Analys
SHB Råvarubrevet 10 februari 2012
- Energi: Positiv
- Basmetaller: Positiv
- Ädelmetaller: Negativ
- Livsmedel: Neutral till Positiv
Den senaste tiden har de flesta marknader färgats av att vara ”smygbull”, dvs marknaderna stiger utan att det kommer några stora makronyheter som talar för en klart bättre konjunktur. Vi tycker ändå att det är motiverat att marknaden och råvarorna stiger på allt bättre konjunkturutsikter och framförallt från dåliga konjunkturutsikter under hösten.
USA fortsätter att gå klart bättre än vad ekonomer förväntar sig. Förväntansbilden borde dock ha skruvats upp nu och sannolikheten att makrodata väster om Atlanten kommer fortsätta att vara positiva överraskningar bli allt lägre. De lärda tvistar om huruvida det blir QE3 efter FEDs nästa räntemöte i mars. FED förutsåg under januarimötet att inflationen skulle hamna under målet under 2012-2014 och att arbetslösheten skulle hamna över den naturliga nivån. Det skapade omedelbart förhoppningar om att FED skulle köra QE3 i marknaden. Efter förra fredagens starka arbetsmarknadsdata från USA så har dock utsikterna för QE3 mattats. Arbetslösheten är redan under Feds prognos för slutet av 2012.
I Europa bidrar ekonomisk stimulans från ECB till allmän glädjeyra och stigande tillgångspriser. Under tisdagen fick vi lite sämre än väntat industriproduktion från Tyskland men det är inget man ska övertolka. Ledande indikatorer talar för att tyska industriproduktionen har vänt upp och det kommer synas i statistiken i januari.
Den kinesiska ekonomin har fortsatt att kylas ner de senaste månaderna i spåren av åtstramningar i landet och den globala avmattningen. Den kinesiska centralbanken har börjat släppa åtstramningarna och vi förväntar oss att man kommer fortsätta i den riktningen de kommande månaderna.
I rådande makroklimat så är fundamenta speciellt starkt för konjunkturhandlade råvaror som basmetaller och energiråvaror.
Energi (positiv)
Olja
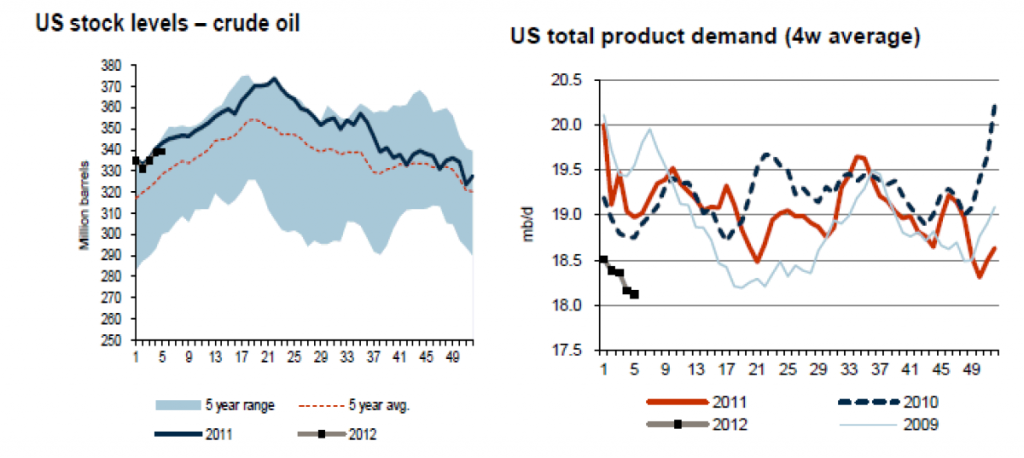
Oljepriset (Brent) stärktes 2,2% i veckan till $ 117.2/fat. Den geopolitiska oron har ökat i Mellanöstern med oro i Syrien och Irans hot mot USA, vilket hjälpte till att pressa upp oljepriset till $ 118.8/fat i torsdags. Irans oljeexport kommer påverkas allvarligt av sanktionerna mot landet i mars. Siffror om den amerikanska efterfrågan på olja är för närvarande svåra att relatera till, eftersom förutsättningarna för export för tillfället är väldigt osäkra. Samtidigt har hösten / vintern präglats av varma temperaturer, medan det motsatta var fallet förra året. Siffrorna för efterfrågan denna vecka anges till 17.6m fat / dag, att jämföra med 18.7m fat / dag vid samma tidpunkt förra veckan. Råoljelagert steg den här veckan med 0,3 M fat (väntat 2,4 m), destillat ökade med 1,2 m fat (väntat 0,7), medan bensin ökade med 1,6 miljoner fat (väntat 0,7).
Europeiska gaspriser har gått upp 30% på en vecka, som följd av sträng kyla i Europa. Samtidigt har Ryssland undanhållit gas från export på grund av hög inhemsk efterfrågan. Det kalla vädret väntas fortsätta i helgen med -31 grader till -34 grader i Kiev och Moskva. Terminsräntekurvan indikerar dock att prisökningen är av tillfällig natur.
Elmarknaden
Oron på elmarknaden fortsatte även denna vecka eftersom viktig kärnkraftskapacitet inte kommit tillbaka som planerat samtidigt som kylan biter sig fast över hela Europa. Lägg därtill en stark utveckling på fossila bränslen. Spotpriset befinner sig kvar på den högre nivån även om det i regel inte påverkar utvecklingen på det andra kvartalet så där värst mycket. Sentimentet har dock försvagats mot slutet av veckan då prognoserna har svängt från ett ganska torrt scenario till en mer nederbördsbetonad period än tidigare väntat. Energibalansen förväntas dock försvagas något ytterligare de kommande tio dagarna vilket innebär att vi kanske kommer ner strax under +5TWh efter perioden. Om man skall tror på något är det en fortsatt nedgång och svag inledning på nästa vecka tills dess att köparna åter visar sig.
Basmetaller (positiv)
Basmetallerna har haft en vecka med stora svängningar till följd av med osäkerhet kring huruvida Grekland ska klara de besparingskrav som ställs för en andra utbetalning som ska rädda landet från en default. De flesta metallerna lyckas ändå avsluta veckan på plus med bland annat hjälp från av en svagare dollar. Tenn visar återigen på styrka och stiger med ytterligare 4 % på 5 dagar, upp på året med 30 %. Exporten från Indonesien, världen störta exportör av tenn, föll med 64 % under januari, från 15 103 ton till 5 380 ton, på grund av kraftigt regn. Risk finns för fortsatt oväder vilket kan påverka kommande export. Februari månads export beräknas hamna på ca 4000 ton. LMEs lager sjönk under veckan till den lägsta nivån sedan mars 2009.
Övriga metaller har stärkts de senaste 5 dagarna med cirka 1 % medan zink avslutar vecka ned med 0,8 %. I veckan stod det även klart att Glencore köper resterande aktier i Xstrata för 41 miljarder dollar och blir därmed en av de största aktörerna på marknaden och kan nu konkurrera med BHP Billiton och Rio Tinto Group.
Koppar
Koppar har haft en volatil vecka med kraftiga upp – och nedgångar. Nyhetsflödet mot slutet av veckan dominerades av negativa nyheter från Grekland vilket resulterade i en veckonedgång på 0.20%. Uppgången på drygt 11 % sedan årets början kan bland annat härledas från rapporter om kraftigt minskande lager. LME (London Metal Exchange) kontrollerar cirka 80 % av världens kopparlager och deras rapporter visar på att lagren minskat med 32 % sedan oktober månad. Vi anser att dagens nivåer är relativt nära produktionskostnaden och med en ekonomi som börjar ta fart, asner vi metallen köpvärd.
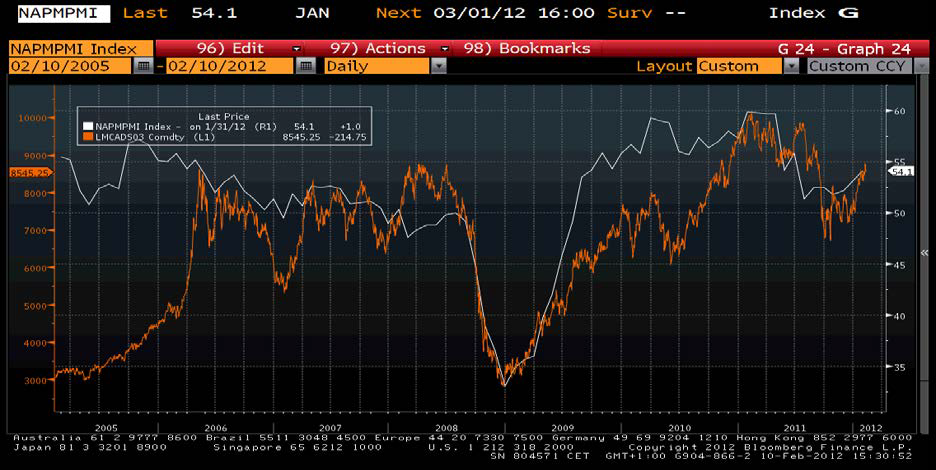
Bilden nedan visar kopparpriset (orange) och inköpschefsindex för USA (PMI). Indexet brukar vara anses vara en god indikator på vart ekonomin är på väg och tolkas som en framåtblickande indikator. Givetvis vill ekonomiska bedömare följa någon ännu bättre ekonomisk indikator och ibland används kopparpriset som en sådan. Följsamheten mot den ekonomiska utvecklingen har de senaste åren varit god (före år 2005 var den inte lika god). Slutsatsen blir därför att hålla reda på kopparpriset för att få en känsla för vartåt ekonomin är på väg.
Ädelmetaller (negativ)
Vi lägger en väldigt lugn vecka till handlingarna, Handelsbankens ädelmetallindex är helt oförändrat sedan förra fredagen, och har rört sig inom ett intervall om 1.5 %. Veckans ganska positiva nyhetsflöde på makrosidan har inte skapat någon försäljning av guld, och inte heller fredagens besked om att Grekland säger nej till trojkans räddningspaket skapade något intresse att köpa guld som en risk-hedge.
Vi bibehåller vår negativa syn på ädelmetaller, motiverat av lång positionering och en ljusare syn på konjunkturen för 2012 än vad marknaden prisar in.
Livsmedel (neutral till positiv)
Kakao
Skörden kring Elfenbenskusten är i stort sett är avklarad, detta två månader tidigare än normalt för säsongen och därmed fortsätter exporten att minska markant från området. Det kommer rapporter om kraftiga vindar i regionen och man befarar sämre kvalitet av bönorna eller i värsta fall att bönorna blåser bort. Det torra vädret kan leda till att produktionen får svårt att möta konsumtionen för säsongen. Även Indonesiens export har minskat kraftigt.
Vid månadsskiftet släpptes en rapport som pekar på att Elfenbenskusten kommer att börja sälja bönor innan nästa skördeperiods start i oktober. Detta satte press på kakaopriset och priset har fallit något under februari. Vi ser detta som en stabilisering av prisnivån efter den kraftiga uppgången under årets första månad som en reaktion på spekulationer på en globalt fallande kakaoproduktion.
Socker
Sockerpriset steg ett par procent dels efter att regnet försenade skörden i Thailand, världens andra största exportör av socker och dels p.g.a. fortsatt oro över lägre produktion i Brasilien som en följd av sämre väderförhållanden i de södra regionerna. Marknaden ser en försämring av efterfrågan på socker om det ekonomiska läget i Europa försämras. Men vi har även noterat rapporter om god tillgång på socker på marknaden och mer kan det komma att bli då Indien väntas exportera ytterligare en miljon ton. Sockerproduktionen kan komma att överstiga konsumtionen men 6-8 miljoner ton 2012/13. Ett överskott skulle på sikt mycket väl sätta press ner på sockerpriset, men på lite kortare sikt är vädret i Brasilien och Thailand mer avgörande för prisutveckling.
Kaffe
Vår vy har de senaste veckorna varit en prisutveckling av kaffepriset i sidleds. Och så har det sett ut, inga kraftiga rörelser. Och nu kommer det rapporter om att reservlagren av kaffebönor har sjunkit i Japan för fjärde månaden i rad. Samtidigt som god produktion väntas från Vietnam och Brasilien, världens största kaffeproducent, så har exporten minskat markant jämfört med förra året. Viktigt att notera är även Colombias skörd som ännu inte återhämtat sig från tidigare års höga nivåer, trots en förväntad ökning av produktionen för 2012/13. Vi ser därför en svag uppgång av priset den närmaste tiden.
Vete
Vetepriserna har gått ned sedan förra veckan i både Paris och Chicago, påverkat bland annat av bättre väderutsikter för Europa och höjt exporttak i Ryssland. Väderprognoserna lovar just nu något varmare väder i kommande vecka, samt mer snö, vilket lindrar oron för utvintring av det europeiska höstvetet. Att viss skada redan skett är ganska säkert, men ingen vet omfattningen av detta – och lär inte göra det förrän våren. I Ukraina ser det däremot ut att förbli kallt, vilket nog kommer göra att det redan dåliga höstvetet kommer försämras i skick ytterligare något.
Precis som vi antog i förra veckans jordbruksbrev så valde Ryssland att höja taket för exporterad volym spannmål innan de eventuellt inför exportavgifter till 27 miljoner ton. Volymen under perioden juli-januari uppgår till 21 miljoner ton så resterande del av säsongen bör undgå exportavgifter, delvis beroende av kommande väderlek – kyla, is och vind har fortsatt skapa logistikproblem både inom landet och vid hamn.
Om utsikterna om bättre väder i Europa består bör vetepriserna kunna falla tillbaka ytterligare något. Att USDA igår justerade upp sin prognos för utgående lager av vete för världen till rekordhöga 213 miljoner ton ger även det skäl till press nedåt på priset.
Majs
Terminspriserna på majs har gått ned sedan förra veckan, en nedgång främst orsakad av lägre priser på vete och mer regn i Sydamerika. Regnet har nog kommit försent för att kunna förbättra skicket på grödan i större omfattning men det minskar i alla fall risken att situationen förvärras ytterligare. Gällande väderprognoser lovar dock lite torrare väder i nästa vecka.
Små majslager gör det svårt att tro alltför mycket på lägre priser på majs men om vetepriserna fortsätter ner lär nog majsen följa med ytterligare något. Förväntad rekordhög areal till våren i USA lär även det ge press nedåt på amerikanska majspriser.
Sojabönor
Terminspriserna på sojabönor stängde igår i stort sett oförändrat sedan förra torsdagen. Regn i Argentina och södra Brasilien har lindrat oron något för den kommande skörden och mer nederbörd ser dessutom ut att vara på väg. Regnet gör att grödorna kan återhämta sig något efter den senaste tidens torra väder, men framförallt att skicket på grödan inte lär försämras framöver. Den brasilianska skörden uppgavs i tisdags vara till 6 procent avklarad – än så länge med ett resultat något över förväntan.
Ovanstående faktorer gör att det i dagsläget är svårt att se stigande priser på sojabönor. Låga lagernivåer och en ganska bred uppfattning om att USDA fortfarande överskattar den sydamerikanska skörden håller dock priset kvar på en hög nivå.
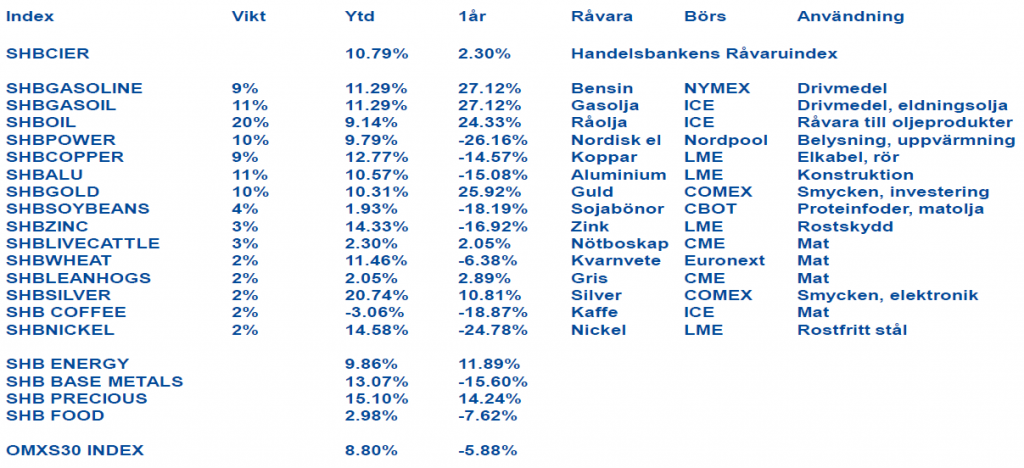
Handelsbankens Råvaruindex
[box]SHB Råvarubrevet är producerat av Handelsbanken och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Ansvarsbegränsning
Detta material är producerat av Svenska Handelsbanken AB (publ) i fortsättningen kallad Handelsbanken. De som arbetar med innehållet är inte analytiker och materialet är inte oberoende investeringsanalys. Innehållet är uteslutande avsett för kunder i Sverige. Syftet är att ge en allmän information till Handelsbankens kunder och utgör inte ett personligt investeringsråd eller en personlig rekommendation. Informationen ska inte ensamt utgöra underlag för investeringsbeslut. Kunder bör inhämta råd från sina rådgivare och basera sina investeringsbeslut utifrån egen erfarenhet.
Informationen i materialet kan ändras och också avvika från de åsikter som uttrycks i oberoende investeringsanalyser från Handelsbanken. Informationen grundar sig på allmänt tillgänglig information och är hämtad från källor som bedöms som tillförlitliga, men riktigheten kan inte garanteras och informationen kan vara ofullständig eller nedkortad. Ingen del av förslaget får reproduceras eller distribueras till någon annan person utan att Handelsbanken dessförinnan lämnat sitt skriftliga medgivande. Handelsbanken ansvarar inte för att materialet används på ett sätt som strider mot förbudet mot vidarebefordran eller offentliggörs i strid med bankens regler.
Analys
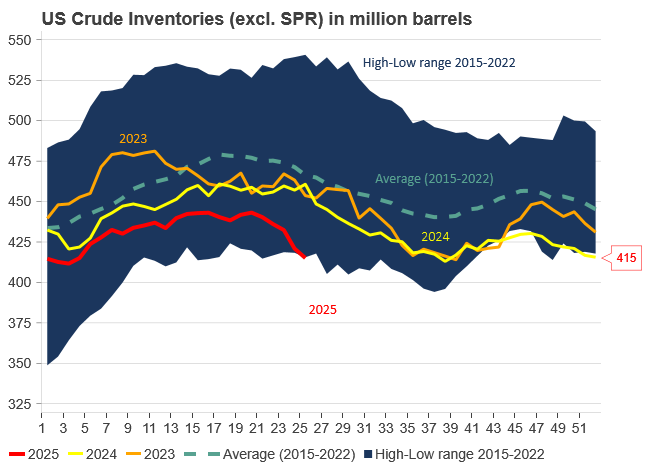
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

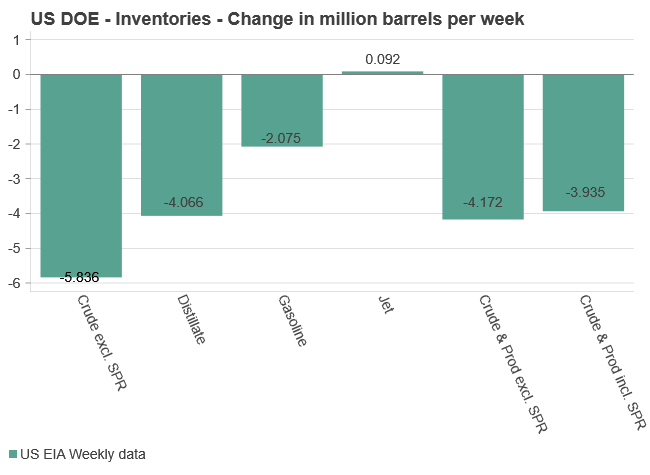
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanOljan, guldet och marknadens oroande tystnad
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanJonas Lindvall är tillbaka med ett nytt oljebolag, Perthro, som ska börsnoteras