Nyheter
Africa: Strongest growth in gold mining
The Gold Report interviews Nana Sangmuah
Last year, Africa was the region that witnessed the strongest growth in goldmining operations. In an exclusive interview with The Gold Report, Nana Sangmuah, managing director of research with Toronto-based Clarus Securities, expects that trend to continue and suggests some immediate smart investments in Ghana, Mali, Liberia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The Gold Report: Gold consultancy GFMS, which is now owned by Thomson Reuters, recently published its 2012 Gold Survey. GFMS predicts that before the end of 2012, the yellow metal will likely reach above its all-time nominal high of $1,920/ounce (oz) in September 2011. The catalysts include inflation concerns and sovereign debt problems in Europe, especially Spain. What are your thoughts on these predictions and conclusions?
 Nana Sangmuah: I agree with those predictions and the drivers. One thing that has been missing from the gold rally is inflation hedge demand. With the significant monetary easing that has occurred to drive a global recovery, inflation is definitely going to be an issue at some point. We haven’t seen inflation trade come into gold throughout these 10+ years. That’s the strong headwind that is going to move gold to another level.
Nana Sangmuah: I agree with those predictions and the drivers. One thing that has been missing from the gold rally is inflation hedge demand. With the significant monetary easing that has occurred to drive a global recovery, inflation is definitely going to be an issue at some point. We haven’t seen inflation trade come into gold throughout these 10+ years. That’s the strong headwind that is going to move gold to another level.
TGR: The survey reported that mine production hit a record high in 2011, rising 2.8% year over year to reach 2,818 metric tons (mt). That marks the second straight year that gold production reached a new all-time high. Does that mean the theory of peak gold is dead?
NS: Not exactly. If you peel back the data over the past two years, the greater part of this growth has come from mines digging into their stockpiles and people revisiting old resources that previously were thought not to be economic but at these price levels look economic. There have been very few discoveries despite the fact that there’s been quite a lot of money spent on the exploration front. That rate of increase is not sustainable going forward. And the bigger picture still looks grim because the last big discovery of 5+ million ounces (Moz) is the Aurelian discovery—the Fruta del Norte deposit in Ecuador, which now belongs to Kinross Gold Corp. (K:TSX; KGC:NYSE)—from early in the 2000s. It takes on average at least five years to move from discovery into production, so we’re looking at a situation where the supply is not going to grow that much. If the investment demand is sustainable going forward, basically there won’t be enough ounces to feed that demand.
TGR: The GFMS survey also reported that new gold-mining operations contributed 47 mt of new gold supply, while Africa was the region that witnessed the strongest growth, increasing production by 51 tons (t) despite a 5 t drop in output from South Africa. Do you believe Africa will continue to lead the way in worldwide gold production?
NS: Certainly. The ground is very favorable, and there are a lot of projects that have only scratched the surface. Even in the more prolific zones, which have seen a lot of dollars thrown at them, the concentration has just been on open-pit, near-surface mining. In some of these greenstone belts, you can trace mineralization down to more than 2.5 kilometers (km) at depth. As people get more comfortable with the region’s politics, more dollars are going to move in, and certain grounds will be tested. The key is political stability. As commodity prices go up, countries move their fiscal regimes around.
But I think a lot of countries will smarten up and realize they can attract more investments, which will ultimately generate more revenues to the government if their current regimes are seen to be stable. The Asankrangwa Belt in Ghana is one example.
This belt is as old as the Ashanti Belt, but we have just recently seen action on it. So far, within a period of less than three years, 10 Moz have been delineated.
Some people would think that certain districts are mature and cannot be coming up with even more discoveries, but that is not true.
TGR: Mali’s interim president said that he wouldn’t hesitate to wage ”total relentless war” against the Tuareg rebels who have seized much of northern Mali. Do his words make you less bullish on all West African gold producers?
NS: He’s trying to send a strong signal that he’s all for maintaining stability in the region. And the regional force, ECOWAS—Economic Community of West African States—acted quickly to prevent this from blowing up. A stabilizing force has made its dominance known in West Africa, which I think is going to foster more stability and get people to be more comfortable investing more dollars in the region. Access in general has not really been impaired. The borders are open. People can focus on the day-to-day running of businesses and mines. There’s the potential for a few situations here and there as they try to push the Tuaregs away. But the Tuaregs’ links with al-Qaeda are definitely going to unify the international community against any issues.
That means that this is not going to drag on for long, and very soon we should see this issue behind us. We’ve seen similar events before and people have hit the panic button and sold off, but as the situations stabilize, valuations come back strongly. So, I see this as a buying opportunity, and I’ll be focusing on assets. If these assets have not been impaired in any way fundamentally, they should be bought at these levels.
TGR: Ghana is second only to South Africa in African gold production. What are some of the companies operating in Ghana that are well positioned to grow their gold production and see it translate to their share price?
NS: In this current environment, we should be watching the balance sheets of companies to see whether they have enough capital to maintain their growth strategies.
One company that I think has a very strong balance sheet is Perseus Mining Ltd. (PRU:TSX; PRU:ASX), which has finished up building a mine in Ghana and announced very strong Q112 results showing good cost containment. Commissioning has gone well and it’s in a ramp-up phase. I think most of the risk is behind it. Perseus is on the cusp of generating a lot of cash flow. That is going to help it bring its second asset, which is not in Ghana, into production. Cast your eyes two years out and Perseus will be producing around 450,000 oz, generating a lot of cash flow that could be channeled into further growth opportunities or shareholder dividends. Currently the resource is 9 Moz and Perseus is spending quite a lot on exploration; about 200,000 meters (m) are being drilled in West Africa. The likelihood of growing 9 Moz into 12 Moz is high. And Perseus has had a very good success rate converting these ounces into reserves, so we should see the production profiles also tip up along the way.
At these levels, with no finance hurdles ahead of it, being in a fully funded position and just on the cusp of generating strong cash flows, Perseus is one that investors should be watching.
TGR: Perseus boosted the resource at the Edikan by 1.03 Moz in December 2011. Is it reasonable to think that it could do that again by December 2012?
NS: It’s doing about 200,000m of drilling this year; last year it drilled about 250,000m split between both assets. The rate of resource growth should be more significant because now it’s switching focus from infill drilling to regional targeted. That’s where you see a lot more growth in the resource. I’m quite optimistic that we should be seeing a lot of wider swings in the resource growth going forward. And the company’s picking up new targets in and around the existing mine.
TGR: Ghana also has a number of smaller companies exploring for gold deposits, some of which have had early success. Could you introduce our readers to some of those companies?
NS: There are a lot of junior companies prospecting for gold in Ghana. One of the more successful ones in recent times has been PMI Gold Corp. (PMV:TSX.V; PVM:ASX; PN3N:FSE). It is advancing a brownfield operation previously operated by Resolute Mining Ltd. (RSG:ASX), which mined about a million ounces at 2.2 grams per ton (g/t). PMI came in and has been able to delineate about 5 Moz on the flagship asset.
What is most exciting about the company is it has more ground toward the south on the Asankrangwa Belt, on the Asanko project and the Obotan project. This is the first time that ground has been developed by one single company. This points to the potential to grow the ounces profile well north of the current 5 Moz. PMI also has ground—the Kubi project—next to one of the world’s most prolific mines, the Obuasi mine, which has produced and delineated about 60 Moz. And it actively drills Kubi, which is just 15km south of Obuasi. For the first half of the year, it’s drilling about 100,000m on all these targets. And we just saw eight new anomalies discovered last week, signaling the potential to add to the current resource envelope.
TGR: The Obuasi gold mine is operated by AngloGold Ashanti Ltd. (AU:NYSE; ANG:JSE; AGG:ASX; AGD:LSE), which is a major gold producer. Would that make PMI a potential takeover target?
NS: Most of these junior companies that have solid resource growth potential are likely targets.
TGR: Any others in Ghana?
NS: There are quite a few, but we can talk about some other early-stage companies, like Abzu Gold Ltd. (ABS:TSX.V; ABZUF:OTCQX). It’s about to come out with a maiden resource on the ground in northern Ghana in a district that is known for goldbearing structures.
TGR: On Jan. 19, 2012, you wrote, ”Abzu’s vast tenement package with a plethora of targets diversifies exploration risk well for shareholders and its proven management team reduces execution risk.” Tell us more about the management team there.
NS: Abzu’s CEO Allan Serwa is a Canadian who’s been in Ghana for quite some time and has built up a lot of relationships there. He brings to the table the ability to manage community relationships very well—better than seamless. You find a lot of companies with good projects but a lot of problems dealing with communities. So Serwa really gives Abzu a solid platform from which to take off. Paul Klipfel has been a geologist with some of the more senior mines, including Placer Dome Inc. [now Barrick Gold Corp. (ABX:TSX; ABX:NYSE)], and has had some decent experience in Ghana as well. Quite a few other accomplished geologists and company CEOs who will provide necessary direction are on Abzu’s board of directors.
TGR: Abzu’s sizeable land package stretches across four different gold belts in Ghana. What sort of exploration success has Abzu had to date?
NS: Abzu has delineated a mineralization trend of 1.5km in one. I have visited that structure and have seen that it extends well to the north and to the south. On the Asafo Belt right on the Kibi Belt in the south, Abzu has been coming up with some very decent grade intersections of 4+ g/t material. It’s still early but indications point to, with additional drilling, sizeable results.
The concessions are in close proximity to prolific mines. Abzu has properties near Newmont Mining Corp.’s (NEM:NYSE) Ahafo and Akyem projects. It’s got property that is close to Keegan Resources Inc.’s (KGN:TSX; KGN:NYSE.A) Esaase mine. So, these are spanning all the belts coming through to the south. And Abzu is on the Kibi Belt as well—that is also close to a past-producing mine. There is the adage that the best place to find gold is within the shadows of a headframe. I think that is the strategy that guided Abzu in staking all these concessions.
TGR: You also cover companies with gold projects or mines in Burkina Faso, Liberia and even the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Please tell us about some of those companies.
NS: In Burkina Faso one of my top picks is SEMAFO (SMF:TSX). It’s seen quite a significant pullback in recent times. It has a very solid balance sheet, $170 million (M) in cash, no debt, and it’s generating an operating cash flow of about $130M per year.
This company is in a position to fund all its organic growth without coming back to the market. Any value from additional expansions flow to the shareholder. SEMAFO has been able to demonstrate the ability to bring that production on for the past three years.
There are a few catalysts coming down the pipeline, including a resource update. And as management continues to show to the market that its large Mana project has resource growth potential with several exploration updates expected, not only in June but after, we should begin to see that attention back into the stock. We will probably see it recover earlier than most of its peers because there’s nothing fundamentally wrong with the company.
TGR: You’ve got a $12 target price on that and a Buy rating. SEMAFO has a promising project in Niger called Samira Hill. What are your thoughts on that?
NS: It is a mine that sits on a mineralized trend that stretches for a good distance. Only about 15% has been tested and developed as pits. So there’s a lot of potential along the strike. In the past, very little capital was reinvested in the mine because ownership was split between Etruscan Resources Inc. (EET:TSX) and SEMAFO, and Etruscan never had enough money to put into expansion activity. The mine has not been performing at its optimum level for some time. That’s changing with SEMAFO now taking full control of the mine and investing a lot more into exploration and capital projects. It’s smaller and we need to see a much, much larger expansion to get more stability in the operation. But I think it’s still a worthy asset to have in the company.
TGR: Tell us about Liberia.
NS: Often people shy away from countries that have had issues. But Aureus Mining Inc. (AUE:TSX; AUE:LSE), which will likely be the first company to commence production in Liberia, is making good strides. Infrastructure-wise Aureus’ New Liberty project is very close to the port, and most of the access to the ground is via a paved highway. That makes it relatively easy to access, compared to other projects in the country. The capital required to kick-start the mine is around $120M—that’s not so huge that it will make this project’s financing risk insurmountable. I see Aureus coming up with its first production sometime in 2014. At this level, it’s one of the highest grade projects in the whole of West Africa near surface. And that’s just the beginning. About 40km north is its main asset, New Liberty, which in itself has a lot of potential to grow in surrounding anomalies that have been delineated. Northwest of the structure is a new 13km anomaly that has been picked up. The grades that Aureus has been picking up from initial intersections on this system are quite encouraging. So, there’s definitely a gold district there and the grades are quite compelling. That would definitely have a good impact on cost.
And we like the DRC. That country has had its issues in the past, but as with any other such situation, there’s always a time when it stabilizes. The fact that the election was conducted is a good thing. There were a lot of irregularities, but post-election issues have not been too severe, and that’s a good sign that the DRC is maturing and stabilizing. You see a huge discount in companies operating in the DRC, which in my opinion is not warranted, because it has one of the most prospective mineral belts in the world.
We just saw the first commercial gold production coming with Banro Corporation (BAA:TSX; BAA:NYSE) picking up the march. And we’re going to be seeing Kibali from Randgold Resources Ltd. (GOLD:NASDAQ) come through. I just visited the Kibali project and was very impressed by the progress made for relocation, which is probably the most challenging part of construction. With a solid technical and minebuilding team in place Randgold expects to bring Kibali into production by 2014 without a lot of challenges. As these two continue to do well, people will change their perception of gold mining in the country.
Another that I would highlight as very cheap at these levels is Kilo Goldmines Ltd. (KGL:TSX.V), which is on the Ngayu greenstone belt and will be commencing drilling very shortly. David Netherway and Alex van Hoeken have taken over, and they are seasoned mining personnel who focus on the exploration growth potential of their large land package. One similar ground to the Kilo ground is Geita, which in the 1990s started as a small resource from old mine workings and has grown to north of 10 Moz. It’s a similar story for Kilo. It has an old mine at Adumbi, which is currently around 1.8 Moz, and there are a whole slew of prospects around it. This is one of the few times that a company has enough drill rigs to chase some of these targets. It’s very early, but there’s a lot of growth ahead of Kilo—including the fact that Kilo also has an iron ore exposure that the market is not paying anything for. So, you rarely get something for free, but Kilo could be an example of where that really works.
TGR: An iron-ore sweetener, as you’ve called it. In a March 30, 2012, report, you said you expected a rerating of the stock. When?
NS: Rigs are on-site and drilling has commenced. It has its own sample prep lot, so turnaround times are not going to be that long. As news starts to flow, which could be as early as midyear right through the end of the year, and people begin to appreciate the size potential of this asset land package and also the grade profiles, that’s when everyone will start waking up to the opportunity and drive the re-rating.
TGR: Do you have some parting thoughts on African gold plays?
NS: People should continue to focus on the fundamentals. Take advantage of the situation, which will turn around and stabilize, to pick up on names that you missed out on and wait for the disconnect between the commodities and the equities to correct. I see very little downside risk at these levels.
TGR: Thanks for your insights today.
Nana Sangmuah is managing director of research at Toronto-based Clarus Securities. His previous industry experience includes the Prestea underground mine, AngloGold Ashanti’s Obuasi and Iduapriem mines, and Gold Fields’ Damang gold mine. He has over eight years of global mining equity research experience that covers more than 60 mining companies worldwide in the gold, base metals and diamond sectors and has in-depth knowledge of mining projects in West Africa. Sangmuah completed a Master of Business Administration in finance at the University of Toronto’s Rotman School of Management in 2004 and obtained his Bachelor of Science in engineering from the University of Mines and Technology, Ghana, in 1999.
Gold watchers, investment analysts, newsletter writers usually have a strong ego. Nothing wrong with that because they have thoroughly thought about what they write. But sometimes it can happen that you read an article by another publisher where the information is of a nature that is striking and can hardly be improved. If and when the subject is on mining in Africa, that does not happen too often. Yet, it does with this interview. Therefore, I have taken steps that you as my audience can enjoy this interview with Nana Sangmuah by The Gold Report, a publication that I always highly regard and enjoy. I thank them kindly for their permission to present it to you.
Henk J. Krasenberg
[hr]
European Gold Centre
European Gold Centre analyzes and comments on gold, other metals & minerals and international mining and exploration companies in perspective to the rapidly changing world of economics, finance and investments. Through its publications, The Centre informs international investors, both institutional and private, primarily in Europe but also worldwide, who have an interest in natural resources and investing in resource companies.
The Centre also provides assistance to international mining and exploration companies in building and expanding their European investor following and shareholdership.
Henk J. Krasenberg
After my professional career in security analysis, investment advisory, porfolio management and investment banking, I made the decision to concentrate on and specialize in the world of metals, minerals and mining finance. From 1983 to 1992, I have been writing and consulting about gold, other metals and minerals and resource companies.
The depressed metal markets of the early 1990’s led me to a temporary shift. I pursued one of my other hobbies and started an art gallery in contemporary abstracts, awaiting a new cycle in metals and mining. That started to come in the early 2000’s and I returned to metals and mining in 2002 with the European Gold Centre.
With my GOLDVIEW reports, I have built an extensive institutional investor following in Europe and more of a private investor following in the rest of the world. In 2007, I introduced my MINING IN AFRICA publication, to be followed by MINING IN EUROPE in 2010 and MINING IN MEXICO in 2012.
For more information: www.europeangoldcentre.com
Nyheter
Tyskland har så höga elpriser att företag inte har råd att använda elektricitet

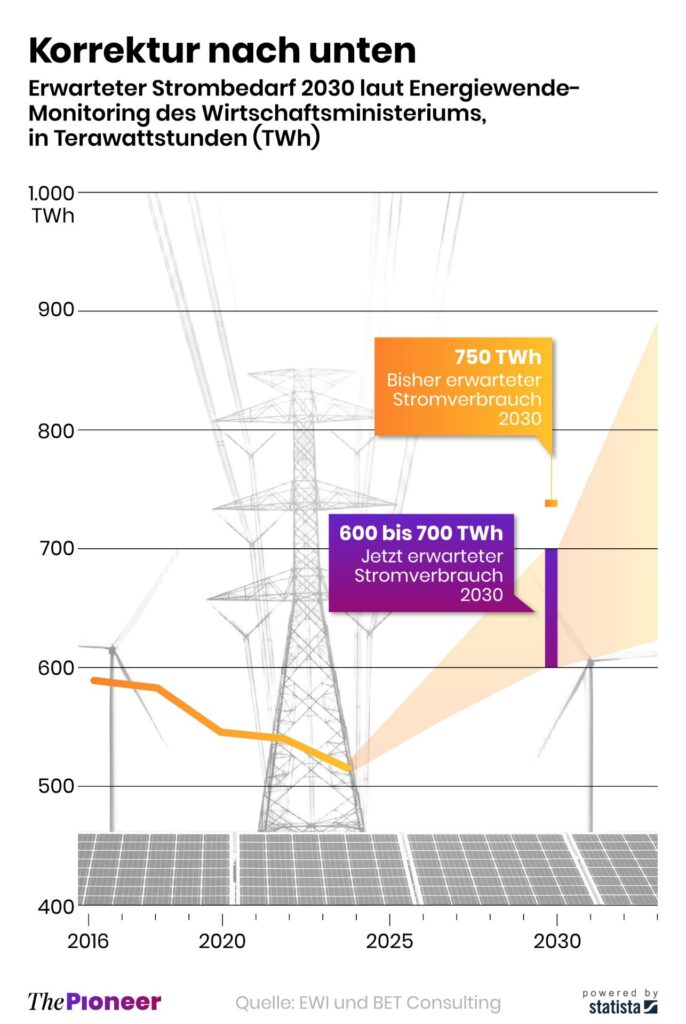
Tyskland har skrivit ner prognosen på hur mycket elektricitet landet kommer att behöva 2030. Hittills har prognosen varit 750 TWh, vilken nu har skrivits ner till 600-700 TWh,
Det kan vid en första anblick låta positivt. Men orsaken är inte att effektiviseringar. Utan priserna är så pass höga att företag inte har råd att använda elektriciteten. Elintensiv industri flyttar sin verksamhet till andra länder och få företag satsar på att etablera energikrävande verksamhet i landet.
Tyskland har inte heller någon plan för att förändra sin havererade energipolitik. Eller rättare sagt, planen är att uppfinna fusionskraft och använda det som energikälla. Något som dock inte löser problemet på några årtionden.
Nyheter
Kinas elproduktion slog nytt rekord i augusti, vilket även kolkraft gjorde
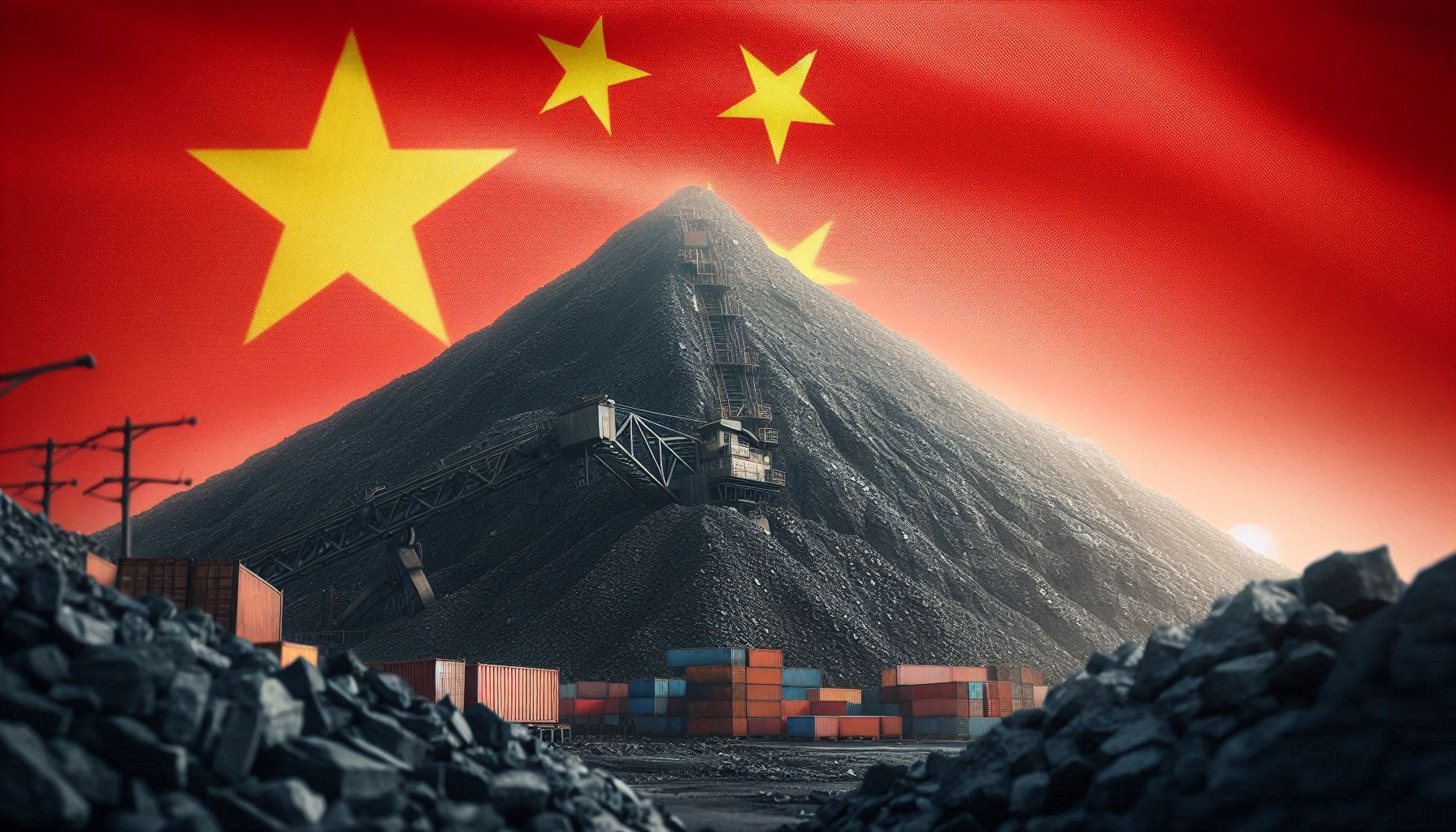

Kinas officiella statistik för elproduktion har släppts för augusti och den visar att landet slog ett nytt rekord. Under augusti producerades 936 TWh elektricitet.
Stephen Stapczynski på Bloomberg lyfter fram att det är ungefär lika mycket som Japan producerar per år, vilket innebär är de producerar ungefär lika mycket elektricitet per invånare.
Kinas elproduktion kom i augusti från:
| Fossil energi | 67 % |
| Vattenkraft | 16 % |
| Vind och Sol | 13 % |
| Kärnkraft | 5 % |
Stapczynskis kollega Javier Blas uppmärksammar även att det totala rekordet inkluderade ett nytt rekord för kolkraft. Termisk energi (där nästan allting är kol) producerade 627,4 TWh under augusti. Vi rapporterade tidigare i år att Kina under första kvartalet slog ett nytt rekord i kolproduktion.
Nyheter
Det stigande guldpriset en utmaning för smyckesköpare
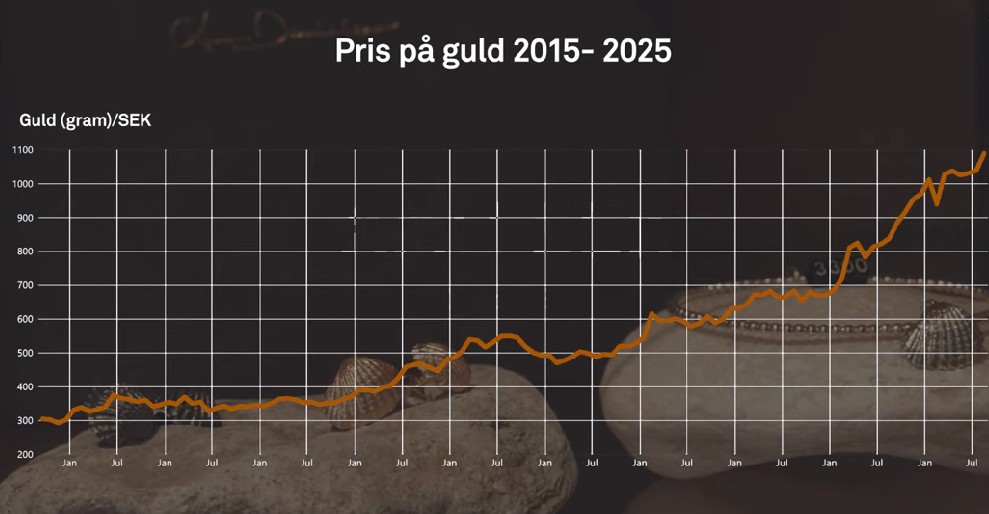
Guldpriset når hela tiden nya höjder och det märks för folk när de ska köpa smycken. Det gör att butikerna måste justera upp sina priser löpande och kunder funderar på om det går att välja något med lägre karat eller mindre diamant. Anna Danielsson, vd på Smyckevalvet, säger att det samtidigt gör att kunderna får upp ögonen för värdet av att äga guld. Det högre guldpriset har även gjort att gamla smycken som ligger hemma i folks byrålådor kan ha fått ett överraskande högt värde.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSommarens torka kan ge högre elpriser i höst
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanBrent edges higher as India–Russia oil trade draws U.S. ire and Powell takes the stage at Jackson Hole
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals är verksamt i guldrikt område i Finland
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanIncreasing risk that OPEC+ will unwind the last 1.65 mb/d of cuts when they meet on 7 September
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanNeil Atkinson spår att priset på olja kommer att stiga till 70 USD
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanOPEC+ in a process of retaking market share