Analys
Donald D-Day in the oil market

 As always it is very difficult to know what Donald Trump is going to do: Reinstate sanctions or not? And today at 2 pm Washington time (5 pm CET) we will know. European diplomats (UK, France, Germany) who have discussed the Iran issues with US negotiators this spring seems to be convinced that Donald will exit the deal today and thus revive the US Iran sanctions from 2012. Trump reiterated on Monday his view that it is a “very badly negotiated deal” sowing little optimism for staying with the deal.
As always it is very difficult to know what Donald Trump is going to do: Reinstate sanctions or not? And today at 2 pm Washington time (5 pm CET) we will know. European diplomats (UK, France, Germany) who have discussed the Iran issues with US negotiators this spring seems to be convinced that Donald will exit the deal today and thus revive the US Iran sanctions from 2012. Trump reiterated on Monday his view that it is a “very badly negotiated deal” sowing little optimism for staying with the deal.
In February 2018 when Donald threatened to exit the deal last time there seemed to be very little understanding among the European allies what Trump really wanted to change in the Iran deal. Versus that there now seems to be quite some progress. Now it seems that there is a general agreement and understanding that the current deal is far from good enough and that it needs to be improved. We’ll see later today whether this is good enough for him to waive the sanctions yet again, kick the can down the road for another 180 days, lowering the gasoline pump prices and pleasing his consumers and mid-term election voters. If sanctions are revived then the impact is likely going to be limited for the 2018 oil market balance. Towards the end of 2019 however Iran’s crude oil exports could be reduced towards 1.3 m bl/d versus an average of 2.1 m bl/d in 2017. Reduced investments would hamper future Iranian production growth.
It seems clear that Donald Trump’s push towards the nuclear deal has opened the eyes of the European allies with the acceptance that the deal needs to be amended and improved. The key points which need to be amended, improved, added or addressed are:
- Iran’s missile program
- Iran’s meddling with other nations in the region like the current proxy war with Saudi Arabia in Yemen. In general curbing any Iranian effort for Iranian based Shia Muslim dominance in the Middle East
- Sunset clauses in the current Iran nuclear deal which currently allows Iran to resume uranium enrichment after 2025 with possible revival of its nuclear program
- Financing of terrorism
Iran however has stated that the current nuclear deal struck 14 July 2015 the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) is non-negotiable. That stand could be a red flag for Donald Trump making him push harder.
One can speculate whether the US mid-term elections might play a part in his decision today. What will be most important for the US voters: 1) Nixing the Iran nuclear deal + high gasoline prices or 2) A strong Donald Trump pushing the parties to the negotiation table + lower gasoline prices? It is clear that higher oil prices and retail US gasoline prices are eroding some of the positives from Donald’s tax cuts thus creating an economic headwind for the US consumers. Whether such considerations are part of his deliberations over the Iran nuclear deal decision today at 2 pm Washington time remains to be seen. He has at least already accused OPEC of manipulating the oil market to higher prices thus showing some sensitivity to the issue of higher oil and gasoline prices.
If Trump today reactivates the 2012 National Defence Authorization Act (NDAA) then importers of Iranian crude oil will need to seek exemptions to import crude oil or face US sanctions towards their state owned financial institutions or central banks. The once seeking exemptions in order to import crude oil from Iran will typically need to reduce imports by 20% every 180 days. China, Japan, South Korea and Japan would be the most important parties in terms of magnitude. Though China does not agree to new sanctions towards China it may still comply with the NDAA if it is revived in order to avoid secondary sanctions towards Chinese financial institutions from the US.
If all current importers of Iranian crude oil decide to ask for exemptions and thus continue to import Iranian crude they would still need to reduce imports by 20% every 180 days. Over the past 6 months Iran exported 2.1 m bl/d. A rolling 180 days 20% reduction would reduce Iranian exports to 1.3 m bl/d at the end of 2019 and close to 1 m bl/d in early 2020. It would have limited impact on the 2018 balance as it takes time to revive the sanctions. It would hamper investments in Iranian oil resources thus leading to a potentially tighter future oil market. This is probably why we have seen oil prices for longer dated contracts rise just as much as the front end of the crude oil curve lately.
The US sanctions towards Iran are multi-layered. The Iran Sanctions Act (ISA) from 1996, the Iran Threat Reduction and Syria Human Act (TRA) and the Iran Freedom and Counter proliferations Act (IFCA) from 2012 are up for their 180 days waiver renewal in July.
Kind regards
Bjarne Schieldrop
Chief analyst, Commodities
SEB Markets
Merchant Banking
Analys
Crude stocks fall again – diesel tightness persists

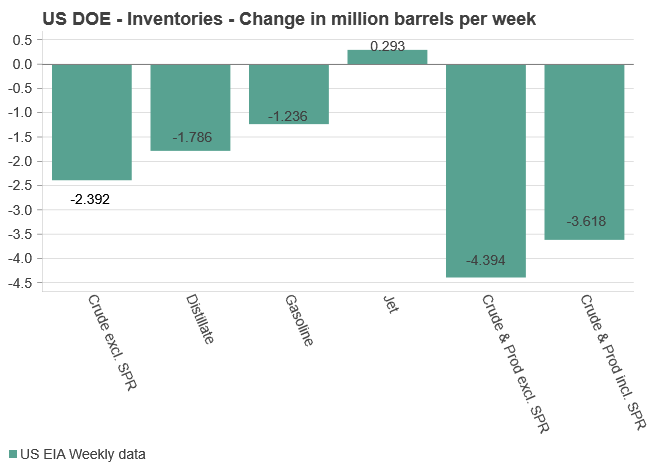
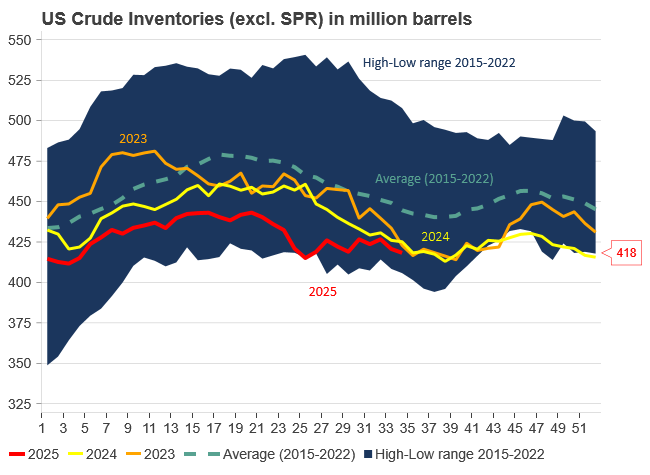
U.S. commercial crude inventories posted another draw last week, falling by 2.4 million barrels to 418.3 million barrels, according to the latest DOE report. Inventories are now 6% below the five-year seasonal average, underlining a persistently tight supply picture as we move into the post-peak demand season.

While the draw was smaller than last week’s 6 million barrel decline, the trend remains consistent with seasonal patterns. Current inventories are still well below the 2015–2022 average of around 449 million barrels.
Gasoline inventories dropped by 1.2 million barrels and are now close to the five-year average. The breakdown showed a modest increase in finished gasoline offset by a decline in blending components – hinting at steady end-user demand.
Diesel inventories saw yet another sharp move, falling by 1.8 million barrels. Stocks are now 15% below the five-year average, pointing to sustained tightness in middle distillates. In fact, diesel remains the most undersupplied segment, with current inventory levels at the very low end of the historical range (see page 3 attached).
Total commercial petroleum inventories – including crude and products but excluding the SPR – fell by 4.4 million barrels on the week, bringing total inventories to approximately 1,259 million barrels. Despite rising refinery utilization at 94.6%, the broader inventory complex remains structurally tight.
On the demand side, the DOE’s ‘products supplied’ metric – a proxy for implied consumption – stayed strong. Total product demand averaged 21.2 million barrels per day over the last four weeks, up 2.5% YoY. Diesel and jet fuel were the standouts, up 7.7% and 1.7%, respectively, while gasoline demand softened slightly, down 1.1% YoY. The figures reflect a still-solid late-summer demand environment, particularly in industrial and freight-related sectors.
Analys
Increasing risk that OPEC+ will unwind the last 1.65 mb/d of cuts when they meet on 7 September

Pushed higher by falling US inventories and positive Jackson Hall signals. Brent crude traded up 2.9% last week to a close of $67.73/b. It traded between $65.3/b and $68.0/b with the low early in the week and the high on Friday. US oil inventory draws together with positive signals from Powel at Jackson Hall signaling that rate cuts are highly likely helped to drive both oil and equities higher.

Ticking higher for a fourth day in a row. Bank holiday in the UK calls for muted European session. Brent crude is inching 0.2% higher this morning to $67.9/b which if it holds will be the fourth trading day in a row with gains. Price action in the European session will likely be quite muted due to bank holiday in the UK today.
OPEC+ is lifting production but we keep waiting for the surplus to show up. The rapid unwinding of voluntary cuts by OPEC+ has placed the market in a waiting position. Waiting for the surplus to emerge and materialize. Waiting for OECD stocks to rise rapidly and visibly. Waiting for US crude and product stocks to rise. Waiting for crude oil forward curves to bend into proper contango. Waiting for increasing supply of medium sour crude from OPEC+ to push sour cracks lower and to push Mid-East sour crudes to increasing discounts to light sweet Brent crude. In anticipation of this the market has traded Brent and WTI crude benchmarks up to $10/b lower than what solely looking at present OECD inventories, US inventories and front-end backwardation would have warranted.
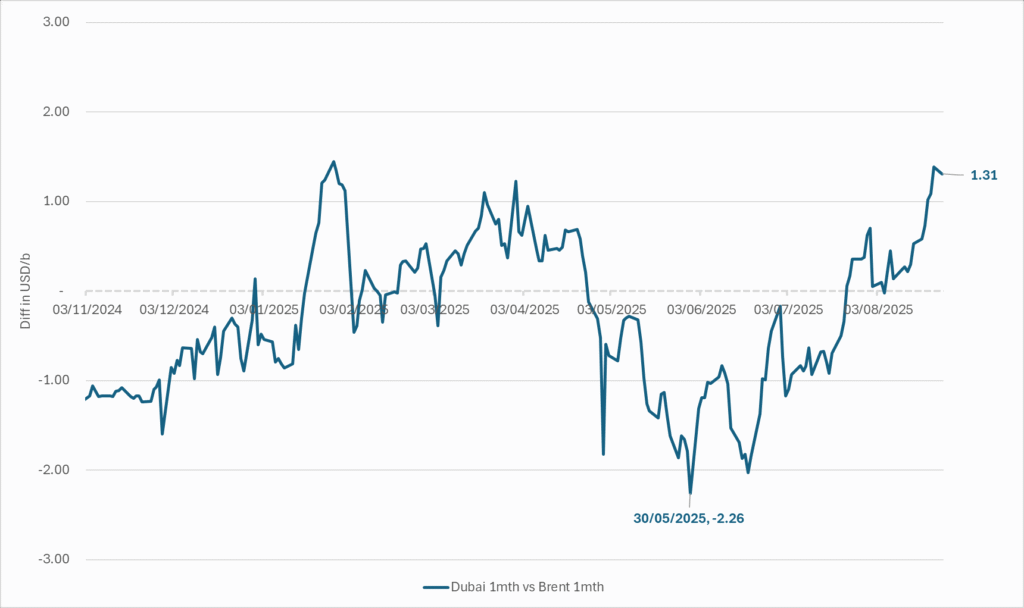
Quite a few pockets of strength. Dubai sour crude is trading at a premium to Brent crude! The front-end of the crude oil curves are still in backwardation. High sulfur fuel oil in ARA has weakened from parity with Brent crude in May, but is still only trading at a discount of $5.6/b to Brent versus a more normal discount of $10/b. ARA middle distillates are trading at a premium of $25/b versus Brent crude versus a more normal $15-20/b. US crude stocks are at the lowest seasonal level since 2018. And lastly, the Dubai sour crude marker is trading a premium to Brent crude (light sweet crude in Europe) as highlighted by Bloomberg this morning. Dubai is normally at a discount to Brent. With more medium sour crude from OPEC+ in general and the Middle East specifically, the widespread and natural expectation has been that Dubai should trade at an increasing discount to Brent. the opposite has happened. Dubai traded at a discount of $2.3/b to Brent in early June. Dubai has since then been on a steady strengthening path versus Brent crude and Dubai is today trading at a premium of $1.3/b. Quite unusual in general but especially so now that OPEC+ is supposed to produce more.
This makes the upcoming OPEC+ meeting on 7 September even more of a thrill. At stake is the next and last layer of 1.65 mb/d of voluntary cuts to unwind. The market described above shows pockets of strength blinking here and there. This clearly increases the chance that OPEC+ decides to unwind the remaining 1.65 mb/d of voluntary cuts when they meet on 7 September to discuss production in October. Though maybe they split it over two or three months of unwind. After that the group can start again with a clean slate and discuss OPEC+ wide cuts rather than voluntary cuts by a sub-group. That paves the way for OPEC+ wide cuts into Q1-26 where a large surplus is projected unless the group kicks in with cuts.
The Dubai medium sour crude oil marker usually trades at a discount to Brent crude. More oil from the Middle East as they unwind cuts should make that discount to Brent crude even more pronounced. Dubai has instead traded steadily stronger versus Brent since late May.
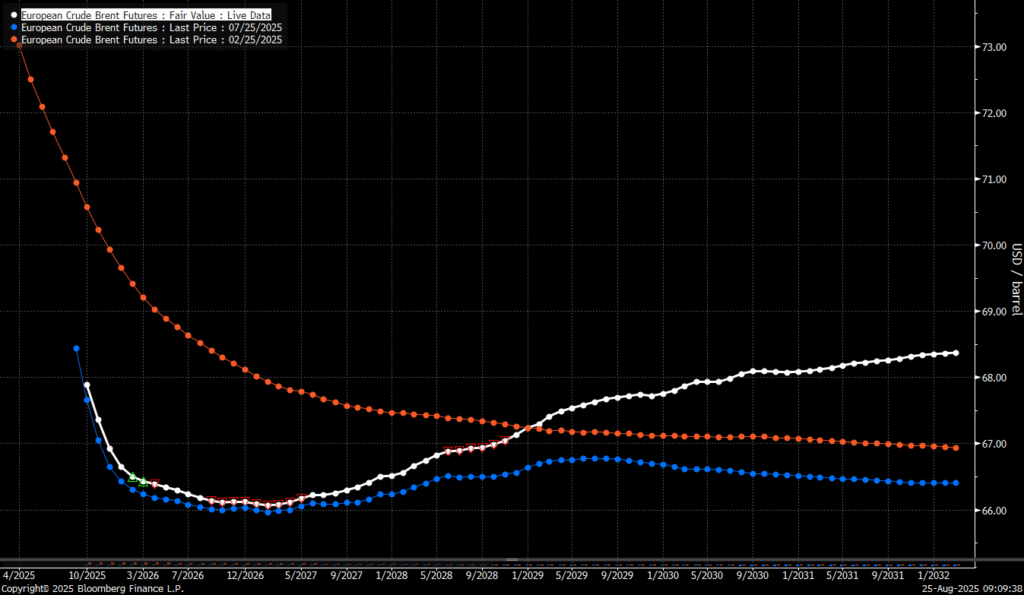
The Brent crude oil forward curve (latest in white) keeps stuck in backwardation at the front end of the curve. I.e. it is still a tight crude oil market at present. The smile-effect is the market anticipation of surplus down the road.
Analys
Brent edges higher as India–Russia oil trade draws U.S. ire and Powell takes the stage at Jackson Hole

Best price since early August. Brent crude gained 1.2% yesterday to settle at USD 67.67/b, the highest close since early August and the second day of gains. Prices traded to an intraday low of USD 66.74/b before closing up on the day. This morning Brent is ticking slightly higher at USD 67.76/b as the market steadies ahead of Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s Jackson Hole speech later today.

No Russia/Ukraine peace in sight and India getting heat from US over imports of Russian oil. Yesterday’s price action was driven by renewed geopolitical tension and steady underlying demand. Stalled ceasefire talks between Russia and Ukraine helped maintain a modest risk premium, while the spotlight turned to India’s continued imports of Russian crude. Trump sharply criticized New Delhi’s purchases, threatening higher tariffs and possible sanctions. His administration has already announced tariff hikes on Indian goods from 25% to 50% later this month. India has pushed back, defending its right to diversify crude sourcing and highlighting that it also buys oil from the U.S. Moscow meanwhile reaffirmed its commitment to supply India, deepening the impression that global energy flows are becoming increasingly politicized.
Holding steady this morning awaiting Powell’s address at Jackson Hall. This morning the main market focus is Powell’s address at Jackson Hole. It is set to be the key event for markets today, with traders parsing every word for signals on the Fed’s policy path. A September rate cut is still the base case but the odds have slipped from almost certainty earlier this month to around three-quarters. Sticky inflation data have tempered expectations, raising the stakes for Powell to strike the right balance between growth concerns and inflation risks. His tone will shape global risk sentiment into the weekend and will be closely watched for implications on the oil demand outlook.
For now, oil is holding steady with geopolitical frictions lending support and macro uncertainty keeping gains in check.
Oil market is starting to think and worry about next OPEC+ meeting on 7 September. While still a good two weeks to go, the next OPEC+ meeting on 7 September will be crucial for the oil market. After approving hefty production hikes in August and September, the question is now whether the group will also unwind the remaining 1.65 million bpd of voluntary cuts. Thereby completing the full phase-out of voluntary reductions well ahead of schedule. The decision will test OPEC+’s balancing act between volume-driven influence and price stability. The gathering on 7 September may give the clearest signal yet of whether the group will pause, pivot, or press ahead.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanOmgående mångmiljardfiasko för Equinors satsning på Ørsted och vindkraft
-
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLundin Gold hittar ny koppar-guld-fyndighet vid Fruta del Norte-gruvan
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGuld stiger till över 3500 USD på osäkerhet i världen
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanWhat OPEC+ is doing, what it is saying and what we are hearing
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAlkane Resources och Mandalay Resources har gått samman, aktör inom guld och antimon
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanLyten, tillverkare av litium-svavelbatterier, tar över Northvolts tillgångar i Sverige och Tyskland







