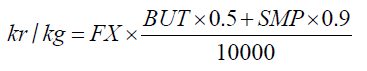Analys
SEB Jordbruksprodukter, 28 januari 2013
 Torkan i USA fortsätter att skapa oro för USA:s skörd i år. Samtidigt fortsätter vädret i Brasilien, världens nya kornbod, att vara gynnsamt. Vi gör inga ändringar av rekommendationer den här veckan. Majs ska man hålla ett öga på. Om priset bryter nedåt i veckan som kommer kan en sådan prisnedgång få en förlängning. Den kan i så fall smitta av sig på vetemarknaden och sojamarknaden.
Torkan i USA fortsätter att skapa oro för USA:s skörd i år. Samtidigt fortsätter vädret i Brasilien, världens nya kornbod, att vara gynnsamt. Vi gör inga ändringar av rekommendationer den här veckan. Majs ska man hålla ett öga på. Om priset bryter nedåt i veckan som kommer kan en sådan prisnedgång få en förlängning. Den kan i så fall smitta av sig på vetemarknaden och sojamarknaden.
Odlingsväder
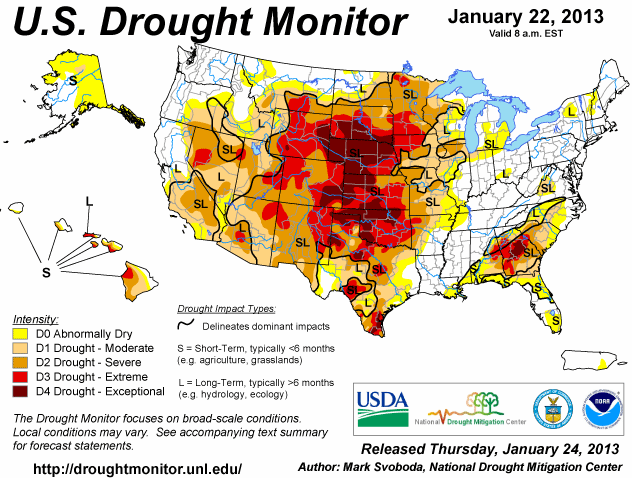
Torkan i USA håller i sig, som vi ser i den senaste ”Drought Monitor”, som publicerades i torsdags. Sedan förra veckan har torkan förbättrats marginellt.
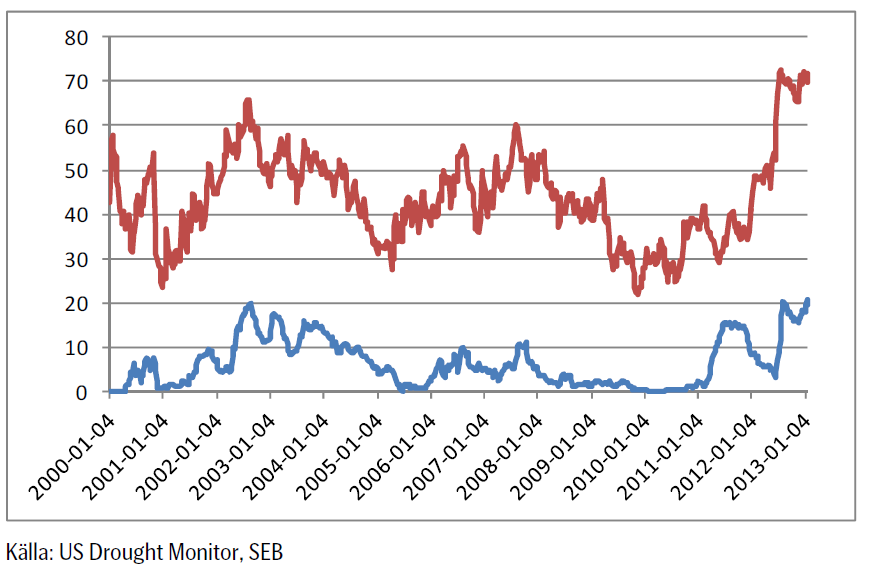
Andelen av USA:s yta som är drabbad av torka minskade marginellt i veckan fram till den rapport som kom förra veckan. Den övre röda linjen visar hur många procent av USA:s areal som är drabbad av någon form av torka. Den nedre blå linjen visar hur många procent som är drabbat av de två värsta varianterna av torka ”extreme” och ”exceptional”.
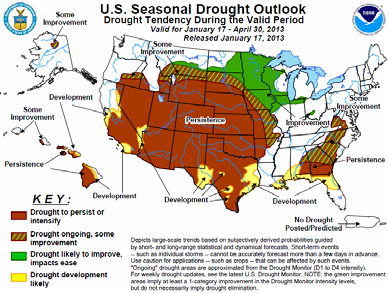
Nedan ser vi prognosen fram till den sista april / första maj, alltså till dess sådden av majs och sojabönor börjar. Alla färgade (ej vita) områden innebär att torkan håller i sig. Det lär alltså vara tämligen torrt när såningsmaskinerna dammar ut på fälten.
Över hela Europa har det kommit nederbörd den senaste tiden, vilket gynnar vintervetet. I västra Ryssland / Ukraina likaså, utom i de allra mest södra delarna. Även Turkiet och nordvästra Afrika har fått ordentlig nederbörd. I nordvästra Afrika avslutade detta en torr period på en månad. Det har också regnat i Sydostasien, vilket gynnar odlingen av ris. I Argentina har det kommit lättare nederbörd i de södra delarna.
De torra delarna av världen är norra Argentina, som är ett viktigt odlingsområde. Australien är rekordtorrt och så USA, som vi sett ovan är nästan rekordtorrt, nästan som 1939, det sista året av ”Dust Bowl” på 1930-talet.
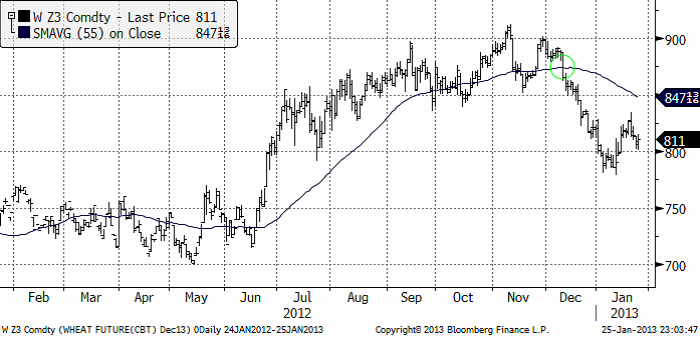
Vete
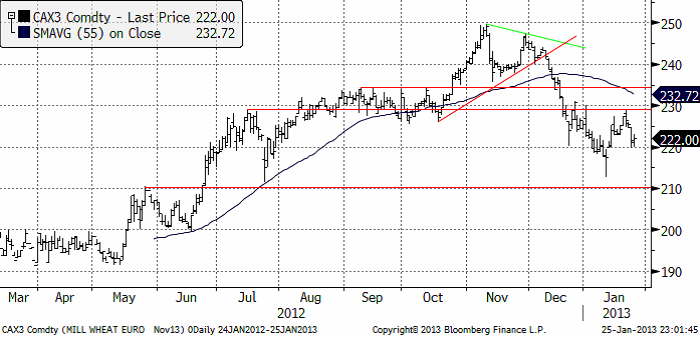
Priset på november (2013) kontraktet nådde upp till den tekniska motståndslinjen på 229 euro per ton, där det fanns tillräckligt med säljare för att trycka ner priset till 220. Veckan stängde på 222 euro.
Nedan ser vi decemberkontraktet på CBOT. Uppgången i januari framträder nu allt mer som vi beskrev den i förra veckobrevet. Som en rekyl mot en fallande trend. Marknaden fann dock stöd i torsdags och fredags på 800 cent (en jämn siffra; jämna siffror är naturliga platser att vänta sig stöd och motstånd). Om måndagens handel öppnar uppåt, får vi ta det som tecken på ytterligare en rekyl uppåt, mot trenden. Omvänt, om marknaden öppnar veckans handel med att sjunka under 800 cent, eller gör det senare i veckan, ska vi tolka det som att marknaden kan vara beredd på att fortsätta den nedåtgående trenden.
Det gick rykten i veckan om att Ryssland skulle ta bort importskatten på 5% på vetet. Det har kommit rapporter om brist på vete från Ryssland. I fredags gick dock Rysslands vice premiärminister ut och dementerade att landet skulle ta bort importskatten. Förmodligen är det tullsamarbetet med spannmålsrika Kazakstan som hindrar detta. Till bilden av spannmålsbrist i Ryssland kan fogas nyheten om att den ryska Spannmålsorganisationen skrev av 8% av vintervetet då detta inte grott. De sade också i veckan att 7% sannolikt skadas pga bristen på skyddande snötäcke i kölden. Det ser ut som om Ryssland skulle behöva importera ett par ton.
EU:s vete tar slut den 24 juli med USDA:s prognos för utgående lager. EU:s export har däremot varit ännu högre än USDA räknat med. Därför måste EU:s höga exporttakt resten av säsongen ligga 13% lägre än hittills för att hålla USDA:s prognos, som knappast kan bli lägre, eftersom lagret i praktiken nästan innebär att det är tomt på sina håll.
Fundamentalt ser det alltså ganska oroligt ut. Den globala vetesituationen kan utvecklas både åt det bättre hållet, eller åt det sämre. Just nu ser det ut tämligen oroväckande ut och vi kan trots det höga priset inte rekommendera sälj. Vi fortsätter med neutral rekommendation.
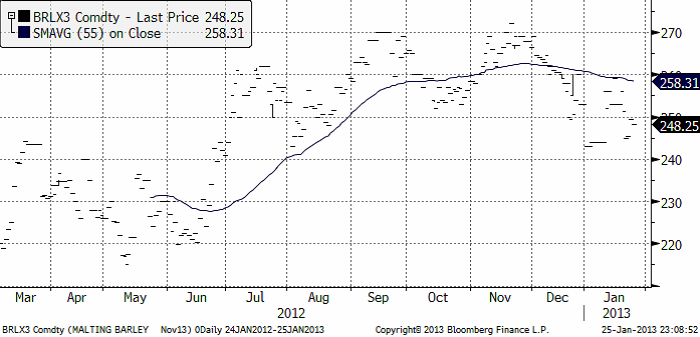
Maltkorn
November 2013-kontraktet föll under veckans oroliga handel från 253 till 248.25 euro per ton. Maltkornet gick därmed ner – samtidigt som vetet steg.
Potatis
Potatispriset för leverans i april nästa år (2014) föll marginellt från 15.90 förra veckan till 15.80 i fredags vid stängning.
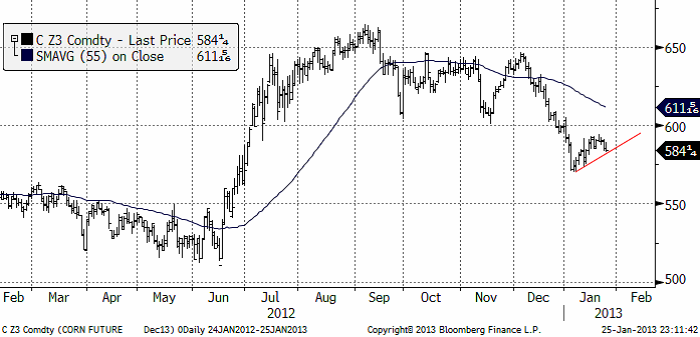
Majs
Majspriset (december 2013) fortsatte sin rekyl uppåt, men slutade veckan med prisnedgångar. Priset ligger nu precis på rekylens tekniska stöd. Om marknaden börjar veckan med att falla, bryts stödet och vi får anse rekylen överstökad. Då finns potential att testa den föregående bottennoteringen från januari på 570 cent. Nästa stöd finns i så fall på 550 cent.
Sådden i Argentina är ännu inte klar, därför att det har varit för torrt. Normalt sett börjar majsen blomma i januari. Den engelska termen är ”silking”, som beskriver mer hur majsen ser ut när den blommar. Effekten tolkas motstridigt av BAGE och regeringen i Argentina, där regeringen är mer avslappnad och frikostig med exportlicenser. Jag tror man ska tolka detta med vetskapen om den allmänna kortsiktighet som präglar landets styrning.
I övrigt väntas rekordstor areal (mitt i torkan i USA, vilket ger enorm osäkerhet). Hur det här kommer att utveckla sig får vi tolka en dag i taget. Den tekniska analysen blir viktig i detta. Just nu ligger som ovan nämnt, priset precis på en stödlinje. Bryts den nedåt i veckan, får vi tolka detta som en kortisktig säljsignal. I annat fall får vi hålla oss neutrala.
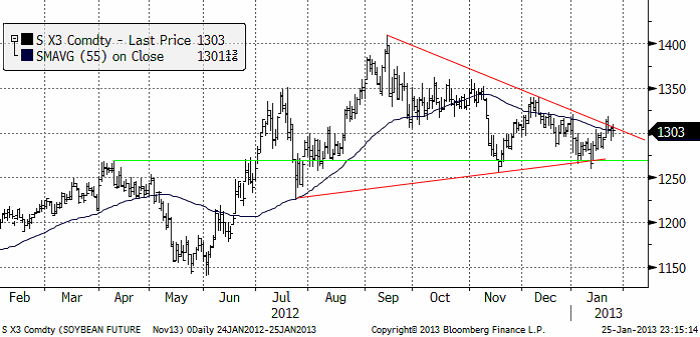
Sojabönor
Sojabönorna (november 2013) var i veckan uppe på ett pris över motståndslinjen från toppen i september.
USA:s export ligger över förra årets. Argentinas export ligger dock efter. En tolkning är att bönderna behåller lager som en inflationshedge. Även här får vi ta marknadens utveckling en dag i taget. Den tekniska analysen säger just nu ingenting. Så vi får vänta i neutralt läge.
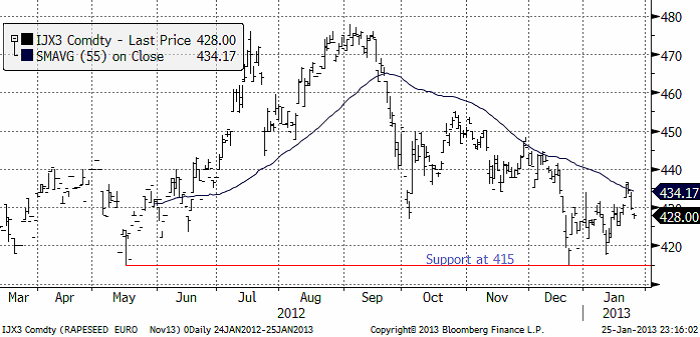
Raps
Rapspriset (november 2013) fortsatte upp i början av veckan, men vände sedan ner. Tekniskt ser diagrammet ut som rörelsen sedan december är en rekyl i en fallande marknad. Vi fortsätter därför med säljrekommendationen.
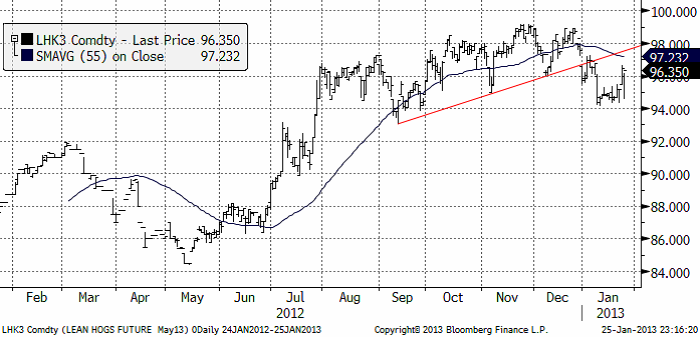
Gris
Grispriset (Maj 13), amerikansk Lean Hogs, har rekylerat uppåt efter brottet nedåt av stödlinjen vid årsskiftet. Rekylen uppåt följer ett klassiskt mönster. Den är ett säljtillfälle.
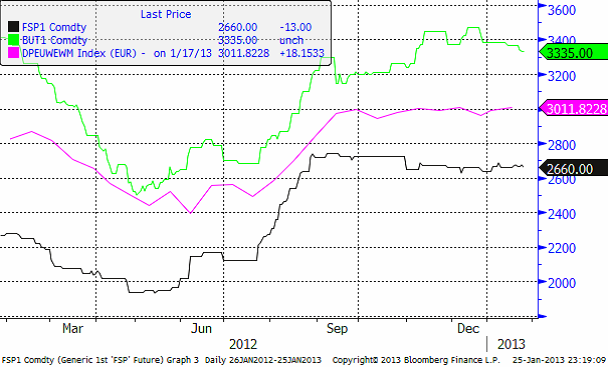
Mjölk
I diagrammet nedan ser vi tre kurvor.Den gröna linjen är priset på skummjölkspulver i euro per ton på Eurex-börsen. Den blå är priset på smör på Eurex börsen. Priserna på Eurex anges i euro per ton.
Slutligen så den gröna linjen. Den visar priset på helmjölkspulver (WMP) FOB Västeuropa. Källan är USDA och priserna uppdateras varannan vecka. Vi ser att WMP-priset legat stabilt det fjärde kvartalet förra året, med en liten nedgång mot slutet av året. 2013 har dock börjat med en liten prisuppgång.
Det börsbaserade priset i svenska kronor beräknas med formeln:
där
BUT = priset på smör i euro per ton
SMP = priset på skummjölkspulver i euro per ton
FX = växelkursen för EURSEK.
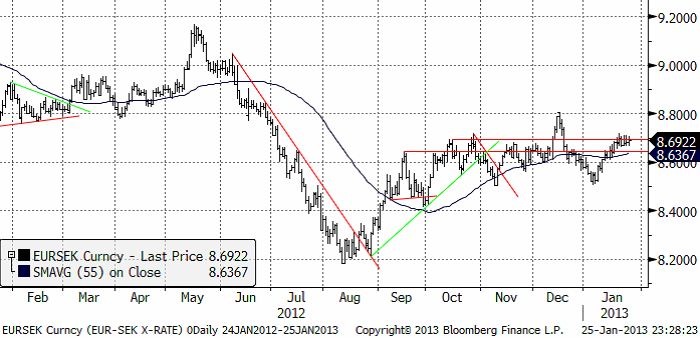
EURSEK
EURSEK rörde sig ”sidledes” i veckan som gick. De som läste vårt förra veckobrev minns att vi skrev att det var det mest troliga. Nu står marknaden och väger, precis på det övre motståndet. Vanligtvis brukar marknaden falla tillbaka i lägen som det här. Men, om veckan börjar med stigande kurser, kan det bli en förlängning på uppgången, i så fall till 8 kronor jämnt i första hand.
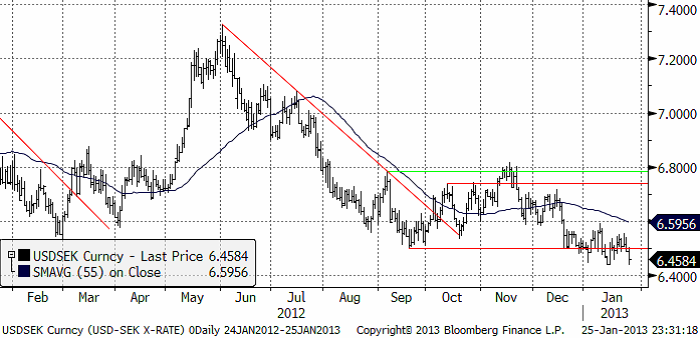
USDSEK
Dollarn har fortsatt att utveckla sig svagt mot kronan. I fredags föll kursen ner mot den senaste månadens stödnivå, som dock höll. I alla fall i fredags. Men det ser ut som om trenden nedåt är stark och gissningsvis vinner den. Vi tror att dollarförsvagningen fortsätter, drivet av att ”Fiscal Cliff” återigen rycker allt närmare.
[box]SEB Veckobrev Jordbruksprodukter är producerat av SEB Merchant Banking och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been compiled by SEB Merchant Banking, a division within Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) (“SEB”).
Opinions contained in this report represent the bank’s present opinion only and are subject to change without notice. All information contained in this report has been compiled in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. However, no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made with respect to the completeness or accuracy of its contents and the information is not to be relied upon as authoritative. Anyone considering taking actions based upon the content of this document is urged to base his or her investment decisions upon such investigations as he or she deems necessary. This document is being provided as information only, and no specific actions are being solicited as a result of it; to the extent permitted by law, no liability whatsoever is accepted for any direct or consequential loss arising from use of this document or its contents.
About SEB
SEB is a public company incorporated in Stockholm, Sweden, with limited liability. It is a participant at major Nordic and other European Regulated Markets and Multilateral Trading Facilities (as well as some non-European equivalent markets) for trading in financial instruments, such as markets operated by NASDAQ OMX, NYSE Euronext, London Stock Exchange, Deutsche Börse, Swiss Exchanges, Turquoise and Chi-X. SEB is authorized and regulated by Finansinspektionen in Sweden; it is authorized and subject to limited regulation by the Financial Services Authority for the conduct of designated investment business in the UK, and is subject to the provisions of relevant regulators in all other jurisdictions where SEB conducts operations. SEB Merchant Banking. All rights reserved.
Analys
Diesel concerns drags Brent lower but OPEC+ will still get the price it wants in Q3

Brent rallied 2.5% last week on bullish inventories and bullish backdrop. Brent crude gained 2.5% last week with a close of the week of USD 89.5/b which also was the highest close of the week. The bullish drivers were: 1) Commercial crude and product stocks declined 3.8 m b versus a normal seasonal rise of 4.4 m b, 2) Solid gains in front-end Brent crude time-spreads indicating a tight crude market, and 3) A positive backdrop of a 2.7% gain in US S&P 500 index.

Brent falling back 1% on diesel concerns this morning. But positive backdrop may counter it later. This morning Brent crude is pulling back 0.9% to USD 88.7/b counter to the fact that the general backdrop is positive with a weaker USD, equity gains both in Asia and in European and US futures and not the least also positive gains in industrial metals with copper trading up 0.4% at USD 10 009/ton. This overall positive market backdrop clearly has the potential to reverse the initial bearish start of the week as we get a little further into the Monday trading session.
Diesel concerns at center stage. The bearish angle on oil this morning is weak diesel demand with diesel forward curves in front-end contango and predictions for lower refinery runs in response this down the road. I.e. that the current front-end strength in crude curves (elevated backwardation) reflecting a current tight crude market will dissipate in not too long due to likely lower refinery runs.
But gasoline cracks have rallied. Diesel weakness is normal this time of year. Overall refining margin still strong. Lots of focus on weakness in diesel demand and cracks. But we need to remember that we saw the same weakness last spring in April and May before the diesel cracks rallied into the rest of the year. Diesel cracks are also very seasonal with natural winter-strength and likewise natural summer weakness. What matters for refineries is of course the overall refining margin reflecting demand for all products. Gasoline cracks have rallied to close to USD 24/b in ARA for the front-month contract. If we compute a proxy ARA refining margin consisting of 40% diesel, 40% gasoline and 20% bunkeroil we get a refining margin of USD 14/b which is way above the 2015-19 average of only USD 6.5/b. This does not take into account the now much higher costs to EU refineries of carbon prices and nat gas prices. So the picture is a little less rosy than what the USD 14/b may look like.
The Russia/Ukraine oil product shock has not yet fully dissipated. What stands out though is that the oil product shock from the Russian war on Ukraine has dissipated significantly, but it is still clearly there. Looking at below graphs on oil product cracks the Russian attack on Ukraine stands out like day and night in February 2022 and oil product markets have still not fully normalized.
Oil market gazing towards OPEC+ meeting in June. OPEC+ will adjust to get the price they want. Oil markets are increasingly gazing towards the OPEC+ meeting in June when the group will decide what to do with production in Q3-24. Our view is that the group will adjust production as needed to gain the oil price it wants which typically is USD 85/b or higher. This is probably also the general view in the market.
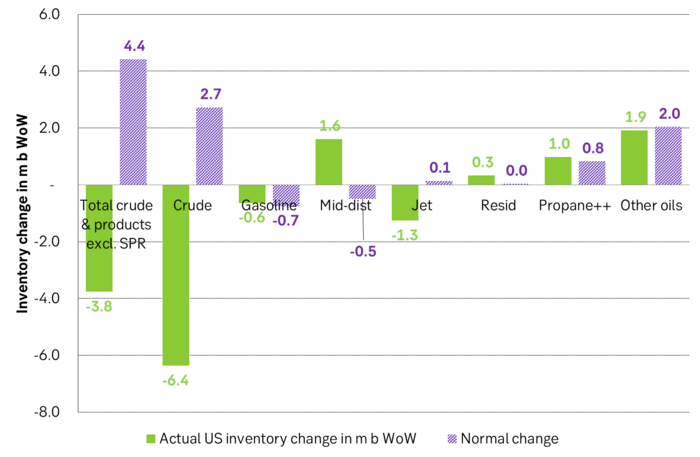
Change in US oil inventories was a bullish driver last week.
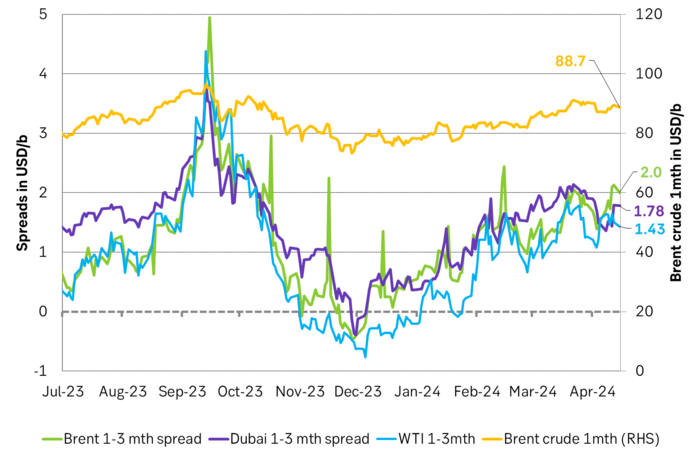
Crude oil time-spreads strengthened last week
ICE gasoil forward curve has shifted from solid backwardation to front-end contango signaling diesel demand weakness. Leading to concerns for lower refinery runs and softer crude oil demand by refineries down the road.
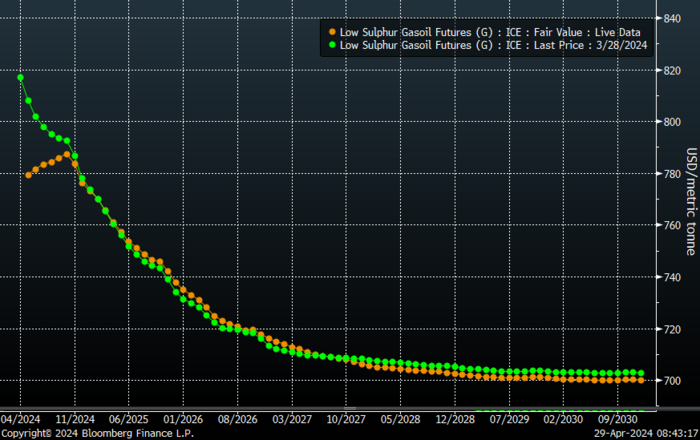
ARA gasoline crack has rallied towards while Gasoil crack has fallen back. Not a totally unusual pattern.
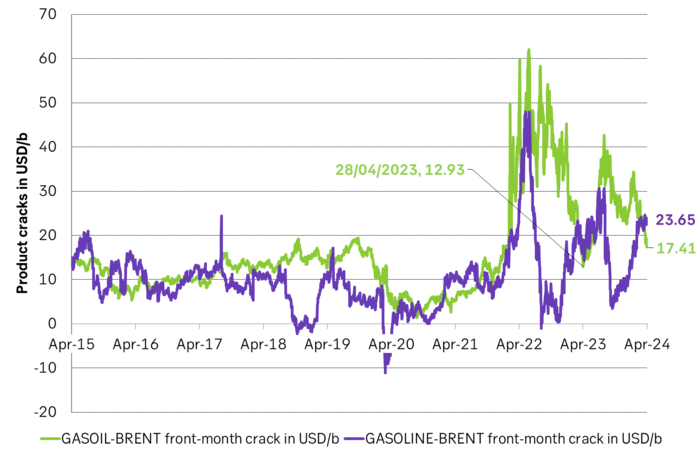
Proxy ARA refining margin with 40% gasoil crack, 40% gasoline crack and 20% bunker oil crack.
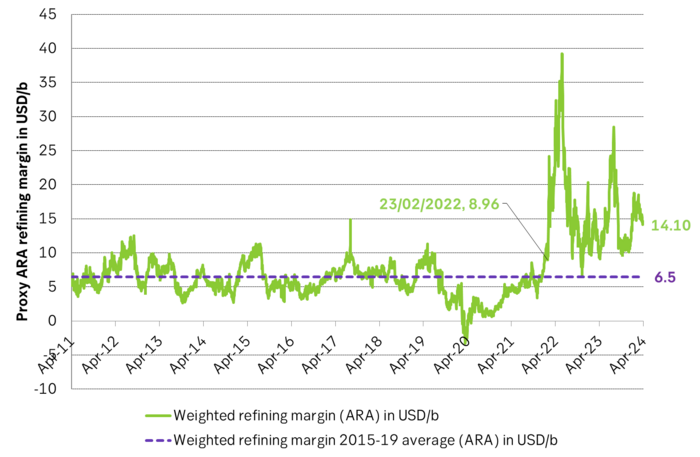
ARA diesel cracks saw the exact same pattern last year. Dipping low in April and May before rallying into the second half of the year. Diesel cracks have fallen back but are still clearly above normal levels both in spot and on the forward curve. I.e. the ”Russian diesel stress” hasn’t fully dissipated quite yet.
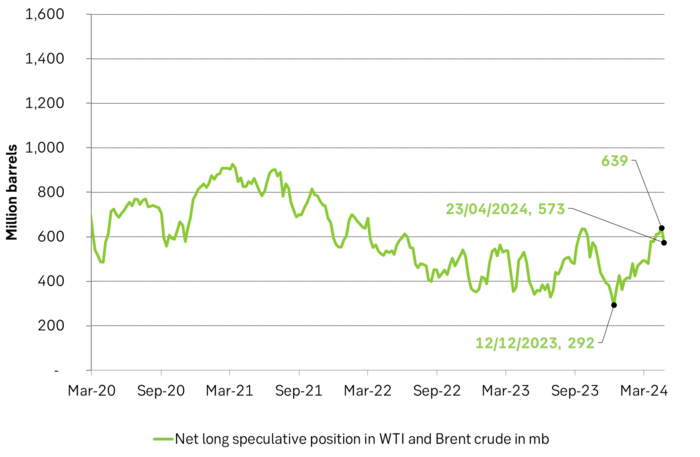
Net long specs fell back a little last week.
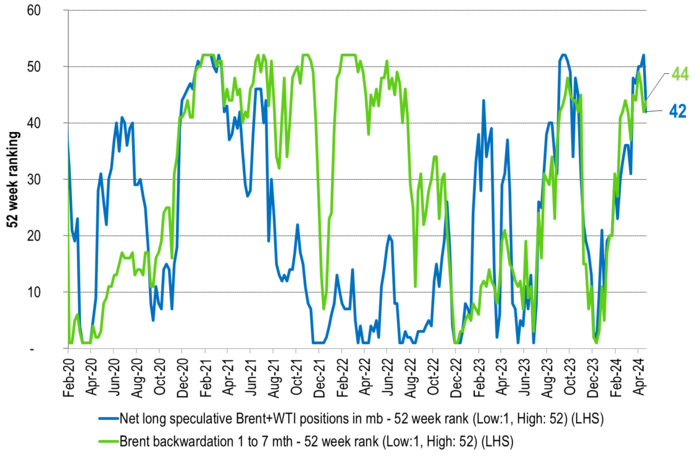
52-week ranking of net long speculative positions in Brent and WTI as well as 52-week ranking of the strength of the Brent 1-7 mth backwardation
Analys
’wait and see’ mode

So far this week, Brent Crude prices have strengthened by USD 1.3 per barrel since Monday’s opening. While macroeconomic concerns persist, they have somewhat abated, resulting in muted price reactions. Fundamentals predominantly influence global oil price developments at present. This week, we’ve observed highs of USD 89 per barrel yesterday morning and lows of USD 85.7 per barrel on Monday morning. Currently, Brent Crude is trading at a stable USD 88.3 per barrel, maintaining this level for the past 24 hours.

Additionally, there has been no significant price reaction to Crude following yesterday’s US inventory report (see page 11 attached):
- US commercial crude inventories (excluding SPR) decreased by 6.4 million barrels from the previous week, standing at 453.6 million barrels, roughly 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
- Total motor gasoline inventories decreased by 0.6 million barrels, approximately 4% below the five-year average.
- Distillate (diesel) inventories increased by 1.6 million barrels but remain weak historically, about 7% below the five-year average.
- Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude + products) decreased by 3.8 million barrels last week.
Regarding petroleum products, the overall build/withdrawal aligns with seasonal patterns, theoretically exerting limited effect on prices. However, the significant draw in commercial crude inventories counters the seasonality, surpassing market expectations and API figures released on Tuesday, indicating a draw of 3.2 million barrels (compared to Bloomberg consensus of +1.3 million). API numbers for products were more in line with the US DOE.
Against this backdrop, yesterday’s inventory report is bullish, theoretically exerting upward pressure on crude prices.
Yet, the current stability in prices may be attributed to reduced geopolitical risks, balanced against demand concerns. Markets are adopting a wait-and-see approach ahead of Q1 US GDP (today at 14:30) and the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, “core PCE prices” (tomorrow at 14:30). A stronger print could potentially dampen crude prices as market participants worry over the demand outlook.
Geopolitical “risk premiums” have decreased from last week, although concerns persist, highlighted by Ukraine’s strikes on two Russian oil depots in western Russia and Houthis’ claims of targeting shipping off the Yemeni coast yesterday.
With a relatively calmer geopolitical landscape, the market carefully evaluates data and fundamentals. While the supply picture appears clear, demand remains the predominant uncertainty that the market attempts to decode.
Analys
Also OPEC+ wants to get compensation for inflation

Brent crude has fallen USD 3/b since the peak of Iran-Israel concerns last week. Still lots of talk about significant Mid-East risk premium in the current oil price. But OPEC+ is in no way anywhere close to loosing control of the oil market. Thus what will really matter is what OPEC+ decides to do in June with respect to production in Q3-24 and the market knows this very well. Saudi Arabia’s social cost-break-even is estimated at USD 100/b today. Also Saudi Arabia’s purse is hurt by 21% US inflation since Jan 2020. Saudi needs more money to make ends meet. Why shouldn’t they get a higher nominal pay as everyone else. Saudi will ask for it

Brent is down USD 3/b vs. last week as the immediate risk for Iran-Israel has faded. But risk is far from over says experts. The Brent crude oil price has fallen 3% to now USD 87.3/b since it became clear that Israel was willing to restrain itself with only a muted counter attack versus Israel while Iran at the same time totally played down the counterattack by Israel. The hope now is of course that that was the end of it. The real fear has now receded for the scenario where Israeli and Iranian exchanges of rockets and drones would escalate to a point where also the US is dragged into it with Mid East oil supply being hurt in the end. Not everyone are as optimistic. Professor Meir Javedanfar who teaches Iranian-Israeli studies in Israel instead judges that ”this is just the beginning” and that they sooner or later will confront each other again according to NYT. While the the tension between Iran and Israel has faded significantly, the pain and anger spiraling out of destruction of Gaza will however close to guarantee that bombs and military strifes will take place left, right and center in the Middle East going forward.
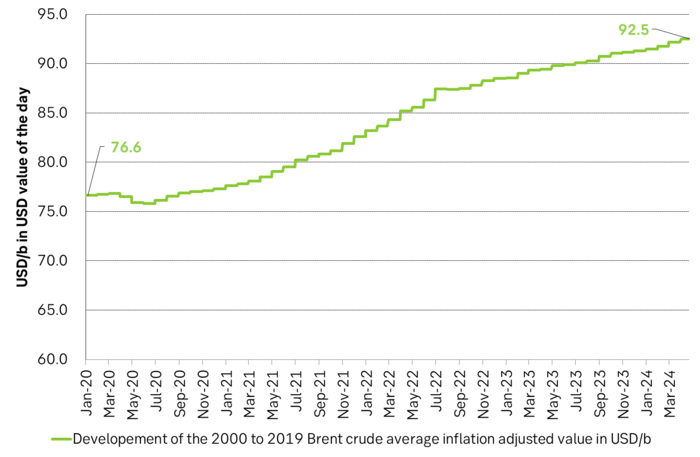
Also OPEC+ wants to get paid. At the start of 2020 the 20 year inflation adjusted average Brent crude price stood at USD 76.6/b. If we keep the averaging period fixed and move forward till today that inflation adjusted average has risen to USD 92.5/b. So when OPEC looks in its purse and income stream it today needs a 21% higher oil price than in January 2020 in order to make ends meet and OPEC(+) is working hard to get it.
Much talk about Mid-East risk premium of USD 5-10-25/b. But OPEC+ is in control so why does it matter. There is much talk these days that there is a significant risk premium in Brent crude these days and that it could evaporate if the erratic state of the Middle East as well as Ukraine/Russia settles down. With the latest gains in US oil inventories one could maybe argue that there is a USD 5/b risk premium versus total US commercial crude and product inventories in the Brent crude oil price today. But what really matters for the oil price is what OPEC+ decides to do in June with respect to Q3-24 production. We are in no doubt that the group will steer this market to where they want it also in Q3-24. If there is a little bit too much oil in the market versus demand then they will trim supply accordingly.
Also OPEC+ wants to make ends meet. The 20-year real average Brent price from 2000 to 2019 stood at USD 76.6/b in Jan 2020. That same averaging period is today at USD 92.5/b in today’s money value. OPEC+ needs a higher nominal price to make ends meet and they will work hard to get it.
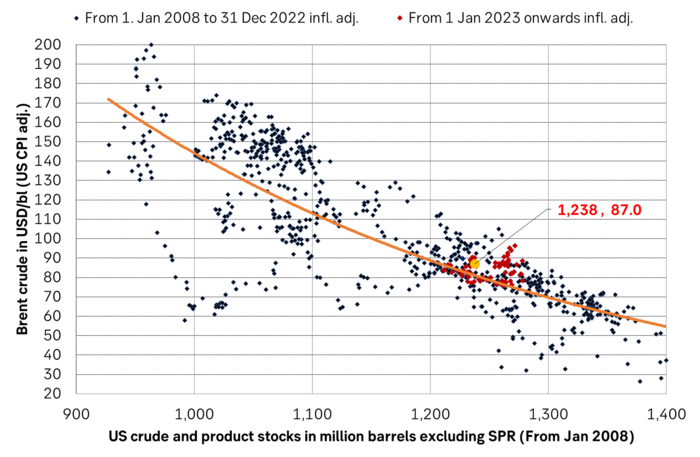
Inflation adjusted Brent crude price versus total US commercial crude and product stocks. A bit above the regression line. Maybe USD 5/b risk premium. But type of inventories matter. Latest big gains were in Propane and Other oils and not so much in crude and products
Total US commercial crude and product stocks usually rise by 4-5 m b per week this time of year. Gains have been very strong lately, but mostly in Propane and Other oils
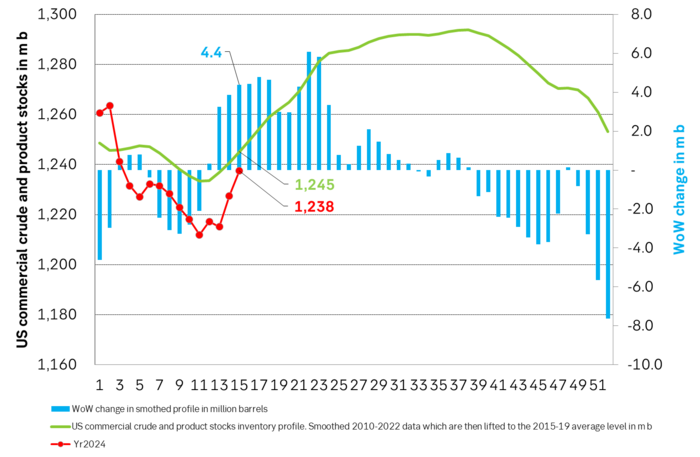
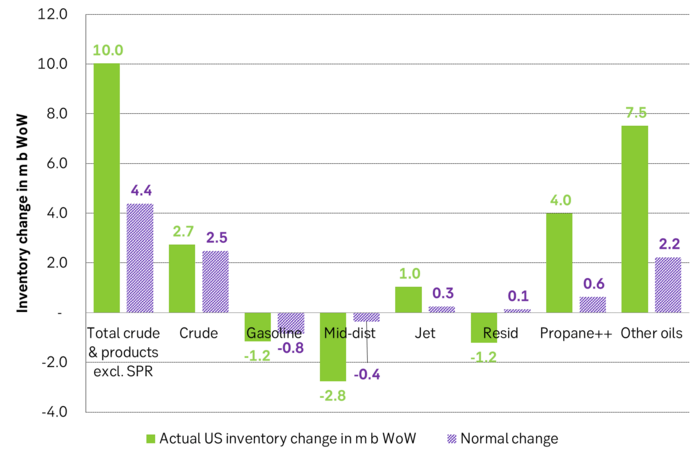
Last week’s US inventory data. Big rise of 10 m b in commercial inventories. What really stands out is the big gains in Propane and Other oils
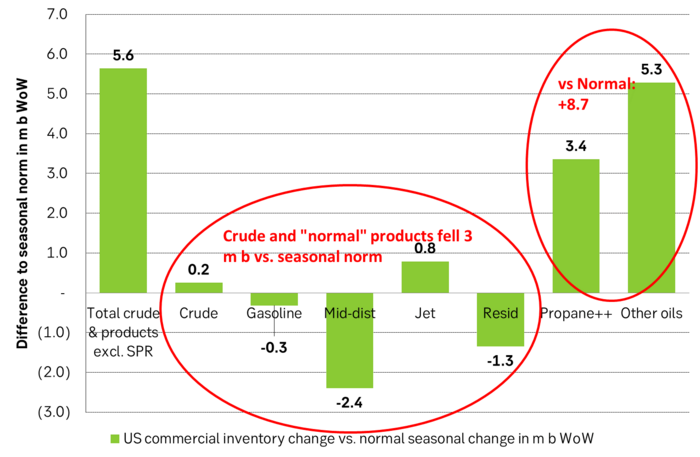
Take actual changes minus normal seasonal changes we find that US commercial crude and regular products like diesel, gasoline, jet and bunker oil actually fell 3 m b versus normal change.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanFortum och Vargön Alloys tecknar femårigt avtal om kärnkraftsel
-
 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanOljan letar efter en högre botten
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanBrace for Covert Conflict
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanAlso OPEC+ wants to get compensation for inflation
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanElpriset fortsätter att sjunka – halverade priser i april jämfört med 2023
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanAI ökar det totala elbehovet i USA med 100 % kommande 15 år
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanBörsveckan ger en köprekommendation till aktien i oljeservicebolaget Beerenberg
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanKaffepriserna rör på sig