Analys
LME Week 2013 på en sida

![]() LME-veckan är dagarna då industrin för basmetaller samlas i London och försöker bilda sig en uppfattning om var priserna på metallerna ska ta vägen. Hemma efter årets LME-vecka sammanfattar vi diskussioner, teman och frågor.
LME-veckan är dagarna då industrin för basmetaller samlas i London och försöker bilda sig en uppfattning om var priserna på metallerna ska ta vägen. Hemma efter årets LME-vecka sammanfattar vi diskussioner, teman och frågor.
Lagerköer
För tredje året i rad, och med eskalerande intensitet diskuterades problemet med köer för att få ut metall ur LME:s lagerhus. LME:s karismatiske ledare Charles Li adresserade problemet med eftertryck (precis som förra året) men mellan orden ekade det tomt. Intet nytt under solen alltså när det gäller LME:s förmåga att få bukt med problemet att få ut metall ur lagerhusen. Situationen förklarar mycket av de höga premier på fysisk metall som vi sett under 2013. Zink och aluminium handlas omkring sina 10 års medelvärde men premien för fysisk metall ligger omkring 50-100 % över 10 års-snittet.
CFTC
”Commitment of Traders Report” har varit hett i försnacket inför veckan. Rapporteringen för råvaror handlade i USA ger en föredömlig översikt hur investerare är positionerade i respektive råvara. Trycket ökar på LME att avlägga motsvaran de data för de LME-handlade metallerna och Charles Li sade sig välkomna initiativet. LME har nog mycket att vinna på ökad transparens. LME säger att handelsvolymerna är 7 % högre hittills i år men de flesta metallhandlare vi talar med vittnar om lägre handlade volymer. En märklig diskrepans.
Överskott puttar ner koppar från tronen
LME index handlas 8 procent lägre under årets konferens än under 2012 års dito. Koppar har gått från att under 2012 vara den starkaste metallen till att hittills i år falla med 12 %. Starkare utsikter för ökad produktion är huvudskälet. Bland de metaller som fallit mest av samma skäl hittar vi nickel som tappat 19 % i år. Tenn är den enda basmetall som stigit hittills i år. Handlarna återspeglar också marknaden; bly och tenn var de metaller som flest trodde skulle stiga kommande 12 månader. En plats som koppar haft under de senaste åren. Favoritmetall att vara kort var återigen aluminium. Överskottet på metallmarknaden verkar vara det som plågar flest av deltagarna, främst på stål där antalet handelstvister (AD/ CVD) ökar kraftigt och utgör ett hot mot den öppna marknaden trots ett globalt kapacitetsutnyttjande om ca 75 %.
Olönsam produktion
Den senaste tiden har tvingat flera producenter att stänga produktion på grund av de låga priserna. Glencore:s nickelgruva Falcondo med kapacitet för 30 kt Nickel per år i Dominikanska rep är ett bra exempel. Alcoa och Rusal har stängt ner viss aluminiumproduktion. Stängningarna har varit inom nickel och aluminium, de två metaller som har högst lager och störst överskott. Ser vi till stål är efterfrågan i EU ned 30 % utan några större stängningar. Ca 5-7 ugnar kan tvingas stänga inom EU vilket blir en het politisk fråga precis som med Ilvas verk i Taranto.
Firm floor & soft ceiling
Supercykeln på råvaror är långt från över, kanske om man ser till cykeln av kraftiga prisrörelser, men fokus förflyttas till alla utmaningar på utbudssidan för att möta efterfrågan på längre sikt. Kraftigt ökade kostnader (vikande halter, geografiska och teknologiska utmaningar, miljöavgifter, brist på kvalificerad arbetskraft etc.) och svårigheter att få finansiering är oroande. Stora nedskrivningar av tillgångsvärden har gjort att investerarkollektivet fokuserar mer på projekt med starka kassaflöden och undviker projekt i riskzoner.
Fjolårets kinafokus fanns kvar men det rådde större tillit till landets framtid efter årets ledarskapsskifte. I likhet med vår egen tro på en starkare kinesisk utveckling de kommande 6 månaderna så får Kinesisk makro representera det mest positiva inslaget från dagarna i London.
Analys
More weakness and lower price levels ahead, but the world won’t drown in oil in 2026

Some rebound but not much. Brent crude rebounded 1.5% yesterday to $65.47/b. This morning it is inching 0.2% up to $65.6/b. The lowest close last week was on Thursday at $64.11/b.

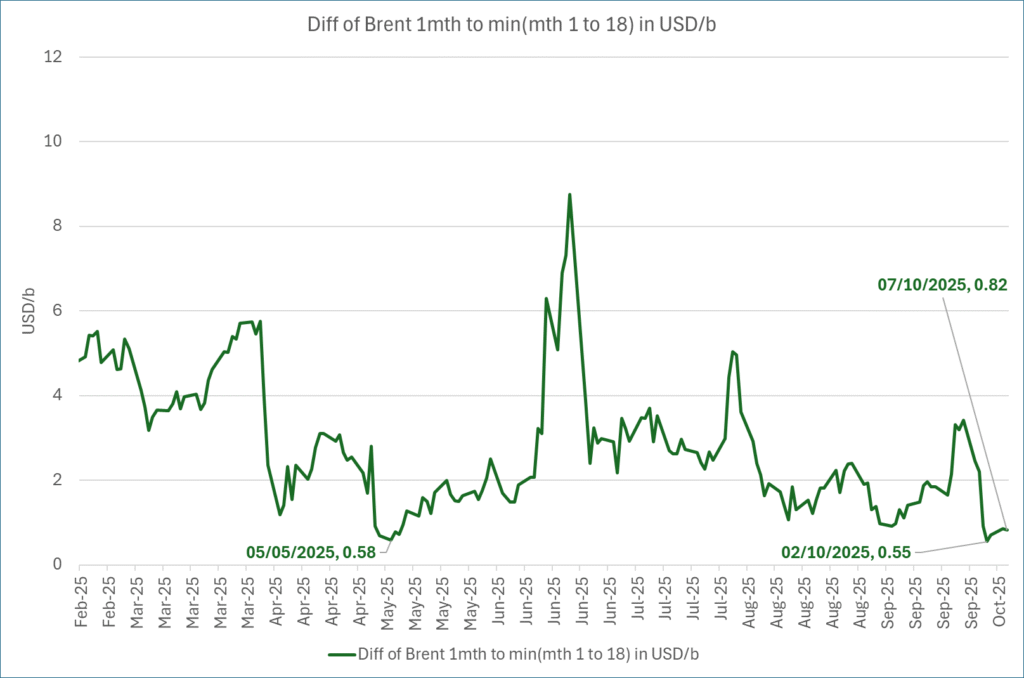
The curve structure is almost as week as it was before the weekend. The rebound we now have gotten post the message from OPEC+ over the weekend is to a large degree a rebound along the curve rather than much strengthening at the front-end of the curve. That part of the curve structure is almost as weak as it was last Thursday.
We are still on a weakening path. The message from OPEC+ over the weekend was we are still on a weakening path with rising supply from the group. It is just not as rapidly weakening as was feared ahead of the weekend when a quota hike of 500 kb/d/mth for November was discussed.
The Brent curve is on its way to full contango with Brent dipping into the $50ies/b. Thus the ongoing weakening we have had in the crude curve since the start of the year, and especially since early June, will continue until the Brent crude oil forward curve is in full contango along with visibly rising US and OECD oil inventories. The front-month Brent contract will then flip down towards the $60/b-line and below into the $50ies/b.
At what point will OPEC+ turn to cuts? The big question then becomes: When will OPEC+ turn around to make some cuts? At what (price) point will they choose to stabilize the market? Because for sure they will. Higher oil inventories, some more shedding of drilling rigs in US shale and Brent into the 50ies somewhere is probably where the group will step in.
There is nothing we have seen from the group so far which indicates that they will close their eyes, let the world drown in oil and the oil price crash to $40/b or below.
The message from OPEC+ is also about balance and stability. The world won’t drown in oil in 2026. The message from the group as far as we manage to interpret it is twofold: 1) Taking back market share which requires a lower price for non-OPEC+ to back off a bit, and 2) Oil market stability and balance. It is not just about 1. Thus fretting about how we are all going to drown in oil in 2026 is totally off the mark by just focusing on point 1.
When to buy cal 2026? Before Christmas when Brent hits $55/b and before OPEC+ holds its last meeting of the year which is likely to be in early December.
Brent crude oil prices have rebounded a bit along the forward curve. Not much strengthening in the structure of the curve. The front-end backwardation is not much stronger today than on its weakest level so far this year which was on Thursday last week.
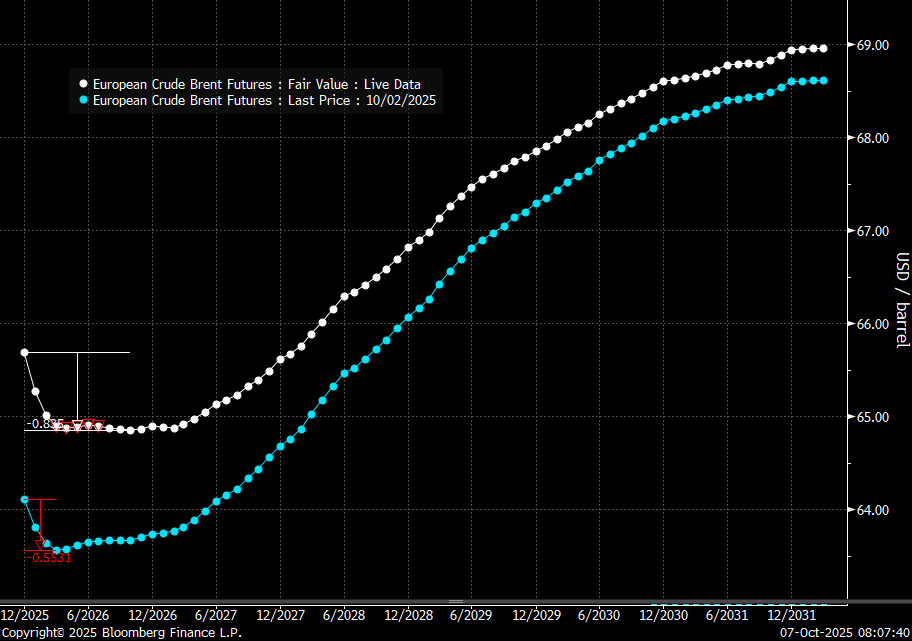
The front-end backwardation fell to its weakest level so far this year on Thursday last week. A slight pickup yesterday and today, but still very close to the weakest year to date. More oil from OPEC+ in the coming months and softer demand and rising inventories. We are heading for yet softer levels.
Analys
A sharp weakening at the core of the oil market: The Dubai curve

Down to the lowest since early May. Brent crude has fallen sharply the latest four days. It closed at USD 64.11/b yesterday which is the lowest since early May. It is staging a 1.3% rebound this morning along with gains in both equities and industrial metals with an added touch of support from a softer USD on top.

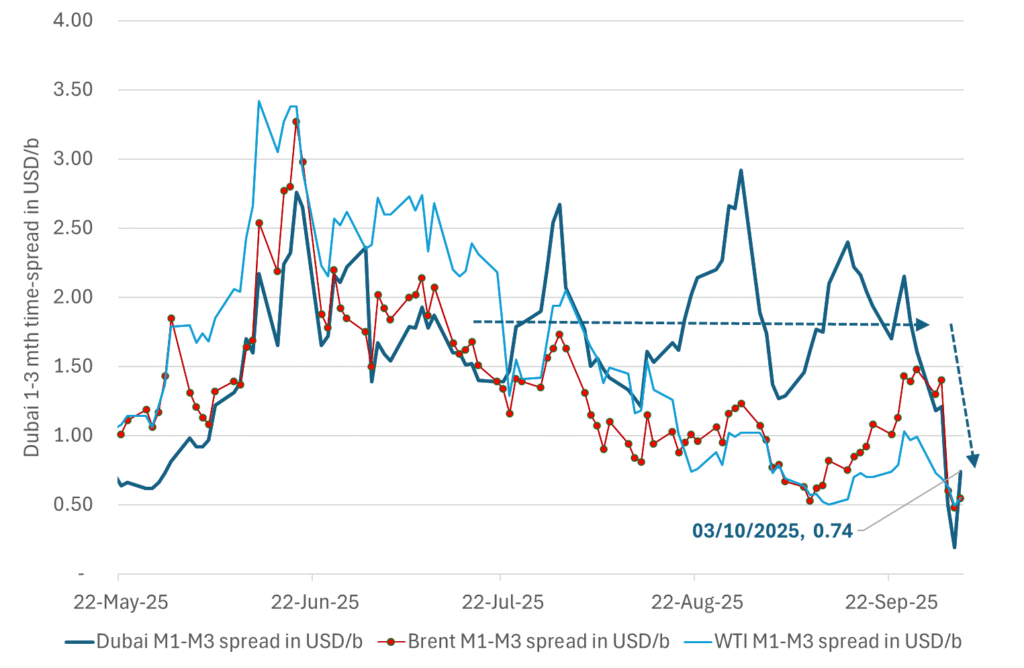
What stands out the most to us this week is the collapse in the Dubai one to three months time-spread.
Dubai is medium sour crude. OPEC+ is in general medium sour crude production. Asian refineries are predominantly designed to process medium sour crude. So Dubai is the real measure of the balance between OPEC+ holding back or not versus Asian oil demand for consumption and stock building.
A sharp weakening of the front-end of the Dubai curve. The front-end of the Dubai crude curve has been holding out very solidly throughout this summer while the front-end of the Brent and WTI curves have been steadily softening. But the strength in the Dubai curve in our view was carrying the crude oil market in general. A source of strength in the crude oil market. The core of the strength.
The now finally sharp decline of the front-end of the Dubai crude curve is thus a strong shift. Weakness in the Dubai crude marker is weakness in the core of the oil market. The core which has helped to hold the oil market elevated.
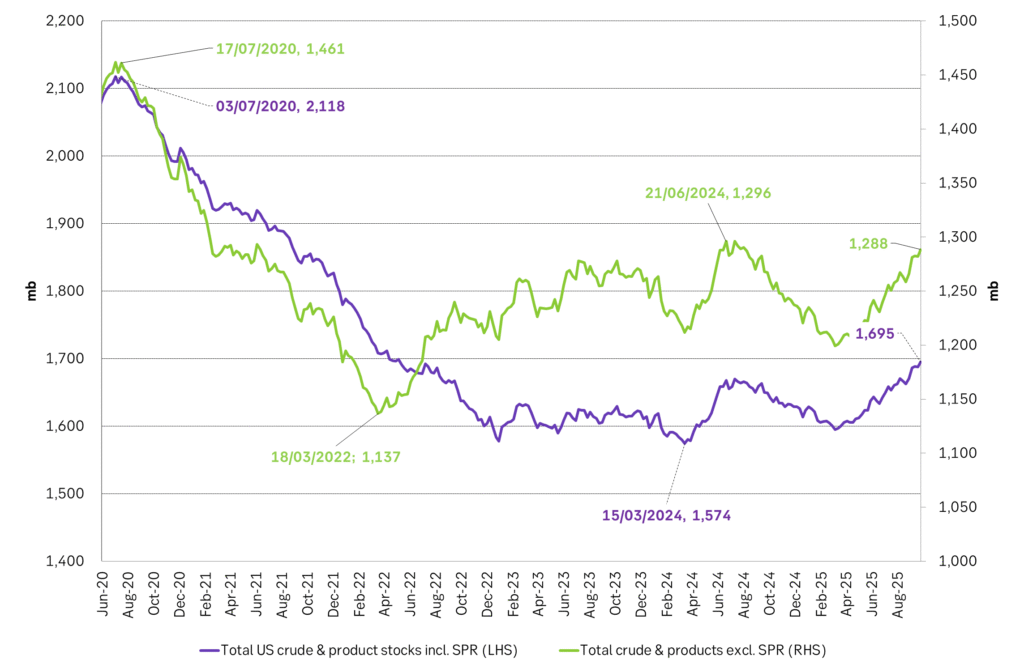
Facts supports the weakening. Add in facts of Iraq lifting production from Kurdistan through Turkey. Saudi Arabia lifting production to 10 mb/d in September (normal production level) and lifting exports as well as domestic demand for oil for power for air con is fading along with summer heat. Add also in counter seasonal rise in US crude and product stocks last week. US oil stocks usually decline by 1.3 mb/week this time of year. Last week they instead rose 6.4 mb/week (+7.2 mb if including SPR). Total US commercial oil stocks are now only 2.1 mb below the 2015-19 seasonal average. US oil stocks normally decline from now to Christmas. If they instead continue to rise, then it will be strongly counter seasonal rise and will create a very strong bearish pressure on oil prices.
Will OPEC+ lift its voluntary quotas by zero, 137 kb/d, 500 kb/d or 1.5 mb/d? On Sunday of course OPEC+ will decide on how much to unwind of the remaining 1.5 mb/d of voluntary quotas for November. Will it be 137 kb/d yet again as for October? Will it be 500 kb/d as was talked about earlier this week? Or will it be a full unwind in one go of 1.5 mb/d? We think most likely now it will be at least 500 kb/d and possibly a full unwind. We discussed this in a not earlier this week: ”500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d”
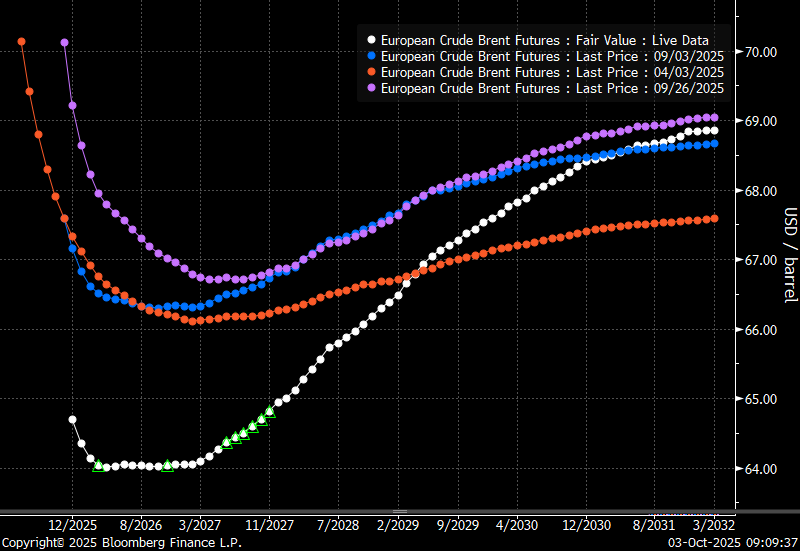
The strength in the front-end of the Dubai curve held out through summer while Brent and WTI curve structures weakened steadily. That core strength helped to keep flat crude oil prices elevated close to the 70-line. Now also the Dubai curve has given in.
Brent crude oil forward curves
Total US commercial stocks now close to normal. Counter seasonal rise last week. Rest of year?
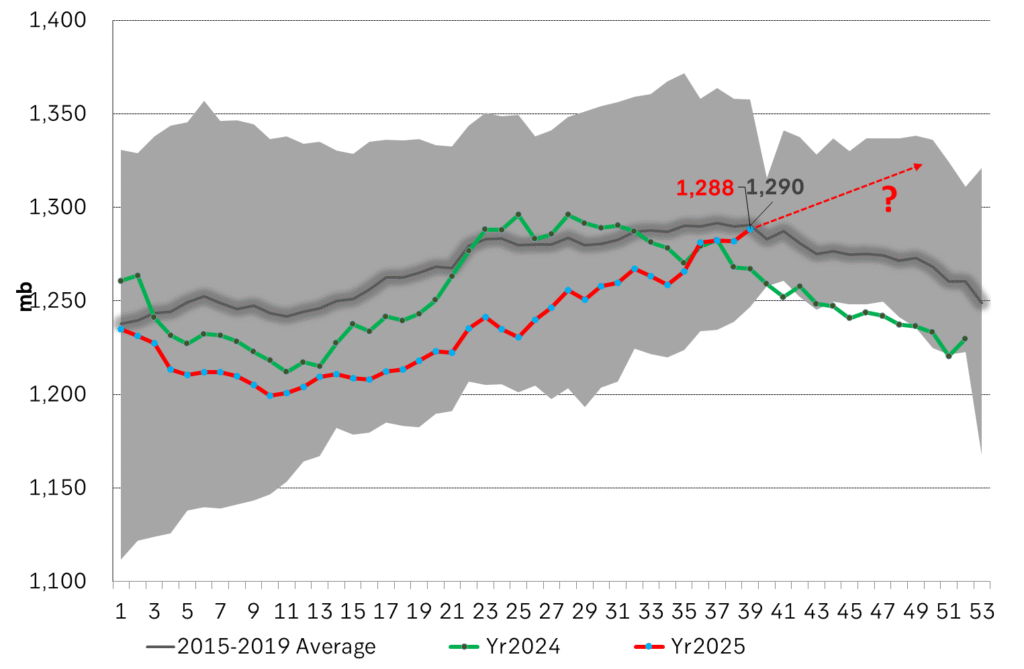
Total US crude and product stocks on a steady trend higher.
Analys
OPEC+ will likely unwind 500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d in one go could be in the cards

Down to mid-60ies as Iraq lifts production while Saudi may be tired of voluntary cut frugality. The Brent December contract dropped 1.6% yesterday to USD 66.03/b. This morning it is down another 0.3% to USD 65.8/b. The drop in the price came on the back of the combined news that Iraq has resumed 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan with exports through Turkey while OPEC+ delegates send signals that the group will unwind the remaining 1.65 mb/d (less the 137 kb/d in October) of voluntary cuts at a pace of 500 kb/d per month pace.

Signals of accelerated unwind and Iraqi increase may be connected. Russia, Kazakhstan and Iraq were main offenders versus the voluntary quotas they had agreed to follow. Russia had a production ’debt’ (cumulative overproduction versus quota) of close to 90 mb in March this year while Kazakhstan had a ’debt’ of about 60 mb and the same for Iraq. This apparently made Saudi Arabia angry this spring. Why should Saudi Arabia hold back if the other voluntary cutters were just freeriding? Thus the sudden rapid unwinding of voluntary cuts. That is at least one angle of explanations for the accelerated unwinding.
If the offenders with production debts then refrained from lifting production as the voluntary cuts were rapidly unwinded, then they could ’pay back’ their ’debts’ as they would under-produce versus the new and steadily higher quotas.
Forget about Kazakhstan. Its production was just too far above the quotas with no hope that the country would hold back production due to cross-ownership of oil assets by international oil companies. But Russia and Iraq should be able to do it.
Iraqi cumulative overproduction versus quotas could reach 85-90 mb in October. Iraq has however steadily continued to overproduce by 3-5 mb per month. In July its new and gradually higher quota came close to equal with a cumulative overproduction of only 0.6 mb that month. In August again however its production had an overshoot of 100 kb/d or 3.1 mb for the month. Its cumulative production debt had then risen to close to 80 mb. We don’t know for September yet. But looking at October we now know that its production will likely average close to 4.5 mb/d due to the revival of 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan. Its quota however will only be 4.24 mb/d. Its overproduction in October will thus likely be around 250 kb/d above its quota with its production debt rising another 7-8 mb to a total of close to 90 mb.
Again, why should Saudi Arabia be frugal while Iraq is freeriding. Better to get rid of the voluntary quotas as quickly as possible and then start all over with clean sheets.
Unwinding the remaining 1.513 mb/d in one go in October? If OPEC+ unwinds the remaining 1.513 mb/d of voluntary cuts in one big go in October, then Iraq’s quota will be around 4.4 mb/d for October versus its likely production of close to 4.5 mb/d for the coming month..
OPEC+ should thus unwind the remaining 1.513 mb/d (1.65 – 0.137 mb/d) in one go for October in order for the quota of Iraq to be able to keep track with Iraq’s actual production increase.
October 5 will show how it plays out. But a quota unwind of at least 500 kb/d for Oct seems likely. An overall increase of at least 500 kb/d in the voluntary quota for October looks likely. But it could be the whole 1.513 mb/d in one go. If the increase in the quota is ’only’ 500 kb/d then Iraqi cumulative production will still rise by 5.7 mb to a total of 85 mb in October.
Iraqi production debt versus quotas will likely rise by 5.7 mb in October if OPEC+ only lifts the overall quota by 500 kb/d in October. Here assuming historical production debt did not rise in September. That Iraq lifts its production by 190 kb/d in October to 4.47 mb/d (August level + 190 kb/d) and that OPEC+ unwinds 500 kb/d of the remining quotas in October when they decide on this on 5 October.
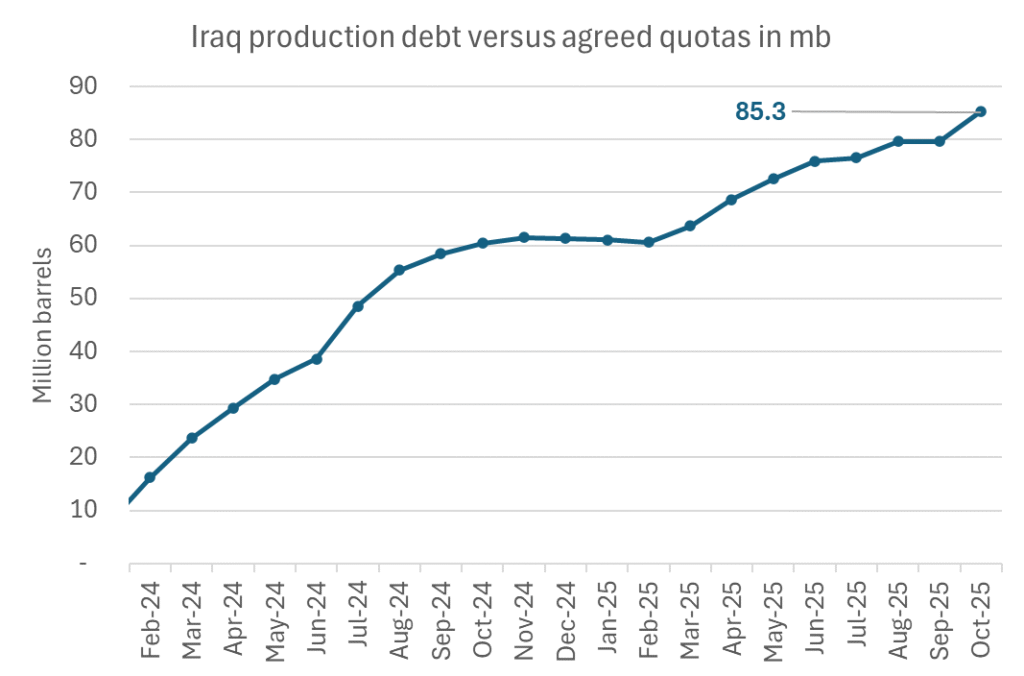
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals i en guldtrend
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanVolatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk
-
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAktier i guldbolag laggar priset på guld
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanKinas elproduktion slog nytt rekord i augusti, vilket även kolkraft gjorde
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanTyskland har så höga elpriser att företag inte har råd att använda elektricitet
-
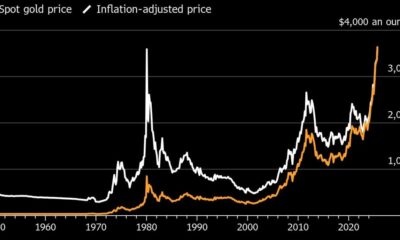
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuld når sin högsta nivå någonsin, nu även justerat för inflation
-
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanDet stigande guldpriset en utmaning för smyckesköpare
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanBrent crude ticks higher on tension, but market structure stays soft









