Analys
Cyklisk rotation driver rekordstora inflöden till olje-ETPer och utflöden från guld

 Råvaror fortsatte att prestera dåligt under Q4 2014 och året som helhet är det sämsta för tillgångsklassen sedan finanskrisen. En perfekt storm av faktorer – starkt utbud inom de flesta råvarusektorerna, oro över efterfrågan från Kina och en starkare amerikansk dollar – ligger bakom de låga råvarupriserna och att det globala förvaltade kapitalet sjönk till 101,5 miljarder dollar i Q4, en minskning med 9,2 miljarder dollar jämfört med Q3. Nettoflödena till råvaru-ETPer var neutrala och minskningen av förvaltat kapital bestod i sin helhet av prisändringar. Investerarna tycks se det nuvarande läget som ett tillfälle att öka sin exponering mot cykliska råvarutillgångar och rotera bort från mer defensiva exponeringar som guld.
Råvaror fortsatte att prestera dåligt under Q4 2014 och året som helhet är det sämsta för tillgångsklassen sedan finanskrisen. En perfekt storm av faktorer – starkt utbud inom de flesta råvarusektorerna, oro över efterfrågan från Kina och en starkare amerikansk dollar – ligger bakom de låga råvarupriserna och att det globala förvaltade kapitalet sjönk till 101,5 miljarder dollar i Q4, en minskning med 9,2 miljarder dollar jämfört med Q3. Nettoflödena till råvaru-ETPer var neutrala och minskningen av förvaltat kapital bestod i sin helhet av prisändringar. Investerarna tycks se det nuvarande läget som ett tillfälle att öka sin exponering mot cykliska råvarutillgångar och rotera bort från mer defensiva exponeringar som guld.
Det rekordstora inflödet till energisektorn vägde i stort sett upp det stora utflödet från guld-ETPer i Q4 2014 och resultatet blev ett nettoutflöde för råvaru-ETPer på måttliga 30 miljoner dollar. Guld-ETPer hade det största kvartalsutflödet på ett år, totalt 3,1 miljarder dollar, och flödena kom framförallt från amerikanska investerare (78 %) som fått ökat förtroende för USAs återhämtning. Amerikanska investerare drev även det starka inflödet till energi-ETPer och stod för 85 % av det totala inflödet på 3,2 miljarder dollar.
”Investerarna återvänder till råvaror, attraherade av priser som ligger på eller under produktionskostnaden. I det korta perspektivet kan företag och gruvor fortsätta producera trots att priserna ligger under produktionskostnaden, men det är inte hållbart i längden. Om vi inte börjar se en prisuppgång snart kommer produktionen förr eller senare sjunka. Minskat utbud kommer resultera i högre råvarupriser under 2015”, säger Peter Lidblom, Nordenchef på ETF Securities.
Den starka amerikanska dollarn har också bidragit till att dämpa råvarupriserna. Dollarns framfart är dock pådriven av en stark amerikansk ekonomisk tillväxt vilket i grunden är positivt för efterfrågan på råvaror. Samtidigt förväntas beslutsfattare i både Kina och Europa fortsätta reagera starkt på den senaste tidens svaga ekonomiska utveckling i de båda regionerna.
Cykliska råvaror förväntas bli de stora vinnarna av den ekonomiska återhämtningen i USA och Kina under 2015. Kina fortsätter stimulera sin ekonomi och planerar fler råvaruintensiva infrastrukturinvesteringar under 2015 vilket kommer ha en positiv inverkan på de råvaror som är beroende av ekonomisk aktivitet. De bästa investeringsmöjligheterna inför 2015 finns inom cykliska tillgångar givet den tilltagande globala återhämtningen. Men det finns risker, inte minst gällande svagare tillväxt och hot om deflation i Euroområdet och Japan, samt den trögare ekonomiska återhämtningen i Storbritannien. Våra främsta tips inför 2015 är råvarusektorer med exponering mot industrin, som till exempel metaller och energi.
Sammanfattning av de främsta trenderna under 2014:
Förvaltat kapital i råvaru-ETPer sjönk med 20,6 miljarder dollar till 101,5 miljarder dollar i slutet av 2014. En stark amerikansk dollar och oro över tillväxten i Kina och Europa pressade ner många råvarupriser under produktionskostnad.
Taktiska investerare har varit aktiva i råvaror under hela 2014 och investerarnas uthållighet reflekterar den strategiska karaktären hos innehavare av råvaru-ETPer.
Nästan 100 % av nedgången i förvaltat kapital för råvaror under 2014 berodde på prisfall. Nettoutflödet uppgick till måttliga 30 miljoner dollar vilket visar att investerarna verkar rotera in i mer cykliska råvaruexponeringar.
Många råvaror handlas nu på eller under produktionskostnaden. Detta lockar ett antal långsiktiga värdeinvesterare till enskilda råvaror och sektorer där prisnedgången varit särskilt aggressiv.
Ädelmetall-ETPer stod för över 70 % av nedgången i förvaltat kapital för råvaror under 2014. Det förvaltade kapitalet i ädelmetall-ETPer uppgick i slutet av året till 79 miljarder dollar, efter en minskning på 14,8 miljarder dollar under 2014. Utflödena från guld kom huvudsakligen från amerikanska investerare, troligen som ett resultat av mindre defensiva portföljpositioneringar.
Palladium var den enda ädelmetallen som gick mot trenden med ökat förvaltat kapital på 0,9 miljarder dollar. Bakom ökningen låg hotet om utbudsstörningar och en positiv efterfråga vilket höll priserna uppe under 2014. Ökningen i förvaltat kapital bestod till hälften av inflöden.
Guld undantaget hade alla ädelmetaller nettoinflöden under året. Platina och palladium gynnades av potentiella utbudsstörningar i Sydafrika och Ryssland och hade de största inflödena på 432 respektive 376 miljoner dollar.
Energi-ETPer hade starka inflöden under 2014, framförallt under de sista tre månaderna då prisfallet för råolja och naturgas upplevdes överdrivet. Råolja hade den största andelen inflöden medan naturgas stod för runt 25 %. De globala inflödena var mestadels drivna av amerikanska investerare som stod för runt 85 %. Hela inflödet till naturgas kom från amerikanska investerare då stora lager och milt väder tvingade ner priserna på den lägsta nivån sedan 2012.
Näst efter energisektorn hade breda råvaruindex-ETPer de största inflödena (1,1 miljarder dollar) under 2014. Detta indikerar att investerarna börjar se råvaror som en tillgångsklass med högt relativt värde när värderingarna på aktie- och räntemarknaderna skjutit i höjden samtidigt som råvarupriserna gått ner.
Investerarna eftersökte större exponering mot korn, vilket delvis kompenserade utflöden från breda jordbruks-ETPer under 2014. Låga priser på majs och vete attraherade långsiktiga investerare som tror att odlingsförhållandena sannolikt inte kommer vara lika goda den här säsongen som förra. Kaffe hade det största utflödet eftersom möjligheten att El-Nino inträffar under 2015 skulle kunna öka utbudet.
Industrimetaller hade blandade flöden och slutade året med ett utflöde på måttliga 2 miljoner dollar. Problem på utbudssidan gjorde att nickel hade inflöden under varje kvartal under 2014, totalt 122 miljoner dollar. Oro över Kinesisk efterfrågan och ökad finansieringsrisk fick investerarna att dra sig ur koppar-ETPer (52 miljoner dollar). Diversifierade industrimetaller och zink-ETPer hade också utflöden.
Analys
Brent crude set to dip its feet into the high $50ies/b this week

Parts of the Brent crude curve dipping into the high $50ies/b. Brent crude fell 2.3% over the week to Friday. It closed the week at $61.29/b, a slight gain on the day, but also traded to a low of $60.14/b that same day and just barely avoided trading into the $50ies/b. This morning it is risk-on in equities which seems to help industrial metals a little higher. But no such luck for oil. It is down 0.8% at $60.8/b. This week looks set for Brent crude to dip its feet in the $50ies/b. The Brent 3mth contract actually traded into the high $50ies/b on Friday.

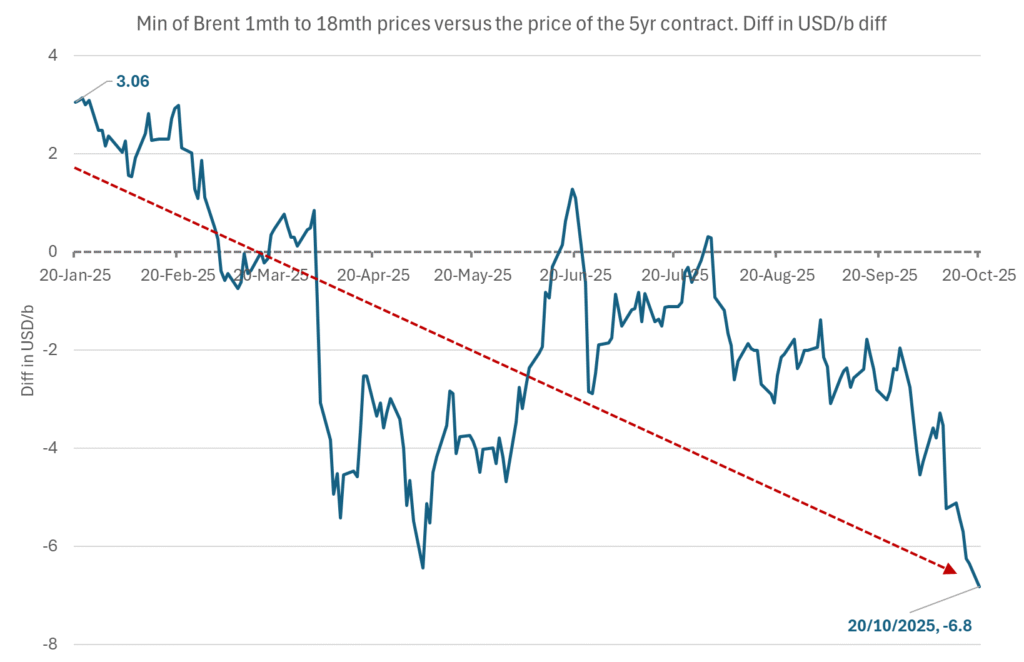
The front-end backwardation has been on a weakening foot and is now about to fully disappear. The lowest point of the crude oil curve has also moved steadily lower and lower and its discount to the 5yr contract is now $6.8/b. A solid contango. The Brent 3mth contract did actually dip into the $50ies/b intraday on Friday when it traded to a low point of $59.93/b.
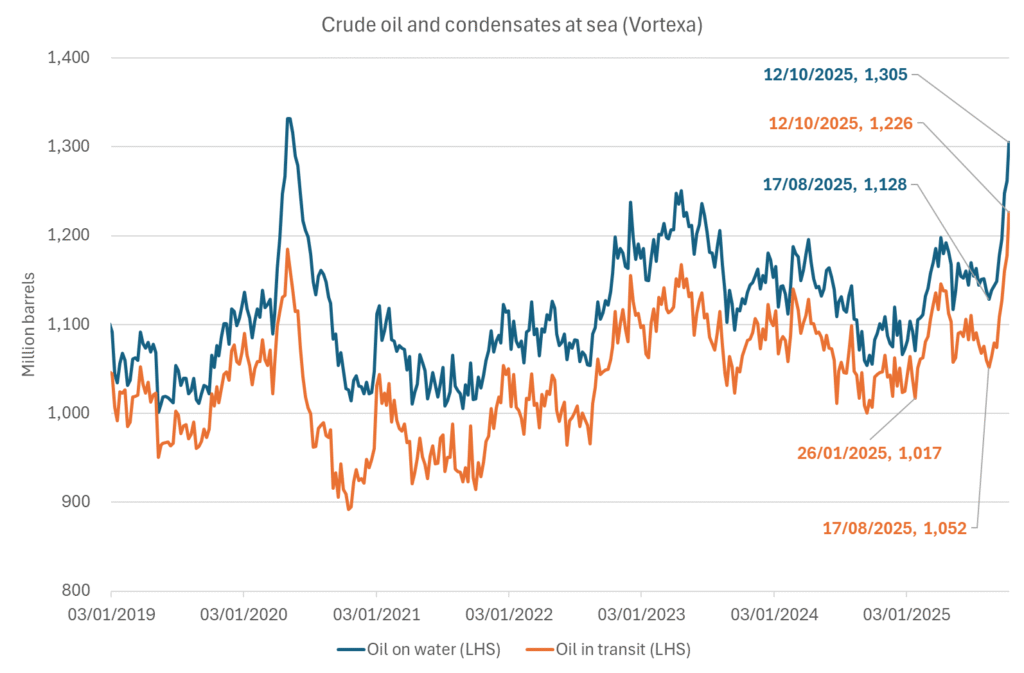
More weakness to come as lots of oil at sea comes to ports. Mid-East OPEC countries have boosted exports along with lower post summer consumption and higher production. The result is highly visibly in oil at sea which increased by 17 mb to 1,311 mb over the week to Sunday. Up 185 mb since mid-August. On its way to discharge at a port somewhere over the coming month or two.
Don’t forget that the oil market path ahead is all down to OPEC+. Remember that what is playing out in the oil market now is all by design by OPEC+. The group has decided that the unwind of the voluntary cuts is what it wants to do. In a combination of meeting demand from consumers as well as taking back market share. But we need to remember that how this plays out going forward is all at the mercy of what OPEC+ decides to do. It will halt the unwinding at some point. It will revert to cuts instead of unwind at some point.
A few months with Brent at $55/b and 40-50 US shale oil rigs kicked out may be what is needed. We think OPEC+ needs to see the exit of another 40-50 drilling rigs in the US shale oil patches to set US shale oil production on a path to of a 1 mb/d year on year decline Dec-25 to Dec-26. We are not there yet. But a 2-3 months period with Brent crude averaging $55/b would probably do it.
Oil on water increased 17 mb over the week to Sunday while oil in transit increased by 23 mb. So less oil was standing still. More was moving.
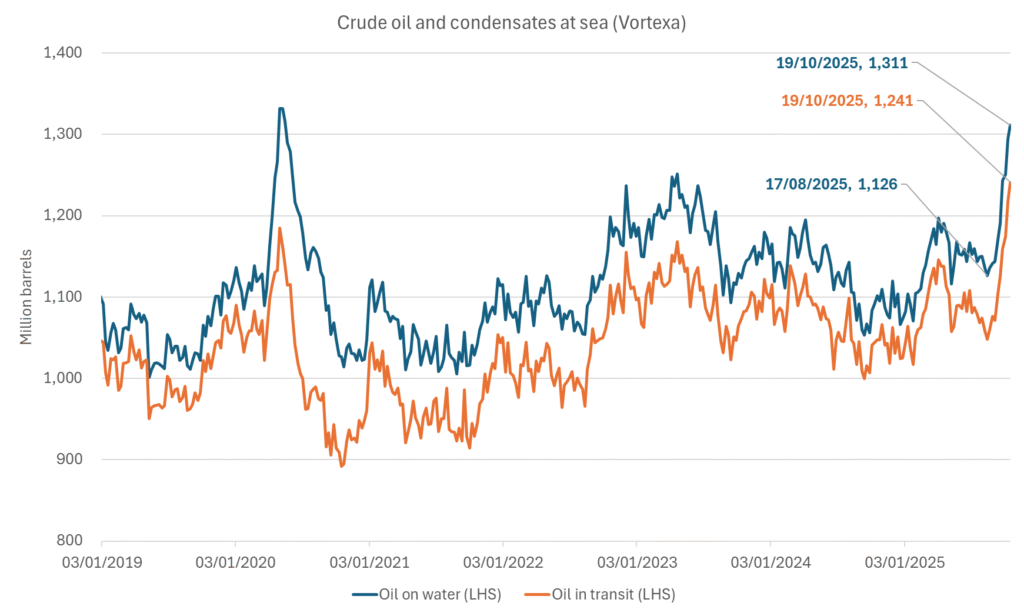
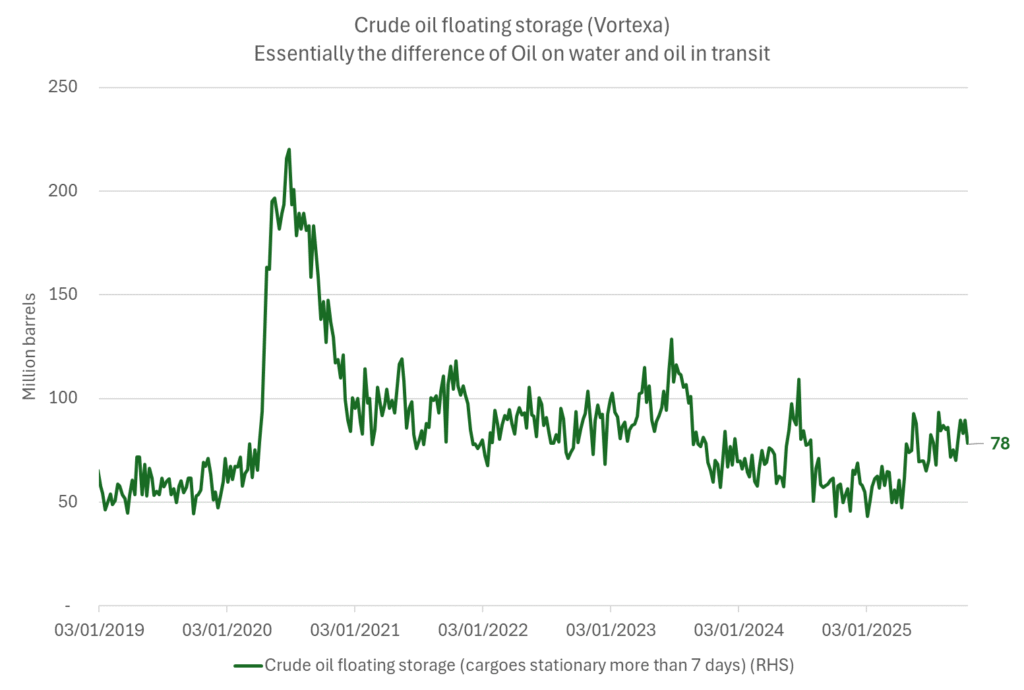
Crude oil floating storage (stationary more than 7 days). Down 11 mb over week to Sunday
The lowest point of the Brent crude oil curve versus the 5yr contract. Weakest so far this year.
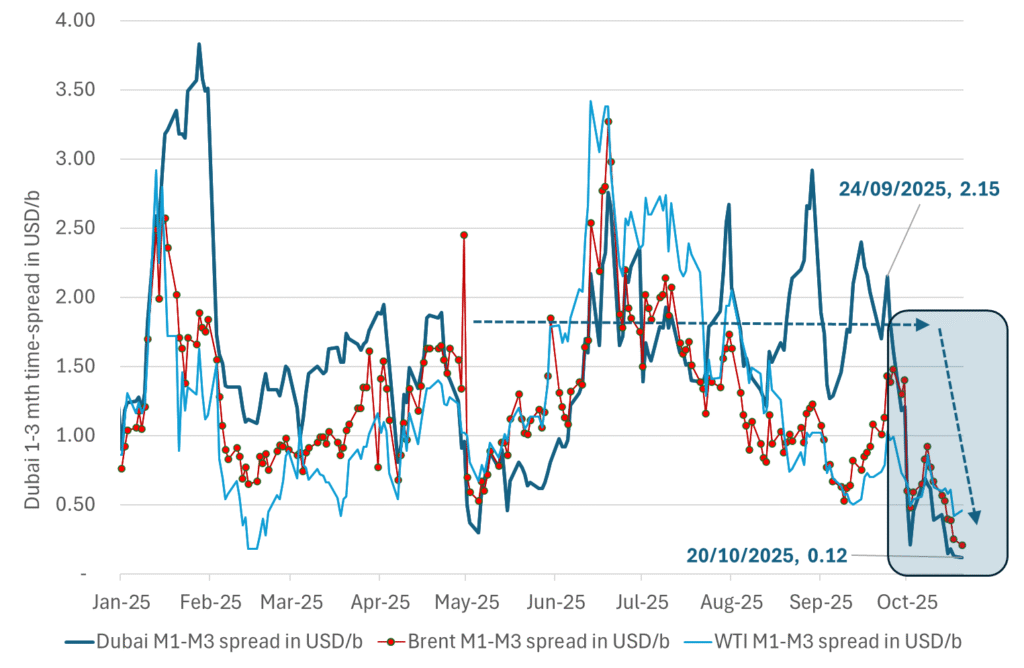
Crude oil 1mth to 3mth time-spreads. Dubai held out strongly through summer, but then that center of strength fell apart in late September and has been leading weakness in crude curves lower since then.
Analys
Crude oil soon coming to a port near you

Rebounding along with most markets. But concerns over solidity of Gaza peace may also contribute. Brent crude fell 0.8% yesterday to $61.91/b and its lowest close since May this year. This morning it is bouncing up 0.9% to $62.5/b along with a softer USD amid positive sentiment with both equities and industrial metals moving higher. Concerns that the peace in Gaza may be less solid than what one might hope for also yields some support to Brent. Bets on tech stocks are rebounding, defying fears of trade war. Money moving back into markets. Gold continues upwards its strong trend and a softer dollar helps it higher today as well.

US crude & products probably rose 5.6 mb last week (API) versus a normal seasonal decline of 2.4 mb. The US API last night partial and thus indicative data for US oil inventories. Their data indicates that US crude stocks rose 7.4 mb last week, gasoline stocks rose 3.0 mb while Distillate stocks fell 4.8 mb. Altogether an increase in commercial crude and product stocks of 5.6 mb. Commercial US crude and product stocks normally decline by 2.4 mb this time of year. So seasonally adjusted the US inventories rose 8 mb last week according to the indicative numbers by the API. That is a lot. Also, the counter seasonal trend of rising stocks versus normally declining stocks this time of year looks on a solid pace of continuation. If the API is correct then total US crude and product stocks would stand 41 mb higher than one year ago and 6 mb higher than the 2015-19 average. And if we combine this with our knowledge of a sharp increase in production and exports by OPEC(+) and a large increase in oil at sea, then the current trend in US oil inventories looks set to continue. So higher stocks and lower crude oil prices until OPEC(+) switch to cuts. Actual US oil inventory data today at 18:00 CET.
US commercial crude and product stocks rising to 1293 mb in week 41 if last nights indicative numbers from API are correct.
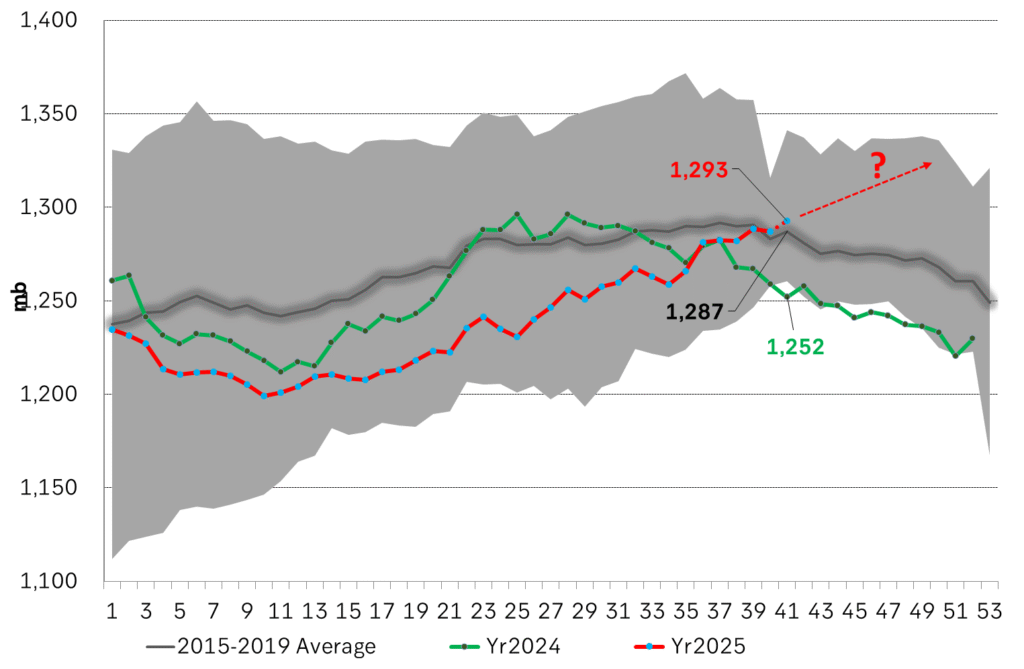
Crude oil soon coming to a port near you. OPEC has lifted production sharply higher this autumn. At the same time demand for oil in the Middle-East has fallen as we have moved out of summer heat and crude oil burn for power for air-conditioning. The Middle-East oil producers have thus been able to lift exports higher on both accounts. Crude oil and condensates on water has shot up by 177 mb since mid-August. This oil is now on its way to ports around the world. And when they arrive, it will likely help to lift stocks onshore higher. That is probably when we will lose the last bit of front-end backwardation the the crude oil curves. That will help to drive the front-month Brent crude oil price down to the $60/b line and revisit the high $50ies/b. Then the eyes will be all back on OPEC+ when they meet in early November and then again in early December.
Crude oil and condensates at sea have moved straight up by 177 mb since mid-August as OPEC(+) has produced more, consumed less and exported more.
Analys
The Mid-East anchor dragging crude oil lower

When it starts to move lower it moves rather quickly. Gaza, China, IEA. Brent crude is down 2.1% today to $62/b after having traded as high as $66.58/b last Thursday and above $70/b in late September. The sell-off follows the truce/peace in Gaze, a flareup in US-China trade and yet another bearish oil outlook from the IEA.

A lasting peace in Gaze could drive crude oil at sea to onshore stocks. A lasting peace in Gaza would probably calm down the Houthis and thus allow more normal shipments of crude oil to sail through the Suez Canal, the Red Sea and out through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait. Crude oil at sea has risen from 48 mb in April to now 91 mb versus a pre-Covid normal of about 50-60 mb. The rise to 91 mb is probably the result of crude sailing around Africa to be shot to pieces by the Houthis. If sailings were to normalize through the Suez Canal, then it could free up some 40 mb in transit at sea moving onshore into stocks.
The US-China trade conflict is of course bearish for demand if it continues.
Bearish IEA yet again. Getting closer to 2026. Credibility rises. We expect OPEC to cut end of 2025. The bearish monthly report from the IEA is what it is, but the closer we get to 2026, the more likely the IEA is of being ball-park right in its outlook. In its monthly report today the IEA estimates that the need for crude oil from OPEC in 2026 will be 25.4 mb/d versus production by the group in September of 29.1 mb/d. The group thus needs to do some serious cutting at the end of 2025 if it wants to keep the market balanced and avoid inventories from skyrocketing. Given that IEA is correct that is. We do however expect OPEC to implement cuts to avoid a large increase in inventories in Q1-26. The group will probably revert to cuts either at its early December meeting when they discuss production for January or in early January when they discuss production for February. The oil price will likely head yet lower until the group reverts to cuts.
Dubai: The Mid-East anchor dragging crude oil lower. Surplus emerging in Mid-East pricing. Crude oil prices held surprisingly strong all through the summer. A sign and a key source of that strength came from the strength in the front-end backwardation of the Dubai crude oil curve. It held out strong from mid-June and all until late September with an average 1-3mth time-spread premium of $1.8/b from mid-June to end of September. The 1-3mth time-spreads for Brent and WTI however were in steady deterioration from late June while their flat prices probably were held up by the strength coming from the Persian Gulf. Then in late September the strength in the Dubai curve suddenly collapsed. Since the start of October it has been weaker than both the Brent and the WTI curves. The Dubai 1-3mth time-spread now only stands at $0.25/b. The Middle East is now exporting more as it is producing more and also consuming less following elevated summer crude burn for power (Aircon) etc.
The only bear-element missing is a sudden and solid rise in OECD stocks. The only thing that is missing for the bear-case everyone have been waiting for is a solid, visible rise in OECD stocks in general and US oil stocks specifically. So watch out for US API indications tomorrow and official US oil inventories on Thursday.
No sign of any kind of fire-sale of oil from Saudi Arabia yet. To what we can see, Saudi Arabia is not at all struggling to sell its oil. It only lowered its Official Selling Prices (OSPs) to Asia marginally for November. A surplus market + Saudi determination to sell its oil to the market would normally lead to a sharp lowering of Saudi OSPs to Asia. Not yet at least and not for November.
The 5yr contract close to fixed at $68/b. Of importance with respect to how far down oil can/will go. When the oil market moves into a surplus then the spot price starts to trade in a large discount to the 5yr contract. Typically $10-15/b below the 5yr contract on average in bear-years (2009, 2015, 2016, 2020). But the 5yr contract is usually pulled lower as well thus making this approach a moving target. But the 5yr contract price has now been rock solidly been pegged to $68/b since 2022. And in the 2022 bull-year (Brent spot average $99/b), the 5yr contract only went to $72/b on average. If we assume that the same goes for the downside and that 2026 is a bear-year then the 5yr goes to $64/b while the spot is trading at a $10-15/b discount to that. That would imply an average spot price next year of $49-54/b. But that is if OPEC doesn’t revert to cuts and instead keeps production flowing. We think OPEC(+) will trim/cut production as needed into 2026 to prevent a huge build-up in global oil stocks and a crash in prices. But for now we are still heading lower. Into the $50ies/b.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanOPEC+ missar produktionsmål, stöder oljepriserna
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanGoldman Sachs höjer prognosen för guld, tror priset når 4900 USD
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanBlykalla och amerikanska Oklo inleder ett samarbete
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGuld nära 4000 USD och silver 50 USD, därför kan de fortsätta stiga
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanAre Ukraine’s attacks on Russian energy infrastructure working?
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanLeading Edge Materials är på rätt plats i rätt tid
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanEtt samtal om guld, olja, koppar och stål
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanNytt prisrekord, guld stiger över 4000 USD









