Analys
Iranian nuclear negotiations at center stage


Brent crude is trading like it is April with snow one day and sunshine the next. We currently have spring refinery maintenance with reduced processing of crude by refineries and rising crude stocks. The strength of the crude curve is weakening, floating crude stocks are rising, speculative positions in crude are taking some exit and Brent crude prices have been ticking lower. Gasoline refinery margins are however extremely strong and oil product demand is set to revive yet more in the months to come. Over the market however hangs a dark shadow of Iran nuclear negotiations in Vienna which if successful would add more crude to the market.

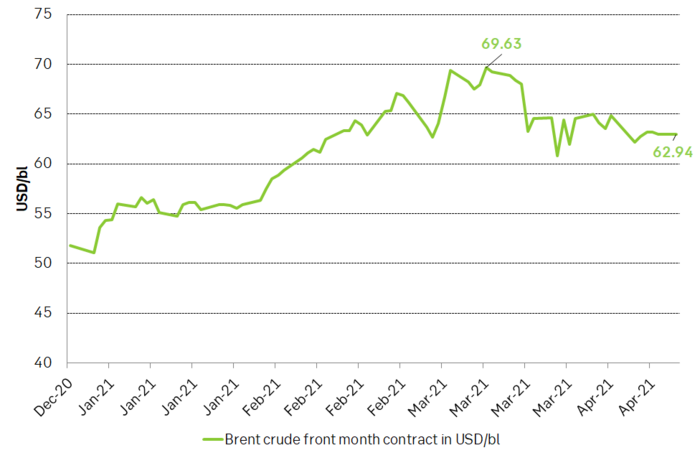
Brent crude traded down 2.9% last week with a close of USD 62.95/bl and is trading down another 0.5% this morning to USD 62.6/bl. Since 19 March Brent crude has averaged USD 63.4/bl. While currently not far from this average but in general it is clear that prices have been ticking lower since late March and still are.
Center stage in the oil market these days is the ongoing negotiations in Vienna where world powers are trying to revive the Iranian Nuclear deal (JCPOA) which Biden helped to create when he was Vice President under Obama. There is a lot of noise around the ongoing negotiations with a lot of crossing interests. Israel and Saudi Arabia probably both want Iran to be in constant lock-down rather than to revive. And the Iranian Revolutionary Gard might also want to see a continued status quo rather than a normalization and a reopening of the country as this might threaten its current grip on power. But fundamentally all parties in the negotiations in Vienna wants to see the JCPOA deal revived and reinstated. Thus, fundamentally the outcome should be successful in the end. When is of course a large open question with most observers predict a lengthy and difficult process with revival of Iranian production in late 2021 or into 2022. President Rouhani of Iran is however set to end his presidency in June this year with expectations that Iran’ hard-liners will take over which would make it more difficult to succeed. Thus, the window of opportunity might be quite narrow. And President Biden seems to want to undo all of Donald Trump’s deeds as quickly as possible. So sooner rather than later could be the outcome of the Vienna negotiations. But sitting far from Vienna this is hard to tell. But what is clear is that the ongoing Iranian nuclear negotiations in Vienna is posing a bearish risk for oil.
On the physical part of the crude oil market it is obvious that there is currently not a continued strong draw-down in crude stocks as we have seen previously, and which has underpinned the previously increasing Brent crude oil backwardation.
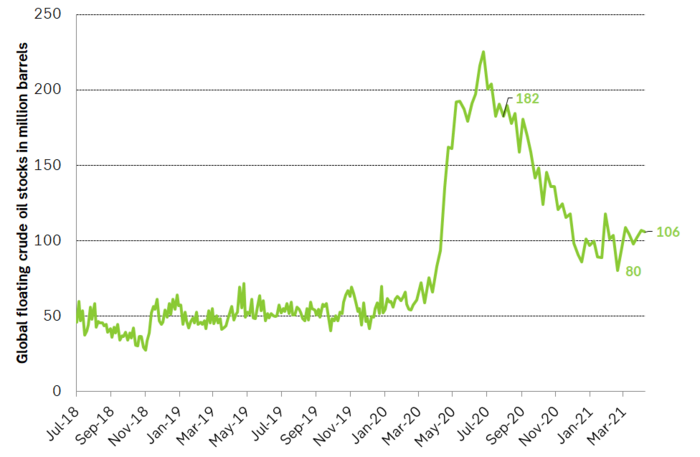
Refineries are currently in spring maintenance; Chinese crude stocks are reportedly very high and April/May refinery maintenance there is unusually strong this year as well. OPEC ME Gulf loadings rose 1.6 m bl/d month on month in March and OPEC+ production is set to rise further in May, June and July. Floating crude oil stocks have as a result of all this been ticking higher from a low of 80 m bl in February to now 106 m bl versus a normal of 50-60 m bl.
Parts of the weakness right now is clearly the refinery turnaround season in combination with further production increases lined up by OPEC+ in the months ahead (600, 700, 841 k bl/d for May, June, July).
But all is not grim, and the current crude oil weakness is clearly exacerbated by the ongoing refinery maintenance season.
If we instead look at the oil products, we see that US crude based products are only 1.5 m bl/d below the 2019 level. And US oil demand is set to revive more. Gasoline is being shipped from east of Suez to West Africa at the highest rate since 2016 and diesel is being shipped from Europe to the US in an unusual reverse flow.
So amid all the noise of Iran JCPOA negotiations, crude oil weakness, refinery maintenance it is easy to forget the broad, underlying fundamental here that vaccines are increasingly rolled out and product demand is on its way back in the US and a little later in the EU.
Brent crude oil prices have fallen back. Ticking lower since the recent fall from USD 69.63/bl. From recent high-close to to recent low-closes we have still spanned less than USD 10/bl. Normal pull-backs during price recoveries are typically USD 10-12/bl. Thus the pull-back is still not all that big.
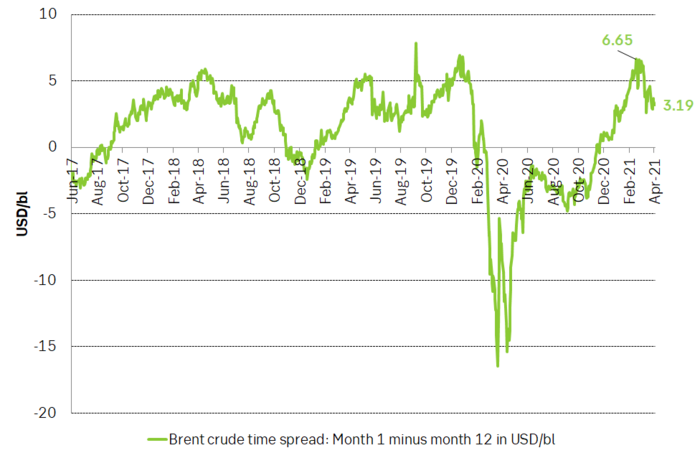
Backwardation of the Brent crude oil curve has consistently softened since late February when the front month contract traded at a premium of USD 6.6/bl vs the 12 months contract. It now trades at only USD 3.1/bl. In comparison this backwardation averaged USD 2.9/bl through 2018 and 2019. Thus, current backwardation is very normal though it is clearly on a weakening trend right now.
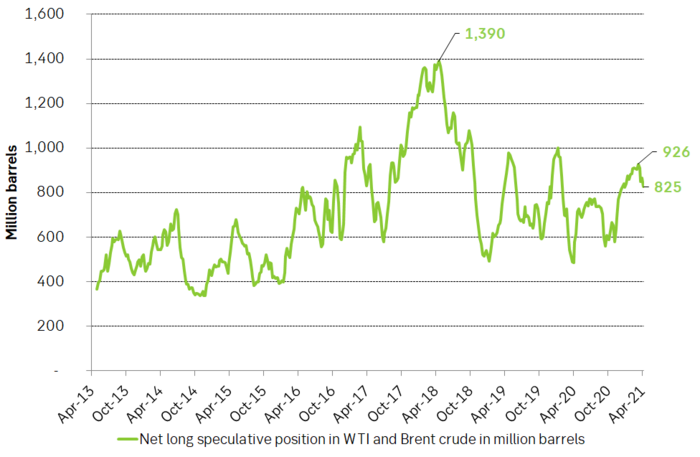
Net long speculative positions in Brent and WTI has declined about 100 m bl from 926 m bl in early March to now 825 m bl. In comparison the average position in 2019 was 733 m bl. Speculative positions are thus still some 100 m bl above this level and could draw down to below 600 m bl if speculators take more exits.
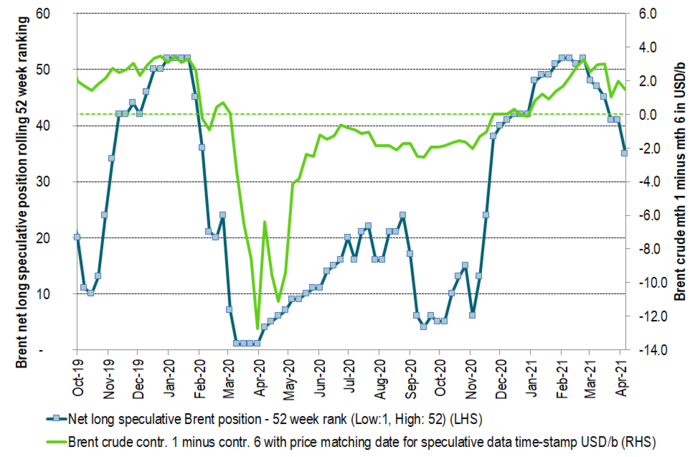
The time-spread of the Brent crude oil curve given as month 1 minus month 6 versus the ranking of net long speculative positions in Brent crude. The backwardation/contango of the Brent crude oil curve is not solely a reflection of the physical market. It is also a reflection of ebbs and flows of speculative positions. As these moves in and out of the front-end of the front-end contracts of the crude curve they typically drag front-end prices higher or lower versus longer dated contracts. Further speculative exits would weaken the Brent crude backwardation yet more (flatten the curve) with the front-end contract then moving closer to longer dated prices.
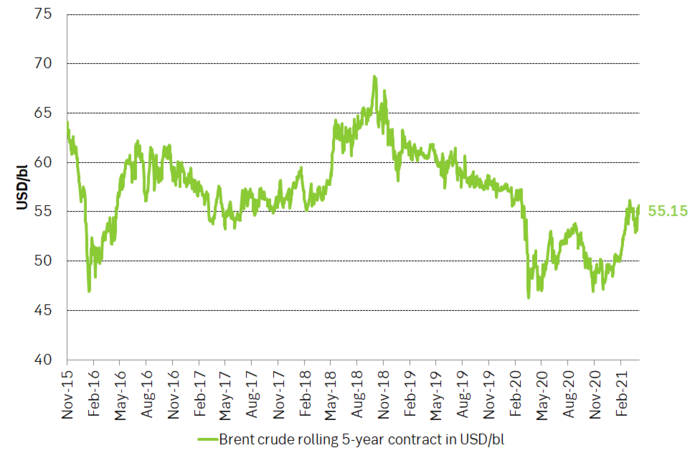
The 5-year Brent contract now trades at USD 55/bl which is just USD 3.5/bl below the average of the 5-year contract from Jan 2016 to Dec 2019 of USD 58.5/bl. Thus, longer dated Brent crude oil contracts are now very close to “normal” so to speak. In a total flattening of the Brent crude oil curve if crude stocks build more and speculative positions takes yet more exit the Brent crude prices would naturally decline to USD 55/bl where the longer dated contracts are located right now. Though this is not our main scenario it paints a picture of where Brent crude would naturally head if further bearishness unfolds. And in terms of price-pullbacks we have still not spanned a full USD 10/bl since the recent high close of USD 69.63/bl on 11 March. Pull-backs of USD 10-12/bl are normal during price recoveries.
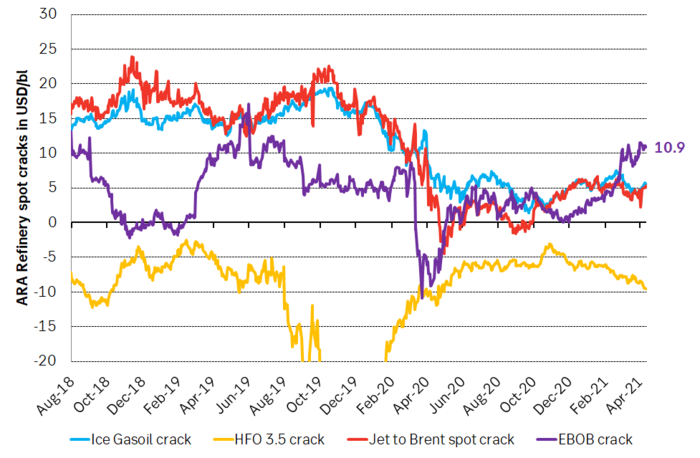
If we however look at oil products we see that gasoline refining margins are now USD 11/bl in Europe versus a more normal USD 5-6/bl. I.e. they are very strong. And with more to come. This reflects strengthening gasoline demand together with strong naphtha (for plastics) demand where both products are at the lighter end of the barrel. Diesel and middle distillate cracks are still weak versus normal as demand for jet fuel is still subdued. Fuel oil 3.5 cracks are weakening and reports are that floating stocks of 3.5% is building off the coast of Iraq as it struggles to process this part of the barrel. Increasing exports of medium sour crude from OPEC+ is also weakening this part of the complex while production of light sweet crude from the US is overall still ticking lower.
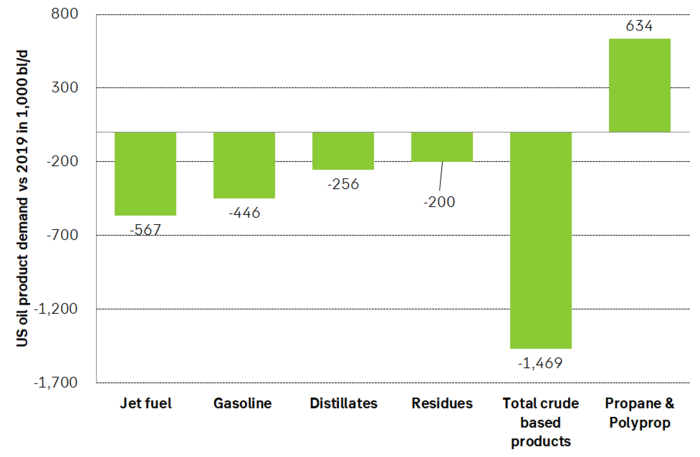
US oil product demand is now only 1.5 m bl/d below its 2019 level if we only count crude oil based products. And more demand is set to come back by the day as the US economy opens up over the coming 2 months. If we include propane and polypropylene then US product demand is already very close to normal.
Global, floating crude stocks have ticked higher from a low of 80 m barrels and now at 106 m barrels. Current refinery maintenance is part of this. The trend and the goal of OPEC+ was to move down to 50-60 million barrels (normal). But not yet.
US oil rig count did not rise last week and there is now an emerging difference between the activation of drilling rigs from June 2016 versus the one that started in September 2020. Will shale oil producers actually be true to their words that this time will be different and that they won’t spend all income on drilling and instead be prudent? This emerging picture is lending support to longer dated contracts for 2022/23/24
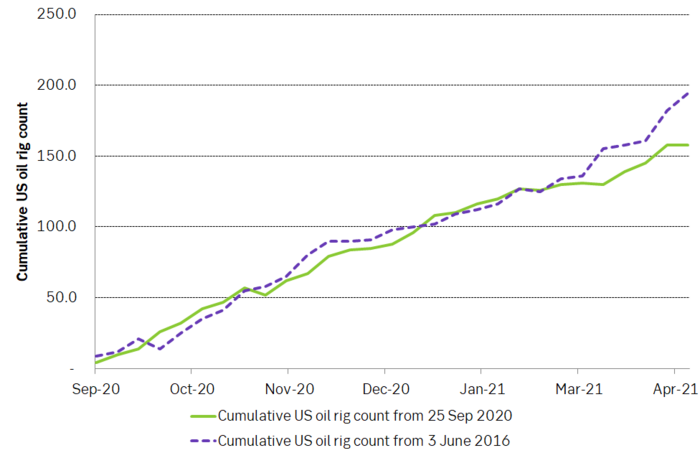
Source: SEB, Bloomberg
Analys
A sharp weakening at the core of the oil market: The Dubai curve

Down to the lowest since early May. Brent crude has fallen sharply the latest four days. It closed at USD 64.11/b yesterday which is the lowest since early May. It is staging a 1.3% rebound this morning along with gains in both equities and industrial metals with an added touch of support from a softer USD on top.

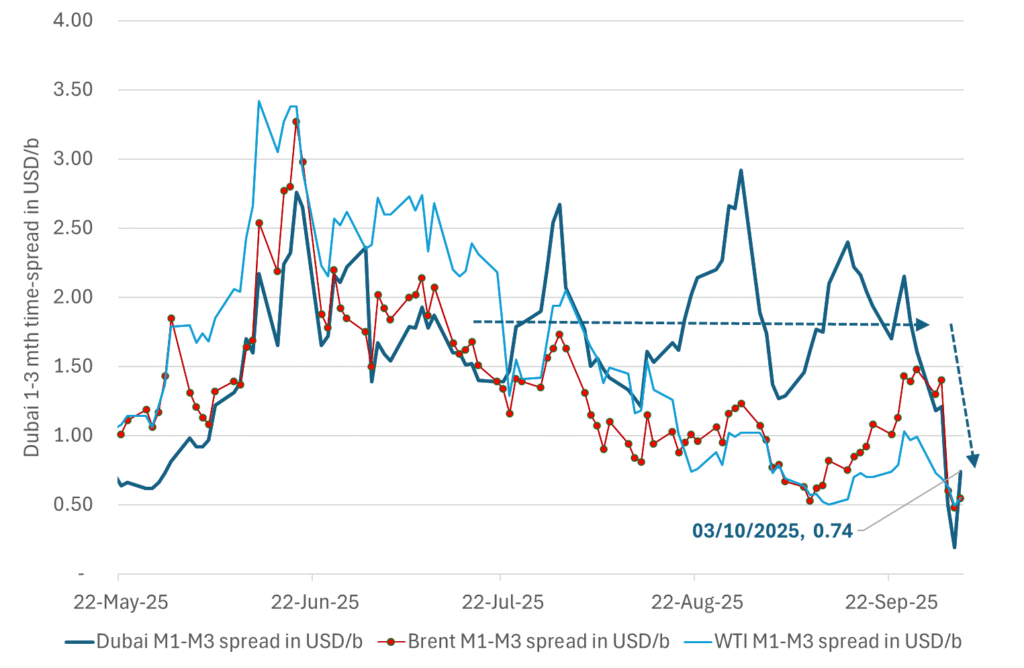
What stands out the most to us this week is the collapse in the Dubai one to three months time-spread.
Dubai is medium sour crude. OPEC+ is in general medium sour crude production. Asian refineries are predominantly designed to process medium sour crude. So Dubai is the real measure of the balance between OPEC+ holding back or not versus Asian oil demand for consumption and stock building.
A sharp weakening of the front-end of the Dubai curve. The front-end of the Dubai crude curve has been holding out very solidly throughout this summer while the front-end of the Brent and WTI curves have been steadily softening. But the strength in the Dubai curve in our view was carrying the crude oil market in general. A source of strength in the crude oil market. The core of the strength.
The now finally sharp decline of the front-end of the Dubai crude curve is thus a strong shift. Weakness in the Dubai crude marker is weakness in the core of the oil market. The core which has helped to hold the oil market elevated.
Facts supports the weakening. Add in facts of Iraq lifting production from Kurdistan through Turkey. Saudi Arabia lifting production to 10 mb/d in September (normal production level) and lifting exports as well as domestic demand for oil for power for air con is fading along with summer heat. Add also in counter seasonal rise in US crude and product stocks last week. US oil stocks usually decline by 1.3 mb/week this time of year. Last week they instead rose 6.4 mb/week (+7.2 mb if including SPR). Total US commercial oil stocks are now only 2.1 mb below the 2015-19 seasonal average. US oil stocks normally decline from now to Christmas. If they instead continue to rise, then it will be strongly counter seasonal rise and will create a very strong bearish pressure on oil prices.
Will OPEC+ lift its voluntary quotas by zero, 137 kb/d, 500 kb/d or 1.5 mb/d? On Sunday of course OPEC+ will decide on how much to unwind of the remaining 1.5 mb/d of voluntary quotas for November. Will it be 137 kb/d yet again as for October? Will it be 500 kb/d as was talked about earlier this week? Or will it be a full unwind in one go of 1.5 mb/d? We think most likely now it will be at least 500 kb/d and possibly a full unwind. We discussed this in a not earlier this week: ”500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d”
The strength in the front-end of the Dubai curve held out through summer while Brent and WTI curve structures weakened steadily. That core strength helped to keep flat crude oil prices elevated close to the 70-line. Now also the Dubai curve has given in.
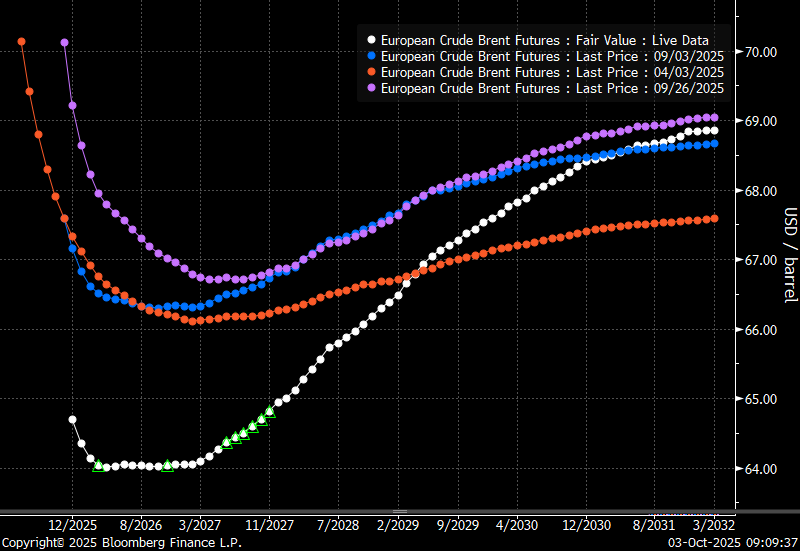
Brent crude oil forward curves
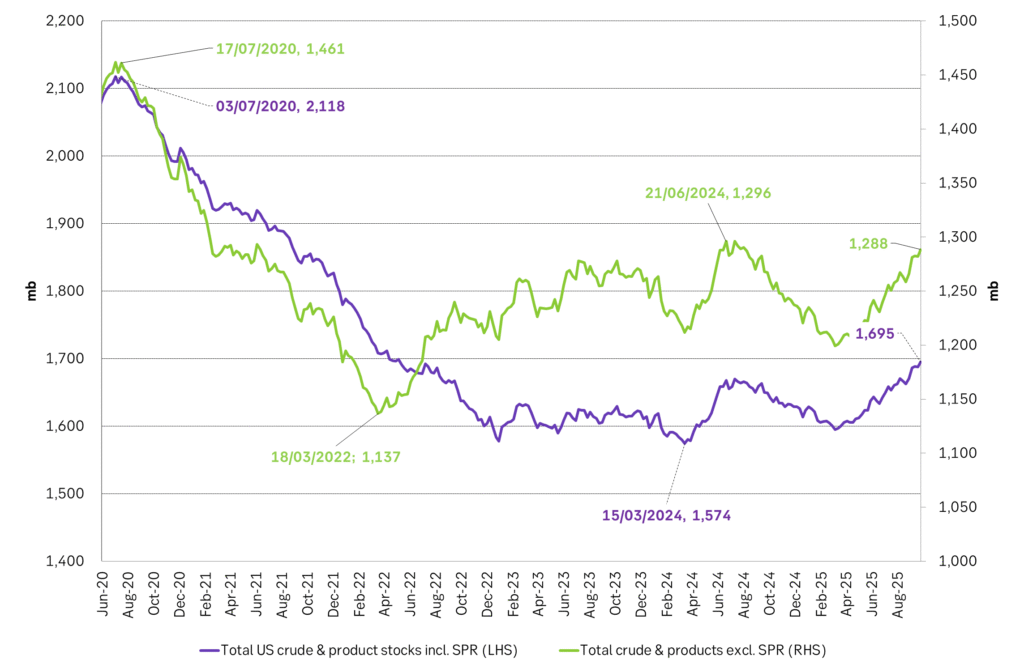
Total US commercial stocks now close to normal. Counter seasonal rise last week. Rest of year?
Total US crude and product stocks on a steady trend higher.
Analys
OPEC+ will likely unwind 500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d in one go could be in the cards

Down to mid-60ies as Iraq lifts production while Saudi may be tired of voluntary cut frugality. The Brent December contract dropped 1.6% yesterday to USD 66.03/b. This morning it is down another 0.3% to USD 65.8/b. The drop in the price came on the back of the combined news that Iraq has resumed 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan with exports through Turkey while OPEC+ delegates send signals that the group will unwind the remaining 1.65 mb/d (less the 137 kb/d in October) of voluntary cuts at a pace of 500 kb/d per month pace.

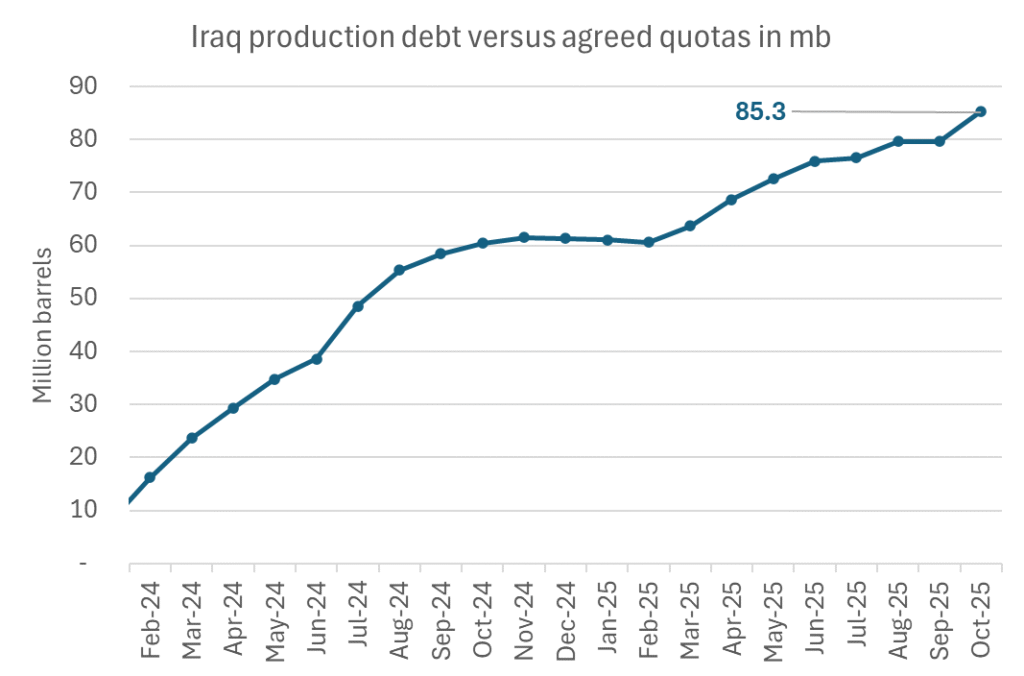
Signals of accelerated unwind and Iraqi increase may be connected. Russia, Kazakhstan and Iraq were main offenders versus the voluntary quotas they had agreed to follow. Russia had a production ’debt’ (cumulative overproduction versus quota) of close to 90 mb in March this year while Kazakhstan had a ’debt’ of about 60 mb and the same for Iraq. This apparently made Saudi Arabia angry this spring. Why should Saudi Arabia hold back if the other voluntary cutters were just freeriding? Thus the sudden rapid unwinding of voluntary cuts. That is at least one angle of explanations for the accelerated unwinding.
If the offenders with production debts then refrained from lifting production as the voluntary cuts were rapidly unwinded, then they could ’pay back’ their ’debts’ as they would under-produce versus the new and steadily higher quotas.
Forget about Kazakhstan. Its production was just too far above the quotas with no hope that the country would hold back production due to cross-ownership of oil assets by international oil companies. But Russia and Iraq should be able to do it.
Iraqi cumulative overproduction versus quotas could reach 85-90 mb in October. Iraq has however steadily continued to overproduce by 3-5 mb per month. In July its new and gradually higher quota came close to equal with a cumulative overproduction of only 0.6 mb that month. In August again however its production had an overshoot of 100 kb/d or 3.1 mb for the month. Its cumulative production debt had then risen to close to 80 mb. We don’t know for September yet. But looking at October we now know that its production will likely average close to 4.5 mb/d due to the revival of 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan. Its quota however will only be 4.24 mb/d. Its overproduction in October will thus likely be around 250 kb/d above its quota with its production debt rising another 7-8 mb to a total of close to 90 mb.
Again, why should Saudi Arabia be frugal while Iraq is freeriding. Better to get rid of the voluntary quotas as quickly as possible and then start all over with clean sheets.
Unwinding the remaining 1.513 mb/d in one go in October? If OPEC+ unwinds the remaining 1.513 mb/d of voluntary cuts in one big go in October, then Iraq’s quota will be around 4.4 mb/d for October versus its likely production of close to 4.5 mb/d for the coming month..
OPEC+ should thus unwind the remaining 1.513 mb/d (1.65 – 0.137 mb/d) in one go for October in order for the quota of Iraq to be able to keep track with Iraq’s actual production increase.
October 5 will show how it plays out. But a quota unwind of at least 500 kb/d for Oct seems likely. An overall increase of at least 500 kb/d in the voluntary quota for October looks likely. But it could be the whole 1.513 mb/d in one go. If the increase in the quota is ’only’ 500 kb/d then Iraqi cumulative production will still rise by 5.7 mb to a total of 85 mb in October.
Iraqi production debt versus quotas will likely rise by 5.7 mb in October if OPEC+ only lifts the overall quota by 500 kb/d in October. Here assuming historical production debt did not rise in September. That Iraq lifts its production by 190 kb/d in October to 4.47 mb/d (August level + 190 kb/d) and that OPEC+ unwinds 500 kb/d of the remining quotas in October when they decide on this on 5 October.
Analys
Modest draws, flat demand, and diesel back in focus

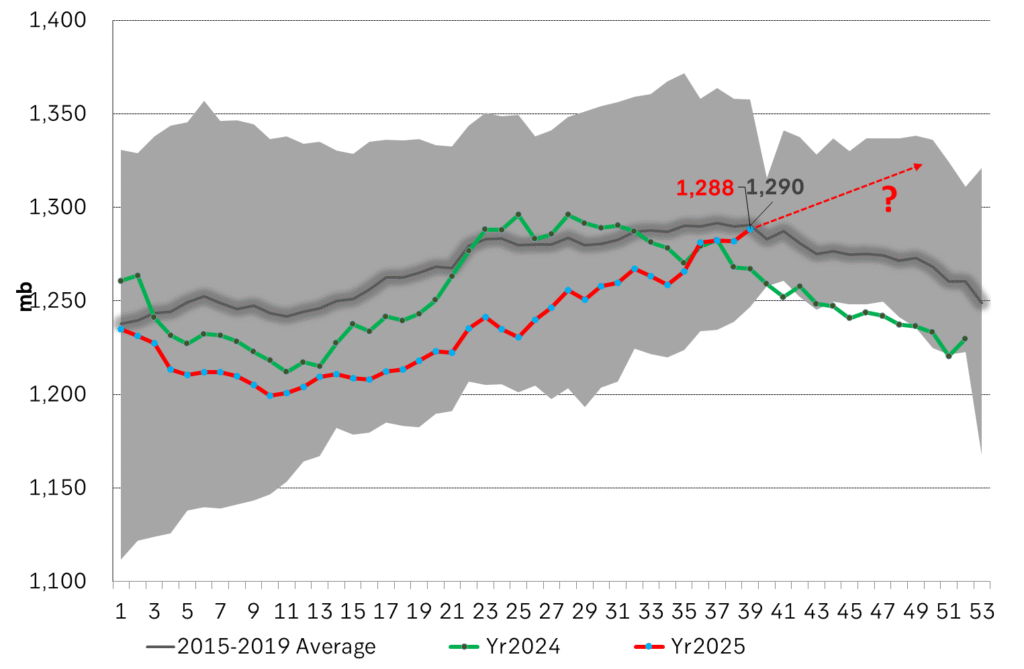
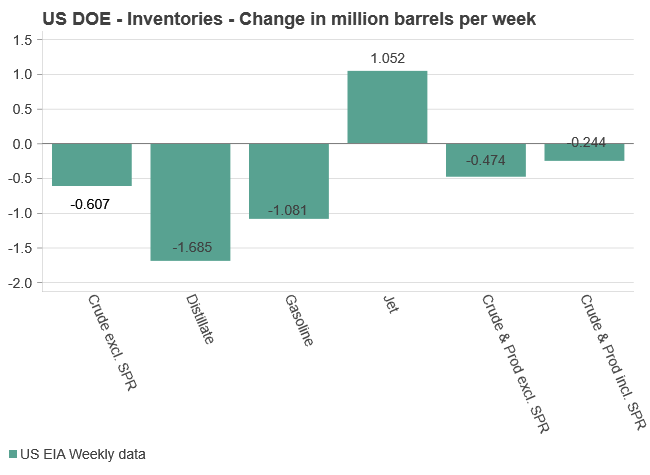
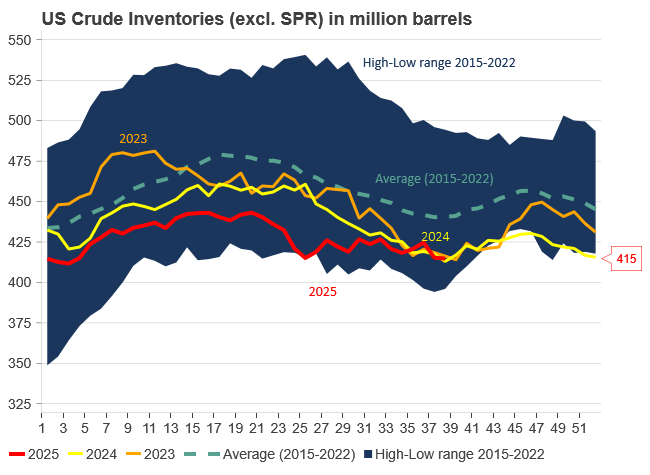
U.S. commercial crude inventories posted a marginal draw last week, falling by 0.6 million barrels to 414.8 million barrels. Inventories remain 4% below the five-year seasonal average, but the draw is far smaller than last week’s massive 9.3-million-barrel decline. Higher crude imports (+803,000 bl d WoW) and steady refinery runs (93% utilization) helped keep the crude balance relatively neutral.

Yet another drawdown indicates commercial crude inventories continue to trend below the 2015–2022 seasonal norm (~440 million barrels), though at 414.8 million barrels, levels are now almost exactly in line with both the 2023 and 2024 trajectory, suggesting stable YoY conditions (see page 3 attached).
Gasoline inventories dropped by 1.1 million barrels and are now 2% below the five-year average. The decline was broad-based, with both finished gasoline and blending components falling, indicating lower output and resilient end-user demand as we enter the shoulder season post-summer (see page 6 attached).
On the diesel side, distillate inventories declined by 1.7 million barrels, snapping a two-week streak of strong builds. At 125 million barrels, diesel inventories are once again 8% below the five-year average and trending near the low end of the historical range.
In total, commercial petroleum inventories (excl. SPR) slipped by 0.5 million barrels on the week to ish 1,281.5 million barrels. While essentially flat, this ends a two-week streak of meaningful builds, reflecting a return to a slightly tighter situation.
On the demand side, the DOE’s ‘products supplied’ metric (see page 6 attached), a proxy for implied consumption, softened slightly. Total demand for crude oil over the past four weeks averaged 20.5 million barrels per day, up just 0.9% YoY.
Summing up: This week’s report shows a re-tightening in diesel supply and modest draws across the board, while demand growth is beginning to flatten. Inventories remain structurally low, but the tone is less bullish than in recent weeks.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanEurobattery Minerals satsar på kritiska metaller för Europas självförsörjning
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals i en guldtrend
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuldpriset kan närma sig 5000 USD om centralbankens oberoende skadas
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanOPEC signalerar att de inte bryr sig om oljepriset faller kommande månader
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanVolatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk
-
 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
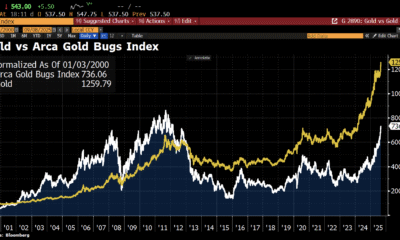
Nyheter3 veckor sedanAktier i guldbolag laggar priset på guld
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanKinas elproduktion slog nytt rekord i augusti, vilket även kolkraft gjorde
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanTyskland har så höga elpriser att företag inte har råd att använda elektricitet






