Analys
SHB Råvarubrevet 1 juni 2012
 Råvaror Allmänt
Råvaror Allmänt
- Energi: Neutral
- Basmetaller: Neutral
- Ädelmetaller: Negativ
- Livsmedel: Neutral
Majraset för råvaror är en kombination av cyklisk nedgång i Kina som ger lägre fysisk efterfrågan parat med investerares utflöden baserat både på en omvärdering av kinas tillväxtutsikter och en rädsla för Europas skuldkris.
Vi har sedan i mars påpekat konjunkturrisken i Kina. Under våren har också Kinas ekonomiska utveckling varit klart sämre än vad marknaden hade förväntat sig och det har gjort att efterfrågan på kinaexponerade råvaror varit lägre. Under senaste månaden har dessutom investerare flytt volatila investeringar som råvaror för att sätta sina pengar i tillgångar som känns säkrare när det stormat på de europeiska finansiella marknaderna.
Dessa två oberoende händelser har inträffat simultant och gjort att de flesta råvaror handlas på klart lägre nivåer än i början av året. Även om mycket ser svårt ut i Sydeuropa så tenderar den finansiella marknaden att överreagera på kort sikt och vi tror att investerare kommer söka sig tillbaka till råvaruinvesteringar under andra halvan av året. Då råvaror i sig inte är speciellt exponerade mot den europeiska konjunkturen. I tumultet har dollarn varit en vinnare och i en svag makromiljö är det svårt för de dollarnoterade råvarorna att stå upp mot en stigande dollar.
När det gäller Kina så har landet under våren börjat beta av de höga lager som byggts upp utav färdiga produkter och obearbetade råvaror vilket gör att lagercykeln kommer att behöva fyllas på. Dessutom har vi sett flera politiska utspel senaste veckorna om att stimulansåtgärder är på väg för att hålla tillväxten på stabila nivåer omkring 7-8 %. Stimulansåtgärderna är precis som 2008 inriktade på investeringar i infrastruktur (där 50 % av landets kopparkonsumtion sker) och denna gång också till fordonsindustrin och energisnåla vitvaror (där mycket rostfritt stål med nickel används).
Vi tror att flera faktorer tvingat ner priserna men att mycket talar för att vi kommer se klart högre nivåer på 1-2 års sikt för de konjunkturhandlade råvarorna.
På kort sikt är det sentimentet i Europa som avgör var priserna tar vägen. Tyvärr finns det inte mycket i juni som kan tjäna som en trigger för att vända sentimentet. Kina har aviserat stimulanser som skapar intrycket att landet förstår alvaret i vårens nedgång och prioriterar att hålla tillväxten stabil. Under Q3 förväntar vi oss stimulanser från Kina, ECB/Eurozonen och kanske också från Fed, idag tror vi att det blir riktmärket för när sentimentet vänder.
Energi (neutral)
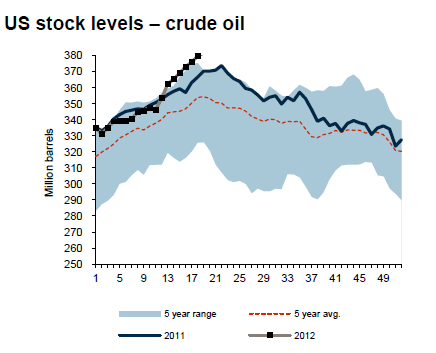
Oljemarknaden föll tillbaka till 15-månaders lägsta och under 100 dollar efter att usla amerikanska jobbsiffror tyngde sentimentet ännu mer. Endast 69,000 nya jobb samtidigt som vårens siffror reviderades ned och arbetslösheten steg till 8.2 procent. De pågående förhandlingarna med Iran går framåt vilket förbättrat utsikterna för ett avtal och minskad risk för utbudsstörningar i den Persiska viken. På kort sikt finns det inte mycket som talar för ett ökande oljepris om man ser till lagersituationen , svag makrostatistik samt en fördjupad skuldkris i Europa. Lagertrenden på olja, se nedan, bör dock vända när vi nu går in i den amerikanska sk körsäsongen.
Saudi har vidare gjort sitt för att pressa priset till nivå man tidigare flaggat för som bra för marknaden. Oljeproduktionen från OPEC (31.595 miljoner fat per dag) har under maj varit den högsta sedan maj 2008 och det är framför allt Saudiarabien som nått sin högsta produktionsnivå på 23 år. Skulle priset falla för mycket tror vi dock att Saudi ganska snabbt går in och drar ned sin produktion för att stabilisera priset kring 100-dollar.
Elmarknaden och tredje kvartalet föll tillbaka med över 3 procent denna vecka efter att prognoserna återigen slagit om till ett våtare scenario samtidigt som kolmarknaden är under fortsatt press (brytpriset på kol för tredje kvartalet ligger nu på ca 37.75 euro). En tillfällig återhämtning till följd av en svagare dollar men sentimentet tyngs av en rad cancellerade ordrar in till Kina samt svag efterfrågan från övriga tillväxtmarknader vilket gör att kolet nu måste avsättas på andra marknader. De cancellerade ordrar vi sett från Kinesiska verk är ett resultat av en kraftig lageruppbyggnad, lagren är nu är uppe på rekordnivåer (+6% bara under maj) vilket gör att verken har begränsade möjligheter att ta emot mer kol. Vi räknar därför med att sentimentet på energikol kan komma att försvagas något ytterligare inom den närmsta tiden. Detta i kombination med en förbättrad energibalans om 1 TWh till ca 6.9 TWh (prognos) talar därför för fortsatt låga elpriser i Norden.
Basmetaller
Metallerna dras med i det allmänna börsraset och LME index tappar 2.5 procent över veckan, ett visst stöd från höga produktionskostnader och förväntan om Kinesisk stimulans. Koppar backar hela 3.8 procent och handlas på 5 månaders lägsta nivå vilket gör att fokus nu riktas mot Kineserna för att se hur stort intresset kan vara på dessa lägre nivåer. Premierna stiger när kurvan (backwardation) planat ut vilket minskar behovet av att sälja eller exportera lagermaterial men vi ligger kvar med negativ rekommendation på Koppar. Övriga basmetaller och Aluminium i synnerhet med en högre cash cost håller emot bättre.
Ser vi till stålmarknaden och Kina finns tydliga förhoppningar om stödåtgärder. Den inhemska produktionen nådde denna vecka hela 2.04 ton per dag vilket skulle innebära en bra bit över 700 miljoner ton i årsproduktion och nära rekordnivåer. Marginalerna är det dock sämre med och flertalet verk producerar med förlust på dessa stålprisnivåer. China Iron & Steel Association förväntar sig att produktionen i landet ligger kvar kring ca 2mtpd som ett resultat av nya stimulansåtgärder och infrastrukturella projekt i landet. Vi noterar även att BMA´s (BHP Billiton & Mitsubishi som är världens största aktör på den fraktade metallurgiska kolmarknaden) gruvarbetare nu återvänt från en veckolång strejk men förhandlingarna förväntas pågå även en bit inpå nästa vecka. Likviditeten på den finansiella marknaden för met. kol (ex Queensland) är för övrigt väldigt blygsam med totalt ngn last eller två i veckan som omsätts så även om det för närvarande är svårt att avsätta ngn egentlig risk har vi goda förhoppningar om att denna marknad utvecklas i god takt med övriga insatsvaror.
Ädelmetaller (Negativ)
Ädelmetallerna har spenderat en ganska lugn vecka med små rörelser utan någon riktning alls. Trots en tilltagande oro över situationen i sydeuropa under slutet av veckan, och fallande räntor i euroland (tyska tvååriga statsobligationer handlade på 0 % igår) så har guldet inte velat stiga. Inte förrän idag då USA:s för marknaden så viktiga arbetslöshetsstatistik presenterades med en massiv besvikelse.
Det ser ut som att denna siffra fick marknaden att kapitulera in i ”sälj allt”-stämning, och guldet har under de senaste timmarna rejält återtagit sin status som säker hamn! En uppgång på hela 3,5 % på två timmar, och inga tendenser ännu så länge till att trycket uppåt skulle avta. Marknaderna översköljs just nu av rykten om större räddningsaktioner under helgen med sänkta räntor som en ingrediens.
Ett massivt stimulanspaket, i en situation som av marknaden ser som genomrutten, skulle med stor sannolikhet skicka guldpriset vidare uppåt, varför vi måste hålla örat väldigt nära rälsen den närmaste tiden. Vi bibehåller dock vår negativa syn på guldet i väntan på konkreta nyheter, baserat på guldets uteblivna värdestegring under den tilltagande riskaversionen.
Softs
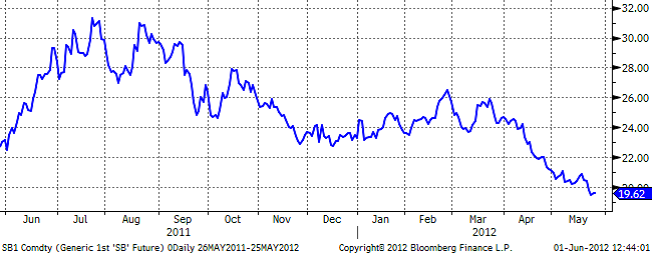
Socker
Det råder fortsättningsvis ovisshet om den Brasilianska skördens kommande exportvolym. Torka tidigare under säsongen kan påverka volymen samtidigt som det finns förväntningar på ökad volym tackvare större odlingsområden i landet. Regn fördröjer skördeprocessen och jämför man med Brasilianska skördevolymen samma månad förra året har man hittills endast skördat en tredjedel av den volymen. Brasiliens valuta Real har försvagats gentemot USD och handlade den 23/5 på treårs lägsta. Detta innebär att det är gynnsammare för landet att exportera sitt socker jämfört med en försäljning på den egna marknaden.
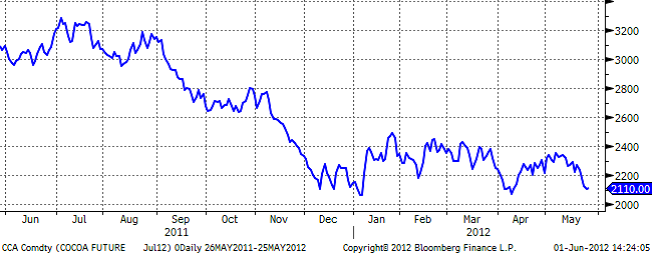
Kakao
Den rådande ekonomiska situationen i Europa fortsätter påverka priset även på kakao. Ett eventuellt grekiskt utträde ur euroområdet, Egan-Jones Rating Co:s sänkning av spaniens kreditbetyg samt en långsammare asiatisk tillväxt är alla faktorer som kan komma att påverka efterfrågan på kakao.
Samtidigt rapporteras goda skördar och gynnsamt väder. Samtliga väst afrikanska länder skördar sitt kakao nu och volymerna rapporteras vara goda. Ghana som inför denna säsong sänkte estimatet på sin skörd till ca 900000 ton (att jämföra med rekord skörden 2010-11 på över 1M ton) till följd av torka och storm, rapporterade positivt i veckan. Gynnsamt väder mot slutet av perioden har haft positiv inverkan på skörden och man förväntas uppnå estimatet på 900K ton. NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) publicerade väderleksrapporter för Elfenbenskusten och Ghana tidigare i veckan, regn är att vänta fram till 5 juni vilket självklart har positiv inverkan för skörden som löper från april till september. Stora delar av elfenbenskusten samt Ghana kan komma att få nederbörd upp till 75 mm.
Den senaste veckans data med potentiellt avtagande efterfrågan och goda tillgångar fick priset på kakao att på onsdagen sjunka till lägsta nivån sedan 16 april.
Handelsbankens Råvaruindex
Handelsbankens råvaruindex består av de underliggande indexen för respektive råvara. Vikterna är bestämda till hälften från värdet av global produktion och till hälften från likviditeten i terminskontrakten.
[box]SHB Råvarubrevet är producerat av Handelsbanken och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Ansvarsbegränsning
Detta material är producerat av Svenska Handelsbanken AB (publ) i fortsättningen kallad Handelsbanken. De som arbetar med innehållet är inte analytiker och materialet är inte oberoende investeringsanalys. Innehållet är uteslutande avsett för kunder i Sverige. Syftet är att ge en allmän information till Handelsbankens kunder och utgör inte ett personligt investeringsråd eller en personlig rekommendation. Informationen ska inte ensamt utgöra underlag för investeringsbeslut. Kunder bör inhämta råd från sina rådgivare och basera sina investeringsbeslut utifrån egen erfarenhet.
Informationen i materialet kan ändras och också avvika från de åsikter som uttrycks i oberoende investeringsanalyser från Handelsbanken. Informationen grundar sig på allmänt tillgänglig information och är hämtad från källor som bedöms som tillförlitliga, men riktigheten kan inte garanteras och informationen kan vara ofullständig eller nedkortad. Ingen del av förslaget får reproduceras eller distribueras till någon annan person utan att Handelsbanken dessförinnan lämnat sitt skriftliga medgivande. Handelsbanken ansvarar inte för att materialet används på ett sätt som strider mot förbudet mot vidarebefordran eller offentliggörs i strid med bankens regler.
Analys
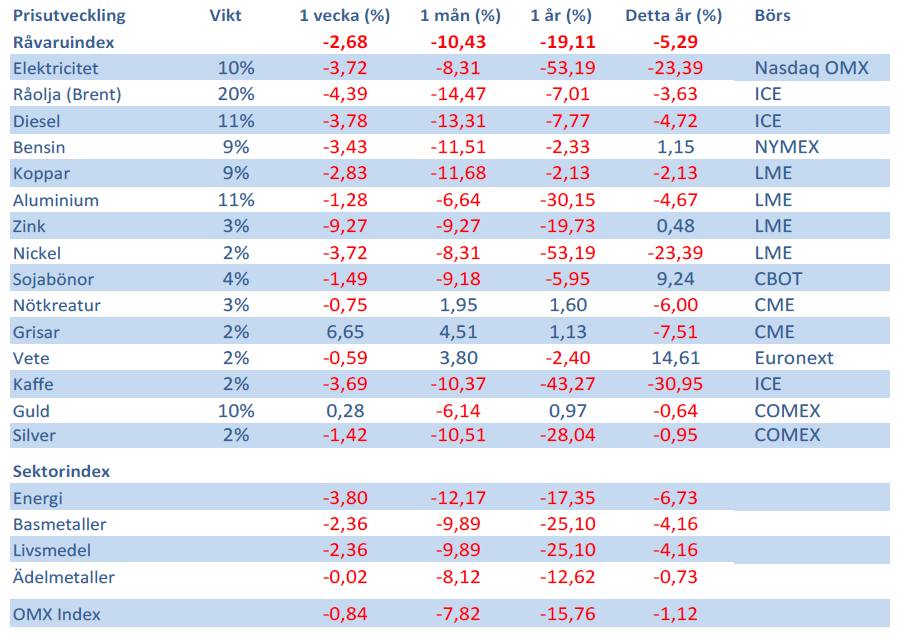
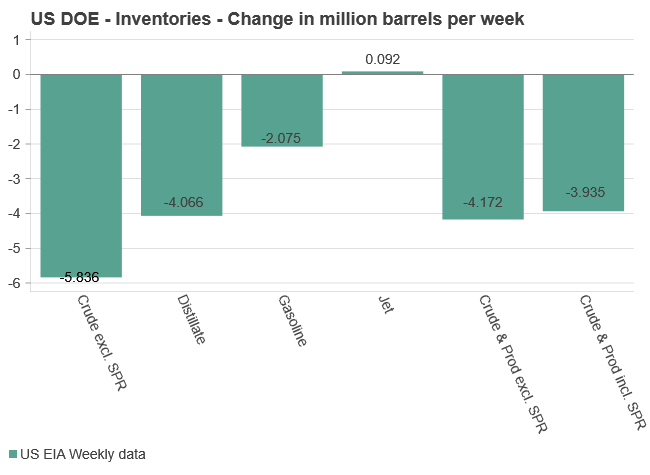
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

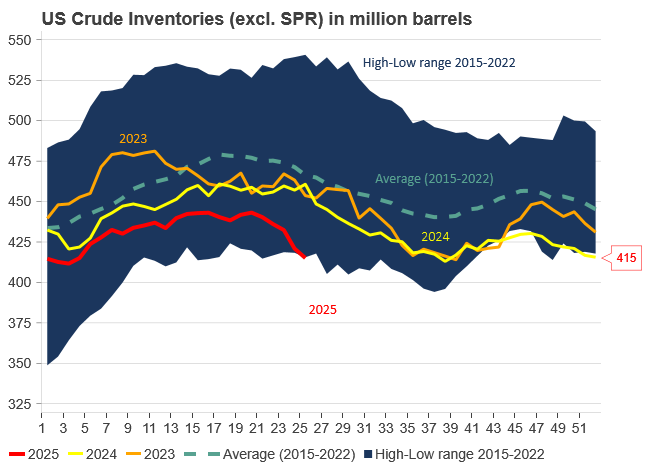
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanOljan, guldet och marknadens oroande tystnad
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanJonas Lindvall är tillbaka med ett nytt oljebolag, Perthro, som ska börsnoteras