Analys
Solid demand growth and strained supply to push Brent above USD 100/b


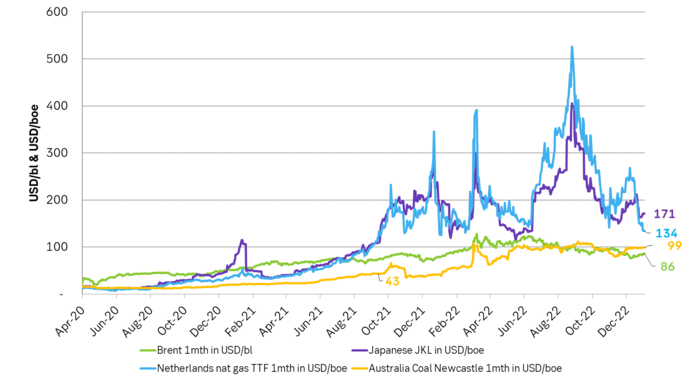
Brent crude had a strong end of the year as it traded at the highest level since 1 December. It is a slow start to the new year due to bank holidays and Dated Brent trades close to USD 85/b. It averaged USD 99.9/b in 2022. We expect it to average more than USD 100/b on average for the coming year amid strained supply and rebounding demand. Chinese oil demand is set to recover strongly along with re-openings while non-OECD will continue to move higher. At the moment oil looks absurdly cheap as it is cheaper than natural gas in both EU and Japan and also cheaper than coal in Australia.
Some price strength at the end of the year. The Dated Brent crude oil price index gained 2.3% on Friday with a close at USD 84.97/b. It was the highest close since 1 December. This morning it is trading slightly lower at USD 84.8/b but the market is basically void of action due to bank holidays.

Gloom and doom but IEA, OPEC and US EIA project global crude oil demand to rise between 1 m b/d and 2.2 m b/d YoY in 2023. They also expect call-on-OPEC to rise between 0.3 m b/d and 1.0 m b/d. The US EIA projects demand to increase 1 m b/d in 2023 on the back of a growth of 1.3 m b/d in non-OECD where demand in India rises by 0.2 m b/d and China by 0.6 m b/d. In China this is of course to a large degree due to re-opening after Covid-19 lock-downs. But it is still a good reminder of the low base of oil demand in non-OECD versus OECD. India last year consumed 5 m b/d which only amounts to 1.3 b/capita/year versus a world average of 4.5 b/capita/year and European demand of 10 b/capita/year. Even China is still below the world average as its demand in 2022 stood at 15.2 m b/d or 4.0 b/capita/yr. Non-OECD oil demand thus still has a long way to go in terms of oil demand and that is probably one of the things we’ll be reminded of in 2023 as Covid-19 lock-downs disappear entirely.
Solid demand growth in the face of strained supply. Important to remember is that the world has lost a huge amount of fossil supply from Russia due to the war in Ukraine. First in terms of natural gas where supply to the EU and thus to the world has declined by some 2.5 m boe/d versus pre-war levels. Secondly in terms of crude and products. The latter is of course a constant guessing game in terms of how much Russian crude and product exports has declined. The US EIA however projects that crude oil production in the Former Soviet Union will be down 2 m b/d in 2023 versus pre-Covid levels and down 1.3 m b/d YoY from 2022 to 2023. We are thus talking up to 4.5 m boe/d of lost supply from Russia/FSU. That is a huge loss. It is the reason why coal prices are still trading at USD 200 – 400/ton versus normal USD 85/ton as coal is an alternative to very expensive natural gas.
Overall for 2023 we are looking at a market where we’ll have huge losses in supply of fossil energy supply from Russia while demand for oil is set to rebound solidly (+1.0 – 2.2 m b/d) along with steady demand growth in non-OECD plus a jump in demand from China due to Covid-19 reopening. Need for oil from OPEC is set to rise by up to 1.0 m b/d YoY while the group’s spare capacity is close to exhausted.
We expect Brent crude to average more than USD 100/b in 2023. Despite all the macro economic gloom and doom due to inflation and rising interest rates we cannot help having a positive view for crude oil prices for the year to come due to the above reasons. The Dated Brent crude oil price index averaged USD 99.9/b in 2022. We think Brent crude will average more than USD 100/b in 2023. Oil is today absurdly cheap at USD 85/b. It is cheaper than both coal in Australia and natural gas both in Japan and the EU. This is something you hardly ever see. The energy market will work hard to consume more what is cheap (oil) and less of what is expensive (nat gas and coal).
Latest forecasts by IEA, OPEC and US EIA for oil demand growth and call-on-OPEC YoY for 2023. Solid demand growth and rising need for oil from OPEC.
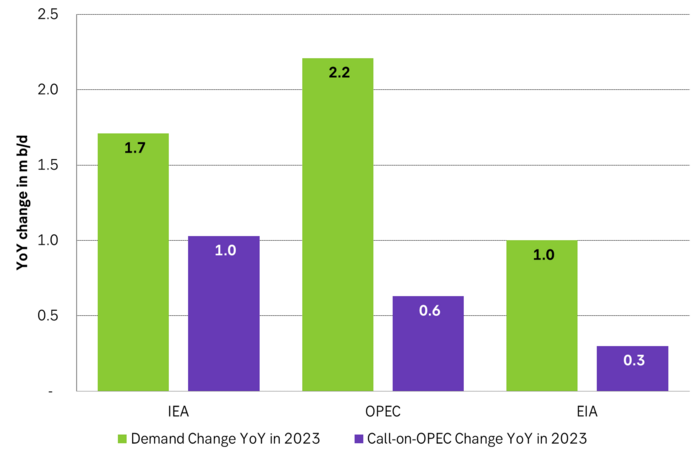
Oil demand projections from the main agencies and estimated call-on-OPEC. More demand and higher need for oil from OPEC
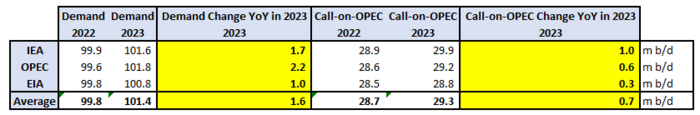
EIA STEO projected change in oil demand for different countries and regions YoY to 2023
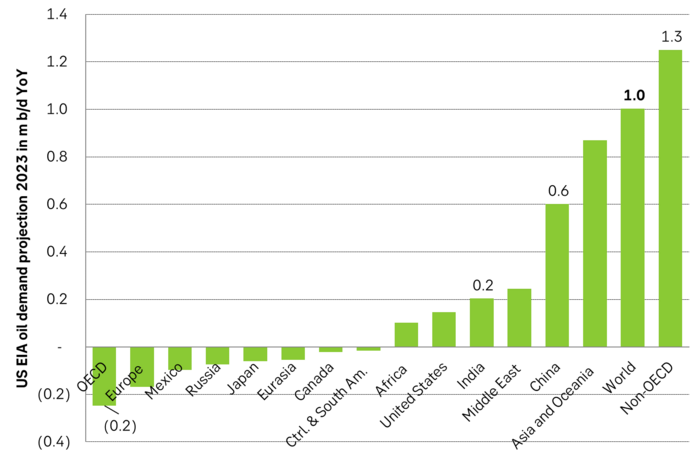
US EIA Dec STEO forecast for FSU oil production. Solid decline projected for 2023.
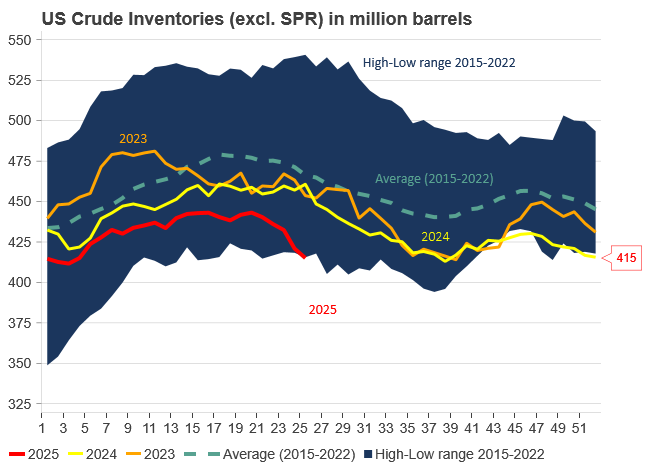
US commercial crude and product stocks still below normal
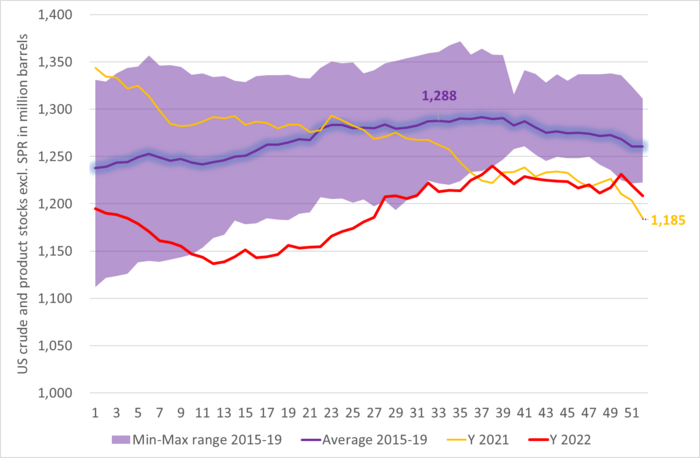
Total US crude and product stocks including SPR. Declining, declining, declining.
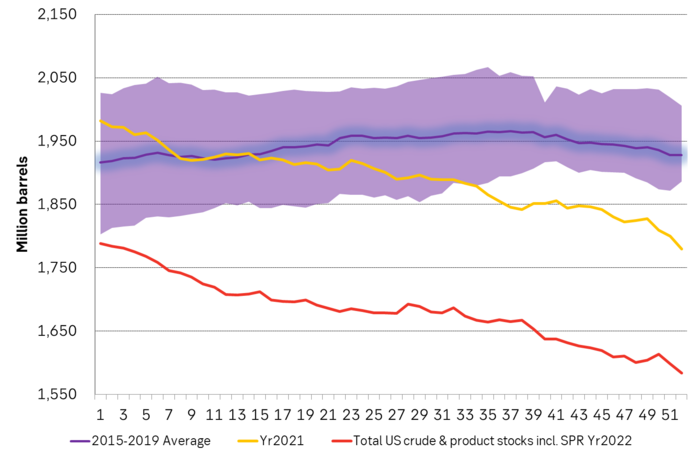
US crude and product inventories both excluding and including Strategic Petroleum Reserves
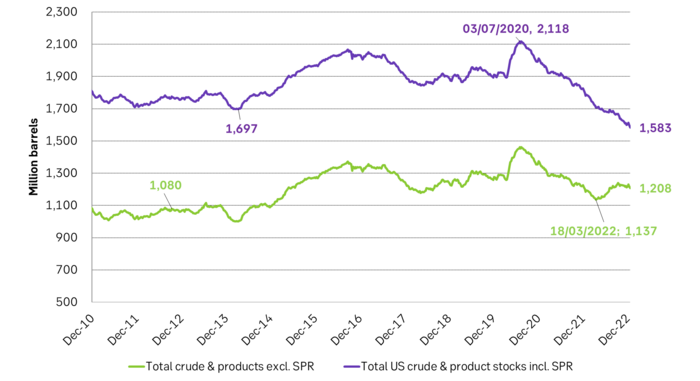
US oil sales from US SPR is now coming to an end. Will make the market feel much tighter as it really is.
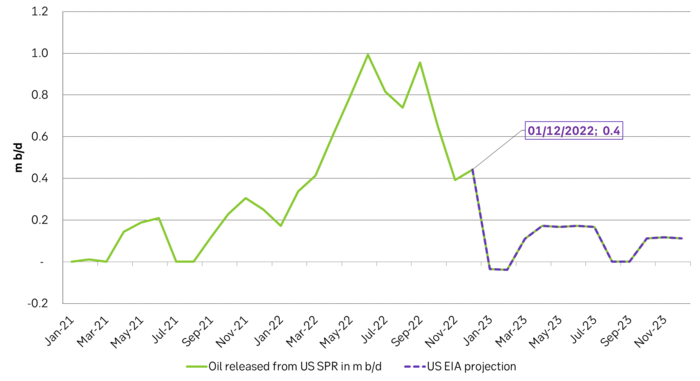
Brent crude oil is absurdly cheap as it today trades below both Australian coal and natural gas in both Japan and the EU. Coal and natural gas prices should trade lower while oil should trade higher.
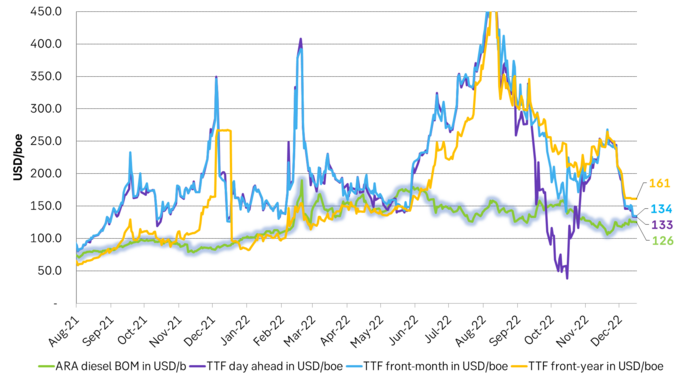
EU diesel prices versus natural gas prices. Could start to move towards a more natural price-balance in terms of substitution.
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

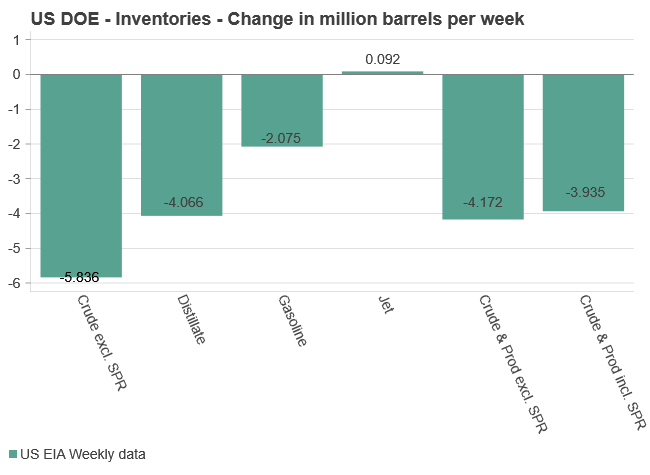
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBrookfield ska bygga ett AI-datacenter på hela 750 MW i Strängnäs
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanTradingfirman XTX Markets bygger datacenter i finska Kajana för 1 miljard euro
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld









