Analys
Extremely tight platinum and palladium markets

 The South African platinum mining industry has been affected by strikes for more than ten weeks now. Because stocks are dwindling, the mining companies concerned are finding it increasingly difficult to fulfil their contractual delivery obligations. The situation as regards palladium is dominated by concerns about how Russia might react if the West were to impose further-reaching sanctions on the country. At the same time, demand on both markets is robust, driven by the automotive industry. The situation appears to be tightening noticeably, which in our opinion suggests that platinum and palladium prices will rise.
The South African platinum mining industry has been affected by strikes for more than ten weeks now. Because stocks are dwindling, the mining companies concerned are finding it increasingly difficult to fulfil their contractual delivery obligations. The situation as regards palladium is dominated by concerns about how Russia might react if the West were to impose further-reaching sanctions on the country. At the same time, demand on both markets is robust, driven by the automotive industry. The situation appears to be tightening noticeably, which in our opinion suggests that platinum and palladium prices will rise.
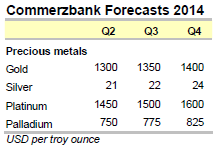 Platinum came under pressure from the weak gold price in March and declined noticeably as a result. For a time it dropped below the $1,400 per troy ounce mark to a six-week low. Palladium fared somewhat better and trended sideways while fluctuating significantly. For the first time since August 2011, it actually exceeded the $800 per troy ounce mark for a while, though it was unable to maintain this level (Chart 1). We believe that both precious metal prices are too low from a fundamental viewpoint given the risks to supply. In this Commodity Spotlight we will be assessing the supply situation in South Africa, the world’s biggest platinum producer and the world’s number two palladium producer, as well as taking a look at Russia, the biggest supplier of palladium.
Platinum came under pressure from the weak gold price in March and declined noticeably as a result. For a time it dropped below the $1,400 per troy ounce mark to a six-week low. Palladium fared somewhat better and trended sideways while fluctuating significantly. For the first time since August 2011, it actually exceeded the $800 per troy ounce mark for a while, though it was unable to maintain this level (Chart 1). We believe that both precious metal prices are too low from a fundamental viewpoint given the risks to supply. In this Commodity Spotlight we will be assessing the supply situation in South Africa, the world’s biggest platinum producer and the world’s number two palladium producer, as well as taking a look at Russia, the biggest supplier of palladium.
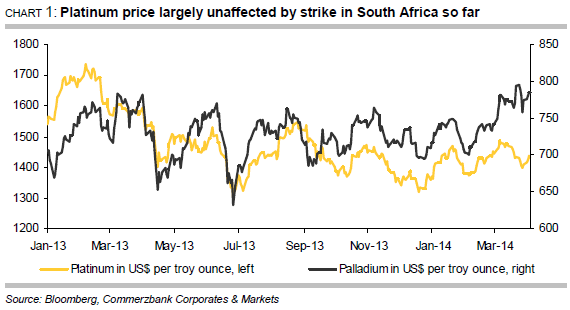
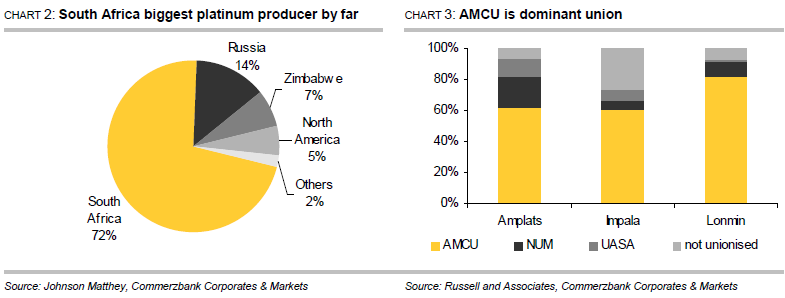
According to figures from Johnson Matthey, South Africa produced 4.12 million ounces of platinum and 2.35 million ounces of palladium last year, thus accounting for 72% of global platinum mining production and 37% of global palladium mining production (Chart 2). Palladium is generally mined together with platinum. However, a strike has been underway in the South African platinum mining industry since 23 January. The radical AMCU (Association of Mineworkers and Construction Union) called its members out on strike to lend emphasis to its calls for wage hikes. The union, which was established in 1998 and formally registered in 2001, represents the majority of workers in the platinum mining industry and has meanwhile overtaken the more moderate union NUM (National Union of Mineworkers) in terms of membership. The world’s three biggest platinum producers are affected: Anglo American Platinum, Impala Platinum and Lonmin, 87% of whose workers are union members. Accounting for 66% of these, the AMCU predominates (Chart 3). Over 70,000 workers went out on strike when called upon to do so. The strike is the biggest to hit the South African mining sector since the Apartheid regime ended in 1994. 350,000 workers took to the streets in 1987 to protest for better working conditions, though this strike was brought to an end after around three weeks and cost the mining companies around ZAR 250 million at the time, according to the NUM.
Union and companies still far apart
The AMCU is calling for producers to increase wages significantly, its core demand being that entry-level salaries be doubled to ZAR 12,500 per month. Originally, the AMCU urged the mining companies to meet its demands immediately, though it has meanwhile shown itself willing to “make some concessions”. AMCU has “eased” its core demand in two stages, with the result that it now wishes to see wages doubled within four years. For their part, the companies have offered staggered wage increases over the course of three years – 9% in the first year, 8% in the second and 7.5% in the third. In February, the rate of inflation in South Africa was 5.9%. In other words, the two parties still maintain positions that are very far apart. To date, the state mediator engaged to help (CCMA – Commission for Conciliation, Mediation and Arbitration) has failed to bring the two parties any closer together. In fact, talks were actually suspended for a time because the mediator saw no possibility of agreement.
Politicians exercise restraint ahead of elections
So far, politicians have chosen not to intervene in the strike, clearly because of the upcoming elections in South Africa. Parliamentary elections will be held on 7 May, with presidential elections to follow in the second half of the year. The mine workers make up a major group of voters which neither the governing party ANC (African National Congress) nor the opposition parties wish to alienate. Polls indicate that the ANC is likely to win the elections, though it remains to be seen whether this will subsequently result in the necessary reforms being implemented which would also steer the mining industry into calmer waters. Recently, the South African finance minister played down the strike’s negative impact on the local economy, claiming that the current strike is causing less damage than the industrial actions taken two years ago. In 2012, a series of strikes cost gold and platinum producers more than ZAR 16 billion.
High revenue losses for companies and lost earnings for workers
By their own account, the mining companies concerned are losing 9,900 ounces of platinum production every day – 4,000 ounces at Anglo American Platinum, 2,800 ounces at Impala Platinum and 3,100 ounces at Lonmin. Assuming that work generally continues in the mines seven days a week, the producers have thus lost nearly 700,000 ounces of production since the beginning of the strike. The companies claim that they have lost revenues totalling over ZAR 11 billion as a result. So far, workers who are not being paid while they are out on strike have lost earnings of around ZAR 5 billion.
Company stocks dwindling
Although production has been at a standstill since the beginning of the strike, the companies have been able at least partly to fulfil their delivery obligations by drawing on stocks. By their own account, the producers had piled up considerable stocks in the run-up to the strike, which industrial sources estimated would last two months. The situation is not the same in all the companies, however. Anglo American Platinum had for example announced at the end of March that it had used up half of its 430,000 ounces of stocks up to that point, saying that material would be bought on the market if stocks ran out. By contrast, Impala Platinum had already declared “force majeure” in early March and has no longer been able to guarantee deliveries since the beginning of April. Impala is likewise considering buying in material on the market in order to meet its contractual obligations. Lonmin had also downwardly revised its sales forecasts for this year at an early stage.
Negative long-term impact cannot be excluded
Even if the strike can be brought to an end, it will take weeks if not months before platinum production achieves its pre-strike levels again. After all, the damage in shafts and galleries resulting from the lack of use first has to be identified and, most importantly of all, safety has to be restored. In some cases the companies are already talking about irreparable damage and are considering shutting down individual shafts entirely. There are also likely to be some redundancies because the companies claim that they will otherwise no longer be able to operate at a profit. This could spark renewed protests and set in motion a vicious circle which would harm the entire country.
Concers about supply outages in Russia
As far as palladium is concerned, we need to take a look at Russia. According to data from Johnson Matthey, Russia accounted for 42% of worldwide palladium supply in 2013 (primary production and reserve sales together totalling 2.7 million ounces) and for 14% of global platinum production (780,000 ounces), making the country the largest producer of palladium and the second-largest producer of platinum. The situation here is dominated by concerns about the extent to which possible sanctions imposed by the West on Russia could hit this sector and how Russia might react to further-reaching sanctions against its economy. That said, there are no signs so far that deliveries from Russia are at risk. According to the UK’s Financial Times, however, Norilsk Nickel, the world’s largest palladium producer, is currently negotiating longterm palladium and platinum supply contracts with Chinese and Japanese buyers. Although this might not mean anything, it could perhaps be viewed as a not particularly subtle hint to the West.
Robust demand from the automotive industry
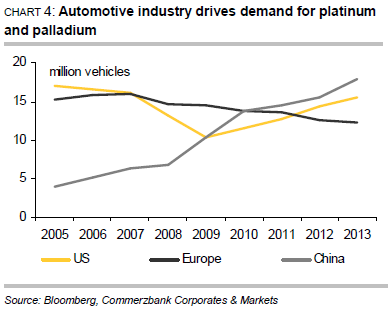 Driven by the automotive industry, demand for both platinum and palladium is robust. March saw the seasonally adjusted annualized vehicle sales rate in the US rise to 16.33 million units, the highest figure since May 2007. At 3.16 million units, car sales in China in January and February combined were a good 11% up on the same period last year. It would therefore seem that the 2014 target of an increase in sales of up to 10%, set by the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, is achievable. The European auto industry may also have bottomed out, for car sales in February increased year-on-year for the sixth consecutive month (Chart 4).
Driven by the automotive industry, demand for both platinum and palladium is robust. March saw the seasonally adjusted annualized vehicle sales rate in the US rise to 16.33 million units, the highest figure since May 2007. At 3.16 million units, car sales in China in January and February combined were a good 11% up on the same period last year. It would therefore seem that the 2014 target of an increase in sales of up to 10%, set by the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, is achievable. The European auto industry may also have bottomed out, for car sales in February increased year-on-year for the sixth consecutive month (Chart 4).
New palladium ETF on the market
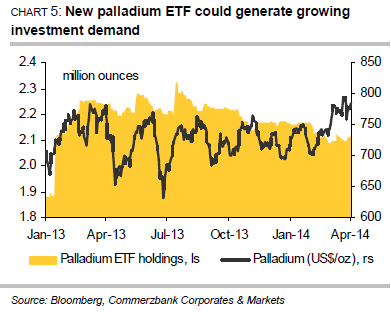 When it comes to investment demand, market participants evidently switched their allegiance from palladium to platinum in the first quarter. While the palladium ETFs tracked by Bloomberg recorded outflows of 51,900 ounces, the platinum ETFs saw inflows of 53,600 ounces. That said, the trend could soon be reversed in the case of palladium (Chart 5), for South African investment bank Absa Capital launched its long-awaited palladium ETF at the end of March. The ETF is listed on the Johannesburg Stock Exchange and solely sourced with palladium from South Africa. If the palladium ETF follows the same course as Absa Capital’s platinum ETF, which was launched at the end of April 2013, a great deal of supply could be stripped from the market. Within just four months of its launch, the platinum ETF became the world’s biggest platinum ETF and at the end of March had a market share of 37% with over 952,000 ounces. Holdings in all platinum ETFs combined are equivalent to more than five months of global mining production, while holdings in palladium ETFs equate to nearly four months of global production.
When it comes to investment demand, market participants evidently switched their allegiance from palladium to platinum in the first quarter. While the palladium ETFs tracked by Bloomberg recorded outflows of 51,900 ounces, the platinum ETFs saw inflows of 53,600 ounces. That said, the trend could soon be reversed in the case of palladium (Chart 5), for South African investment bank Absa Capital launched its long-awaited palladium ETF at the end of March. The ETF is listed on the Johannesburg Stock Exchange and solely sourced with palladium from South Africa. If the palladium ETF follows the same course as Absa Capital’s platinum ETF, which was launched at the end of April 2013, a great deal of supply could be stripped from the market. Within just four months of its launch, the platinum ETF became the world’s biggest platinum ETF and at the end of March had a market share of 37% with over 952,000 ounces. Holdings in all platinum ETFs combined are equivalent to more than five months of global mining production, while holdings in palladium ETFs equate to nearly four months of global production.
Higher prices expected during the course of the year
In our opinion, risks to supply in conjunction with robust demand point to higher platinum and palladium prices. According to data from Johnson Matthey, the supply-demand situation was already tight on both markets last year, the global platinum market showing a supply deficit of 605,000 ounces in 2013 and demand outstripping supply on the global palladium market by 740,000 ounces. Assuming the supply problems are not resolved in the near future and demand remains robust, the situation on both markets will doubtless tighten further. By year’s end we continue to envisage a platinum price of $1,600 per troy ounce, while palladium is likely to be trading at $825 per troy ounce.
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

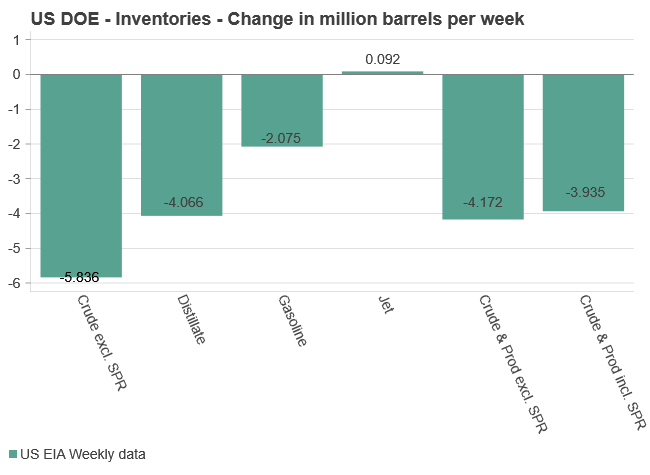
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

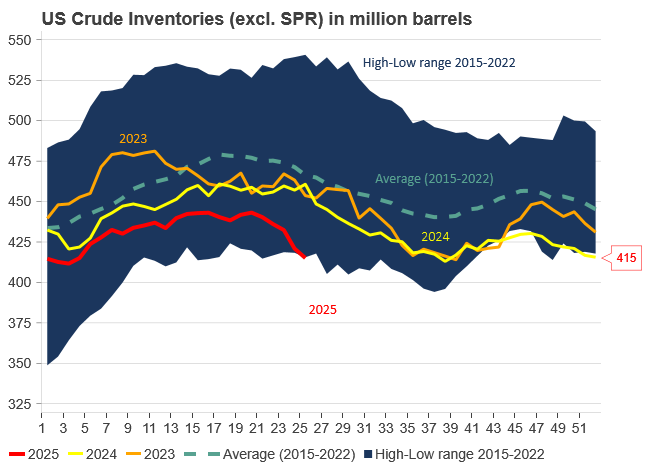
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBrookfield ska bygga ett AI-datacenter på hela 750 MW i Strängnäs
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSommaren inleds med sol och varierande elpriser
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanBrent needs to fall to USD 58/b to make cheating unprofitable for Kazakhstan
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanTradingfirman XTX Markets bygger datacenter i finska Kajana för 1 miljard euro
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning

















