Analys
The Permian pipes are coming and it is no small potato


Between 2.2 m bl/d to 2.5 m bl/d of new pipeline capacity from the Permian basin to the US Gulf will be put into operation in a flash of just three quarters (Q3-2019 to Q1-2020). Effective capacity is probably about 1.7 m bl/d to 2.0 m bl/d assuming an 80% utilization rate. The Cactus II (670 k bl/d) from the Permian Basin to the USGC is coming online already the 1st of August. I.e. in only 23 days.
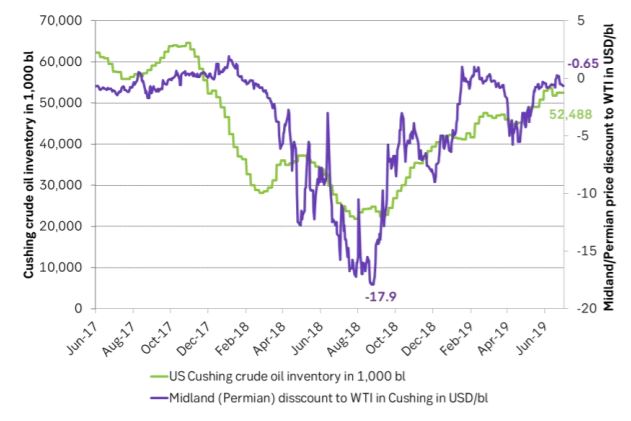
Changes to Texas pipelines had a huge impact on oil prices just one year ago. The Basin/Sunrise pipeline from Midland/Permian to Wichita falls and Cushing Oklahoma then expanded its capacity by a full 500 k bl/d to a total 800 k bl/d. This relieved bulging inventories at depressed prices in the Permian to flow into then very low inventories in Cushing Oklahoma where the WTI is priced. Cushing Oklahoma crude stocks rose strongly, the WTI price crashed, the Brent price crashed and the Midland/Permian price spread to WTI moved from minus $17.9/bl to only minus $0.7/bl today. That is last year’s price action seen from a pipeline perspective.
Now we are set for a much larger change to pipelines in the Permian and it will happen in just three quarters and start already in 23 days.

There has been a significant dislocation between Brent crude oil prices and WTI prices in 2019. The WTI crude curve has been in front end contango while the Brent curve has been in full backwardation and in period exceptionally strong front end backwardation. The two crude curves have told completely different stories. Global Brent market: Too little oil. Local US WTI Cushing Oklahoma market: Too much oil.
When the Cactus II from Wink in Texas (Permian Basin) to Corpus Christi at the USGC (670 k bl/d) comes into operation on 1 August it will release some 4 m barrels from the Permian to the USGC each week (assuming 80% utilization). This will relieve the pressure on other pipelines in Texas. It will for example be much less need to send crude oil from Permian via the Basin/Sunrise pipeline to Cushing Oklahoma. I.e. less crude will flow into Cushing crude stocks from the Permian. It will thus become easier to drain the currently elevated Cushing crude stocks via pipelines to the USGC.
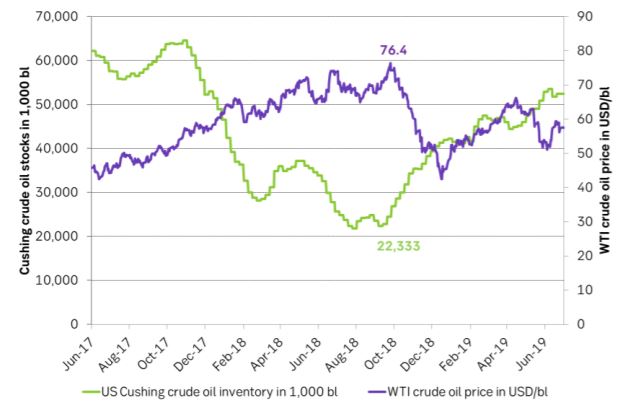
US Cushing crude oil stocks today stands at 52.5 m barrels versus only 22.3 m barrels on the 20th of September last year when the WTI price spiked at $76.4/bl. Cushing is today probably receiving a full flow of crude oil from the Permian Basin via the Basin/Sunrise 800 k bl/d pipeline. At 80% utilization that equals about 4.5 m barrels per week.
This flow of oil from the Permian into Cushing Oklahoma will likely fall partially silent starting 1 August and over the coming three quarters it will definitely fall silent and stop pumping crude oil into Cushing Oklahoma. As the three new pipelines (Cactus II (670 k bl/d), Epic crude (600 – 900 k bl/d) and the Grey Oak (900 k bl/d)) all come online over the next three quarters we might even see that Basin/Sunrise could change direction and help drain Cushing stocks via the Permian to the USGC.
But just halting the flow of oil of about 4.5 m barrels per week from the Permian to Cushing via the Basin/Sunrise pipeline could lead to a decline in Cushing Oklahoma crude oil stocks of 20 m barrels in just one month. That would drag Cushing stocks from 52.3 m barrels today to only 32 m barrels over the course of August alone.
Bullish for WTI and Bearish for Brent. A $2/bl spread is very probable in our view. Needless to say this is bullish for the WTI crude oil curve structure as well as the WTI crude oil flat price. It is also bearish for the Brent crude oil price and crude oil curve structure. The Brent and WTI crude oil price spread will tighten further and the shape of the two crude curves will converge further. Tightness in the global market place will be partially relieved while the WTI market will tighten up significantly.
Will the WTI price move up to Brent or will Brent move down to the WTI price? Global oil producers have enjoyed the luxury of getting a $7.8/bl premium over the WTI price since the start of 2018. The general assumption has been that Brent crude oil will trade in the $60-70/bl range while WTI will trade in the $50-60/bl range. And further that when the new Permian pipelines comes online the next three quarters it will shift the WTI price up towards the global benchmark Brent crude. Or will they maybe meet in the middle or will the Brent crude oil price marker move down to WTI.
We think that the initial action will be a strengthening of the WTI price. The WTI price has over the past 4 years firmly established a price to US inventory relationship. So as US inventories move lower as a result of Permian pipes coming online it will push the WTI price higher on the basis of this established price/inventory relationship.
The Brent crude oil price and curve structure will move towards the WTI curve. The Brent crude curve could move a little lower towards WTI. But a bullish sentiment hitting the WTI price on the back of declining US Cushing crude stocks could even smitten over to the Brent crude oil price and actually lift both the benchmarks. WTI the most and Brent a little.
Our view is that an overweight of global oil investors are hugely focused on the WTI price. Firstly because a large part of them are located in the U.S. Secondly because U.S. oil data are of high quality and published at a high frequency.
It gives a sense of control and that you know what you are doing when you trade WTI on the basis of data you can really trust and see on a high frequency. In other words many oil investors treat the WTI benchmark as THE global benchmark and as a reflection of the global market.
So when US crude inventories decline both in total and locally in Cushing Oklahoma it is taken by investors as a sign of a tightening global oil market even if it in this case is only a shift of oil out of the US and into the global market due to new pipelines coming online from the Permian to the USGC.
Global growth is cooling and oil demand growth along with it but it will likely be countered by an IMO-boost. The global oil market is currently weighted down by continuously deteriorating global growth indicators in combination with still strongly growing US crude oil production. Restraint from OPEC+ and losses of supply from Iran and Venezuela as well as the Russian Druzhba pipeline is helping to prevent oil prices from heading lower and trail the deteriorating global economic growth picture. But elevated US oil inventories and a weak global economic backdrop is preventing oil prices from moving higher.
Global middle distillate demand will likely rise sharply in Q4-19 and H1-20 due to the new IMO 2020 regulations which requires global shipping to consume low sulphur bunker oil. Refineries will have to run hard to meet the added mid-dist demand. We expect this to counter the cooling global growth picture.
H2-19 could see a mix of sharply declining Cushing crude oil stocks and strongly rising mid-dist demand. This could be a very bullish set-up for crude oil prices. Pushing WTI higher on the basis of Cushing crude inventory declines and pulling Brent crude higher on the back of bullish WTI sentiment and strong global mid-dist demand from the shipping side.
Down the road it could be a bit different. WTI would need to move back down to control US shale oil supply growth while Brent crude would follow lower as there would be very little pipeline capacity strains to keep the two benchmarks apart. I.e. we could see WTI back to $55-60/bl and Brent crude only a couple of USD above.
That is of course if we assume that US investors continues to bankroll under-water US shale oil production growth. If US investors demand profits and a positive cash flow from US shale oil producers then WTI would need to move higher in order to keep U.S. shale oil production growing robustly.
More pipelines are coming in 2021. In addition to the 2.2 to 2.5 m bl/d of new pipeline capacity coming online the next three quarters there will be an additional 1.4 to 1.8 m bl/d of pipeline capacity coming online in 2021: The Wink (Permian) to Webster (Houston) 1000 bl/d pipeline and the Seahorse – Tallgrass from Cushing Oklahoma to Louisiana.
What it means is that 1) The Brent to WTI price spread will be narrow over the coming years. 2) That US shale oil producers will receive a crude oil price close to the global price level and the global oil price will stimulate US shale oil production directly without a $7-10/bl discount and 3) That rising U.S. crude oil production will flow freely into the global market place and challenge OPEC+ production in all markets.
US production boom so far has meant declining US oil imports. The effect on OPEC and other non-US producers has been a redirection of oil supply away from the US and instead towards growing demand in Asia. I.e the first phase of the US oil production boom has not been so painful for non-OPEC producers as it primarily has meant a redirection of oil exports.
The next leg of the US oil production boom means US oil exports will challenge non-US producers in the global market. It may be much more difficult for non-US producers to swallow that growing US oil exports challenge them head to head in the global market place. Either stealing all demand growth or even pushing them aside. OPEC+ can probably accept to see their exports at a fixed volume level loosing percentage global market share but with no loss of volumes in absolute terms. But accepting declining volumes in absolute terms is probably a definitely no-go for OPEC+.
This means that US production growth going forward will not be allowed by OPEC+ to grow by more than global demand growth minus production declines (like we have seen in Mexico, China,..).
Ch1: Cushing crude oil stocks were very low one year ago and crude oil was locked up in the Permian basin leading to a very large discount for WTI Midland (Permian) versus WTI Cushing. Then the Basin/Sunrise pipeline expanded capacity by 500 k bl/d to a total of 800 k bl/d in Q4-18. It released oil from Permian to Cushing. Helped to drive Cushing stocks strictly higher and the spread between WTI Midland and WTI Cushing shrank from minus $17.9/bl about in September 2018 to now only minus $0.7/bl
Ch2: As the Cushing crude stocks rose sharply from late September last year the WTI crude oil price totally tanked and dragged the Brent crude oil price lower along with it.
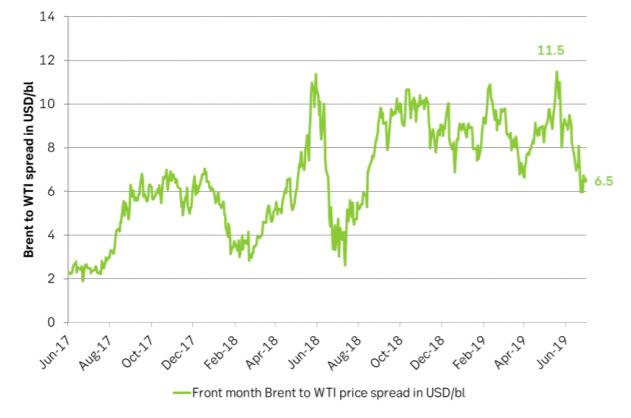
Ch3: The Brent-WTI price spread has moved from a high of $11.5/bl in May last year to now only $5.6/bl. Going forward there will be less and less pipeline constraints and the two grades will move much closer together.
Analys
OPEC+ in a process of retaking market share

Oil prices are likely to fall for a fourth straight year as OPEC+ unwinds cuts and retakes market share. We expect Brent crude to average USD 55/b in Q4/25 before OPEC+ steps in to stabilise the market into 2026. Surplus, stock building, oil prices are under pressure with OPEC+ calling the shots as to how rough it wants to play it. We see natural gas prices following parity with oil (except for seasonality) until LNG surplus arrives in late 2026/early 2027.

Oil market: Q4/25 and 2026 will be all about how OPEC+ chooses to play it
OPEC+ is in a process of unwinding voluntary cuts by a sub-group of the members and taking back market share. But the process looks set to be different from 2014-16, as the group doesn’t look likely to blindly lift production to take back market share. The group has stated very explicitly that it can just as well cut production as increase it ahead. While the oil price is unlikely to drop as violently and lasting as in 2014-16, it will likely fall further before the group steps in with fresh cuts to stabilise the price. We expect Brent to fall to USD 55/b in Q4/25 before the group steps in with fresh cuts at the end of the year.

Natural gas market: Winter risk ahead, yet LNG balance to loosen from 2026
The global gas market entered 2025 in a fragile state of balance. European reliance on LNG remains high, with Russian pipeline flows limited to Turkey and Russian LNG constrained by sanctions. Planned NCS maintenance in late summer could trim exports by up to 1.3 TWh/day, pressuring EU storage ahead of winter. Meanwhile, NE Asia accounts for more than 50% of global LNG demand, with China alone nearing a 20% share (~80 mt in 2024). US shale gas production has likely peaked after reaching 104.8 bcf/d, even as LNG export capacity expands rapidly, tightening the US balance. Global supply additions are limited until late 2026, when major US, Qatari and Canadian projects are due to start up. Until then, we expect TTF to average EUR 38/MWh through 2025, before easing as the new supply wave likely arrives in late 2026 and then in 2027.
Analys
Manufacturing PMIs ticking higher lends support to both copper and oil

Price action contained withing USD 2/b last week. Likely muted today as well with US closed. The Brent November contract is the new front-month contract as of today. It traded in a range of USD 66.37-68.49/b and closed the week up a mere 0.4% at USD 67.48/b. US oil inventory data didn’t make much of an impact on the Brent price last week as it is totally normal for US crude stocks to decline 2.4 mb/d this time of year as data showed. This morning Brent is up a meager 0.5% to USD 67.8/b. It is US Labor day today with US markets closed. Today’s price action is likely going to be muted due to that.

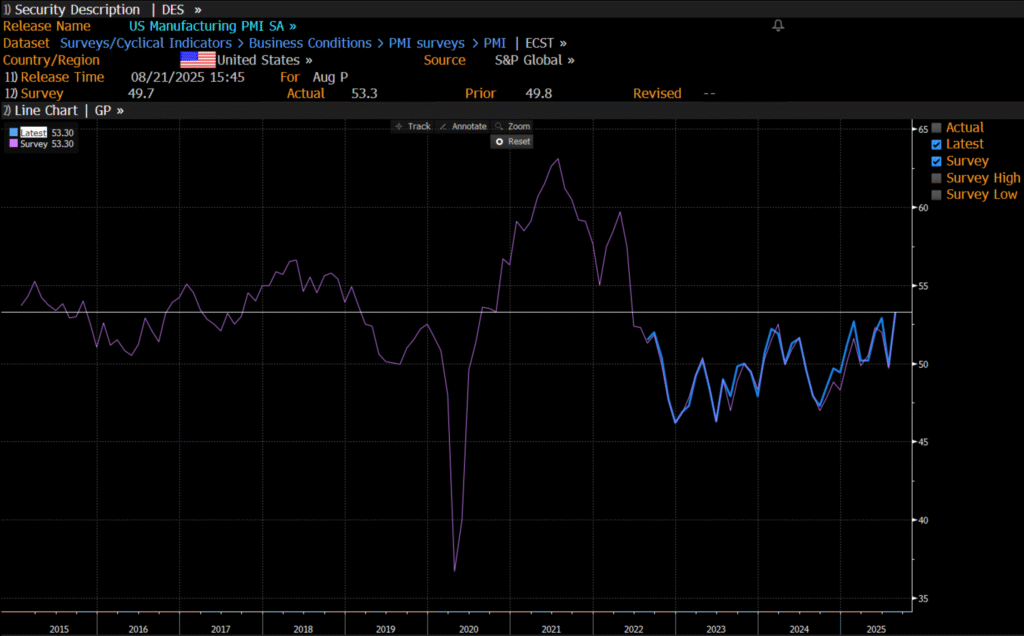
Improving manufacturing readings. China’s manufacturing PMI for August came in at 49.4 versus 49.3 for July. A marginal improvement. The total PMI index ticked up to 50.5 from 50.2 with non-manufacturing also helping it higher. The HCOB Eurozone manufacturing PMI was a disastrous 45.1 last December, but has since then been on a one-way street upwards to its current 50.5 for August. The S&P US manufacturing index jumped to 53.3 in August which was the highest since 2022 (US ISM manufacturing tomorrow). India manufacturing PMI rose further and to 59.3 for August which is the highest since at least 2022.
Are we in for global manufacturing expansion? Would help to explain copper at 10k and resilient oil. JPMorgan global manufacturing index for August is due tomorrow. It was 49.7 in July and has been below the 50-line since February. Looking at the above it looks like a good chance for moving into positive territory for global manufacturing. A copper price of USD 9935/ton, sniffing at the 10k line could be a reflection of that. An oil price holding up fairly well at close to USD 68/b despite the fact that oil balances for Q4-25 and 2026 looks bloated could be another reflection that global manufacturing may be accelerating.
US manufacturing PMI by S&P rose to 53.3 in August. It was published on 21 August, so not at all newly released. But the US ISM manufacturing PMI is due tomorrow and has the potential to follow suite with a strong manufacturing reading.
Analys
Crude stocks fall again – diesel tightness persists

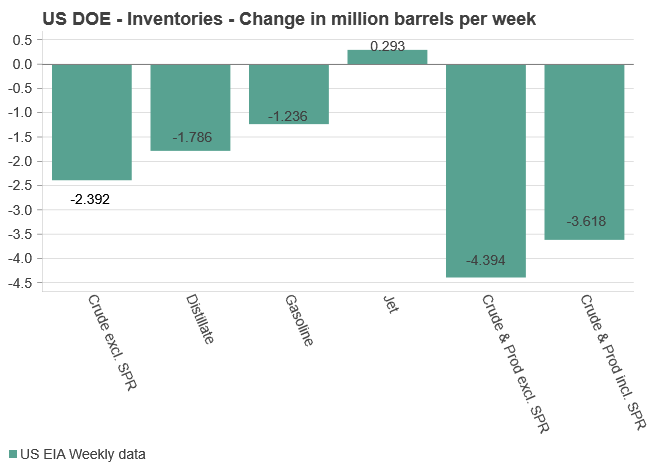
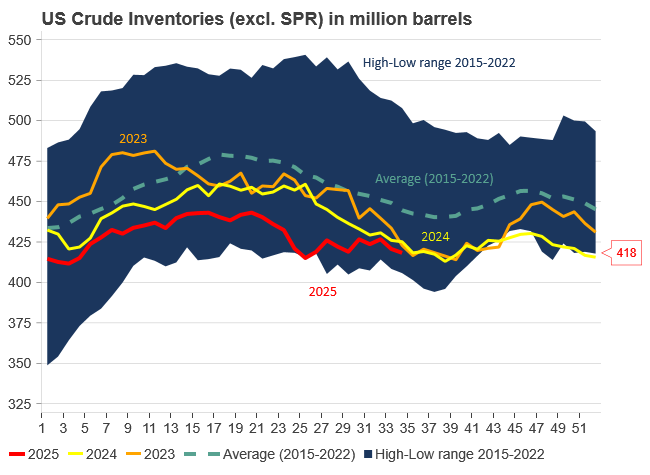
U.S. commercial crude inventories posted another draw last week, falling by 2.4 million barrels to 418.3 million barrels, according to the latest DOE report. Inventories are now 6% below the five-year seasonal average, underlining a persistently tight supply picture as we move into the post-peak demand season.

While the draw was smaller than last week’s 6 million barrel decline, the trend remains consistent with seasonal patterns. Current inventories are still well below the 2015–2022 average of around 449 million barrels.
Gasoline inventories dropped by 1.2 million barrels and are now close to the five-year average. The breakdown showed a modest increase in finished gasoline offset by a decline in blending components – hinting at steady end-user demand.
Diesel inventories saw yet another sharp move, falling by 1.8 million barrels. Stocks are now 15% below the five-year average, pointing to sustained tightness in middle distillates. In fact, diesel remains the most undersupplied segment, with current inventory levels at the very low end of the historical range (see page 3 attached).
Total commercial petroleum inventories – including crude and products but excluding the SPR – fell by 4.4 million barrels on the week, bringing total inventories to approximately 1,259 million barrels. Despite rising refinery utilization at 94.6%, the broader inventory complex remains structurally tight.
On the demand side, the DOE’s ‘products supplied’ metric – a proxy for implied consumption – stayed strong. Total product demand averaged 21.2 million barrels per day over the last four weeks, up 2.5% YoY. Diesel and jet fuel were the standouts, up 7.7% and 1.7%, respectively, while gasoline demand softened slightly, down 1.1% YoY. The figures reflect a still-solid late-summer demand environment, particularly in industrial and freight-related sectors.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanOmgående mångmiljardfiasko för Equinors satsning på Ørsted och vindkraft
-
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLundin Gold hittar ny koppar-guld-fyndighet vid Fruta del Norte-gruvan
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuld stiger till över 3500 USD på osäkerhet i världen
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanWhat OPEC+ is doing, what it is saying and what we are hearing
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAlkane Resources och Mandalay Resources har gått samman, aktör inom guld och antimon
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLyten, tillverkare av litium-svavelbatterier, tar över Northvolts tillgångar i Sverige och Tyskland






