Analys
A two currency oil market

 China today launched its long awaited yuan denominated oil contract at the International Energy Exchange (INE) in Shanghai. Seven crude streams from UAE, Qatar, Oman, Yemen Iraq and China will define the pricing of the contract. There is substantial scepticism towards the contract. Most of the sceptical arguments will in our view dissipate over time as rules, regulations and capital controls are adapted and adjusted as time goes by. The Chinese government likely has plenty of leverage to make the contract a success making it into an Asian oil benchmark representing a vibrant and growing oil demand which today accounts for 27% of global demand.
China today launched its long awaited yuan denominated oil contract at the International Energy Exchange (INE) in Shanghai. Seven crude streams from UAE, Qatar, Oman, Yemen Iraq and China will define the pricing of the contract. There is substantial scepticism towards the contract. Most of the sceptical arguments will in our view dissipate over time as rules, regulations and capital controls are adapted and adjusted as time goes by. The Chinese government likely has plenty of leverage to make the contract a success making it into an Asian oil benchmark representing a vibrant and growing oil demand which today accounts for 27% of global demand.
The launch of the contract will open up for international participation in China’s commodity market for the first time. International oil players will need to hold renminbi books reflecting an oil market which here onwards will roll on two currency wheels.
The rapidly rising risk that Donald, Mike and John will tear up the current Iranian nuclear deal in mid-May makes it likely that Iran will accept crude oil settlement in renminbi in not too long in order to avert the risk of renewed dollar sanctions which it experienced so painfully from 2012 to 2015.
Price action: Brent jumps while equities fall as Venezuela and Iran supply risk increases on John Bolton
The front month Brent crude oil contract jumped 2.2% on Friday to $70.45/bl on news that John Bolton was replacing Lt. Gen. H:R: McMaster as the US national security advisor. John Bolton is known to be abrasive, undiplomatic, deeply conservative and nationalistic with hawkish views on Iran and North Korea. As such he matches both Donald Trump and his new secretary of state Mike Pompeo. It is now difficult to see how the Iran Nuclear deal can survive beyond mid-May when a new round of US waivers is needed to carry the deal forward yet another quarter, unless of course the deal is significantly re-worked. Apparently however the non-US signatories to the Iran nuclear deal are still in the dark with respect to what and how Donald Trump want’s the deal to be re-written. The May waiver deadline is approaching rapidly and as far as we know there is no real work in progress in order to re-work the deal. The appointment of John Bolton also increases the risk for sanctions towards Venezuela. Venezuela’s oil production and export is already in free fall but hanging on a thread by US refineries who are supplying Venezuela with naphtha in exchange of heavy crude oil. Venezuela would not be able to export much oil without the naphtha or light crude which is critical for diluting its heavy crude to a quality which is exportable. Thus US oil sanctions towards Venezuela would cut the last thread.
A two currency oil market
After years and years of waiting the Chinese Yuan denominated oil contract quoted at the Shanghai International Energy Exchange (INE) is finally here. China did try to launch an oil futures contract back in 1993 but it basically blew up due to uncontrollable price volatility. This time around China has taken good time to prepare the launch of its new oil contract in order to make sure that there is no second round flop like in 1993. China last year became the world’s top oil importer with an average import of 8.4 m bl/d. At the same time it is also the world’s sixth biggest oil producer with an average production last year of 3.8 m bl/d.
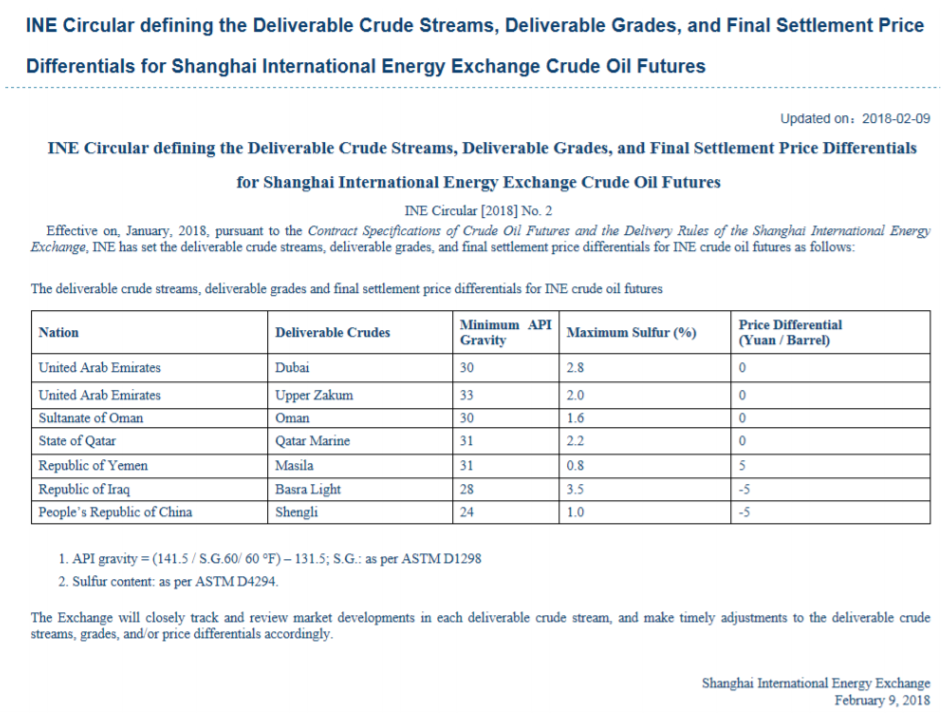
Seven crude streams in the INE contract with characteristics close to the Dubai crude slate
Seven deliverable crude streams in Shanghai will be used to settle the INE crude oil contract. They originate from UAE, Oman, Qatar, Yemen and China itself. The crude streams are distinctly different from the light, sweet crude benchmarks of Brent crude and WTI. The INE crude streams are on average (across the different grades) required to have an API gravity of more than 29.6 and a sulphur content of less than 2%. In comparison the WTI benchmark is very light with an API of 39.6 and only about 0.24% sulphur. As such the INE benchmark is distinctly different from both Brent crude and WTI. It is however very close to the Dubai crude oil marker which has an API of 31 and a sulphur content of 2%. As such one could say that the INE contract is the Dubai marker in Asia quoted in renminbi.
The new INE contract could be a representation of 27 m bl/d of vibrant Asian oil demand
The new Chinese oil contract will likely over time come to represent Asian oil demand in general. In 2018 Asian demand is set to average 27 m bl/d (IEA) or 27% of global consumption. It has been argued that the new benchmark will be a bad price hedge for oil deliveries in other places in Asia than Shanghai. This is based on the assumption that the oil price fundamentally is set either in the US (WTI), in the Gulf (Dubai marker) or in Europe (Brent). And as such it should mathematically be better to hedge with one of these three price points rather than the new Chinese INE contract. However, if the driver of the global oil market and thus oil price dynamics is instead really set by the vibrant oil demand in Asia rather than the three mentioned oil price benchmarks then it would clearly be better to hedge with the INE contract.
In our view the new INE contract is not an effort to replace the existing global crude oil benchmarks. It is instead filling a needed vacuum in the global oil market: A marker for the Asian market. It has been argued that the existing crude benchmarks are successful since they are located at hubs with both large production and consumption. But this is also actually true for the new benchmark with China being the sixth largest oil producer in the world as well as the biggest oil importer in the world.
The INE contract has several disadvantages but these are likely to dissipate over time
To start with the INE contract seems to have several disadvantages. It will have limited trading hours with the last trading slot ending at 0700 am GMT and thus just before the London market opens. The Chinese government has also set crude oil storage costs at twice the global average level in order to avoid excessive price volatility due from potential games between the physical market and the new INE contract. Such high storage costs will be negative for the necessary interplay and price discovery between the local physical market (derived from storage economics) and the INE financial instruments. Another reason for the very high storage cost may be to avoid commodity storage games used for shadow financing and circumvention of capital controls which has flourished for other commodities traded in China. The quotation of the INE contract in renminbi will also be a negative as seen by most current oil market participants in the current dollar dominated oil market. And lastly Chinese capital controls and unpredictable regulations will also be a concern for many potential participants.
Many of these negatives will however dissipate over time. Trading hours will expand, storage costs will normalize, general capital controls will ease and rules and regulations will stabilize. And lastly the renminbi will be more and more accepted currency world-wide. The Chinese government does have time to adjust and the current mode of the INE market is launch phase with some trail and error. The front month INE contract is actually the September 2018 contract allowing plenty of time for adjustment. So we do not think that one should judge the contract in the early phase on the many negative traits which have been highlighted.
Plenty of participants ready to transact – Open interest will be the measure of success
More than 6,000 trading accounts have been opened for the INE contract including China’s largest oil companies and 150 brokerage firms. Larger foreign financial institutions like J.P.Morgan have also opened accounts. To further attract foreign participants the Chinese Government has waived income taxes for foreign investors for the first three years. An addition attraction of the INE oil contract is that it will be the first time foreigners will be able to trade commodities in China.
We agree that over time it will be the size of the number of open contracts and not turnover per se which will be the sign of success for the contract. So the open interest in the INE contract will be the parameter to watch. It will be the fingerprint showing that the INE contract fills a need and is actively used as a hedging tool.
The Chinese government has power to tilt the market towards the new contract
The Chinese government has a lot of power in order to ensure that the INE contract becomes a success with widespread use. The easy way is of course to demand that all domestic crude oil purchasing is done with settlement versus the INE contract benchmark. In that way any oil producer who would like to sell oil to China would have to accept the INE contract and settlement in renminbi. China could of course also lean on the countries who cooperate with China on the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) with six major infrastructure projects in overdrive this year. Asking the involved countries in these BRI projects to use or support the new INE oil contract could be a natural request.
We think that the launch of the INE contract in China is a natural development reflecting that China is the world’s top oil importer, the sixth largest oil producer and a natural benchmark for oil prices in Asia. However, essentially what it all boils down to is that China wants to be able to purchase its oil in renminbi. There are several countries already on-board: Russia, Venezuela, Nigeria and Angola are all already selling oil to China in renminbi. We assume that UAE, Oman, Qatar, Yemen and Iraq also are accepting renminbi as payment for crude delivered to China since six of the seven crude streams in the INE contract originates from them.
No Iranian crude slates in the INE contract yet but Iran should be a natural participant
It is surprising to see that there are no crude oil streams from Iran in the new INE contract. The Iran Heavy crude stream with API = 30.2 and Sulphur = 1.8% should be a natural match the INE crude slate profile.
Iran is one of the countries which have been heavily hit by the weaponized USD. In 2012 the US applied pressure through the SWIFT system. It blocked clearing for every Iranian bank, froze $100 billion of Iranian assets which together with other measures helped to block Iranian oil exports which roughly dropped 1 m bl/d due to this.
US pressure is building up against the Iran nuclear deal – should naturally drive Iran towards the INE contract
Now pressure is rising rapidly towards Iran. In the US forces are gathering to tear apart the Iran nuclear deal with the recent appointment of Mike Pompeo as US secretary of state and John Bolton as the US national security advisor. Donald Trump together with these two now looks ready to tear apart the current Iran nuclear deal as waivers are up for renewal in mid-May. The Saudi crown prince Mohammed bin Salman also seemed to apply pressure against Iran at his meeting with Donald Trump. Thus Saudi Arabia seems like it is sticking with the US while Iran, Iraq, Oman, UAE, Qatar and Yemen are drifting over towards China. China and the US are at the same time drifting apart amid increasing trade tensions with political tensions in the South China Sea being the icing on the cake so to speak. It seems highly plausible in our view that Iran in not too long with explicitly state that they also accept payment in renminbi for oil sales to China.
Saudi Arabia however seems for the time being to stick even tighter to the dollar-oil deal which the House of Saud presumably struck with Nixon and Kissinger back in 1974 in exchange for protection and geopolitical support.
Crude slates in the INE contract
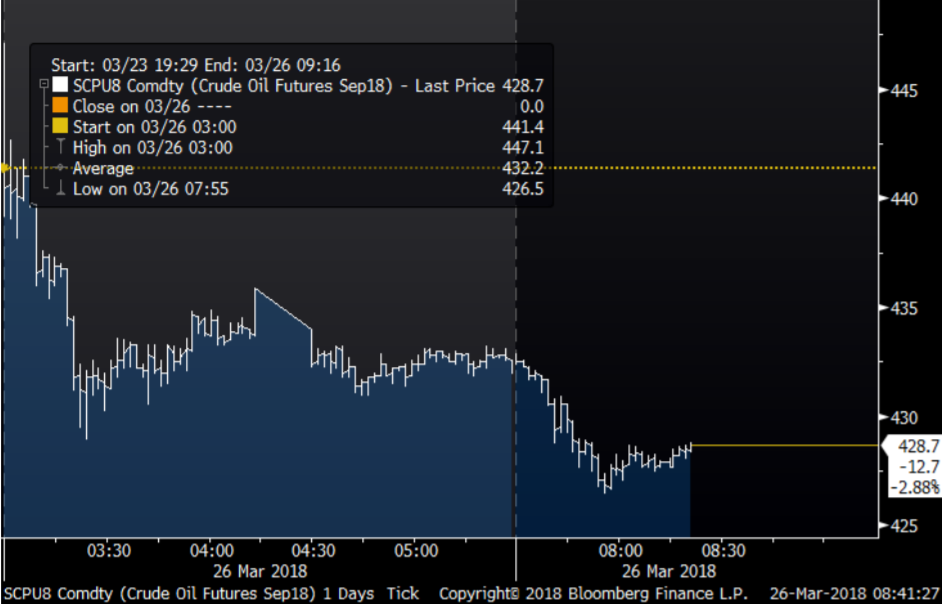
Ch1: Yes, the INE September contract started to trade first time on 26 March 2018
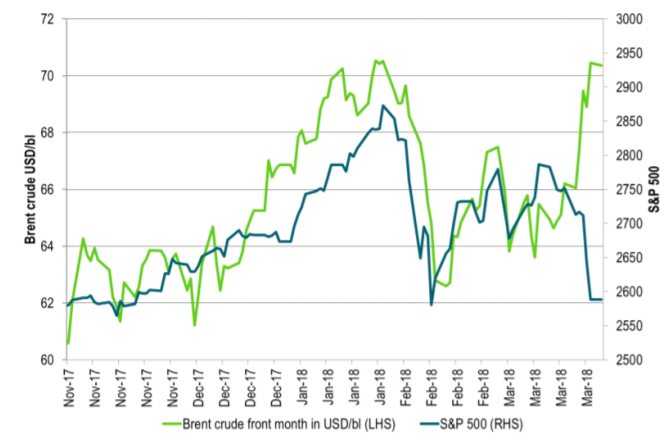
Ch2: Brent crude went opposite of equities last week
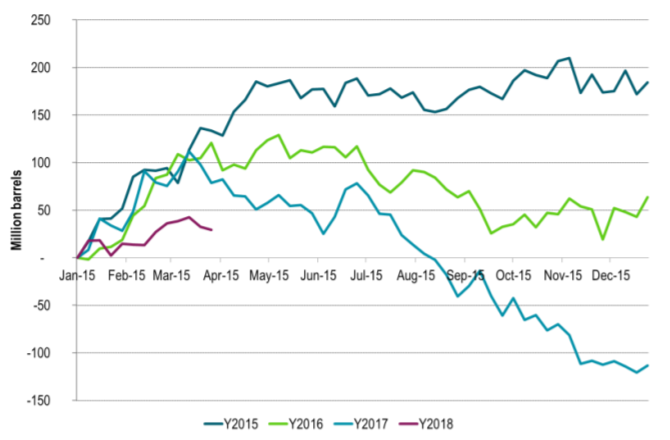
Ch3: Weekly US, EU, Singapore and Floating stocks lower 2nd week
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

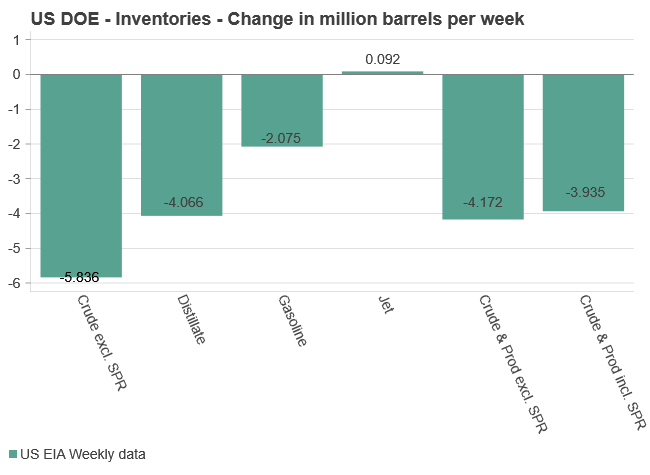
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

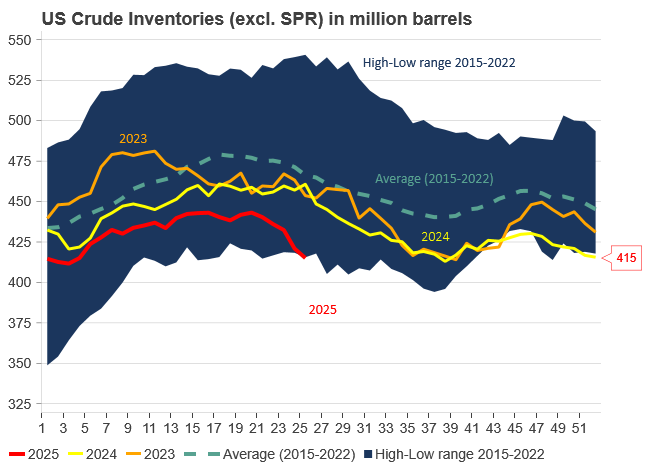
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanOljan, guldet och marknadens oroande tystnad
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanJonas Lindvall är tillbaka med ett nytt oljebolag, Perthro, som ska börsnoteras
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanA muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanDomstolen ger klartecken till Lappland Guldprospektering