Analys
SEB Jordbruksprodukter, 23 september 2013


 Prisrörelserna förra veckan påverkades mycket av den amerikanska centralbanken. Först kom beskedet att det inte blir någon minskning i centralbankens (FED:s) köp av amerikanska obligationer, förrän tidigast år 2015. Anledningen är att man inte sett tillräcklig effekt på ekonomin än av de köp (och utbetalningar av pengar) som skett. Man kan fråga sig var de läst att sedelpressen någonsin skapat sysselsättning. Beslutet fick alla råvarumarknader att hoppa upp. Råvarulandet Brasliens aktiebörs blev den bästa av nästan 100 aktiebörser i världen, den dagen. I fredags gjorde så en medlem i FED ett uttalande som antydde att det ändå kan bli fråga om minskning i centralbankens återköp. Analytiker tolkade detta som en del i FED:s kommunikationsstrategi. Marknaderna föll abrupt på detta sent på fredagen. Jag ser dock detta inte som en medveten kommunikationsstrategi utan som ett tecken på oenighet i FED om fortsatt pengaproduktion är rätt väg. Det viktiga är dock att de som tycker att sedelpressen ska stå på är i majoritet och att dissidenterna är få. Vid det senaste FED-beslutet var det endast en person som var emot en förlängning till 2015. Kanske har marknaden kommit fram till samma slutsats under helgen. I så fall skulle priserna kunna gå upp i veckan
Prisrörelserna förra veckan påverkades mycket av den amerikanska centralbanken. Först kom beskedet att det inte blir någon minskning i centralbankens (FED:s) köp av amerikanska obligationer, förrän tidigast år 2015. Anledningen är att man inte sett tillräcklig effekt på ekonomin än av de köp (och utbetalningar av pengar) som skett. Man kan fråga sig var de läst att sedelpressen någonsin skapat sysselsättning. Beslutet fick alla råvarumarknader att hoppa upp. Råvarulandet Brasliens aktiebörs blev den bästa av nästan 100 aktiebörser i världen, den dagen. I fredags gjorde så en medlem i FED ett uttalande som antydde att det ändå kan bli fråga om minskning i centralbankens återköp. Analytiker tolkade detta som en del i FED:s kommunikationsstrategi. Marknaderna föll abrupt på detta sent på fredagen. Jag ser dock detta inte som en medveten kommunikationsstrategi utan som ett tecken på oenighet i FED om fortsatt pengaproduktion är rätt väg. Det viktiga är dock att de som tycker att sedelpressen ska stå på är i majoritet och att dissidenterna är få. Vid det senaste FED-beslutet var det endast en person som var emot en förlängning till 2015. Kanske har marknaden kommit fram till samma slutsats under helgen. I så fall skulle priserna kunna gå upp i veckan
som kommer.
Inga tekniska stödnivåer bröts i under fredagens prisfall – utom för sojabönor – men ”it had it coming”. Vi är fortsatt negativa till sojabönor och raps, men neutrala till spannmål och vi har köp på socker.
I torsdags var vi på Copenhagen Grain Exchange, som besöktes av rekordmånga från branschen. När man talade med folk var den allmänna bedömningen att priset på spannmål kommer att hålla sig stabilt på den här nivån åtminstone fram till våren. Det är i sig ett observandum, att man tror att volatiliteten kommer att vara låg och att priserna kommer att vara låga. Det finns inget som tyder på det, men skulle det komma nyheter som indikerar högre priser, finns ingen psykologisk förberedelse på detta.
Vete
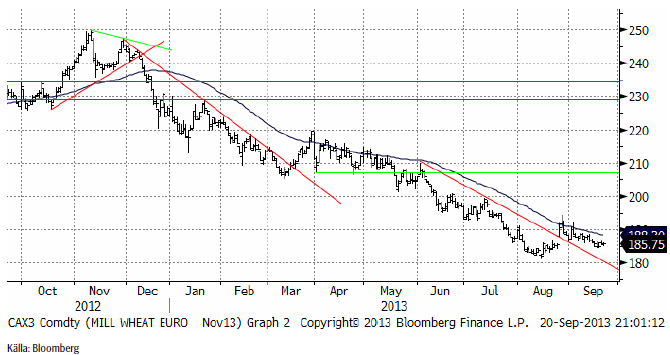
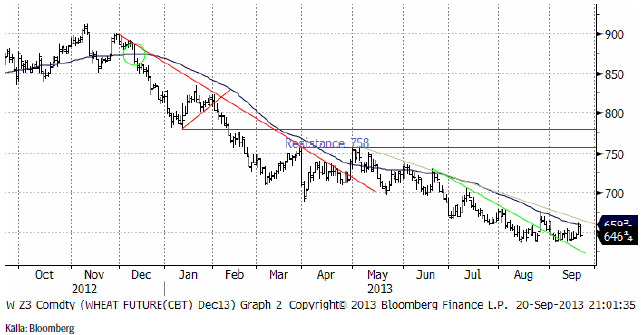
November-vetet på Matif höll sig över stödlinjen, men backade större delen av veckan. Den tekniska analystolkningen är att den huvudsakliga fallande trenden är bruten och att marknaden är i nyhetsmässig stiltje. Ett trendbrott uppåt skulle kunna komma, likväl som en fortsatt prisfall.
Decemberkontraktet på CBOT tycks ha ett stöd strax under dagens pris. Stödet ligger vid 640 cent ungefär.
Nedan ser vi terminskurvorna för Chicagovete och Matif.
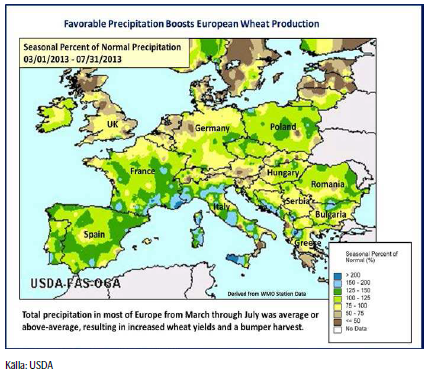
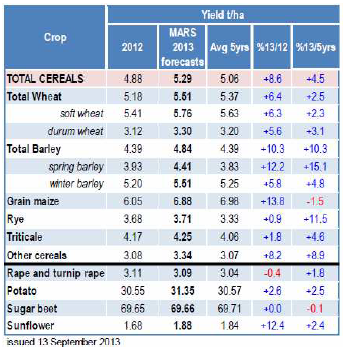
Som vi skrev om i förra veckobrevet, justerade USDA upp sin prognos för produktionen av vete i EU till 142.9 mt, en ökning med 1.5 mt från förra månadens rapport och upp 9.8 mt från förra året. Arealen lämnas oförändrad på 26 miljoner hektar medan avkastningen revideras upp från augustis 5.43 t/ha till 5.49 t/ha. Ovanligt kallt och blött väder under vården resulterade i försenad utveckling för höstvetet medan det varma och torra vädret under juli och augusti fick grödornas utveckling att ta fart i Tyskland, Polen och Storbritannien. Säsongsmässig nederbörd har också bidragit till stora skördar i Rumänien och Bulgarien. Den största förändringen från förra månadens rapport är en ökning av produktionen i Tyskland med 0.5 mt till 24.7 mt. Även produktionen i Rumänien och Bulgarien justeras upp med 0.3 mt respektive 0.2 mt till 7.4 mt och 4.8 mt. Den estimerade produktionen i Storbritannien fortsätter också att justeras upp trots en dålig start på säsongen.
För Kanada beräknar USDA en rekordavkastning, trots en sen start av sådden pga av snötäcket som låg kvar och temperaturer under det normala som resulterade i vattendränkta fält. Bra väder under juni och juli satte dock fart på grödorna vilket kompenserade den sena starten. Den kanadensiska veteproduktionen beräknas uppgå till 31.5 mt, en ökning med 16% från förra året och upp 6.8% från förra månadens rapport.
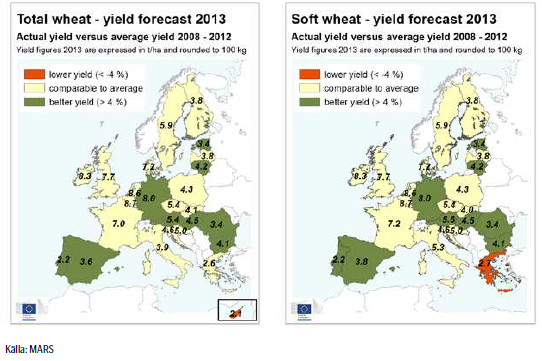
EU Kommissionens MARS-enhet kom med sin rapport i måndags och tar rygg på USDA och fortsätter att justera upp den genomsnittliga avkastningen för vete i EU-28. Avkastningen för korn justerar också upp något medan avkastningen för majs däremot justeras ner. Även raps justeras ner marginellt. Överlag så är utsikterna fortsatt gynnsamma för EU-28 och avkastningen ligger både över förra årets nivåer och det 5-
åriga genomsnittet.
Rapporteringsperioden, från början av juli till slutet av augusti, har präglats av nederbörd under det normala och temperaturer över det normala över stora delar av Europa. Däremot har mer regn än normalt fallit över de östra och södra delarna av Frankrike, norra Polen och över stora delar av Ryssland. De sydöstra delarna av Europa, bl.a Italien och västra Rumänien, drabbades av en exceptionell värmebölja i början av augusti. Under skördetid har dock vädret i allmänhet varit bra i Europa.
Prognosen för hektarskörden avseende vete inom EU-28 justerades upp något till 5.76 t/ha från förra månadens 5.71 t/ha, vilket är en ökning med 6.3% jämfört med förra året och över det femåriga genomsnittet på 5.63 t/ha. Revideringen återspeglar högre hektarskördar i Tyskland, Estland och Litauen.
Måndagens Crop Progress från USDA visar att skörden av amerikanskt vårvete går mot sitt slut. För de 6 stater som rapporterar så är nu 90% av skörden avklarad, en ökning från förra veckans 84%. Vid den här tiden förra året var dock skörden avklarad.
I förra veckan så började USDA också rapportera utvecklingen av den pågående sådden av amerikanskt höstvete.
12% av den förväntade arealen var avklarad per den 15 september, vilket är i linje med det 5-åriga genomsnittet.
Ukraina vill utöka sin export till Kina och den 18 september hölls det tredje mötet mellan länderna för att diskutera möjligheten att öka utbudet av jordbruksprodukter. I slutet av året väntas protokollet med fytosanitära krav undertecknas av bägge parter vilket möjliggör leveranser från Ukraina av korn och sojabönor i år, medan exporten av vete och raps beräknas starta från och med nästa år. Kina är idag en köpare av majs från Ukraina.
Argentinas produktion av vete förväntas återhämta sig från förra årets låga nivå, men mer regn behövs. Drivet av höga priser på den inhemska marknaden ökade sådd areal med nästan 8% från förra årets kraftigt reducerade nivå till 3.4 miljoner hektar. Siffran är dock lägre än förväntningarna i början på en ökning av areal med 23% pga av de torra väderförhållandena under sådden. Nederbörd i början av september har dock varit till gagn för grödorna, i synnerhet i de viktiga producentområdena runt Buenos Aires. Men fortsatt nederbörd behövs under de kommande veckorna, framförallt i de västra delarna. Förutsatt att vädret blir ”normalt” under den fortsatta växtsäsongen så indikerar FAO en preliminär prognos på 9.5 mt för 2013.
Skörden av vete i Brasilien har nu påbörjats. Hos den största producenten, Parana, som står för nästan hälften av den totala produktionen har grödorna drabbats hårt av det ovanligt kalla vädret och frost under augusti månad. Den officiella produktionsprognosen för 2013 har reviderats ner med 13% till 5.1 mt. Dock är denna nivå högre än den kraftigt minskade skörden under 2012, men fortfarande lägre än det 5-åriga genomsnittet. Den ökade produktionen beror främst på en ökning av areal med nästan 13% från förra året.
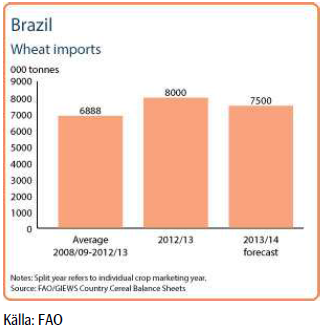
Trots skadorna på grödorna väntas produktionen att öka och importen under 2013/14 väntas minska med 6% till 7.5 mt. Under säsongen 2012/13 har ett minskat utbud, framförallt pga minskad produktion och exportrestriktioner i Argentina, fått Brasilien att istället importera vete från USA och Kanada.
Vi fortsätter att ha en neutral position i vetemarknaden.
Maltkorn
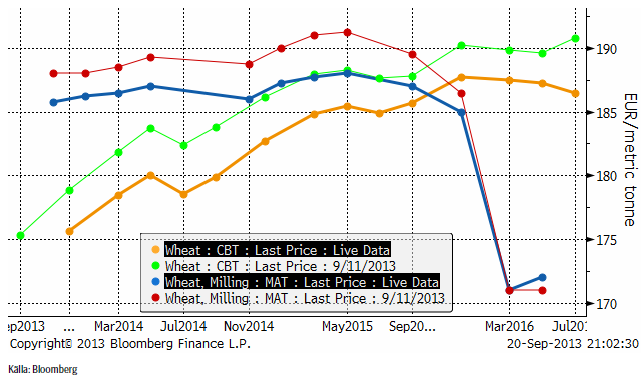
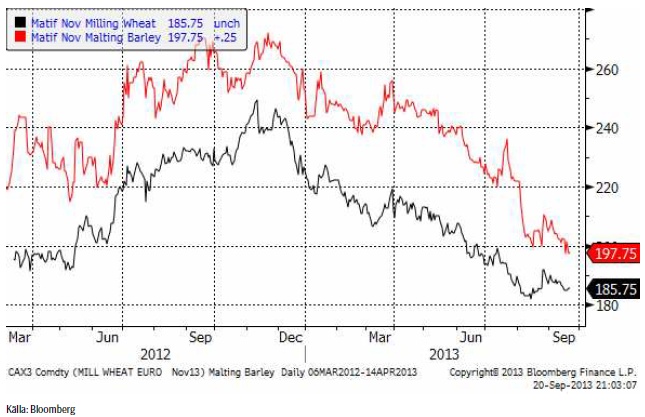
Terminspriset (november) har utvecklats väsentligt svagare än vetet den senaste tiden och bröt 200-euronivån. Det är alltså 190 som är nästa stödnivå. Dit kan priset omöjligen gå just nu, eftersom skillnaden mot Matif på 186 skulle bli för liten. Prisskillnaden mellan maltkorn och Matif-vete är ovanligt låg som den är efter veckans prisrörelser.
Majs
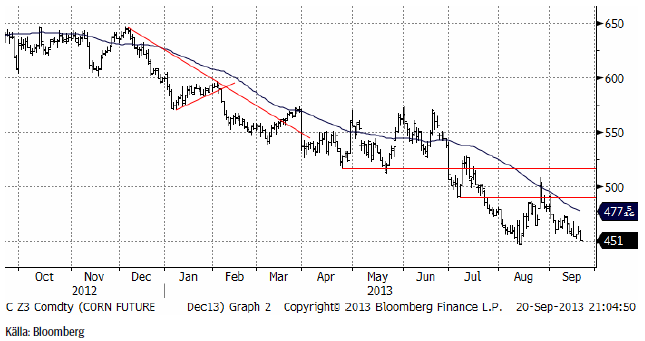
Majspriset (december 2013) föll liksom många råvaror kraftigt i pris sent i fredags och är nu strax över stödet på 450 cent.
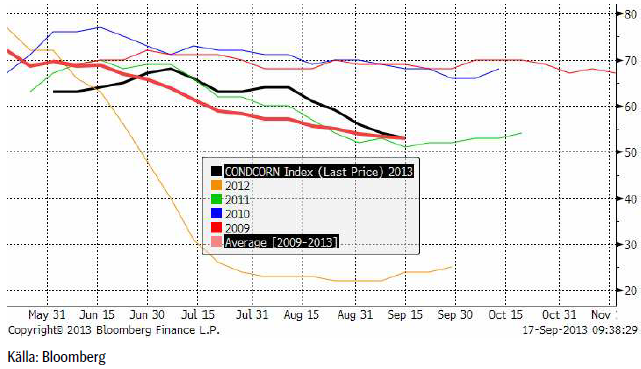
I måndags för en vecka sedan kom de senaste crop rating, som var ytterligare en nedjustering av andelen i ”good” eller ”excellent” skick (om än i något långsammare takt). För de 18 stater som rapporterar så klassas nu 53% som ”good/excellent”, ner 1% från veckan innan och nu strax under det 5-åriga genomsnittet på 55%. Omkring 56% respektive 64% av grödorna i Illinois och Indiana klassas som ”good/excellent”, vilket är en förbättring jämfört med veckan innan. Oförändrad från förra veckan är Iowa där endast 35% tillhör denna kategori.
Andelen majs som har uppnått mjölmognad uppgår till 81%, en ökning från förra veckans 64%. Förra året under torkan så hade i stort sett all majs uppnått mjölmognad vid den här tiden, men det 5-åriga genomsnittet för samma datum ligger på 86%. I Illinois har 84% nått detta utvecklingsstadium medan siffran för Indiana ligger på 82%.
Enligt USDA har nu också skörden av majs startat officiellt och per den 15 september var 4% av skörden avklarad, jämfört med 24% vid den här tiden förra året och det 5-åriga genomsnittet på 10%.
Sådden av majs pågår just nu i Argentina inför 2014, vilken dock har blivit försenad på grund av det torra vädret i augusti. Preliminära prognoser indikerar också en minskning av areal med 3% från förra årets rekordnivå. Skörden av majs (2013) var avklarad i juni. FAO’s senaste prognos uppskattar en produktion på 29 mt, en ökning med 37% från året innan och en ny rekordnivå.
BAGE säger att sådden är avklarad till 2.8%, en ökning från förra veckan 1%.
Skörden av majs, safrinha, är nu avslutad i Brasilien. Officiella uppskattningar pekar på en skörd på 45.5 mt, nästan 20% mer än förra året, vilket gör att den totala produktionen för 2013 sätter en ny rekordnivå på 80 mt till följd av ökad sådd, attraktiva höga priser och förbättrad avkastning då växtsäsongen präglats av gynnsamt väder.
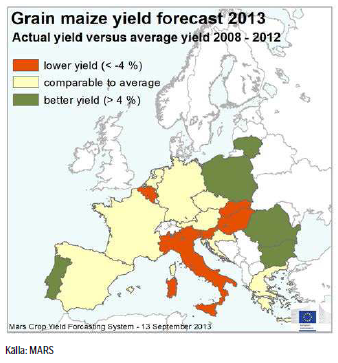
EU Kommissionens MARS-enhet kom med sin rapport i måndags där de justerade ner avkastningen för majs sedan förra månadens rapport då bl.a det varma och torra vädret i Italien, med temperaturer upp till 40 grader i de norra delarna av landet, under blomningen i augusti har skadat grödorna. Den genomsnittliga avkastningen justeras ner från förra månadens 6.97 t/ha till 6.88 t/ha, vilket fortfarande är en nivå som ligger över förra årets 6.05 t/ha. Frankrike är den största producenten av majs i EU-28 och estimeras en avkastning på 9.01 t/ha i år, medan Italien under förra året tog sig upp på en 2:a plats då Rumänen – som annars är näst största producenten – drabbades av värmebölja under sommaren med en lägre produktion som följd. Italienska lantbrukare väntas skörda 8.66 t/ha, vilket är ner från förra månadens 8.92 t/ha.
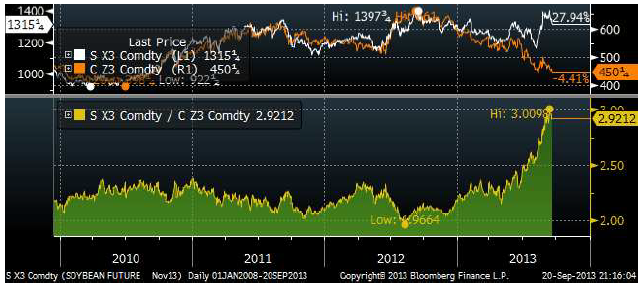
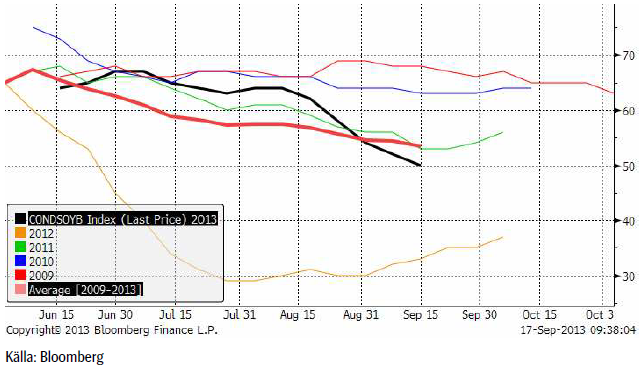
Allt fler börjar nu fråga sig hur nästa år kommer att te sig. De höga sojapriserna – och låga majspriserna har redan fått brasilianarna att överge majs och byta till soja, så att skörden väntas nå en ny rekordnivå. Kvoten mellan priserna på november-soja och december-majs har gått från 2 till 2.92 sedan samma tid förra året. Vi ser detta i diagrammet nedan.
Informa Economics publicerade en rapport i fredags på samma tema. De räknar med att sojaarealen i USA når ett nytt rekord medan sådden av majs minskar från årets rekordnivå 95.5 till 92.7 miljoner acres. 92.7 miljoner som innebär en stor minskning från årets sådd, är ändå den fjärde största arealen majs sedan det andra världskriget.
Antagligen är det av den här anledningen som urea-priserna ligger så pass lågt som de gör just nu. Detta gynnar produktionen av spannmål generellt, i norra delarna av världen, där man inte kan odla majs och soja.
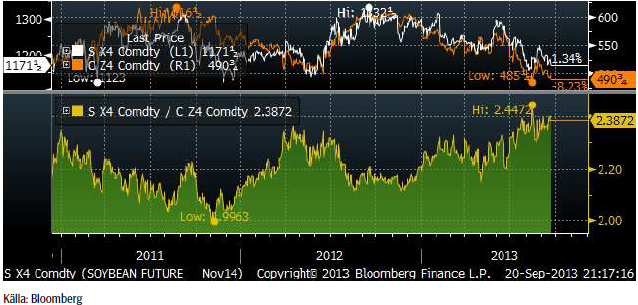
Medan sojapriset dragit i från majsen på årets kontrakt (november, december), är detta inte lika dramatiskt för 2014 års kontrakt, som vi ser nedan. Det är fortfarande så att soja har stigit i pris i förhållande till majs, men inte lika dramatiskt.
Vi behåller neutral rekommendation.
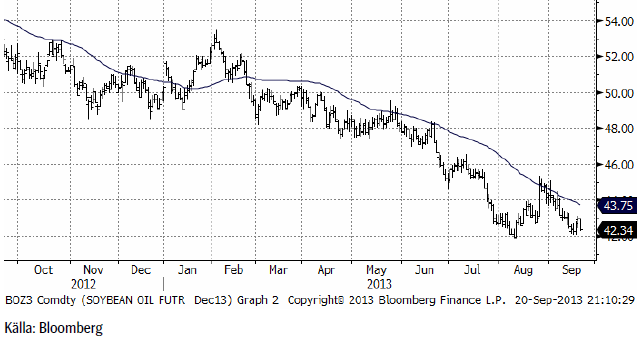
Sojabönor
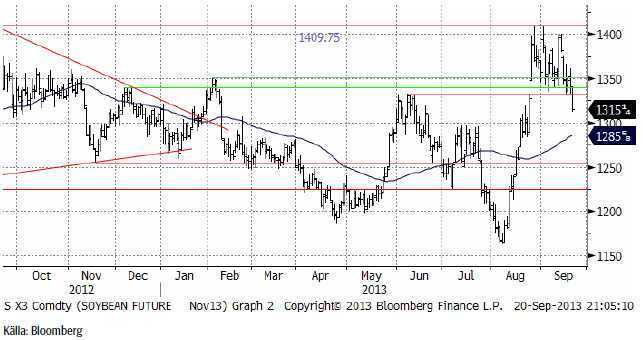
Novemberkontraktet på sojabönor sjönk successivt under veckan som gick, men fall-luckan öppnade sig i fredags och priset föll ner mot stödet på 1300 cent. Priset har potential att falla mer än så, om den nivån bryts.
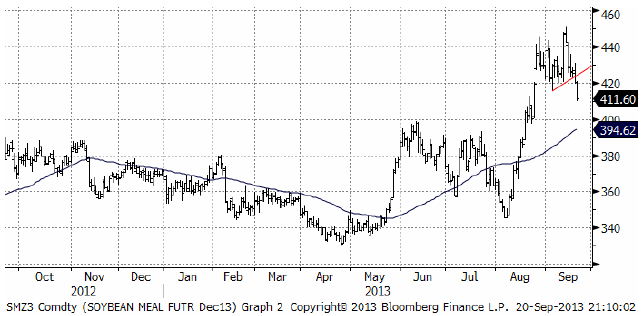
Sojamarknaden är naturligt uppdelad på sojamjöl och sojaolja och det är två helt olika världar. Vi ser prishistoriken på sojamjölet nedan. Köpsignalen på uppsidan visade sig vara ”falsk” när priset föll tillbaka. Falska köpsignaler följs ofta av ett utbrott på nedsidan och det fick vi i fredagskvällens handel. Priset kan nog gå ner till 400 dollar per short ton. Men man ska också komma ihåg att det var helgdag i Asien i fredags och att köparna därför inte var i marknaden.
Och nedan ser vi den mycket baissigare utvecklingen på sojaoljan.
Trots spridda skurar och lägre temperaturer i USA fortsatte USDA att justera ner tillståndet för sojabönorna i måndagens Crop Progress. Andelen ”good/excellent” ligger nu på 50%, en nedjustering med 2% sedan förra veckan och under det 5-åriga genomsnittet på 55%. Hälften av grödorna i Illinois klassas som ”good/excellent”, och i Indiana ligger siffran på 56%. För bägge staterna är det en uppjustering med 1% från veckan innan. Tillståndet för sojabönorna i Iowa är oförändrat med andelen ”good/excellent” på blygsamma 33%.
Brasilianska CEPEA rapporterade i veckan att brasilianska bönder redan prissäkrat 25% av skörden till attraktiva priser, räknat i real.
Vi behåller säljrekommendation.
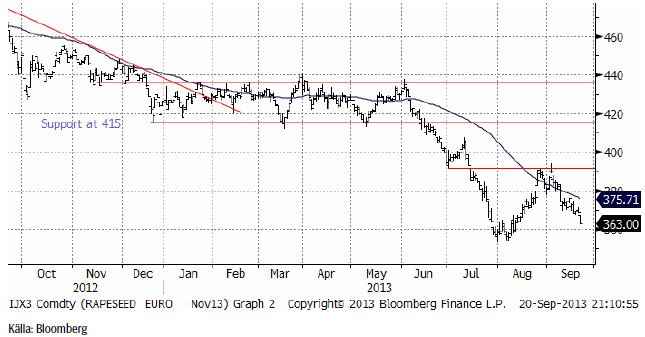
Raps
Rapspriset (november 2013) fortsatte sjönk hela veckan och föll slutligen kraftigt på fredagskvällen. Nyhetsmässigt talas om att Kanada kan få en skörd av canola på 17 mt, 2 mt högre än USDA:s estimat tidigare i september.
Vi behåller säljrekommendationen på raps.
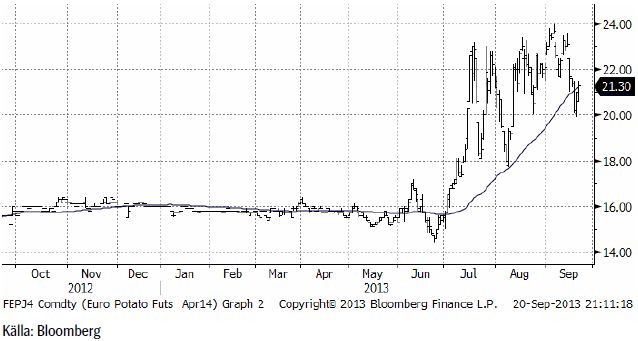
Potatis
Potatispriset var nere och rörde vid 20 euro per deciton i veckan. En stor aktör i Nordeuropa har deklarerat att priset ”ska vara” 21 euro.
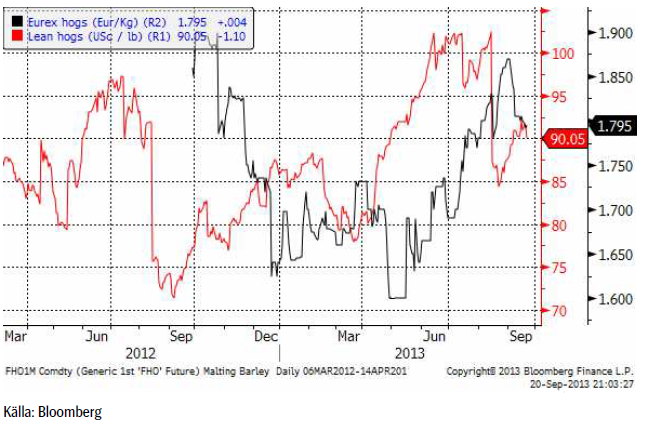
Gris
Eurexpriset fortsatte falla i veckan – och CME:s pris fortsatte stiga.
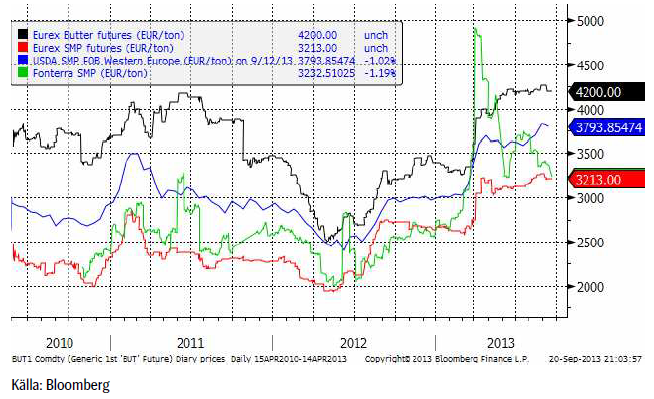
Mjölk
Terminerna på smör och skummjölkspulver vid Eurex-börsen var lite försiktigare i veckan som gick. Som vi har påpekat tidigare har den stigande trenden tappat kraft den senaste tiden. Fonterras notering har varit fallande i flera veckor.
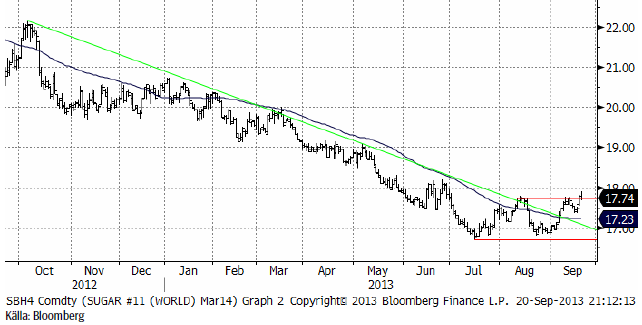
Socker
Marskontraktet på råsocker bröt det tekniska motståndet och vi har nu alltså köpsignal även tekniskt. Marknadsaktörer i Europa, som vi talat med är inställda på fortsatt överskott i sockermarknaden och inställda på fallande pris framöver. Min reflektion är att när branschen är så grundmurat negativ, är det god jordmån för en prisuppgång.
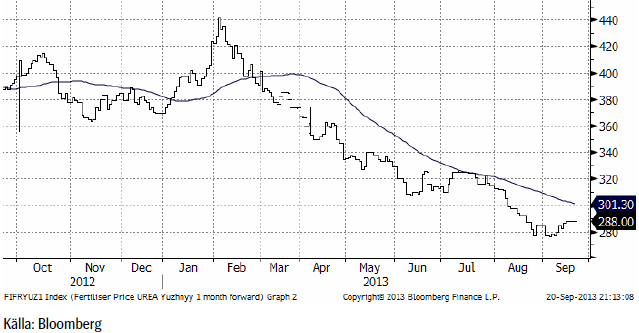
Gödsel
Priset på kväve / urea steg 1 dollar på veckan til 288 dollar per ton. Kanske kan det låga priset tolkas som att amerikanska lantbrukare sänker så mer sojabönor och mindre majs nästa år?
[box]SEB Veckobrev Jordbruksprodukter är producerat av SEB Merchant Banking och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been compiled by SEB Merchant Banking, a division within Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) (“SEB”).
Opinions contained in this report represent the bank’s present opinion only and are subject to change without notice. All information contained in this report has been compiled in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. However, no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made with respect to the completeness or accuracy of its contents and the information is not to be relied upon as authoritative. Anyone considering taking actions based upon the content of this document is urged to base his or her investment decisions upon such investigations as he or she deems necessary. This document is being provided as information only, and no specific actions are being solicited as a result of it; to the extent permitted by law, no liability whatsoever is accepted for any direct or consequential loss arising from use of this document or its contents.
About SEB
SEB is a public company incorporated in Stockholm, Sweden, with limited liability. It is a participant at major Nordic and other European Regulated Markets and Multilateral Trading Facilities (as well as some non-European equivalent markets) for trading in financial instruments, such as markets operated by NASDAQ OMX, NYSE Euronext, London Stock Exchange, Deutsche Börse, Swiss Exchanges, Turquoise and Chi-X. SEB is authorized and regulated by Finansinspektionen in Sweden; it is authorized and subject to limited regulation by the Financial Services Authority for the conduct of designated investment business in the UK, and is subject to the provisions of relevant regulators in all other jurisdictions where SEB conducts operations. SEB Merchant Banking. All rights reserved.
Analys
Fear that retaliations will escalate but hopes that they are fading in magnitude

Brent crude spikes to USD 90.75/b before falling back as Iran plays it down. Brent crude fell sharply on Wednesday following fairly bearish US oil inventory data and yesterday it fell all the way to USD 86.09/b before a close of USD 87.11/b. Quite close to where Brent traded before the 1 April attack. This morning Brent spiked back up to USD 90.75/b (+4%) on news of Israeli retaliatory attack on Iran. Since then it has quickly fallen back to USD 88.2/b, up only 1.3% vs. ydy close.

The fear is that we are on an escalating tit-for-tat retaliatory path. Following explosions in Iran this morning the immediate fear was that we now are on a tit-for-tat escalating retaliatory path which in the could end up in an uncontrollable war where the US unwillingly is pulled into an armed conflict with Iran. Iran has however largely diffused this fear as it has played down the whole thing thus signalling that the risk for yet another leg higher in retaliatory strikes from Iran towards Israel appears low.
The hope is that the retaliatory strikes will be fading in magnitude and then fizzle out. What we can hope for is that the current tit-for-tat retaliatory strikes are fading in magnitude rather than rising in magnitude. Yes, Iran may retaliate to what Israel did this morning, but the hope if it does is that it is of fading magnitude rather than escalating magnitude.
Israel is playing with ”US house money”. What is very clear is that neither the US nor Iran want to end up in an armed conflict with each other. The US concern is that it involuntary is dragged backwards into such a conflict if Israel cannot control itself. As one US official put it: ”Israel is playing with (US) house money”. One can only imagine how US diplomatic phone lines currently are running red-hot with frenetic diplomatic efforts to try to defuse the situation.
It will likely go well as neither the US nor Iran wants to end up in a military conflict with each other. The underlying position is that both the US and Iran seems to detest the though of getting involved in a direct military conflict with each other and that the US is doing its utmost to hold back Israel. This is probably going a long way to convince the market that this situation is not going to fully blow up.
The oil market is nonetheless concerned as there is too much oil supply at stake. The oil market is however still naturally concerned and uncomfortable about the whole situation as there is so much oil supply at stake if the situation actually did blow up. Reports of traders buying far out of the money call options is a witness of that.
Analys
Fundamentals trump geopolitical tensions

Throughout this week, the Brent Crude price has experienced a decline of USD 3 per barrel, despite ongoing turmoil in the Middle East. Price fluctuations have ranged from highs of USD 91 per barrel at the beginning of the week to lows of USD 87 per barrel as of yesterday evening.

Following the release of yesterday’s US inventory report, Brent Crude once again demonstrated resilience against broader macroeconomic concerns, instead focusing on underlying market fundamentals.
Nevertheless, the recent drop in prices may come as somewhat surprising given the array of conflicting signals observed. Despite an increase in US inventories—a typically bearish indicator—we’ve also witnessed escalating tensions in the Middle East, coupled with the reinstatement of US sanctions on Venezuela. Furthermore, there are indications of impending sanctions on Iran in response to the recent attack on Israel.
Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen has indicated that new sanctions targeting Iran, particularly aimed at restricting its oil exports, could be announced as early as this week. As previously highlighted, we maintain the view that Iran’s oil exports remain vulnerable even without further escalation of the conflict. It appears that Israel is exerting pressure on its ally, the US, to impose stricter sanctions on Iran, an action that is unfolding before our eyes.
Iran’s current oil production stands at close to 3.2 million barrels per day. Considering additional condensate production of about 0.8 million barrels per day and subtracting domestic demand of roughly 1.8 million barrels per day, the net export of Iranian crude and condensate is approximately 2.2 million barrels per day.
However, the uncertainty surrounding the enforcement of such sanctions casts doubt on the likelihood of a complete ending of Iranian exports. Approximately 80% of Iran’s exports are directed to independent refineries in China, suggesting that US sanctions may have limited efficacy unless China complies. The prospect of China resisting US pressure on its oil imports from Iran poses a significant challenge to US sanctions enforcement efforts.
Furthermore, any shortfall resulting from sanctions could potentially be offset by other OPEC nations with spare capacity. Saudi Arabia and the UAE, for instance, can collectively produce an additional almost 3 million barrels of oil per day, although this remains a contingency measure.
In addition to developments related to Iran, the Biden administration has re-imposed restrictions on Venezuelan oil, marking the end of a six-month reprieve. This move is expected to impact flows from the South American nation.
Meanwhile, US crude inventories (excluding SPR holdings) surged by 2.7 million barrels last week (page 11 attached), reaching their highest level since June of last year. This increase coincided with a decline in measures of fuel demand (page 14 attached), underscoring a slightly weaker US market.
In summary, while geopolitical tensions persist and new rounds of sanctions are imposed, our market outlook remains intact. We maintain our forecast of an average Brent Crude price of USD 85 per barrel for the year 2024. In the short term, however, prices are expected to hover around the USD 90 per barrel mark as they navigate through geopolitical uncertainties and fundamental factors.
Analys
Brace for Covert Conflict

In the past two trading days, Brent Crude prices have fluctuated between highs of USD 92.2 per barrel and lows of USD 88.7 per barrel. Despite escalation tensions in the Middle East, oil prices have remained relatively stable over the past 24 hours. The recent barrage of rockets and drones in the region hasn’t significantly affected market sentiment regarding potential disruptions to oil supply. The key concern now is how Israel will respond: will it choose a strong retaliation to assert deterrence, risking wider regional instability, or will it revert to targeted strikes on Iran’s proxies in Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, and Iraq? While it’s too early to predict, one thing is clear: brace for increased volatility, uncertainty, and speculation.

Amidst these developments, the market continues to focus on current fundamentals rather than unfolding geopolitical risks. Despite Iran’s recent attack on Israel, oil prices have slid, reflecting a sideways or slightly bearish sentiment. This morning, oil prices stand at USD 90 per barrel, down 2.5% from Friday’s highs.
The attack
Iran’s launch of over 300 rockets and drones toward Israel marks the first direct assault from Iranian territory since 1991. However, the attack, announced well in advance, resulted in minimal damage as Israeli and allied forces intercepted nearly all projectiles. Hence, the damage inflicted was limited. The incident has prompted US President Joe Biden to urge Israel to exercise restraint, as part of broader efforts to de-escalate tensions in the Middle East.
Israel’s response remains uncertain as its war cabinet deliberates on potential courses of action. While the necessity of a response is acknowledged, the timing and magnitude remain undecided.
The attack was allegedly in retaliation for an Israeli airstrike on Iran’s consulate in Damascus, resulting in significant casualties, including a senior leader in the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’ elite Quds Force. It’s notable that this marks the first direct targeting of Israel from Iranian territory, setting the stage for heightened tensions between the two nations.
Despite the scale of the attack, the vast majority of Iranian projectiles were intercepted before reaching Israeli territory. However, a small number did land, causing minor damage to a military base in the southern region.
President Biden swiftly condemned Iran’s actions and pledged to coordinate a diplomatic response with leaders from the G7 nations. The US military’s rapid repositioning of assets in the region underscores the seriousness of the situation.
Iran’s willingness to escalate tensions further depends on Israel’s response, as indicated by General Mohammad Bagheri, chief of staff of the Iranian armed forces. Meanwhile, speculation about a retaliatory attack from Israel persists.
Looking ahead, key questions remain unanswered. Will Iran launch additional attacks? How will Israel respond, and what implications will it have for the region? Moreover, how will Iran’s allies react to the escalating tensions?
Given the potential for a full-scale war between Iran and Israel, concerns about its impact on global energy markets are growing. Both the United States and China have strong incentives to reduce tensions in the region, given the destabilizing effects of a regional conflict.
Our view in conclusion
The recent escalation between Iran and Israel underscores the delicate balance of power in the volatile Middle East. With tensions reaching unprecedented levels and the specter of further escalation looming, the potential for a full-blown conflict cannot be understated. The ramifications of such a scenario would be far-reaching and could have significant implications for regional stability and global security.
Turning to the oil market, there has been much speculation about the possibility of a full-scale blockade of the Strait of Hormuz in the event of further escalation. However, at present, such a scenario remains highly speculative. Nonetheless, it is crucial to note that Iran’s oil production and exports remain at risk even without further escalation. Currently producing close to 3.2 million barrels per day, Iran has significantly increased its production from mid-2020 levels of 1.9 million barrels per day.
In response to the recent attack, Israel may exert pressure on its ally, the US, to impose stricter sanctions on Iran. The enforcement of such sanctions, particularly on Iranian oil exports, could result in a loss of anywhere between 0.5 million to 1 million barrels per day of oil supply. This would likely keep the oil market in deficit for the remainder of the year, contradicting the Biden administration’s wish to maintain oil and gasoline prices at sustainable levels ahead of the election. While other OPEC nations have spare capacity, utilizing it would tighten the global oil market even further. Saudi Arabia and the UAE, for example, could collectively produce an additional almost 3 million barrels of oil per day if necessary.
Furthermore, both Iran and the US have expressed a desire to prevent further escalation. However, much depends on Israel’s response to the recent barrage of rockets. While Israel has historically refrained from responding violently to attacks (1991), the situation remains fluid. If Israel chooses not to respond forcefully, the US may be compelled to promise stronger enforcement of sanctions on Iranian oil exports. Consequently, Iranian oil exports are at risk, regardless of whether a wider confrontation ensues in the Middle East.
Analyzing the potential impact, approximately 2.2 million barrels per day of net Iranian crude and condensate exports could be at risk, factoring in Iranian domestic demand and condensate production. The effectiveness of US sanctions enforcement, however, remains uncertain, especially considering China’s stance on Iranian oil imports.
Despite these uncertainties, the market outlook remains cautiously optimistic for now, with Brent Crude expected to hover around the USD 90 per barrel mark in the near term. Navigating through geopolitical tensions and fundamental factors, the oil market continues to adapt to evolving conflicts in the Middle East and beyond.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGuldpriset når nytt all time high och bryter igenom 2300 USD
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanLundin Mining får köprekommendation av BMO
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanVertikal prisuppgång på kakao – priset toppar nu 9000 USD
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanCentralbanker fortsatte att köpa guld under februari
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanKaffepriserna stiger på lågt utbud och stark efterfrågan
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanHur mår den svenska skogsbraschen? Två favoritaktier
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanBoliden på 20 minuter
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanKakaomarknaden är extrem för tillfället