Analys
USD weakness, inventory draws and a pinch of Venezuela concerns

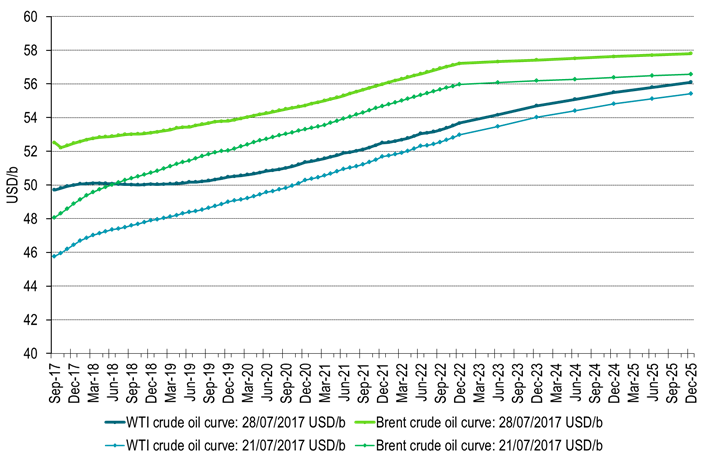
 Last week Brent crude gained 9.3% w/w with a close of $52.52/b on Friday. WTI gained comparably much (+8.6%) with a close of $49.71/b. The main gains were in the front end of the crude curves leading to a substantial flattening of the forward curves. Brent crude Dec 2020 only gained 2.6% with a close of $54.72/b and thus a way smaller gain than in the front end of the forward curves. For WTI the front end contract now only sits $0.34/b below the 18 mth forward WTI contracts which closed the week at $50.05/b.
Last week Brent crude gained 9.3% w/w with a close of $52.52/b on Friday. WTI gained comparably much (+8.6%) with a close of $49.71/b. The main gains were in the front end of the crude curves leading to a substantial flattening of the forward curves. Brent crude Dec 2020 only gained 2.6% with a close of $54.72/b and thus a way smaller gain than in the front end of the forward curves. For WTI the front end contract now only sits $0.34/b below the 18 mth forward WTI contracts which closed the week at $50.05/b.
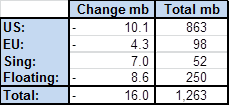
Continued inventory draws last week underpinned the crude oil price rally and the flattening of the forward crude curves. Weekly inventory data last week saw draws of 16 mb of which 10 mb were in the US while a reduction of 8.6 mb in floating storage also took a solid bite. Over the past 5 weeks inventories have drawn down some 70 mb in weekly data. Thus inventory draws kicked in and accelerated almost on the clock as we entered stronger seasonal consumption in Q3-17. Since mid-March weekly data indicate an inventory draw of 104 mb of which 76 mb took place in the US while 18 mb were drawn in floating storage. Refineries are rapidly coming back online with increased crude oil consumption as a result. There are still more refineries to come back online both in Asia and LatAm while Europe and Africa are mostly all up and running. We expect continued draws in H2-17.
Saudi Arabia of course added some extra fuel on the fire last week as they promised exports of no more than 6.6 mb/d in August. That would be their lowest monthly export since early 2011 (not including oil products). From Jan-May Saudi Arabia exported 7.17 kb/d. If it sticks to 6.6 mb/d exports in August it will be a reduction of 705 kb/d y/y versus its pledged production cut of 490 kb/d. The lower export pledged in August of course coincide with high domestic summer demand in Saudi Arabia. As such it remains to be seen whether the export cap of 6.6 mb/d remains in place after August. What it shows more than anything is determination by the Saudi energy minister Al-Falih. Determination to draw inventories down and the time to do it is H2-17 before US shale oil revival extends too far in 2018. It is thus possible that Saudi Arabia maintains its export cap beyond August.
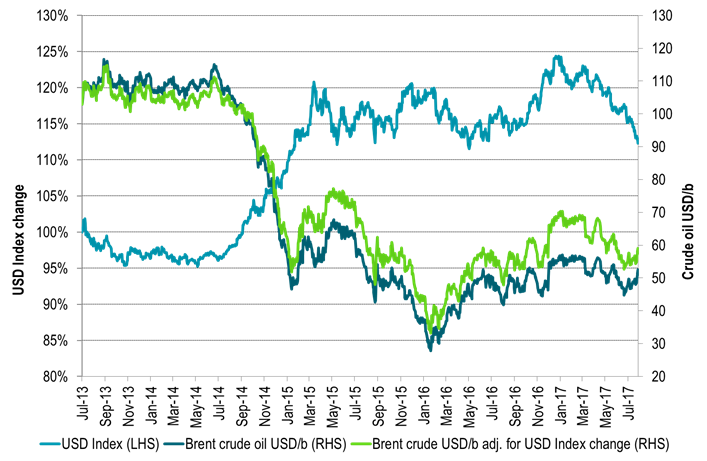
The softening in the US dollar has definitely underpinned the whole crude oil rally. It has underpinned a rally in the whole commodity complex. Over the past 5 weeks Bloomberg’s commodity index has gained 8.3% with 11.9% in Energy, 8.3% in Agri, 7% in Industrial metals and 1% in precious. The USD index has declined a substantial 4.1% over the period with half of the overall commodity index gain being a nominal impact from a softer dollar. IMF’s upgrade last week of growth in Europe, Japan and China while downgrading US growth from 2.3% to 2.1% (little hope for promised tax cuts) is the example in case which drives the dollar lower. US growth has been ahead of the curve for a long time and now the rest of the world is catching up. If the dollar weakness continues it will undoubtedly drive commodity prices in general and oil prices specifically higher in nominal terms. With the 4.1% USD Index decline over the past 5 weeks the Brent crude Dec 2020 contract has gained 5.5%. Thus almost all of this can be attributed to the dollar effect.
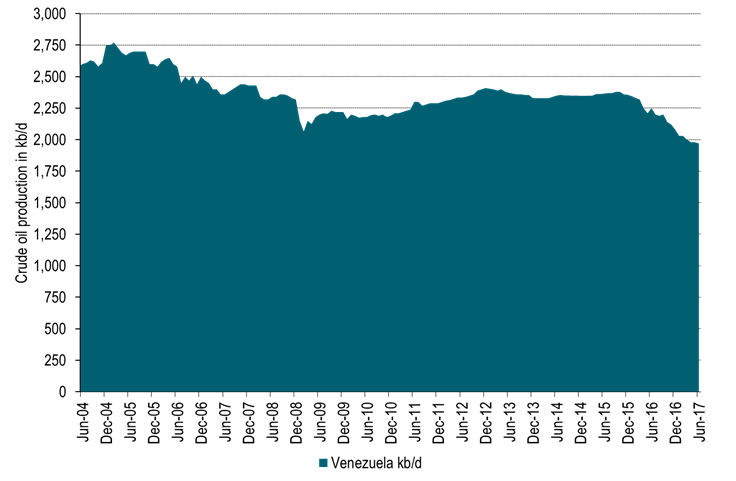
The deteriorating situation in Venezuela probably adds some support to oil prices as well. A national election was held this weekend to vote for members of a National Constituent Assembly. This Assembly will have no fixed term, it will have powers to rewrite the constitution. It will supersede the National Assembly and hand Nicolas Maduro close to dictatorial power and end close to six decades of democracy. At least 10 people were killed in clashes during the election this weekend and some 120 people have been killed in uprisings since April. Venezuela probably holds the world’s largest oil reserves (297 billion barrels) and produced 1.97 mb/d in June (Blberg) which is close to exactly equal to the production cap under the current OPEC production agreement. Its production has however deteriorated steadily due to lack of investments with production standing at 2.37 mb/d back in July 2015. The main concern in the oil market following the election is possible sanctions by Donald Trump. The US buys a third of Venezuela’s oil exports. Extensive US sanctions could make it almost impossible for international oil companies to work in Venezuela. For now the market is awaiting reactions from Donald Trump.
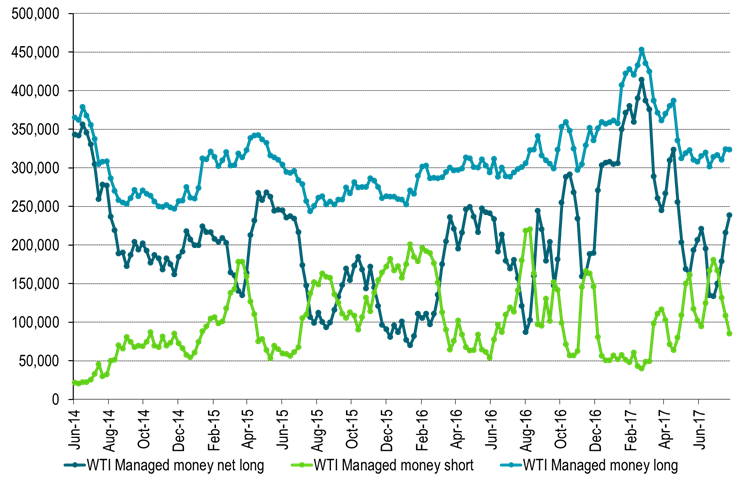
Today equities are up across the board, industrial metals are up 1% and Brent crude traded as much as 0.8% higher before now trading flat at $52.5/b. Thus so far this morning crude oil is lagging behind the gains in industrial metals. Crude oil is trading cautiously following five consecutive days of solid gains. A slight negative this morning is the USD Index which gains 0.3%. We expect to see further oil inventory draws also this week. If the USD Index also continues on its softening trend the two drivers are likely to push crude oil prices yet higher also this week. Money managers have added net long positions for 4 weeks in a row now but probably have room to add more. Producers are likely to sell into the forward crude prices. This is likely to hold back gains for medium term crude prices while inventory draws and investor appetite continues to push upwards in the front leading to a yet flatter crude curve. Potentially shifting the curves into backwardation.
The crude oil inventory draws taking place at the moment are of course real and they will draw down more during H2-17. Still it is important to remember that they are artificially managed by a 1.8 mb/d cut by OPEC and some non-OPEC members. Currently they help to draw down invnetories and to flatten curude curves. When needed however, the volumes will be put back into the market some time in 2018 or 2019.
Ch 1: Inventories in global weekly data drew 16 mb last week.
Over the past 5 weeks inventories have drawn down 70 mb in weekly data
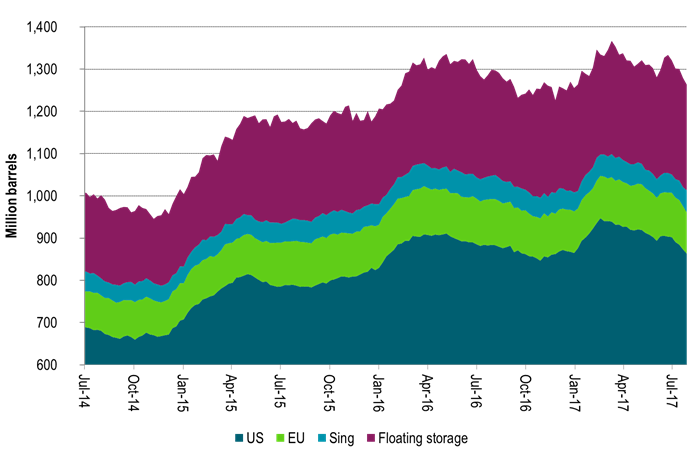
Ch2: US crude and product stocks now well below last year
And down y/y first time since 2014
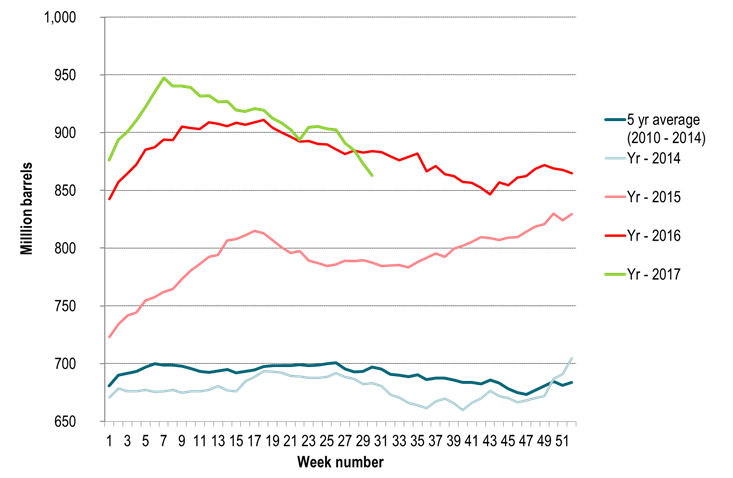
Ch3: The USD Index has moved down 9.6% since the start of the year
More specifically it has moved down 4.2% since crude oil prices bottomed out in June 21st.
It is now the weakest since a brief sell-off in February 2016.
However, it needs to decline another 15% to get down the the weakness it had in 2014.
Ch4: If we had had USD weakness as in 2014 we should nominally have had an oil price of close to $60/b
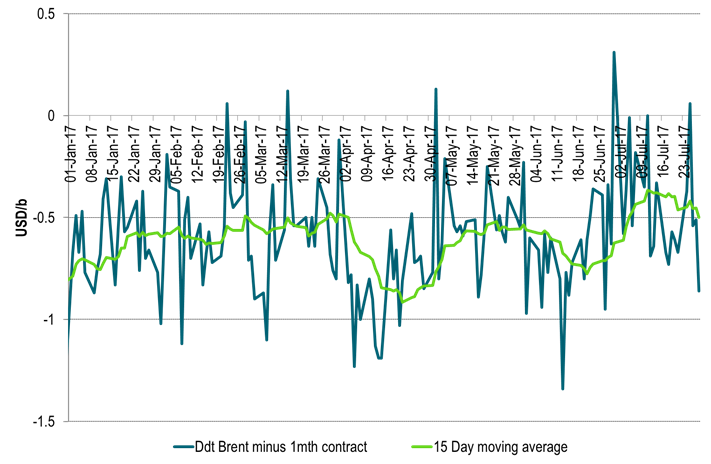
Ch5: Crude oil forward curves flattened substantially last week
As investors and refineries bought the front while producers probably sold into the rally out on the curve
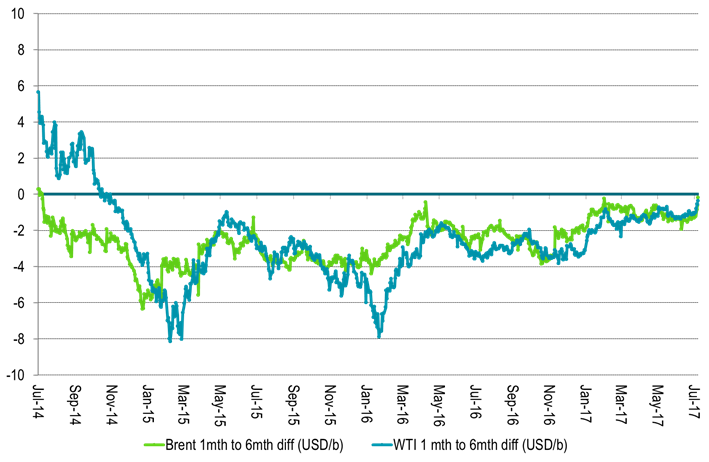
Ch6: The 1 to 6mth crude time spreads got close to zero
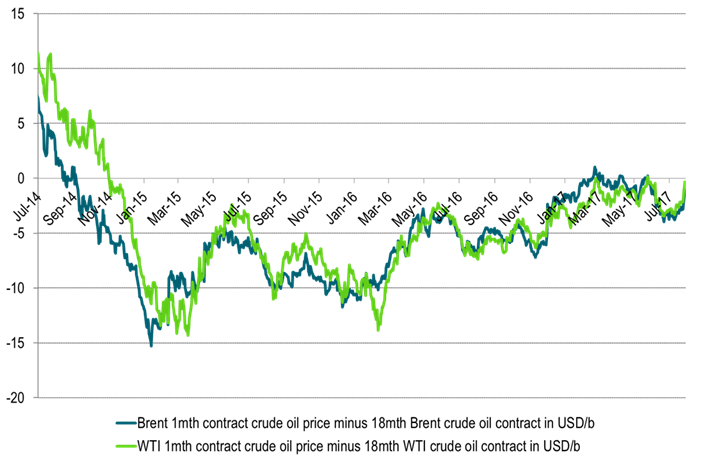
Ch7: And crude time spreads of 1mth to 18mth were not far away either
With WTI 1mth closing just $0.34/b below the 18mth on Friday and trading just $0.19/b below today
Ch8: A word of caution though. The tightness is not so evident in the Brent crude oil spot market
Dated Brent still trades at a $0.5/b discount to the 1mth contract in a sign that deficit of crude oil is still not quite yet here
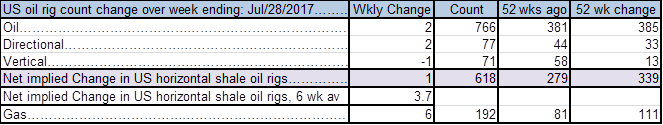
Ch9: US oil players added 2 rigs last week
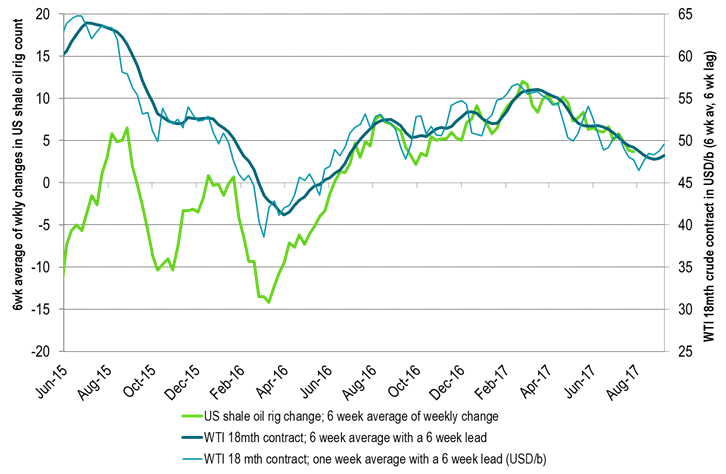
Ch10: Global refineries are rapidly getting back on line consuming more crude oil
More to come in Asia, ME and LatAm
Ch11: Deteriorating crude production in Venezuela
Production could be hit hard by possible US sanctions
Ch12: Net long managed money probably has room to add more length
Even though length has been added 4 weeks in a row now
Kind regards
Bjarne Schieldrop
Chief analyst, Commodities
SEB Markets
Merchant Banking
Analys
OPEC+ will likely unwind 500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d in one go could be in the cards

Down to mid-60ies as Iraq lifts production while Saudi may be tired of voluntary cut frugality. The Brent December contract dropped 1.6% yesterday to USD 66.03/b. This morning it is down another 0.3% to USD 65.8/b. The drop in the price came on the back of the combined news that Iraq has resumed 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan with exports through Turkey while OPEC+ delegates send signals that the group will unwind the remaining 1.65 mb/d (less the 137 kb/d in October) of voluntary cuts at a pace of 500 kb/d per month pace.

Signals of accelerated unwind and Iraqi increase may be connected. Russia, Kazakhstan and Iraq were main offenders versus the voluntary quotas they had agreed to follow. Russia had a production ’debt’ (cumulative overproduction versus quota) of close to 90 mb in March this year while Kazakhstan had a ’debt’ of about 60 mb and the same for Iraq. This apparently made Saudi Arabia angry this spring. Why should Saudi Arabia hold back if the other voluntary cutters were just freeriding? Thus the sudden rapid unwinding of voluntary cuts. That is at least one angle of explanations for the accelerated unwinding.
If the offenders with production debts then refrained from lifting production as the voluntary cuts were rapidly unwinded, then they could ’pay back’ their ’debts’ as they would under-produce versus the new and steadily higher quotas.
Forget about Kazakhstan. Its production was just too far above the quotas with no hope that the country would hold back production due to cross-ownership of oil assets by international oil companies. But Russia and Iraq should be able to do it.
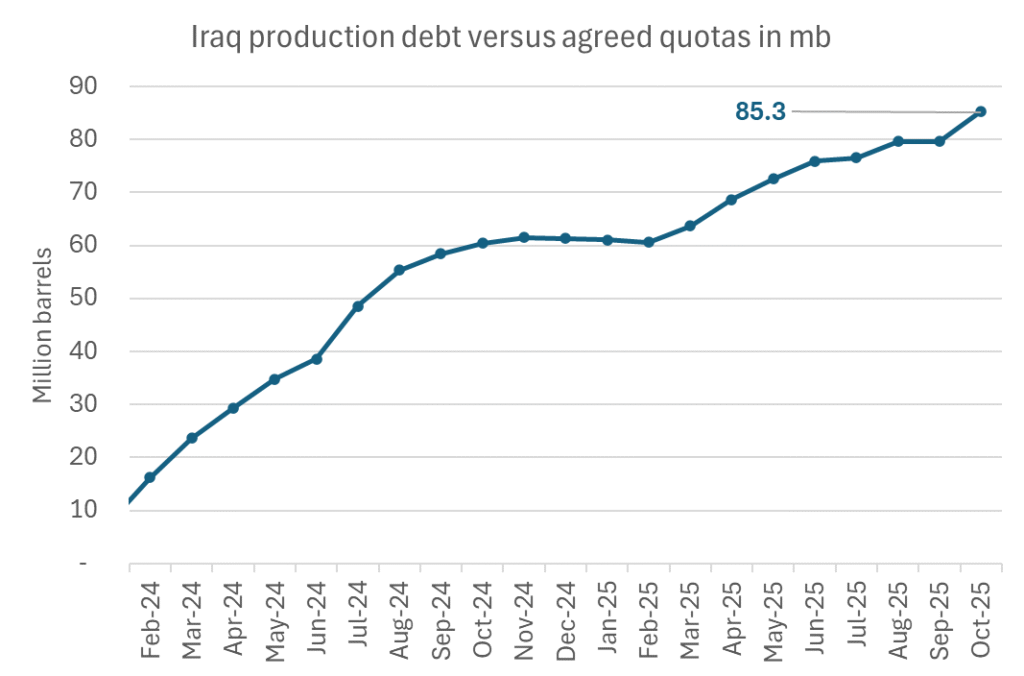
Iraqi cumulative overproduction versus quotas could reach 85-90 mb in October. Iraq has however steadily continued to overproduce by 3-5 mb per month. In July its new and gradually higher quota came close to equal with a cumulative overproduction of only 0.6 mb that month. In August again however its production had an overshoot of 100 kb/d or 3.1 mb for the month. Its cumulative production debt had then risen to close to 80 mb. We don’t know for September yet. But looking at October we now know that its production will likely average close to 4.5 mb/d due to the revival of 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan. Its quota however will only be 4.24 mb/d. Its overproduction in October will thus likely be around 250 kb/d above its quota with its production debt rising another 7-8 mb to a total of close to 90 mb.
Again, why should Saudi Arabia be frugal while Iraq is freeriding. Better to get rid of the voluntary quotas as quickly as possible and then start all over with clean sheets.
Unwinding the remaining 1.513 mb/d in one go in October? If OPEC+ unwinds the remaining 1.513 mb/d of voluntary cuts in one big go in October, then Iraq’s quota will be around 4.4 mb/d for October versus its likely production of close to 4.5 mb/d for the coming month..
OPEC+ should thus unwind the remaining 1.513 mb/d (1.65 – 0.137 mb/d) in one go for October in order for the quota of Iraq to be able to keep track with Iraq’s actual production increase.
October 5 will show how it plays out. But a quota unwind of at least 500 kb/d for Oct seems likely. An overall increase of at least 500 kb/d in the voluntary quota for October looks likely. But it could be the whole 1.513 mb/d in one go. If the increase in the quota is ’only’ 500 kb/d then Iraqi cumulative production will still rise by 5.7 mb to a total of 85 mb in October.
Iraqi production debt versus quotas will likely rise by 5.7 mb in October if OPEC+ only lifts the overall quota by 500 kb/d in October. Here assuming historical production debt did not rise in September. That Iraq lifts its production by 190 kb/d in October to 4.47 mb/d (August level + 190 kb/d) and that OPEC+ unwinds 500 kb/d of the remining quotas in October when they decide on this on 5 October.
Analys
Modest draws, flat demand, and diesel back in focus

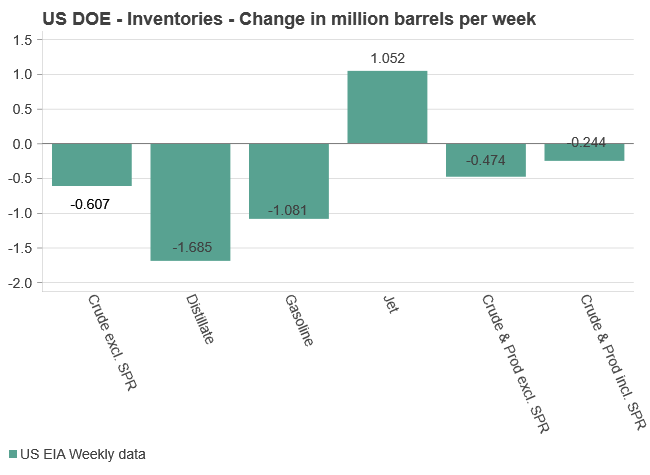
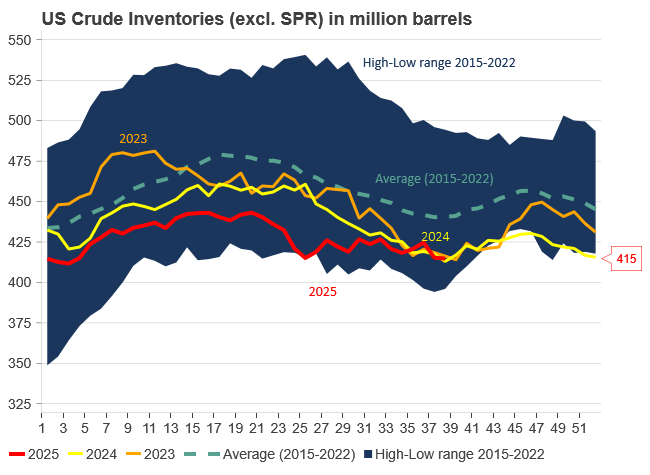
U.S. commercial crude inventories posted a marginal draw last week, falling by 0.6 million barrels to 414.8 million barrels. Inventories remain 4% below the five-year seasonal average, but the draw is far smaller than last week’s massive 9.3-million-barrel decline. Higher crude imports (+803,000 bl d WoW) and steady refinery runs (93% utilization) helped keep the crude balance relatively neutral.

Yet another drawdown indicates commercial crude inventories continue to trend below the 2015–2022 seasonal norm (~440 million barrels), though at 414.8 million barrels, levels are now almost exactly in line with both the 2023 and 2024 trajectory, suggesting stable YoY conditions (see page 3 attached).
Gasoline inventories dropped by 1.1 million barrels and are now 2% below the five-year average. The decline was broad-based, with both finished gasoline and blending components falling, indicating lower output and resilient end-user demand as we enter the shoulder season post-summer (see page 6 attached).
On the diesel side, distillate inventories declined by 1.7 million barrels, snapping a two-week streak of strong builds. At 125 million barrels, diesel inventories are once again 8% below the five-year average and trending near the low end of the historical range.
In total, commercial petroleum inventories (excl. SPR) slipped by 0.5 million barrels on the week to ish 1,281.5 million barrels. While essentially flat, this ends a two-week streak of meaningful builds, reflecting a return to a slightly tighter situation.
On the demand side, the DOE’s ‘products supplied’ metric (see page 6 attached), a proxy for implied consumption, softened slightly. Total demand for crude oil over the past four weeks averaged 20.5 million barrels per day, up just 0.9% YoY.
Summing up: This week’s report shows a re-tightening in diesel supply and modest draws across the board, while demand growth is beginning to flatten. Inventories remain structurally low, but the tone is less bullish than in recent weeks.
Analys
Are Ukraine’s attacks on Russian energy infrastructure working?

Brent crude rose 1.6% yesterday. After trading in a range of USD 66.1 – 68.09/b it settled at USD 67.63/b. A level which we are well accustomed to see Brent crude flipping around since late August. This morning it is trading 0.5% higher at USD 68/b. The market was expecting an increase of 230 kb/d in Iraqi crude exports from Kurdistan through Turkey to the Cheyhan port but that has so far failed to materialize. This probably helped to drive Brent crude higher yesterday. Indications last evening that US crude oil inventories likely fell 3.8 mb last week (indicative numbers by API) probably also added some strength to Brent crude late in the session. The market continues to await the much heralded global surplus materializing as rising crude and product inventories in OECD countries in general and the US specifically.

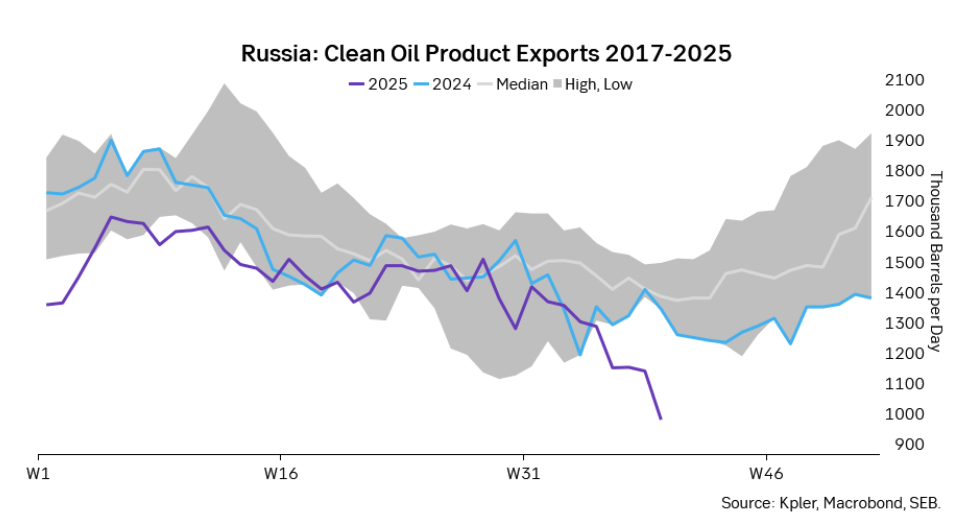
The oil market is starting to focus increasingly on the successful Ukrainian attacks on Russian oil infrastructure. Especially the attacks on Russian refineries. Refineries are highly complex and much harder to repair than simple crude oil facilities like export pipelines, ports and hubs. It can take months and months to repair complex refineries. It is thus mainly Russian oil products which will be hurt by this. First oil product exports will go down, thereafter Russia will have to ration oil product consumption domestically. Russian crude exports may not be hurt as much. Its crude exports could actually go up as its capacity to process crude goes down. SEB’s Emerging Market strategist Erik Meyersson wrote about the Ukrainian campaign this morning: ”Are Ukraine’s attacks on Russian energy infrastructure working?”. Phillips P O’Brian published an interesting not on this as well yesterday: ”An Update On The Ukrainian Campaign Against Russian Refineries”. It is a pay-for article, but it is well worth reading. Amongst other things it highlights the strategic focus of Ukraine towards Russia’s energy infrastructure. A Ukrainian on the matter also put out a visual representation of the attacks on twitter. We have not verified the data representation. It needs to be interpreted with caution in terms of magnitude of impact and current outage.
Complex Russian oil refineries are sitting ducks in the new, modern long-range drone war. Ukraine is building a range of new weapons as well according to O’Brian. The problem with attacks on Russian refineries is thus on the rise. This will likely be an escalating problem for Russia. And oil products around the world may rise versus the crude oil price while the crude oil price itself may not rise all that much due to this.
Russian clean oil product exports as presented by SEB’s Erik Meyersson in his note this morning.
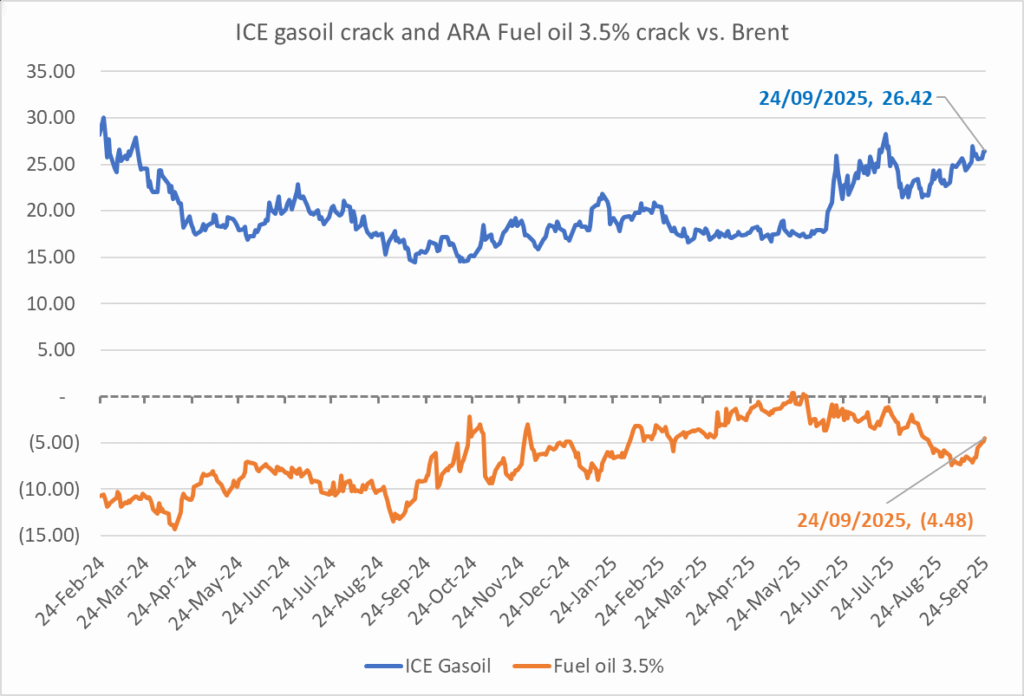
The ICE Gasoil crack and the 3.5% fuel oil crack has been strengthening. The 3.5% crack should have weakened along with rising exports of sour crude from OPEC+, but it hasn’t. Rather it has moved higher instead. The higher cracks could in part be due to the Ukrainian attacks on Russian oil refineries.
Ukrainian inhabitants graphical representation of Ukrainian attacks on Russian oil refineries on Twitter. Highlighting date of attacks, size of refineries and distance from Ukraine. We have not verified the detailed information. And you cannot derive the amount of outage as a consequence of this.

-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanEurobattery Minerals satsar på kritiska metaller för Europas självförsörjning
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals i en guldtrend
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuldpriset kan närma sig 5000 USD om centralbankens oberoende skadas
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanOPEC signalerar att de inte bryr sig om oljepriset faller kommande månader
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanVolatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk
-
 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanAktier i guldbolag laggar priset på guld
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanKinas elproduktion slog nytt rekord i augusti, vilket även kolkraft gjorde
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanTyskland har så höga elpriser att företag inte har råd att använda elektricitet