Analys
The thematic case for nickel


Nickel has exciting long-term prospects as its use in electric vehicle batteries is expected to drive its demand growth in the future. This structural trend has however not immunised it against the recent headwinds facing industrial metals. Industrial metals are cyclical commodities and their performance is fuelled by global economic growth. The sector has therefore been under pressure from trade wars and, more recently, coronavirus. In this blog, we want to shift the focus back to nickel’s strategic case. We remain cognizant that the current storm is not over yet but expect a smoother sail once the existing headwinds subside.
Analysing nickel’s recent history
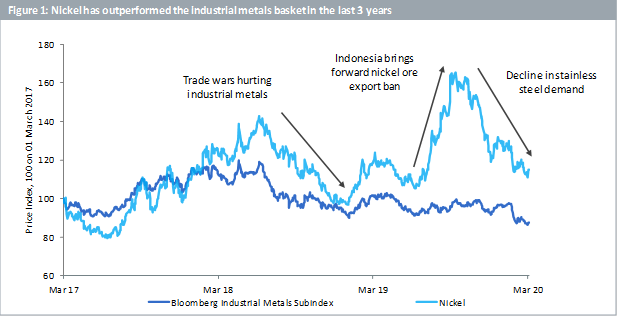
Nickel has strongly outperformed the industrial metals basket (composed of copper, zinc, aluminium and nickel) in the last 3 years (Figure 1). The sector has faced challenges since the advent of trade wars in 2018 both directly due to tariffs and indirectly via a resulting slowdown in global economic activity. Nickel too has had its share of price volatility during this time. The metal rallied sharply in July 2019 on the expectation that Indonesia, which produces a quarter of global nickel supply, will bring forward its nickel ore export ban by 2 years to January 2020. Indonesia announced this decision soon thereafter. Concerns of supply shortages drove the price in a market which was already in a deficit[1]. Nickel’s fortunes reversed in the last quarter of 2019 as stainless-steel demand, which currently accounts for nearly two-thirds of the metal’s use, dwindled. The dynamics of the nickel market are however changing which is why we have an optimistic view of the future.
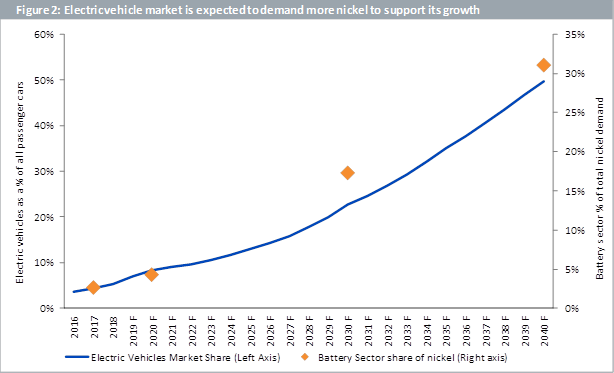
Battery solutions to take a larger share of nickel
According to metal experts Wood Makenzie, battery solutions are expected to account for more than 30% of the total demand for nickel by 2040, up from around 4% today (Figure 2). This is because electric vehicles are forecasted to be around 50% of all passenger car sales by 2040, up from around 8% today. Batteries need to become more efficient to enable this growth and nickel is expected to play a pivotal role. According to the Nickel Institute, nickel containing Lithium-ion batteries are powering the electric vehicle revolution as nickel in batteries helps deliver higher energy density and greater storage capacity at a lower cost. This will allow electric cars to have both a longer range, i.e. the ability to drive longer distances without requiring a recharge, and lower cost promoting wider adoption.
Now, the impact on price from demand growth can, in theory, be offset by an equal increase in supply. We, however, believe that supply growth will be much slower as, according to Wood Mackenzie, the average time for a new nickel mining project to start producing the metal is around 9 years. Miners will seek higher prices to be incentivised to undertake such projects.
It is uncertain how quickly the current headwinds facing industrial metals will dissipate. Having said that, the market dynamics of nickel are changing and the long-term outlook appears promising for the metal supported by a thematic shift towards electric vehicles which is being powered by nickel containing batteries. With the nickel market already in a supply deficit, we expect growing demand to support its price in the long-term.
Mobeen Tahir, Associate Director, Research, WisdomTree
[1] According to the International Nickel Study Group, nickel’s supply deficit was 6.2% in 2018, 3.2% in 2019 and forecasted to be 1.8% in 2020 relative to its demand based on data available as of 31 October 2019.
DISCLAIMER
This material is prepared by WisdomTree and its affiliates and is not intended to be relied upon as a forecast, research or investment advice, and is not a recommendation, offer or solicitation to buy or sell any securities or to adopt any investment strategy. The opinions expressed are as of the date of production and may change as subsequent conditions vary. The information and opinions contained in this material are derived from proprietary and non-proprietary sources. As such, no warranty of accuracy or reliability is given and no responsibility arising in any other way for errors and omissions (including responsibility to any person by reason of negligence) is accepted by WisdomTree, nor any affiliate, nor any of their officers, employees or agents. Reliance upon information in this material is at the sole discretion of the reader. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
Analys
OPEC+ will likely unwind 500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d in one go could be in the cards

Down to mid-60ies as Iraq lifts production while Saudi may be tired of voluntary cut frugality. The Brent December contract dropped 1.6% yesterday to USD 66.03/b. This morning it is down another 0.3% to USD 65.8/b. The drop in the price came on the back of the combined news that Iraq has resumed 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan with exports through Turkey while OPEC+ delegates send signals that the group will unwind the remaining 1.65 mb/d (less the 137 kb/d in October) of voluntary cuts at a pace of 500 kb/d per month pace.

Signals of accelerated unwind and Iraqi increase may be connected. Russia, Kazakhstan and Iraq were main offenders versus the voluntary quotas they had agreed to follow. Russia had a production ’debt’ (cumulative overproduction versus quota) of close to 90 mb in March this year while Kazakhstan had a ’debt’ of about 60 mb and the same for Iraq. This apparently made Saudi Arabia angry this spring. Why should Saudi Arabia hold back if the other voluntary cutters were just freeriding? Thus the sudden rapid unwinding of voluntary cuts. That is at least one angle of explanations for the accelerated unwinding.
If the offenders with production debts then refrained from lifting production as the voluntary cuts were rapidly unwinded, then they could ’pay back’ their ’debts’ as they would under-produce versus the new and steadily higher quotas.
Forget about Kazakhstan. Its production was just too far above the quotas with no hope that the country would hold back production due to cross-ownership of oil assets by international oil companies. But Russia and Iraq should be able to do it.
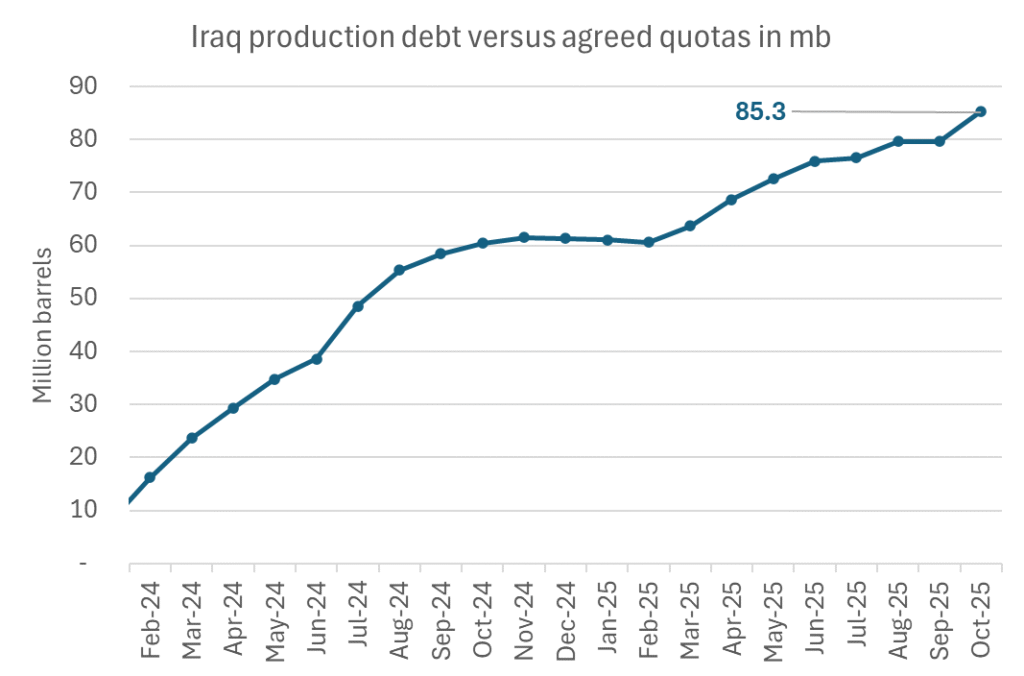
Iraqi cumulative overproduction versus quotas could reach 85-90 mb in October. Iraq has however steadily continued to overproduce by 3-5 mb per month. In July its new and gradually higher quota came close to equal with a cumulative overproduction of only 0.6 mb that month. In August again however its production had an overshoot of 100 kb/d or 3.1 mb for the month. Its cumulative production debt had then risen to close to 80 mb. We don’t know for September yet. But looking at October we now know that its production will likely average close to 4.5 mb/d due to the revival of 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan. Its quota however will only be 4.24 mb/d. Its overproduction in October will thus likely be around 250 kb/d above its quota with its production debt rising another 7-8 mb to a total of close to 90 mb.
Again, why should Saudi Arabia be frugal while Iraq is freeriding. Better to get rid of the voluntary quotas as quickly as possible and then start all over with clean sheets.
Unwinding the remaining 1.513 mb/d in one go in October? If OPEC+ unwinds the remaining 1.513 mb/d of voluntary cuts in one big go in October, then Iraq’s quota will be around 4.4 mb/d for October versus its likely production of close to 4.5 mb/d for the coming month..
OPEC+ should thus unwind the remaining 1.513 mb/d (1.65 – 0.137 mb/d) in one go for October in order for the quota of Iraq to be able to keep track with Iraq’s actual production increase.
October 5 will show how it plays out. But a quota unwind of at least 500 kb/d for Oct seems likely. An overall increase of at least 500 kb/d in the voluntary quota for October looks likely. But it could be the whole 1.513 mb/d in one go. If the increase in the quota is ’only’ 500 kb/d then Iraqi cumulative production will still rise by 5.7 mb to a total of 85 mb in October.
Iraqi production debt versus quotas will likely rise by 5.7 mb in October if OPEC+ only lifts the overall quota by 500 kb/d in October. Here assuming historical production debt did not rise in September. That Iraq lifts its production by 190 kb/d in October to 4.47 mb/d (August level + 190 kb/d) and that OPEC+ unwinds 500 kb/d of the remining quotas in October when they decide on this on 5 October.
Analys
Modest draws, flat demand, and diesel back in focus

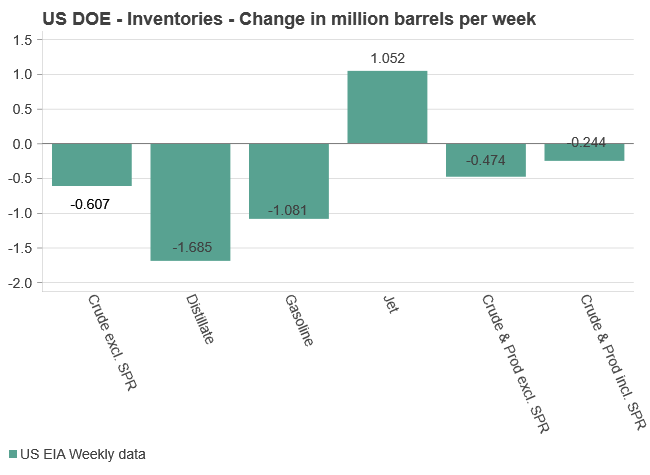
U.S. commercial crude inventories posted a marginal draw last week, falling by 0.6 million barrels to 414.8 million barrels. Inventories remain 4% below the five-year seasonal average, but the draw is far smaller than last week’s massive 9.3-million-barrel decline. Higher crude imports (+803,000 bl d WoW) and steady refinery runs (93% utilization) helped keep the crude balance relatively neutral.

Yet another drawdown indicates commercial crude inventories continue to trend below the 2015–2022 seasonal norm (~440 million barrels), though at 414.8 million barrels, levels are now almost exactly in line with both the 2023 and 2024 trajectory, suggesting stable YoY conditions (see page 3 attached).
Gasoline inventories dropped by 1.1 million barrels and are now 2% below the five-year average. The decline was broad-based, with both finished gasoline and blending components falling, indicating lower output and resilient end-user demand as we enter the shoulder season post-summer (see page 6 attached).
On the diesel side, distillate inventories declined by 1.7 million barrels, snapping a two-week streak of strong builds. At 125 million barrels, diesel inventories are once again 8% below the five-year average and trending near the low end of the historical range.
In total, commercial petroleum inventories (excl. SPR) slipped by 0.5 million barrels on the week to ish 1,281.5 million barrels. While essentially flat, this ends a two-week streak of meaningful builds, reflecting a return to a slightly tighter situation.
On the demand side, the DOE’s ‘products supplied’ metric (see page 6 attached), a proxy for implied consumption, softened slightly. Total demand for crude oil over the past four weeks averaged 20.5 million barrels per day, up just 0.9% YoY.
Summing up: This week’s report shows a re-tightening in diesel supply and modest draws across the board, while demand growth is beginning to flatten. Inventories remain structurally low, but the tone is less bullish than in recent weeks.
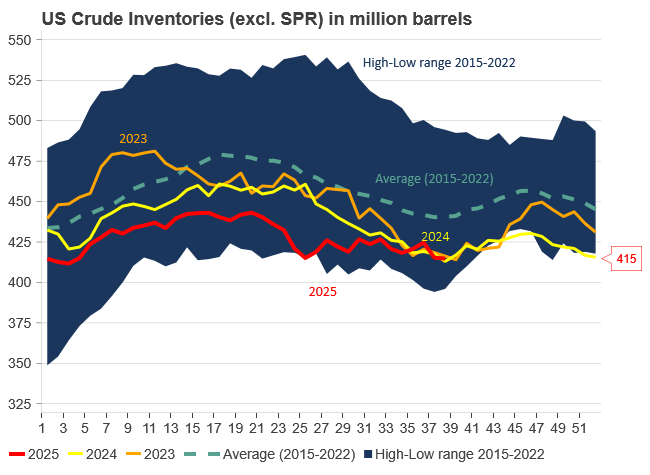
Analys
Are Ukraine’s attacks on Russian energy infrastructure working?

Brent crude rose 1.6% yesterday. After trading in a range of USD 66.1 – 68.09/b it settled at USD 67.63/b. A level which we are well accustomed to see Brent crude flipping around since late August. This morning it is trading 0.5% higher at USD 68/b. The market was expecting an increase of 230 kb/d in Iraqi crude exports from Kurdistan through Turkey to the Cheyhan port but that has so far failed to materialize. This probably helped to drive Brent crude higher yesterday. Indications last evening that US crude oil inventories likely fell 3.8 mb last week (indicative numbers by API) probably also added some strength to Brent crude late in the session. The market continues to await the much heralded global surplus materializing as rising crude and product inventories in OECD countries in general and the US specifically.

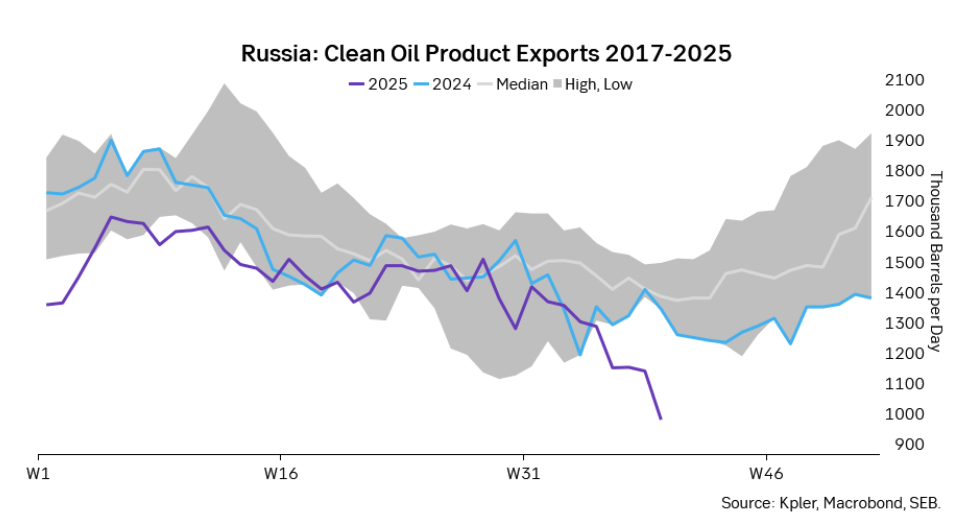
The oil market is starting to focus increasingly on the successful Ukrainian attacks on Russian oil infrastructure. Especially the attacks on Russian refineries. Refineries are highly complex and much harder to repair than simple crude oil facilities like export pipelines, ports and hubs. It can take months and months to repair complex refineries. It is thus mainly Russian oil products which will be hurt by this. First oil product exports will go down, thereafter Russia will have to ration oil product consumption domestically. Russian crude exports may not be hurt as much. Its crude exports could actually go up as its capacity to process crude goes down. SEB’s Emerging Market strategist Erik Meyersson wrote about the Ukrainian campaign this morning: ”Are Ukraine’s attacks on Russian energy infrastructure working?”. Phillips P O’Brian published an interesting not on this as well yesterday: ”An Update On The Ukrainian Campaign Against Russian Refineries”. It is a pay-for article, but it is well worth reading. Amongst other things it highlights the strategic focus of Ukraine towards Russia’s energy infrastructure. A Ukrainian on the matter also put out a visual representation of the attacks on twitter. We have not verified the data representation. It needs to be interpreted with caution in terms of magnitude of impact and current outage.
Complex Russian oil refineries are sitting ducks in the new, modern long-range drone war. Ukraine is building a range of new weapons as well according to O’Brian. The problem with attacks on Russian refineries is thus on the rise. This will likely be an escalating problem for Russia. And oil products around the world may rise versus the crude oil price while the crude oil price itself may not rise all that much due to this.
Russian clean oil product exports as presented by SEB’s Erik Meyersson in his note this morning.
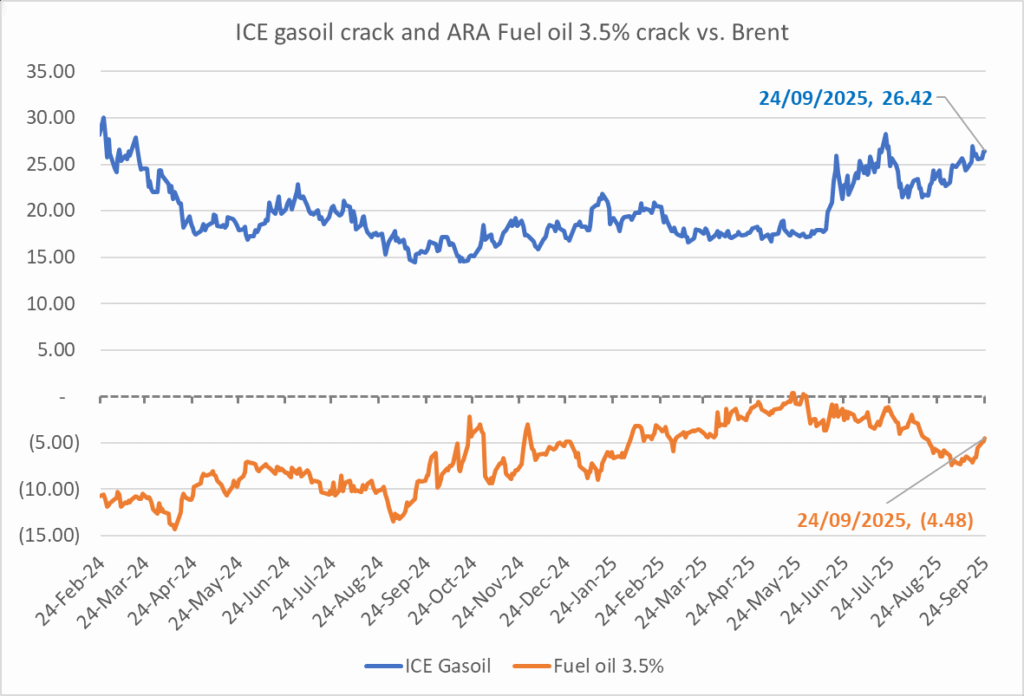
The ICE Gasoil crack and the 3.5% fuel oil crack has been strengthening. The 3.5% crack should have weakened along with rising exports of sour crude from OPEC+, but it hasn’t. Rather it has moved higher instead. The higher cracks could in part be due to the Ukrainian attacks on Russian oil refineries.
Ukrainian inhabitants graphical representation of Ukrainian attacks on Russian oil refineries on Twitter. Highlighting date of attacks, size of refineries and distance from Ukraine. We have not verified the detailed information. And you cannot derive the amount of outage as a consequence of this.

-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanEurobattery Minerals satsar på kritiska metaller för Europas självförsörjning
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals i en guldtrend
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuldpriset kan närma sig 5000 USD om centralbankens oberoende skadas
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanOPEC signalerar att de inte bryr sig om oljepriset faller kommande månader
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanVolatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk
-
 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanAktier i guldbolag laggar priset på guld
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanKinas elproduktion slog nytt rekord i augusti, vilket även kolkraft gjorde
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanTyskland har så höga elpriser att företag inte har råd att använda elektricitet
















