Analys
The long game is the wrong game (from short term intervention to longer term structural battle)

 OPEC yesterday decided to roll existing cuts over for another 9 months lasting all the way to March 2018. Maintaining production cuts also in Q1-18 was however communicated as a measure mainly to avoid driving inventories higher again in the demand wise seasonally weak first quarter of the year. To the surprise of many the market did not take the deal well and Brent crude oil fell $4.6% to a close of the day of $51.46/b with a low of the day of $51.03/b.
OPEC yesterday decided to roll existing cuts over for another 9 months lasting all the way to March 2018. Maintaining production cuts also in Q1-18 was however communicated as a measure mainly to avoid driving inventories higher again in the demand wise seasonally weak first quarter of the year. To the surprise of many the market did not take the deal well and Brent crude oil fell $4.6% to a close of the day of $51.46/b with a low of the day of $51.03/b.
In hindsight we can now clearly say that there must have been a substantial amount of anticipation in the market for not only an extension of cuts but also for deeper cuts. Saudi Arabia’s communication to the market ahead of the meeting has clearly been misinterpreted when he stated that OPEC “will do whatever it takes” to draw inventories down to the 5 year average. The market view must have been that what OPEC & Co. did in H1-17 was far from enough. Thus “whatever it takes” should be MORE. Thus the moment Khalid Al-Falih said to reporters in Vienna yesterday at 10:20 CEST that “deeper cuts are not needed”, that was when the oil price started to fall. Long speculative positions which had run hard into the meeting and then instead ran for cover when the oil price started to tumble.
When OPEC launched the cuts last year they were dubbed as a “short term intervention”. Now it increasingly starts to look like a long haul structural battle. We do think that OPEC’s decision to cut will drive inventories down towards normal by the end of the year. Thus yesterday’s decision by OPEC & Co. is in our view making $60/b a sensible target for the front month Brent crude at the end of 2017. Thus as such we think that yesterday’s sell-off should be used as a buying opportunity. At the same time however it is likely leading to another 9 months during which a positive crude oil price signal leads US shale oil production to accelerate yet more.
US shale oil production has accelerated massively since November when OPEC & Co. decided to cut production. US crude oil production is now up more than 600 kb/d since the start of December 2016 which is more than the total 558 kb/d in pledged cuts from the 11 countries which have joined OPEC in cutting production at the moment. Their cuts are now basically wiped out. The US shale oil stimulus from the price gains following OPEC’s decision to cut in November has added some 250 shale oil rigs to the market. If we assume that there will not be a single additional US shale oil rig added to the market from July 2017 and all through to the end of 2018 we still expect that US crude oil production will grow by 0.5 mb/d y/y in 2017, 1.5 mb/d y/y in 2018 and by 1 mb/d y/y in 2019. However, as a consequence of the extension of the cuts all until March 2018 we are likely going to see a more supportive oil price and thus yet more US shale oil rigs being added to the market over the coming 9 months of cuts. In our view this is likely going to flip the global supply/demand balance for 2018 and 2019 into surplus.
Thus OPEC is increasingly painting itself into a corner. OPEC’s choice next year will be
1) Roll some cuts forward in both 2018 and 2019 (longer term structural battle) or
2) Put 1.8 mb/d of production cuts (OPEC & Co.) back into the market. Produce at will and let the price regulate the market yet again. I.e. the oil price needs to drop in order to push non-OPEC production lower in order to make room for OPEC & Co’s production revival.
It is often said that generals always fight the previous war meaning that they use tactics and strategy from the last war because that is what they know even if these are outdated. In a way this is what OPEC & Co are doing. In a shale oil world they should have med the cuts quick and dirty. It should definitely have been a short term intervention and not a long term structural battle. In the old days when non-OPEC production solely consisted of conventional oil production with a lead time from investments to production of some 5 years then gradual, enduring cuts did work. Now however keeping cuts going just leaves US shale oil producers all the time in the world to respond and revive. Rather than OPEC & Co cutting 1.8 mb/d for a full 5 quarters (2017 + Q1-18) they should rather have cut production by 3 mb/d for one quarter. That would have left little time for US shale oil players to ramp up investments and thus have limited the cumulative production impact on 2018 and 2019.
At yesterday’s meeting they should have decided massive cuts in Q3-17 and then no more. That would have been the right medicine for the market. Draw down the inventories in a flash. No lengthy time for US shale oil producers to revive and voila, inventories down to normal. A flat or backwardated crude oil forward curve where the mid-term WTI forward curve could be kept in check from there onwards.
It is still not too late for Saudi Arabia to follow this kind of strategy. They have basically promised what they are going to produce over the next 9 months. They could possibly do all of it in Q3-17. Rather than placing production at 10.06 mb/d for 9 months (a cut of 486 kb/d) they could instead produce 9.07 mb/d for the three months in Q3-17 which would mean a cut of 1.458 kb/d versus its October 2017 level. That would have drawn the inventories down by an additional 90 mb in Q3-17. At the same time Saudi Arabia should sell a comparable amount of volumes on a forward basis 2018 and 2019. This would help to prevent the medium term forward curve from rising. Thus again limiting the price signals and hedging opportunities for US shale oil producers.
Khalid Al-Falih has said that US shale oil producers are not the enemy. He welcomes their production revival. However, it still needs to be managed in the right way. At least as long as OPEC & Co is trying to manage the market. And the right way in our view is quick and dirty cuts. Do it all in one go rather than extended and do manage the price level of the mid-term forward crude oil prices.
JPM this morning cut its 2018 Brent crude oil price outlook to $45/b. That is great news for OPEC & Co because it will help to hold price expectations low for 2018 and 2019 and thus help to keep the mid-term forward crude prices in check and thus help to limit the positive price signals to US shale oil producers and thus limit further strong additions and activations of rigs.
As of now however the picture is for a lengthy nine months of additional production cuts and thus more US shale oil rigs being activated driving both 2018 and 2019 into surplus. As such there is increasing concern in the market for the exit from cuts. It is easy to take 1.8 mb/d off the market (1.2 mb/d for OPEC and 0.6 for Co.). With further revival of US shale oil it will be increasingly difficult to put the volumes back into the market again. An exit strategy was not discussed at the OPEC meeting. “We will cross that bridge when we get there” was Khalid Al-Falih’s comment. The market is worried however that come April 2018 then OPEC & Co moves back to “produce at will”. If that was the case following 5 quarters of US shale oil stimulating production cuts from OPEC & Co that would mean that the front month Brent crude oil price probably would have to move down to $35/b in order to slow down US shale oil production again.
With increasingly a surplus becoming the likely outlook for 2018 and 2019 (due to nine more months of cuts) the price outlook for these years increasingly becomes tied to OPEC & Co’s strategy of rolling cuts yet further down the road or not.
For now we are positive to oil prices for the rest of the year in 2017 where we expect OECD inventories at normal level at the end of 2017 with the Brent crude curve moving into backwardation with the front end contract standing at $60/b. We then expect the market price structure to be as follows. The WTI 18 month contract standing at $52.5/b. The Brent crude 18 month contract standing at a $2.5/b premium at $55/b and lastly the front month Brent crude oil contract having a $5/b premium backwardation the 18 months contract thus placing Brent crude front month contract at $60/b at year end 2017.
We are however increasingly concerned about the oil market balance and thus oil prices in 2018 and 2019. The fact that Algeria’s Energy Minister, Noureddine Bouterfa, was replaced in a minister re-shuffle yesterday is concerning. He was at the heart of last year’s negotiations. He was the oil diplomat which criss-crossed between OPEC and non-OPEC members to make the production cut deal last year happen. Thus losing him as oil minister is probably not a good thing with respect to further cuts beyond March 2018.
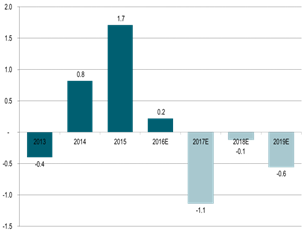
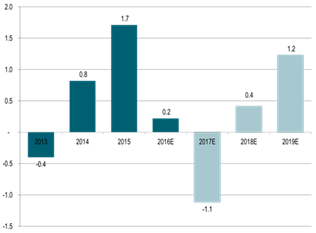
Global supply/demand oil market balance:
This is what OPEC hopes for:
This is however probably what they might get:
Kind regards
Bjarne Schieldrop
Chief analyst, Commodities
SEB Markets
Merchant Banking
Analys
Fear that retaliations will escalate but hopes that they are fading in magnitude

Brent crude spikes to USD 90.75/b before falling back as Iran plays it down. Brent crude fell sharply on Wednesday following fairly bearish US oil inventory data and yesterday it fell all the way to USD 86.09/b before a close of USD 87.11/b. Quite close to where Brent traded before the 1 April attack. This morning Brent spiked back up to USD 90.75/b (+4%) on news of Israeli retaliatory attack on Iran. Since then it has quickly fallen back to USD 88.2/b, up only 1.3% vs. ydy close.

The fear is that we are on an escalating tit-for-tat retaliatory path. Following explosions in Iran this morning the immediate fear was that we now are on a tit-for-tat escalating retaliatory path which in the could end up in an uncontrollable war where the US unwillingly is pulled into an armed conflict with Iran. Iran has however largely diffused this fear as it has played down the whole thing thus signalling that the risk for yet another leg higher in retaliatory strikes from Iran towards Israel appears low.
The hope is that the retaliatory strikes will be fading in magnitude and then fizzle out. What we can hope for is that the current tit-for-tat retaliatory strikes are fading in magnitude rather than rising in magnitude. Yes, Iran may retaliate to what Israel did this morning, but the hope if it does is that it is of fading magnitude rather than escalating magnitude.
Israel is playing with ”US house money”. What is very clear is that neither the US nor Iran want to end up in an armed conflict with each other. The US concern is that it involuntary is dragged backwards into such a conflict if Israel cannot control itself. As one US official put it: ”Israel is playing with (US) house money”. One can only imagine how US diplomatic phone lines currently are running red-hot with frenetic diplomatic efforts to try to defuse the situation.
It will likely go well as neither the US nor Iran wants to end up in a military conflict with each other. The underlying position is that both the US and Iran seems to detest the though of getting involved in a direct military conflict with each other and that the US is doing its utmost to hold back Israel. This is probably going a long way to convince the market that this situation is not going to fully blow up.
The oil market is nonetheless concerned as there is too much oil supply at stake. The oil market is however still naturally concerned and uncomfortable about the whole situation as there is so much oil supply at stake if the situation actually did blow up. Reports of traders buying far out of the money call options is a witness of that.
Analys
Fundamentals trump geopolitical tensions

Throughout this week, the Brent Crude price has experienced a decline of USD 3 per barrel, despite ongoing turmoil in the Middle East. Price fluctuations have ranged from highs of USD 91 per barrel at the beginning of the week to lows of USD 87 per barrel as of yesterday evening.

Following the release of yesterday’s US inventory report, Brent Crude once again demonstrated resilience against broader macroeconomic concerns, instead focusing on underlying market fundamentals.
Nevertheless, the recent drop in prices may come as somewhat surprising given the array of conflicting signals observed. Despite an increase in US inventories—a typically bearish indicator—we’ve also witnessed escalating tensions in the Middle East, coupled with the reinstatement of US sanctions on Venezuela. Furthermore, there are indications of impending sanctions on Iran in response to the recent attack on Israel.
Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen has indicated that new sanctions targeting Iran, particularly aimed at restricting its oil exports, could be announced as early as this week. As previously highlighted, we maintain the view that Iran’s oil exports remain vulnerable even without further escalation of the conflict. It appears that Israel is exerting pressure on its ally, the US, to impose stricter sanctions on Iran, an action that is unfolding before our eyes.
Iran’s current oil production stands at close to 3.2 million barrels per day. Considering additional condensate production of about 0.8 million barrels per day and subtracting domestic demand of roughly 1.8 million barrels per day, the net export of Iranian crude and condensate is approximately 2.2 million barrels per day.
However, the uncertainty surrounding the enforcement of such sanctions casts doubt on the likelihood of a complete ending of Iranian exports. Approximately 80% of Iran’s exports are directed to independent refineries in China, suggesting that US sanctions may have limited efficacy unless China complies. The prospect of China resisting US pressure on its oil imports from Iran poses a significant challenge to US sanctions enforcement efforts.
Furthermore, any shortfall resulting from sanctions could potentially be offset by other OPEC nations with spare capacity. Saudi Arabia and the UAE, for instance, can collectively produce an additional almost 3 million barrels of oil per day, although this remains a contingency measure.
In addition to developments related to Iran, the Biden administration has re-imposed restrictions on Venezuelan oil, marking the end of a six-month reprieve. This move is expected to impact flows from the South American nation.
Meanwhile, US crude inventories (excluding SPR holdings) surged by 2.7 million barrels last week (page 11 attached), reaching their highest level since June of last year. This increase coincided with a decline in measures of fuel demand (page 14 attached), underscoring a slightly weaker US market.
In summary, while geopolitical tensions persist and new rounds of sanctions are imposed, our market outlook remains intact. We maintain our forecast of an average Brent Crude price of USD 85 per barrel for the year 2024. In the short term, however, prices are expected to hover around the USD 90 per barrel mark as they navigate through geopolitical uncertainties and fundamental factors.
Analys
Brace for Covert Conflict

In the past two trading days, Brent Crude prices have fluctuated between highs of USD 92.2 per barrel and lows of USD 88.7 per barrel. Despite escalation tensions in the Middle East, oil prices have remained relatively stable over the past 24 hours. The recent barrage of rockets and drones in the region hasn’t significantly affected market sentiment regarding potential disruptions to oil supply. The key concern now is how Israel will respond: will it choose a strong retaliation to assert deterrence, risking wider regional instability, or will it revert to targeted strikes on Iran’s proxies in Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, and Iraq? While it’s too early to predict, one thing is clear: brace for increased volatility, uncertainty, and speculation.

Amidst these developments, the market continues to focus on current fundamentals rather than unfolding geopolitical risks. Despite Iran’s recent attack on Israel, oil prices have slid, reflecting a sideways or slightly bearish sentiment. This morning, oil prices stand at USD 90 per barrel, down 2.5% from Friday’s highs.
The attack
Iran’s launch of over 300 rockets and drones toward Israel marks the first direct assault from Iranian territory since 1991. However, the attack, announced well in advance, resulted in minimal damage as Israeli and allied forces intercepted nearly all projectiles. Hence, the damage inflicted was limited. The incident has prompted US President Joe Biden to urge Israel to exercise restraint, as part of broader efforts to de-escalate tensions in the Middle East.
Israel’s response remains uncertain as its war cabinet deliberates on potential courses of action. While the necessity of a response is acknowledged, the timing and magnitude remain undecided.
The attack was allegedly in retaliation for an Israeli airstrike on Iran’s consulate in Damascus, resulting in significant casualties, including a senior leader in the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’ elite Quds Force. It’s notable that this marks the first direct targeting of Israel from Iranian territory, setting the stage for heightened tensions between the two nations.
Despite the scale of the attack, the vast majority of Iranian projectiles were intercepted before reaching Israeli territory. However, a small number did land, causing minor damage to a military base in the southern region.
President Biden swiftly condemned Iran’s actions and pledged to coordinate a diplomatic response with leaders from the G7 nations. The US military’s rapid repositioning of assets in the region underscores the seriousness of the situation.
Iran’s willingness to escalate tensions further depends on Israel’s response, as indicated by General Mohammad Bagheri, chief of staff of the Iranian armed forces. Meanwhile, speculation about a retaliatory attack from Israel persists.
Looking ahead, key questions remain unanswered. Will Iran launch additional attacks? How will Israel respond, and what implications will it have for the region? Moreover, how will Iran’s allies react to the escalating tensions?
Given the potential for a full-scale war between Iran and Israel, concerns about its impact on global energy markets are growing. Both the United States and China have strong incentives to reduce tensions in the region, given the destabilizing effects of a regional conflict.
Our view in conclusion
The recent escalation between Iran and Israel underscores the delicate balance of power in the volatile Middle East. With tensions reaching unprecedented levels and the specter of further escalation looming, the potential for a full-blown conflict cannot be understated. The ramifications of such a scenario would be far-reaching and could have significant implications for regional stability and global security.
Turning to the oil market, there has been much speculation about the possibility of a full-scale blockade of the Strait of Hormuz in the event of further escalation. However, at present, such a scenario remains highly speculative. Nonetheless, it is crucial to note that Iran’s oil production and exports remain at risk even without further escalation. Currently producing close to 3.2 million barrels per day, Iran has significantly increased its production from mid-2020 levels of 1.9 million barrels per day.
In response to the recent attack, Israel may exert pressure on its ally, the US, to impose stricter sanctions on Iran. The enforcement of such sanctions, particularly on Iranian oil exports, could result in a loss of anywhere between 0.5 million to 1 million barrels per day of oil supply. This would likely keep the oil market in deficit for the remainder of the year, contradicting the Biden administration’s wish to maintain oil and gasoline prices at sustainable levels ahead of the election. While other OPEC nations have spare capacity, utilizing it would tighten the global oil market even further. Saudi Arabia and the UAE, for example, could collectively produce an additional almost 3 million barrels of oil per day if necessary.
Furthermore, both Iran and the US have expressed a desire to prevent further escalation. However, much depends on Israel’s response to the recent barrage of rockets. While Israel has historically refrained from responding violently to attacks (1991), the situation remains fluid. If Israel chooses not to respond forcefully, the US may be compelled to promise stronger enforcement of sanctions on Iranian oil exports. Consequently, Iranian oil exports are at risk, regardless of whether a wider confrontation ensues in the Middle East.
Analyzing the potential impact, approximately 2.2 million barrels per day of net Iranian crude and condensate exports could be at risk, factoring in Iranian domestic demand and condensate production. The effectiveness of US sanctions enforcement, however, remains uncertain, especially considering China’s stance on Iranian oil imports.
Despite these uncertainties, the market outlook remains cautiously optimistic for now, with Brent Crude expected to hover around the USD 90 per barrel mark in the near term. Navigating through geopolitical tensions and fundamental factors, the oil market continues to adapt to evolving conflicts in the Middle East and beyond.
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanGuldpriset når nytt all time high och bryter igenom 2300 USD
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuld toppar 2200 USD per uns
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanLundin Mining får köprekommendation av BMO
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanVertikal prisuppgång på kakao – priset toppar nu 9000 USD
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanKaffepriserna stiger på lågt utbud och stark efterfrågan
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanCentralbanker fortsatte att köpa guld under februari
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanHur mår den svenska skogsbraschen? Två favoritaktier
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanKakaomarknaden är extrem för tillfället