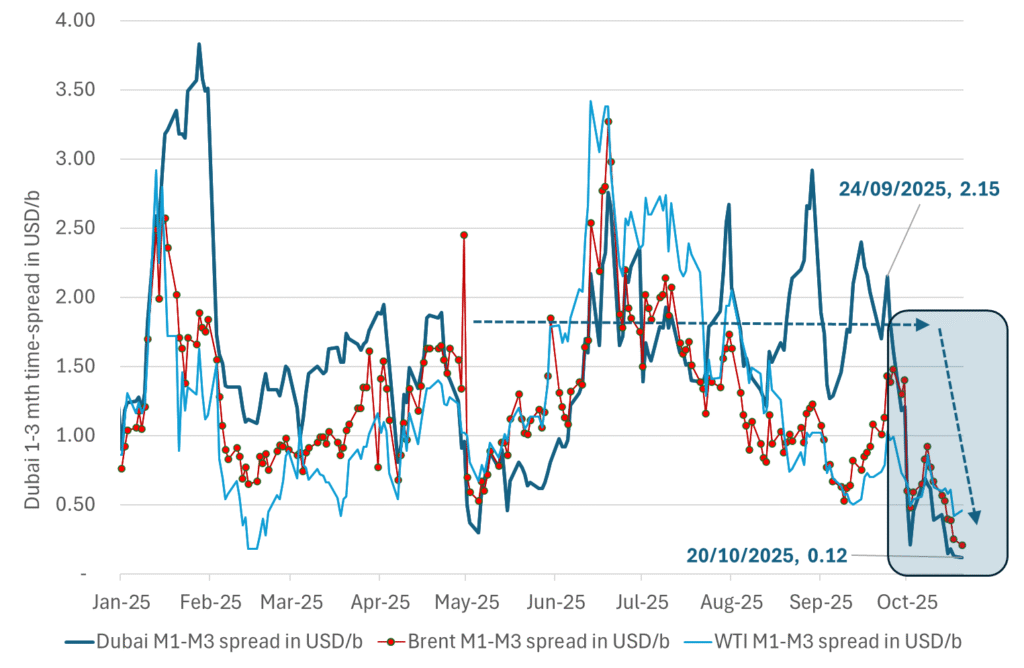
Crude oil 1mth to 3mth time-spreads. Dubai held out strongly through summer, but then that center of strength fell apart in late September and has been leading weakness in crude curves lower since then.
Analys
Crude oil soon coming to a port near you

Rebounding along with most markets. But concerns over solidity of Gaza peace may also contribute. Brent crude fell 0.8% yesterday to $61.91/b and its lowest close since May this year. This morning it is bouncing up 0.9% to $62.5/b along with a softer USD amid positive sentiment with both equities and industrial metals moving higher. Concerns that the peace in Gaza may be less solid than what one might hope for also yields some support to Brent. Bets on tech stocks are rebounding, defying fears of trade war. Money moving back into markets. Gold continues upwards its strong trend and a softer dollar helps it higher today as well.

US crude & products probably rose 5.6 mb last week (API) versus a normal seasonal decline of 2.4 mb. The US API last night partial and thus indicative data for US oil inventories. Their data indicates that US crude stocks rose 7.4 mb last week, gasoline stocks rose 3.0 mb while Distillate stocks fell 4.8 mb. Altogether an increase in commercial crude and product stocks of 5.6 mb. Commercial US crude and product stocks normally decline by 2.4 mb this time of year. So seasonally adjusted the US inventories rose 8 mb last week according to the indicative numbers by the API. That is a lot. Also, the counter seasonal trend of rising stocks versus normally declining stocks this time of year looks on a solid pace of continuation. If the API is correct then total US crude and product stocks would stand 41 mb higher than one year ago and 6 mb higher than the 2015-19 average. And if we combine this with our knowledge of a sharp increase in production and exports by OPEC(+) and a large increase in oil at sea, then the current trend in US oil inventories looks set to continue. So higher stocks and lower crude oil prices until OPEC(+) switch to cuts. Actual US oil inventory data today at 18:00 CET.
US commercial crude and product stocks rising to 1293 mb in week 41 if last nights indicative numbers from API are correct.
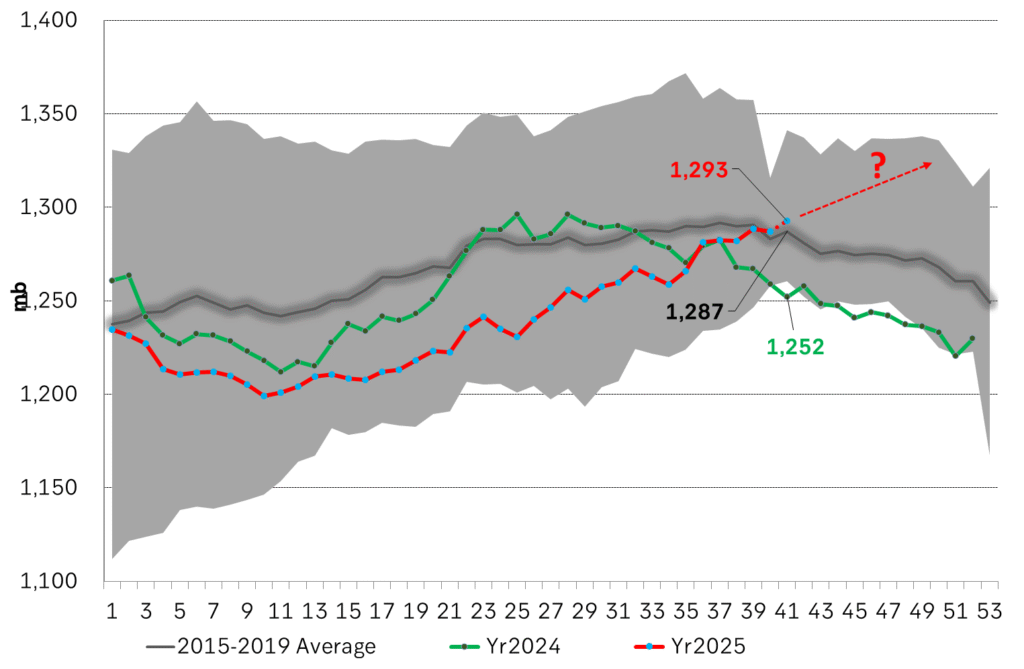
Crude oil soon coming to a port near you. OPEC has lifted production sharply higher this autumn. At the same time demand for oil in the Middle-East has fallen as we have moved out of summer heat and crude oil burn for power for air-conditioning. The Middle-East oil producers have thus been able to lift exports higher on both accounts. Crude oil and condensates on water has shot up by 177 mb since mid-August. This oil is now on its way to ports around the world. And when they arrive, it will likely help to lift stocks onshore higher. That is probably when we will lose the last bit of front-end backwardation the the crude oil curves. That will help to drive the front-month Brent crude oil price down to the $60/b line and revisit the high $50ies/b. Then the eyes will be all back on OPEC+ when they meet in early November and then again in early December.
Crude oil and condensates at sea have moved straight up by 177 mb since mid-August as OPEC(+) has produced more, consumed less and exported more.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanOPEC+ missar produktionsmål, stöder oljepriserna
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGoldman Sachs höjer prognosen för guld, tror priset når 4900 USD
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanBlykalla och amerikanska Oklo inleder ett samarbete
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGuld nära 4000 USD och silver 50 USD, därför kan de fortsätta stiga
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanLeading Edge Materials är på rätt plats i rätt tid
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanNytt prisrekord, guld stiger över 4000 USD
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanEtt samtal om guld, olja, koppar och stål
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanOPEC+ will likely unwind 500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d in one go could be in the cards










