Analys
Getting to zero, getting the job done


Politicians have been talking and talking for decades but with only marginal improvements in terms of emission reductions. Primarily because actually doing the job has earlier been technologically and economically almost impossible. Now suddenly renewable energy has come of age with prices set to decline yet further. And onshore transportation can soon be electrified cost efficiently. For politicians there is now a viable path. It is still a large task but now it is more and more about just getting the job done. In rough terms some € 150 – 250 bn per year to 2050 is probably needed to build EU’s new power system.

In 2019 the EU + UK consumed 15,000 worth of fossil fuels. It all needs to be gone by 2050. In 2019 the EU + UK produced 3,200 TWh of electricity of which 1,295 TWh (40%) was fossil fuel based. Thus 60% of the power supply is already non-fossil. However, if we look at the larger picture of energy we see that the region consumed nearly 15,000 TWh of raw (evaluated pre-combustion) fossil fuels that year of which only 3,000 TWh was used for power. The remaining 12,000 TWh of fossil fuel consumption was consumed for heat, transportation, petrochemical and industrial uses. I.e. the lion’s share of fossil fuel consumption in the region is non-power related.
Thus getting to zero by 2050 is far more than swapping out of the 3,000 TWh of fossil fuels (pre-combustion) used for power supply today which post combustion creates 40% and 1,295 TWh of the regions electricity supply. The challenge is also about replacing the other 12,000 TWh of fossil energy for non-power uses.
As most know the conversion of fossil fuels to useful energy and work done is highly inefficient. In cars one rarely get more than 30% of the energy converted to useful driving with the rest just lost as heat. In large, power plants the conversion ratio is usually around 35% to 55% but mostly below 50%. Gas for heating purposes is of course highly efficient as almost all of it naturally is converted to heat.
The region is now aiming to go green by 2050 and that mostly means going electric. This again means that some 15,000 TWh of fossil energy spent today needs to be replaced by non-fossil based electricity. Given the highly inefficient burn of fossil energy to useful work it is no surprise that we don’t need the same amount of electricity output to replace it but rather something like only 30% to 50% as much.
When it comes to synthetically generated “electric fuels” (power to liquids or hydrogen) we are talking about an up to 200% replacement ratio because up to 50% of the electricity is lost in the conversion of power to liquids. But for most other purposes like electrifying transportation and replacing the burning of fossil fuels for power etc. the replacement ratio is often more like 30% to 50%. When it comes to replacing gas for heating purposes it is a one-to-one replacement.
In our calculations the region is going to need 6,731 TWh of new non-fossil based electricity by 2050 in order to replace the 15,000 TWh worth (pre-combustion) of fossil energy spent today. I.e. a replacement ratio of 46%. It is thus good news that we don’t need at total of 15,000 TWh of new non-fossil based power supply by 2050 but instead “only” 6,731 TWh.
This replacement is still huge! In comparison the supply of electricity in 2019 was 3,200 TWh (including fossil based power). I.e. the region needs to build its total power supply of today more than two times over by 2050 and at that point in time reach a total power supply of 8,574 TWh.
If we equate the challenge to the number of nuclear power units needed to cover it we are talking 570 new nuclear power units each of 1,500 MW capacity. In 2013 there were 131 operational nuclear power plants and today we are probably closer to 110. Thus to do the job by nuclear we need to increase nuclear power by more than 500% by 2050.
While the job is challenging it is by no means impossible. If we take the new UK Hinkley nuclear power plant as an example in terms of capex we have the following. It will generate about 25 TWh of electricity per year and cost about € 27 bn to build. I.e. €1.1 bn for a 1 TWh/year supply rate. Multiply by the needed 6,731 TWh/year of new power supply by 2050 and we get a needed capex € 7,147 bn in total which again equates to € 238 bn/yr over the next 30 years. Nuclear power is today considered to be a quite expensive source of new electricity with renewable energy often being significantly cheaper (up to 50% cheaper) though not providing baseload supply and rather intermittent supply.
Capex spending in the EU + UK should be in the ball-park of € 150 – 250 bn per year or 1.3% of GDP. Capex spending on new power supply over the coming 30 years should probably be in the ball-park of $ 150 – 250bn/year. And then some additional investments for a lot of infrastructure adaptation. EU and UK thus needs to spend some 1.3% of its GDP per year for the energy transition (€ 238 bn/yr divided by GDP of € 18,292 bn in 2019). But that of course assumes that there is no further declines in the cost of new renewable energy which by most measures is projected to continue to fall year by year. And going electric in the transportation sector (on land) will in not too long be a pure net saving as electric cars becomes cheaper than fossil cars while electric cars are also much more energy efficient than fossil cars.
The example of nuclear energy is for simplicity purposes. It is not in the cards at all today that the region is going big-time nuclear. The direction is rather much more renewable energy.
On the table we already have a pledge of 2,100 TWh/year of offshore wind by 2050. On the drawing table we already have an announced build-out of 300 GW of new offshore wind by the EU and 100 GW of offshore wind by the UK. Both by 2050. What does that mean? At a 60% offshore wind utilization ratio this equates to 2,100 TWh/year of new power supply by 2050. Thus already today a total of 31% of the new, needed 6,731 TWh by 2050 is firmly on the drawing table.
For many decades there has been endless political discussions about climate change. As a result we have moved a little forward but not all that much. We have gotten the European emission trading scheme (EU ETS) which is good and where we now have a decent carbon price of € 42/ton which starts to matter and where abatement (carbon reductions) is happening on the margin.
We have now come to the point where it is all bout getting the job done. To actually build what needs to be replaced. However, we have now gotten to the point of crunch-time. The time to act. The time to start the real change. Now it is about figuring out how to get to zero by 2050. Now it is all about getting the job done for real. Our sense is that thousands of engineers across Europe today suddenly are mapping out detailed plans of what we actually need to do to get there. It is not easy. It does not happen by itself. But it is absolutely doable and it will require some €150 – 250/bn per year in capex spending on new non-fossil based power supply over the next 30 years. But probably less than that as the cost of renewable energy continues to decline.
The region is not going to get to zero by 2050 by marginal abatement in the EU ETS emission system. The region is going to get there by outright building the alternative and then increasingly retiring the current system. And what it looks like already is that offshore wind is going to be a major part of the solution with plans already in place to solve 30% of the challenge.
IEA estimated in a report from 2019 that technical offshore wind power resources in Europe is 60,000 TWh worth of power supply. That is almost 10 times as much as what is needed to solve EU + UK’s goal of zero emissions by 2050. And as stated above the two have already committed to build 2,100 TWh/year of offshore wind power supply by 2050. So on the drawing table we are already one third of the way.
Norway is not really on the map here yet but it could easily offer to build 2,000 TWh of offshore wind power supply if EU agreed to buy it and pay for it at an agreeable price. If so this would lead to a real offshore wind bonanza over the coming 30 years equal to the build-out of the oil and gas on the NCS.
The EU + UK needs to kick the habit of consuming close to 15,000 TWh worth of fossil fuels per year by 2050 (evaluated pre-combustion). The replacement is going to happen by building the alternative and governments will be involved big-time to get it done. The current power supply for the region needs to be build more than two times over by 2050 to get the job done.
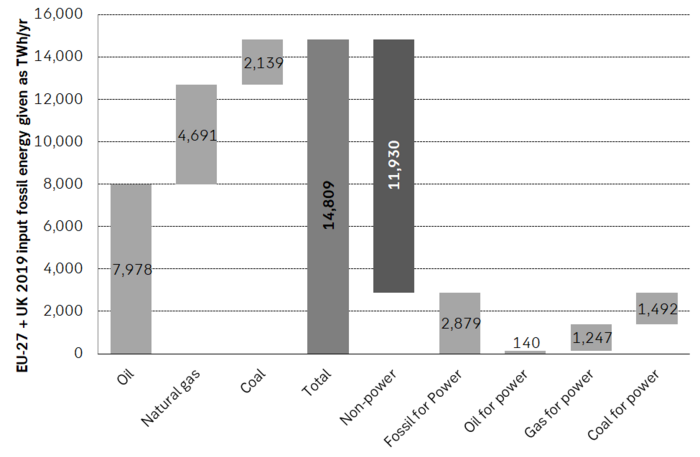
The EU + UK produced a total of 3,200 TWh of power in 2019 of which 1,295 TWh (40%) was generated by fossil fuels. In total the EU + UK will need 6,731 TWh of new non-fossil based power supply by 2050 in order to kick 15,000 worth of fossil fuels (evaluated pre-combustion) out the door. At that point total power supply in the region needs to be 8,574 TWh/year in order for the region to go green. Of the 6,731 TWh of new non-fossil power needed we already have a pledge by the EU and the UK together of 2,100 TWh of new offshore wind power supply by 2050. Thus 31% of the power needed to go fully green by 2050 is already pledged for through offshore wind. In the following graph ”EU” is short of ”EU+UK” for the sake of abbreviation.

The following graph shows how much new non-emitting power supply the EU + UK needs for each sector to go electric and green by 2050. Today’s consumption of 15,000 TWh (pre-combustion) is mostly outside of the power sector. Some 1,900 TWh of current power supply can be kept for the future as it is non-emitting like nuclear, wind and other renewables. Total non-emitting power supply in the region needs to be 8,574 TWh by 2050 in order to go green.
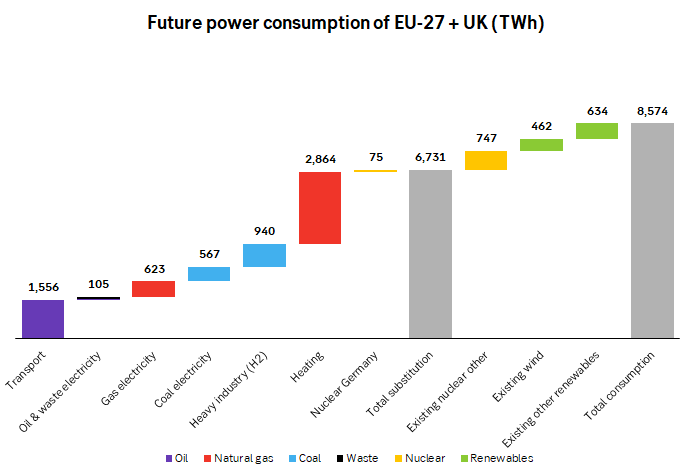
Technical offshore wind potential in Europe is close to 60,000 TWh per year according to a recent report by the IEA published in November 2019. Almost 10x of what the EU + UK needs to go fully green by 2050. And much of the capacity is in the North Sea between the UK and Norway.
Analys
Manufacturing PMIs ticking higher lends support to both copper and oil

Price action contained withing USD 2/b last week. Likely muted today as well with US closed. The Brent November contract is the new front-month contract as of today. It traded in a range of USD 66.37-68.49/b and closed the week up a mere 0.4% at USD 67.48/b. US oil inventory data didn’t make much of an impact on the Brent price last week as it is totally normal for US crude stocks to decline 2.4 mb/d this time of year as data showed. This morning Brent is up a meager 0.5% to USD 67.8/b. It is US Labor day today with US markets closed. Today’s price action is likely going to be muted due to that.

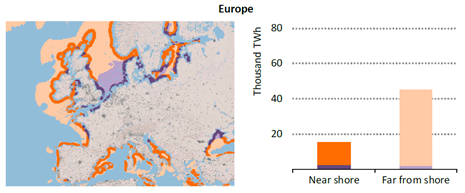
Improving manufacturing readings. China’s manufacturing PMI for August came in at 49.4 versus 49.3 for July. A marginal improvement. The total PMI index ticked up to 50.5 from 50.2 with non-manufacturing also helping it higher. The HCOB Eurozone manufacturing PMI was a disastrous 45.1 last December, but has since then been on a one-way street upwards to its current 50.5 for August. The S&P US manufacturing index jumped to 53.3 in August which was the highest since 2022 (US ISM manufacturing tomorrow). India manufacturing PMI rose further and to 59.3 for August which is the highest since at least 2022.
Are we in for global manufacturing expansion? Would help to explain copper at 10k and resilient oil. JPMorgan global manufacturing index for August is due tomorrow. It was 49.7 in July and has been below the 50-line since February. Looking at the above it looks like a good chance for moving into positive territory for global manufacturing. A copper price of USD 9935/ton, sniffing at the 10k line could be a reflection of that. An oil price holding up fairly well at close to USD 68/b despite the fact that oil balances for Q4-25 and 2026 looks bloated could be another reflection that global manufacturing may be accelerating.
US manufacturing PMI by S&P rose to 53.3 in August. It was published on 21 August, so not at all newly released. But the US ISM manufacturing PMI is due tomorrow and has the potential to follow suite with a strong manufacturing reading.
Analys
Crude stocks fall again – diesel tightness persists

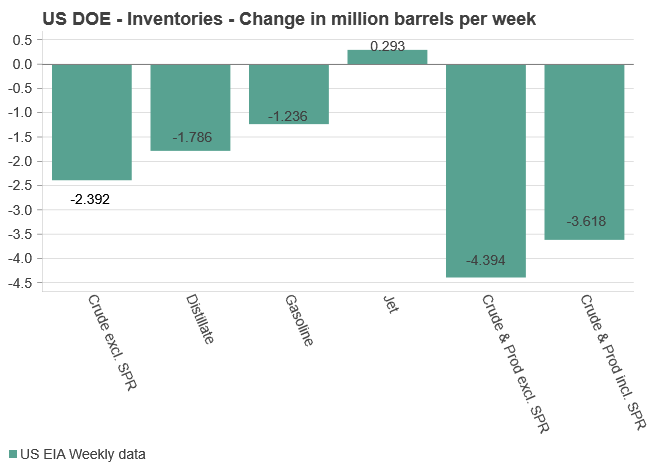
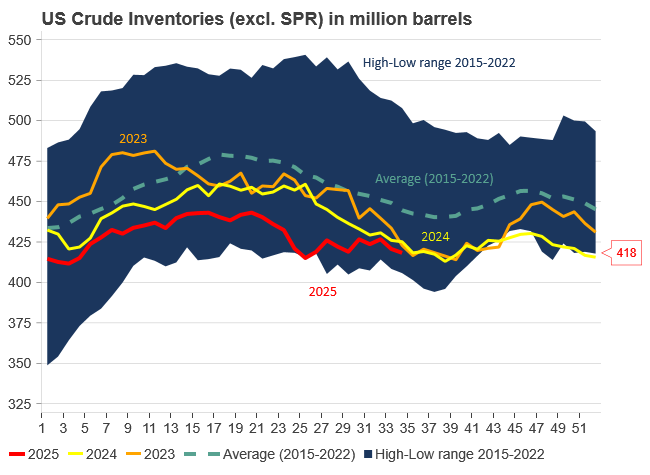
U.S. commercial crude inventories posted another draw last week, falling by 2.4 million barrels to 418.3 million barrels, according to the latest DOE report. Inventories are now 6% below the five-year seasonal average, underlining a persistently tight supply picture as we move into the post-peak demand season.

While the draw was smaller than last week’s 6 million barrel decline, the trend remains consistent with seasonal patterns. Current inventories are still well below the 2015–2022 average of around 449 million barrels.
Gasoline inventories dropped by 1.2 million barrels and are now close to the five-year average. The breakdown showed a modest increase in finished gasoline offset by a decline in blending components – hinting at steady end-user demand.
Diesel inventories saw yet another sharp move, falling by 1.8 million barrels. Stocks are now 15% below the five-year average, pointing to sustained tightness in middle distillates. In fact, diesel remains the most undersupplied segment, with current inventory levels at the very low end of the historical range (see page 3 attached).
Total commercial petroleum inventories – including crude and products but excluding the SPR – fell by 4.4 million barrels on the week, bringing total inventories to approximately 1,259 million barrels. Despite rising refinery utilization at 94.6%, the broader inventory complex remains structurally tight.
On the demand side, the DOE’s ‘products supplied’ metric – a proxy for implied consumption – stayed strong. Total product demand averaged 21.2 million barrels per day over the last four weeks, up 2.5% YoY. Diesel and jet fuel were the standouts, up 7.7% and 1.7%, respectively, while gasoline demand softened slightly, down 1.1% YoY. The figures reflect a still-solid late-summer demand environment, particularly in industrial and freight-related sectors.
Analys
Increasing risk that OPEC+ will unwind the last 1.65 mb/d of cuts when they meet on 7 September

Pushed higher by falling US inventories and positive Jackson Hall signals. Brent crude traded up 2.9% last week to a close of $67.73/b. It traded between $65.3/b and $68.0/b with the low early in the week and the high on Friday. US oil inventory draws together with positive signals from Powel at Jackson Hall signaling that rate cuts are highly likely helped to drive both oil and equities higher.

Ticking higher for a fourth day in a row. Bank holiday in the UK calls for muted European session. Brent crude is inching 0.2% higher this morning to $67.9/b which if it holds will be the fourth trading day in a row with gains. Price action in the European session will likely be quite muted due to bank holiday in the UK today.
OPEC+ is lifting production but we keep waiting for the surplus to show up. The rapid unwinding of voluntary cuts by OPEC+ has placed the market in a waiting position. Waiting for the surplus to emerge and materialize. Waiting for OECD stocks to rise rapidly and visibly. Waiting for US crude and product stocks to rise. Waiting for crude oil forward curves to bend into proper contango. Waiting for increasing supply of medium sour crude from OPEC+ to push sour cracks lower and to push Mid-East sour crudes to increasing discounts to light sweet Brent crude. In anticipation of this the market has traded Brent and WTI crude benchmarks up to $10/b lower than what solely looking at present OECD inventories, US inventories and front-end backwardation would have warranted.
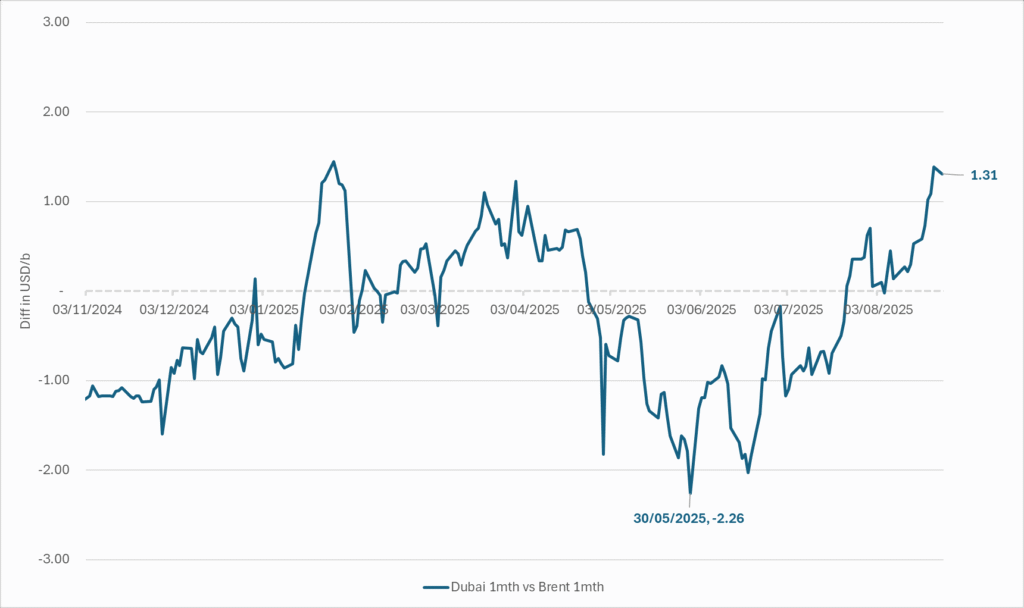
Quite a few pockets of strength. Dubai sour crude is trading at a premium to Brent crude! The front-end of the crude oil curves are still in backwardation. High sulfur fuel oil in ARA has weakened from parity with Brent crude in May, but is still only trading at a discount of $5.6/b to Brent versus a more normal discount of $10/b. ARA middle distillates are trading at a premium of $25/b versus Brent crude versus a more normal $15-20/b. US crude stocks are at the lowest seasonal level since 2018. And lastly, the Dubai sour crude marker is trading a premium to Brent crude (light sweet crude in Europe) as highlighted by Bloomberg this morning. Dubai is normally at a discount to Brent. With more medium sour crude from OPEC+ in general and the Middle East specifically, the widespread and natural expectation has been that Dubai should trade at an increasing discount to Brent. the opposite has happened. Dubai traded at a discount of $2.3/b to Brent in early June. Dubai has since then been on a steady strengthening path versus Brent crude and Dubai is today trading at a premium of $1.3/b. Quite unusual in general but especially so now that OPEC+ is supposed to produce more.
This makes the upcoming OPEC+ meeting on 7 September even more of a thrill. At stake is the next and last layer of 1.65 mb/d of voluntary cuts to unwind. The market described above shows pockets of strength blinking here and there. This clearly increases the chance that OPEC+ decides to unwind the remaining 1.65 mb/d of voluntary cuts when they meet on 7 September to discuss production in October. Though maybe they split it over two or three months of unwind. After that the group can start again with a clean slate and discuss OPEC+ wide cuts rather than voluntary cuts by a sub-group. That paves the way for OPEC+ wide cuts into Q1-26 where a large surplus is projected unless the group kicks in with cuts.
The Dubai medium sour crude oil marker usually trades at a discount to Brent crude. More oil from the Middle East as they unwind cuts should make that discount to Brent crude even more pronounced. Dubai has instead traded steadily stronger versus Brent since late May.
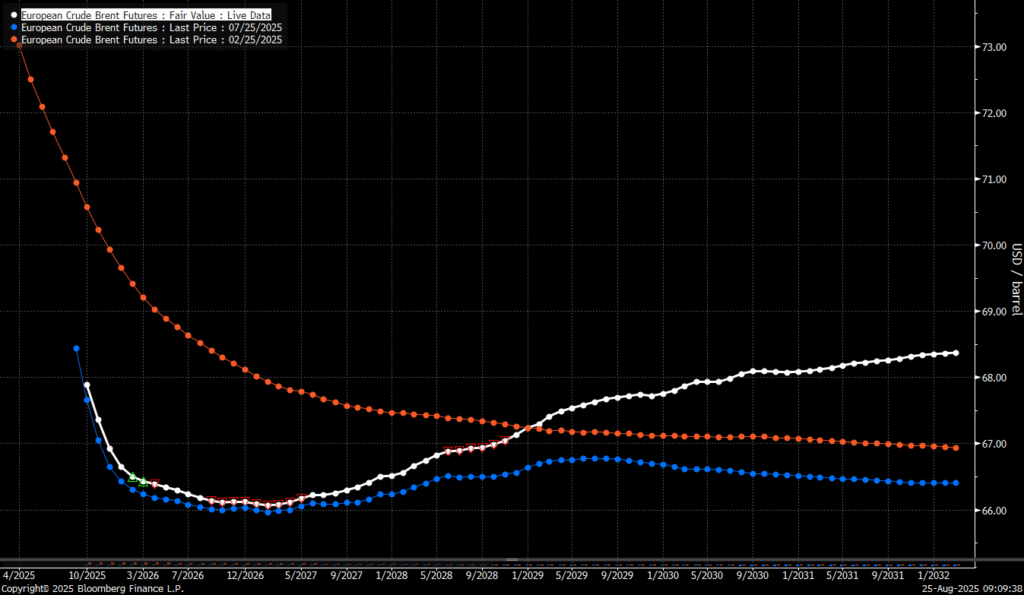
The Brent crude oil forward curve (latest in white) keeps stuck in backwardation at the front end of the curve. I.e. it is still a tight crude oil market at present. The smile-effect is the market anticipation of surplus down the road.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanOmgående mångmiljardfiasko för Equinors satsning på Ørsted och vindkraft
-
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLundin Gold hittar ny koppar-guld-fyndighet vid Fruta del Norte-gruvan
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuld stiger till över 3500 USD på osäkerhet i världen
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanWhat OPEC+ is doing, what it is saying and what we are hearing
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAlkane Resources och Mandalay Resources har gått samman, aktör inom guld och antimon
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLyten, tillverkare av litium-svavelbatterier, tar över Northvolts tillgångar i Sverige och Tyskland






