Analys
Going green? The unexpected investments helping to reduce vehicle emissions


Globally about 15% of the world’s Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions come from the transportation sector. Despite improving fuel efficiency in cars over the past seven decades, the fact that more people in the world use cars means that global emissions from the transport sector continue to rise. However, pollution abatement equipment can help reduce emissions from cars. Autocatalysts are a key technology in this regard.
Platinum and palladium in autocatalysts

An autocatalyst is a device installed in internal combustion engine cars that converts harmful pollutants into safer gases. Platinum group metals (PGM) including platinum, palladium and rhodium are key ingredients in the autocatalysts that generate this chemical conversion. Autocatalysts were first introduced in the mid-1970s and today, are used in almost all internal combustion engine vehicles (including hybrid vehicles). In addition, fuel cell vehicles also use platinum (not palladium or rhodium) as the main catalyst in the reactions to produce electricity and water from hydrogen fuel and water.
How important are autocatalysts for PGM demand?
In 2019, automobiles accounted for 34% of platinum demand and 84% of palladium demand. So, the auto industry is the key driver of demand for both platinum and palladium.
Vehicle sales versus regulation
Tightening emission regulations generally increases the demand for the platinum group metals. Demand for platinum group metals will also vary with the volume of vehicle sales. Historically it has been emission regulation that has had a greater influence on demand. According to World Platinum Investment Council’s calculations, global vehicle sales between 1990 and 2019 rose by 1.6 times whereas the combined demand for platinum, palladium and rhodium in cars rose by 6.2 times. The fact that the rise in automobile platinum group metal demand was more than the increase in car sales indicates that higher loadings have been the chief driver of demand growth. Emission regulations are continuing to tighten globally for both passenger and commercial vehicles.
Gasoline vs. diesel cars
Today, there are higher loadings of palladium in gasoline autocatalysts and higher loadings of platinum in diesel autocatalysts. However, both autocatalysts carry some loadings of each metal. The catalytic efficiency of each metal is influenced by engine temperature, fuel type, all fuel quality and durability of the autocatalyst’s washcoat. Diesel engines operate at lower temperatures than gasoline engines and run with a leaner gas stream containing lots of oxygen. Under these conditions, platinum is a more active catalyst for the conversion of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) to harmless emissions. However, the addition of some palladium to the platinum catalyst can improve its thermal stability. This is an advantage when reducing diesel particulate matter from the exhaust. This process involves trapping the particulate matter in a filter and then raising the temperature of the system to oxidise the matter to CO2. At these higher temperatures, palladium improves the thermal durability of the catalyst, helping it perform optimally for the lifetime of the vehicle.
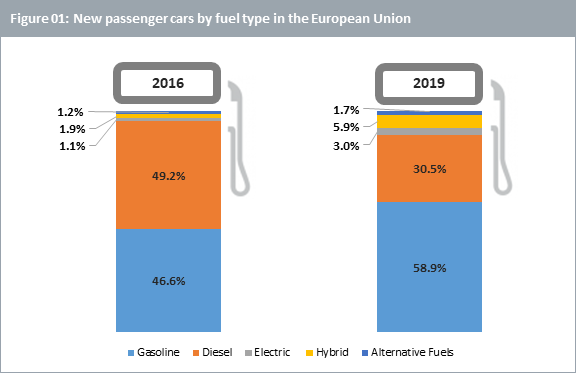
Diesel cars falling out of favour
Europe is the largest diesel passenger car market in the world. In most of the rest of the world, gasoline cars dominate. However, even in Europe, diesel cars have fallen out of favour following ‘Dieselgate’ and tightening particulate emissions standards across Europe, where diesel cars do not perform as well as their gasoline equivalents (see figure 01 below).
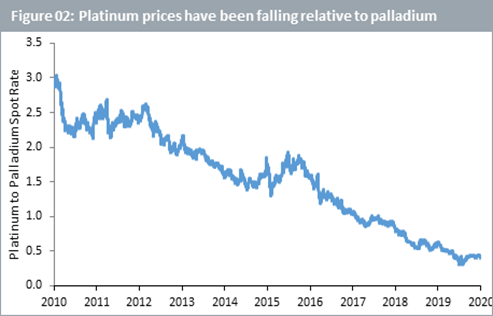
Platinum versus palladium price
In 2010, platinum used to trade close to 3 times the price of palladium. Dieselgate accelerated the trend of rising palladium relative to platinum prices. Today, platinum trades below half the price of palladium. Palladium’s growing demand and tightening supply have been a boon for prices (see figure 02 below).
Economical to substitute?
With such a wide price differential between platinum and palladium, it’s a natural question to ask if platinum can be substituted for palladium? Industry experts including Johnson Matthey, believe there is some limited scope for substitution. Not necessarily in gasoline cars but more in terms of substituting out palladium in diesel cars with higher loadings of platinum. However, auto manufacturers are notoriously secretive about their technologies which makes it difficult to comment on what scale this will occur. In addition, it is rumoured that auto manufacturers are using their scarce engineers to develop electric vehicles and so auto manufacturers are averse to divert them to PGM substitution projects.
Trucking industry
While globally more passenger cars use gasoline than diesel, trucks generally use more diesel. Emission standards for trucks are tightening. Notably in India the government has tightened regulations to broadly match European standards in 20205. China will implement similar standards phased between 2021 and 2023. This is likely to be a strong catalyst for platinum demand.
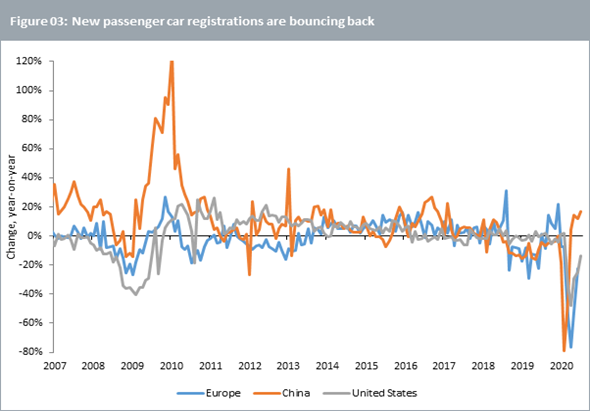
Car sales in COVID-19 era
Passenger car sales had fallen hard during the COVID-19 pandemic, but as lockdown conditions ease, car sales appear to be rebounding strongly in China, Europe, and US (see figure 03 below). China and US are predominantly gasoline markets so the rebound in sales there mainly helps boost palladium prices. The rebound in European car sales should also help platinum prices.
The concentration in supply
Supply in both platinum and palladium is highly concentrated. South Africa accounts for nearly 70% of platinum’s global supply while South Africa and Russia collectively provide around 70% of palladium supply globally. While platinum is expected to be in a slight supply surplus this year, palladium continues to be in an acute supply deficit with demand continuing to grow and supply relatively stable.
Conclusions
Both platinum and palladium are important materials for pollution abatement technology in cars. Platinum, which has been heavily utilised in diesel passenger cars, has fallen out of favour in recent years. However, with tightening regulations for commercial vehicles globally we are likely to see that demand rise. Palladium, which has seen growing demand and is in a supply deficit is likely to see constructive fundamentals for years to come.
Analys
Brent crude ticks higher on tension, but market structure stays soft

Brent crude has climbed roughly USD 1.5-2 per barrel since Friday, yet falling USD 0.3 per barrel this mornig and currently trading near USD 67.25/bbl after yesterday’s climb. While the rally reflects short-term geopolitical tension, price action has been choppy, and crude remains locked in a broader range – caught between supply-side pressure and spot resilience.

Prices have been supported by renewed Ukrainian drone strikes targeting Russian infrastructure. Over the weekend, falling debris triggered a fire at the 20mtpa Kirishi refinery, following last week’s attack on the key Primorsk terminal.
Argus estimates that these attacks have halted ish 300 kbl/d of Russian refining capacity in August and September. While the market impact is limited for now, the action signals Kyiv’s growing willingness to disrupt oil flows – supporting a soft geopolitical floor under prices.
The political environment is shifting: the EU is reportedly considering sanctions on Indian and Chinese firms facilitating Russian crude flows, while the U.S. has so far held back – despite Bessent warning that any action from Washington depends on broader European participation. Senator Graham has also publicly criticized NATO members like Slovakia and Hungary for continuing Russian oil imports.
It’s worth noting that China and India remain the two largest buyers of Russian barrels since the invasion of Ukraine. While New Delhi has been hit with 50% secondary tariffs, Beijing has been spared so far.
Still, the broader supply/demand balance leans bearish. Futures markets reflect this: Brent’s prompt spread (gauge of near-term tightness) has narrowed to the current USD 0.42/bl, down from USD 0.96/bl two months ago, pointing to weakening backwardation.
This aligns with expectations for a record surplus in 2026, largely driven by the faster-than-anticipated return of OPEC+ barrels to market. OPEC+ is gathering in Vienna this week to begin revising member production capacity estimates – setting the stage for new output baselines from 2027. The group aims to agree on how to define “maximum sustainable capacity,” with a proposal expected by year-end.
While the IEA pegs OPEC+ capacity at 47.9 million barrels per day, actual output in August was only 42.4 million barrels per day. Disagreements over data and quota fairness (especially from Iraq and Nigeria) have already delayed this process. Angola even quit the group last year after being assigned a lower target than expected. It also remains unclear whether Russia and Iraq can regain earlier output levels due to infrastructure constraints.
Also, macro remains another key driver this week. A 25bp Fed rate cut is widely expected tomorrow (Wednesday), and commodities in general could benefit a potential cut.
Summing up: Brent crude continues to drift sideways, finding near-term support from geopolitics and refining strength. But with surplus building and market structure softening, the upside may remain capped.
Analys
Volatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk

Brent crude is essentially flat on the week, but after a volatile ride. Prices started Monday near USD 65.5/bl, climbed steadily to a mid-week high of USD 67.8/bl on Wednesday evening, before falling sharply – losing about USD 2/bl during Thursday’s session.

Brent is currently trading around USD 65.8/bl, right back where it began. The volatility reflects the market’s ongoing struggle to balance growing surplus risks against persistent geopolitical uncertainty and resilient refined product margins. Thursday’s slide snapped a three-day rally and came largely in response to a string of bearish signals, most notably from the IEA’s updated short-term outlook.
The IEA now projects record global oversupply in 2026, reinforcing concerns flagged earlier by the U.S. EIA, which already sees inventories building this quarter. The forecast comes just days after OPEC+ confirmed it will continue returning idle barrels to the market in October – albeit at a slower pace of +137,000 bl/d. While modest, the move underscores a steady push to reclaim market share and adds to supply-side pressure into year-end.
Thursday’s price drop also followed geopolitical incidences: Israeli airstrikes reportedly targeted Hamas leadership in Doha, while Russian drones crossed into Polish airspace – events that initially sent crude higher as traders covered short positions.
Yet, sentiment remains broadly cautious. Strong refining margins and low inventories at key pricing hubs like Europe continue to support the downside. Chinese stockpiling of discounted Russian barrels and tightness in refined product markets – especially diesel – are also lending support.
On the demand side, the IEA revised up its 2025 global demand growth forecast by 60,000 bl/d to 740,000 bl/d YoY, while leaving 2026 unchanged at 698,000 bl/d. Interestingly, the agency also signaled that its next long-term report could show global oil demand rising through 2050.
Meanwhile, OPEC offered a contrasting view in its latest Monthly Oil Market Report, maintaining expectations for a supply deficit both this year and next, even as its members raise output. The group kept its demand growth estimates for 2025 and 2026 unchanged at 1.29 million bl/d and 1.38 million bl/d, respectively.
We continue to watch whether the bearish supply outlook will outweigh geopolitical risk, and if Brent can continue to find support above USD 65/bl – a level increasingly seen as a soft floor for OPEC+ policy.
Analys
Waiting for the surplus while we worry about Israel and Qatar

Brent crude makes some gains as Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar rattles markets. Brent crude spiked to a high of USD 67.38/b yesterday as Israel made a strike on Hamas in Qatar. But it wasn’t able to hold on to that level and only closed up 0.6% in the end at USD 66.39/b. This morning it is starting on the up with a gain of 0.9% at USD 67/b. Still rattled by Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar yesterday. Brent is getting some help on the margin this morning with Asian equities higher and copper gaining half a percent. But the dark cloud of surplus ahead is nonetheless hanging over the market with Brent trading two dollar lower than last Tuesday.

Geopolitical risk premiums in oil rarely lasts long unless actual supply disruption kicks in. While Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar is shocking, the geopolitical risk lifting crude oil yesterday and this morning is unlikely to last very long as such geopolitical risk premiums usually do not last long unless real disruption kicks in.
US API data yesterday indicated a US crude and product stock build last week of 3.1 mb. The US API last evening released partial US oil inventory data indicating that US crude stocks rose 1.3 mb and middle distillates rose 1.5 mb while gasoline rose 0.3 mb. In total a bit more than 3 mb increase. US crude and product stocks usually rise around 1 mb per week this time of year. So US commercial crude and product stock rose 2 mb over the past week adjusted for the seasonal norm. Official and complete data are due today at 16:30.
A 2 mb/week seasonally adj. US stock build implies a 1 – 1.4 mb/d global surplus if it is persistent. Assume that if the global oil market is running a surplus then some 20% to 30% of that surplus ends up in US commercial inventories. A 2 mb seasonally adjusted inventory build equals 286 kb/d. Divide by 0.2 to 0.3 and we get an implied global surplus of 950 kb/d to 1430 kb/d. A 2 mb/week seasonally adjusted build in US oil inventories is close to noise unless it is a persistent pattern every week.
US IEA STEO oil report: Robust surplus ahead and Brent averaging USD 51/b in 2026. The US EIA yesterday released its monthly STEO oil report. It projected a large and persistent surplus ahead. It estimates a global surplus of 2.2 m/d from September to December this year. A 2.4 mb/d surplus in Q1-26 and an average surplus for 2026 of 1.6 mb/d resulting in an average Brent crude oil price of USD 51/b next year. And that includes an assumption where OPEC crude oil production only averages 27.8 mb/d in 2026 versus 27.0 mb/d in 2024 and 28.6 mb/d in August.
Brent will feel the bear-pressure once US/OECD stocks starts visible build. In the meanwhile the oil market sits waiting for this projected surplus to materialize in US and OECD inventories. Once they visibly starts to build on a consistent basis, then Brent crude will likely quickly lose altitude. And unless some unforeseen supply disruption kicks in, it is bound to happen.
US IEA STEO September report. In total not much different than it was in January
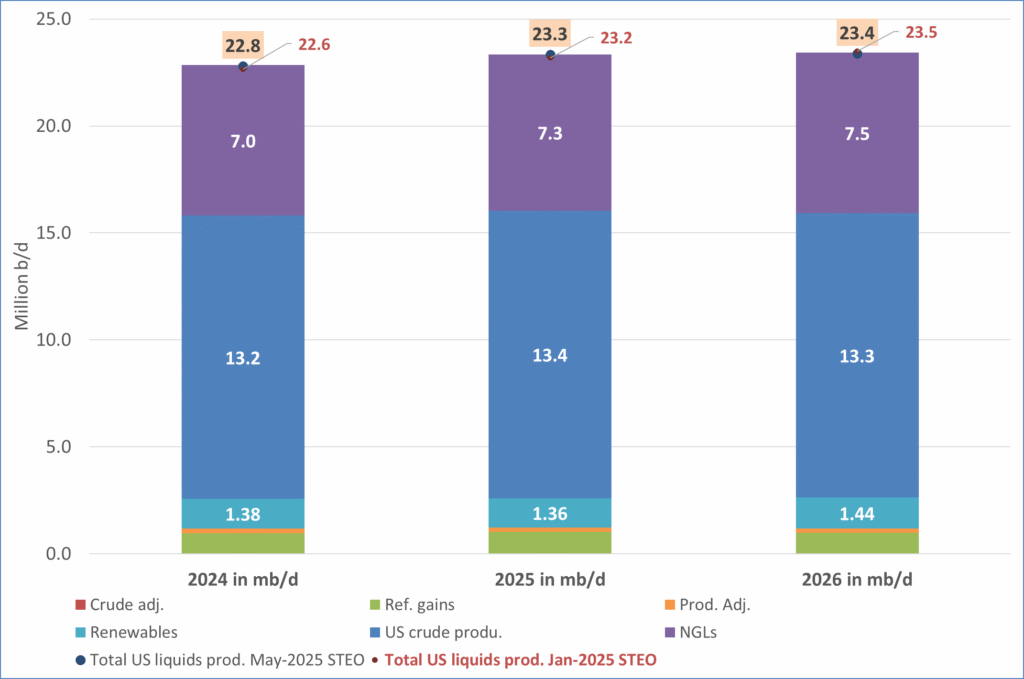
US IEA STEO September report. US crude oil production contracting in 2026, but NGLs still growing. Close to zero net liquids growth in total.
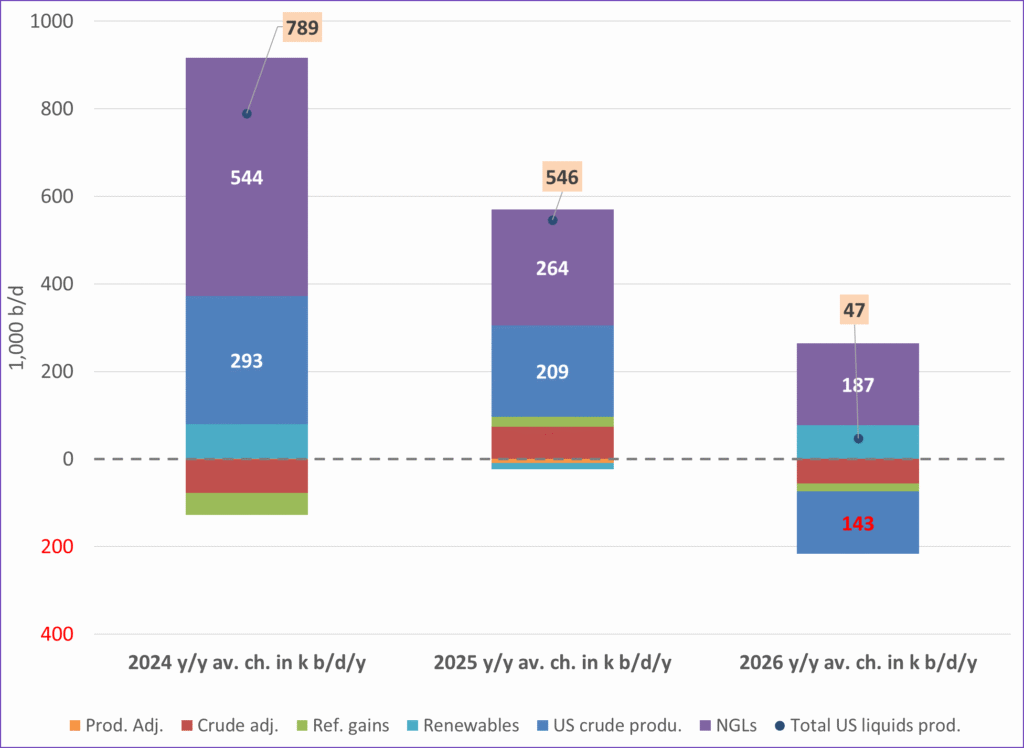
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanEtt samtal om koppar, kaffe och spannmål
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanBrent sideways on sanctions and peace talks
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSommarens torka kan ge högre elpriser i höst
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanBrent edges higher as India–Russia oil trade draws U.S. ire and Powell takes the stage at Jackson Hole
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals är verksamt i guldrikt område i Finland
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanIncreasing risk that OPEC+ will unwind the last 1.65 mb/d of cuts when they meet on 7 September