Analys
SEB – Jordbruksprodukter, vecka 5 2012
 Vinnare sedan föregående vecka har de olika veteterminerna varit med uppgångar på 4 till 5%. Eurex-terminerna på tyska grisar ligger 10% högre den här veckan, men det beror bara på att vi nu tittar på ett längre terminskontrakt än förra veckan. Det är dock en liten prisuppgång på gris i Europa och också en liten i USA.
Vinnare sedan föregående vecka har de olika veteterminerna varit med uppgångar på 4 till 5%. Eurex-terminerna på tyska grisar ligger 10% högre den här veckan, men det beror bara på att vi nu tittar på ett längre terminskontrakt än förra veckan. Det är dock en liten prisuppgång på gris i Europa och också en liten i USA.
I fokus för vetemarknaden har oron för ryskt exportstopp varit. Marknaden har också oroat sig för det kalla och torra vädret i Ryssland.
Oron för torkan i Argentina har lagt sig och när nederbörden kommit tillbaka anses majsskörden kunna stabilisera sig på 18 – 22 mt (USDA:s senaste WASDE låg på 23 mt). WASDE släpps nästa vecka.
Vete
Oro över det kalla vädret i Ryssland och Östeuropa samt ett eventuellt införande av ett ryskt exportförbud har fortsatt att driva vete priset uppåt.
Den ryska regeringen diskuterar frågan om att eventuellt införande av skatter / tullar på spannmålsexporten för att bromsa den höga exporttakten.
Jordbruksministeriet i Ryssland övervakar dock kontinuerligt volymen som exporteras, och som fortfarande är stabil, och kommer att basera sitt beslut på den volym som har exporterats per februari månad. I mitten av februari kommer regeringen att kunna estimera volymen för hela månaden och då ta ställning i frågan.
 Samtidigt betonar ministeriet att detta inte kan komma som någon överraskning för marknaden och att informationen som har cirkulerat om att skatter / tullar ska införas per april 2012 är ”helt grundlösa”. Som vi har skrivit om tidigare var Putin ute redan i oktober och pratade om att spannmålsexporten för 2011/12 skulle komma att uppgå till 24-25 miljoner ton och därefter skulle eventuella restriktioner införas för att inte ”landet skulle bli utan bröd och för att upprätthålla lager”.
Samtidigt betonar ministeriet att detta inte kan komma som någon överraskning för marknaden och att informationen som har cirkulerat om att skatter / tullar ska införas per april 2012 är ”helt grundlösa”. Som vi har skrivit om tidigare var Putin ute redan i oktober och pratade om att spannmålsexporten för 2011/12 skulle komma att uppgå till 24-25 miljoner ton och därefter skulle eventuella restriktioner införas för att inte ”landet skulle bli utan bröd och för att upprätthålla lager”.
Rosstat’s statistik visar att produktionen av spannmål och baljväxter i Ryssland under 2011 uppgår till 93.9 miljoner ton, inklusive 56,2 miljoner ton vete, 16,9 miljoner korn, 6,7 miljoner ton majs och 14,1 milj i andra sädesslag och baljväxter. Detta är en uppgång med 54 procent sedan 2010 då landet led av svår torka. Veteproduktionen är upp 36% och produktionen av korn har mer än fördubblats. Det är dock bara 3 procent högre än det 5-åriga genomsnittet. Majsproduktionen matchar rekordåret 2008. Den enorma ökningen är nästan helt och hållet avkastningsrelaterad, då odlad areal endast ökade med 1 procent från 2010 till 43,6 miljoner hektar.
Som ett resultat av den stora spannmålsskörden ökade också exporten av spannmål kraftigt under första halvan av året (juli – december 2011) där Ryssland exporterade över 18 miljoner ton spannmål och baljväxter, inklusive 14,8 miljoner ton vete och det var tre av Rysslands södra regioner (Rostov oblast, Krasnodar och Stavropol krays) som stod för 85 procent av och den totala exporten. Den totala exporten för 2011/12 väntas nå 24 miljoner ton. Trots de höga exportsiffrorna under det första halvåret kommer det att bli en betydlig nedgång i exporttakten under den andra halvan av 2011/12 (januari – juni). Dels är exportpotentialen från de tre södra regionerna i stort sett klar och kommer därmed att vara nästan obefintlig de sista månaderna, dels är det problem med logistiken under vinterhalvåret. Den inhemska efterfrågan på spannmål till foderindustrin är också fortsatt stark och lagren av spannmål för export har minskat.
Vädret har också ställt till det i Ukraina då svårt frost i de flesta ukrainska regioner dramatiskt har bromsat takten på landets spannmålsexport.
En temperatur på runt minus 20 grader gör det i stort sett omöjligt att lasta spannmål på järnvägsvagnar inne i landet medan stark vind och snö hindrar lastningen i hamnarna och flera stora fartyg ligger bara och väntar.
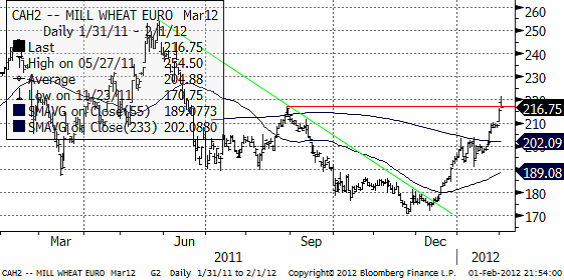
Nedan ser vi kursdiagrammet för marskontraktet på Matif, där priset rusat över motståndet på 217, men faktiskt gick ner på onsdagskvällen och stängde under. Det är en negativ signal.
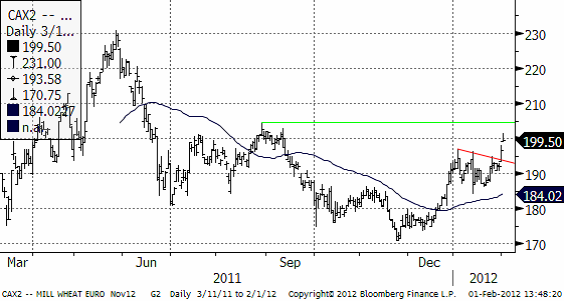
Nedan ser vi novemberkontraktet, som inte bröt ur sin konsolidering i tisdags morse, men som ännu inte nått motståndsnivån på 205 euro.
Matif har gått ännu mer i backwardation och contangot har minskat för Chicagovetet. Det talas om att den europeiske bonden inte säljer något, utan sitter och håller på sin spannmål. Vi tänker, det kan bli trångt i dörren framåt våren, när alla vill sälja samtidigt.
Vi tror att vi såg en ”key reversal day” igår i och med att marskontraktet tvärvände under dagen och stängde på den lägsta nivån. Ett sådant omslag från uppgång till tvär nedgång brukar vara värt att ta fasta på.
Maltkorn
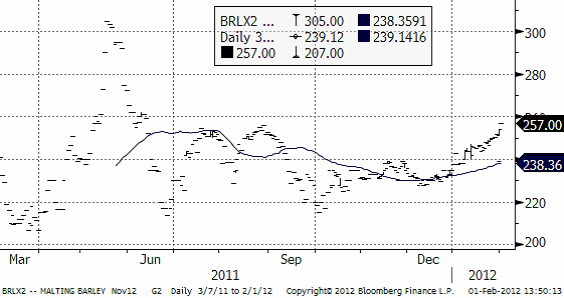
Maltkornet har handlats upp eftersom vetet handlats upp. Det finns inget specifikt att säga om maltkornet.
Potatis
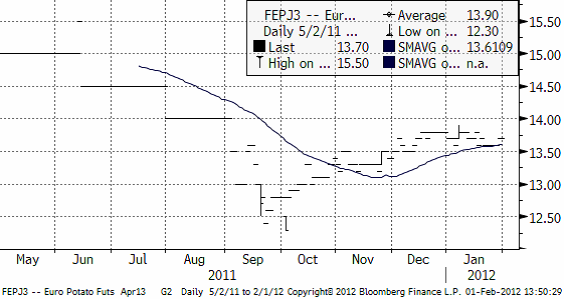
Priset på industripotatis ligger kvar på samma nivå som förra veckan för skörd 2012.
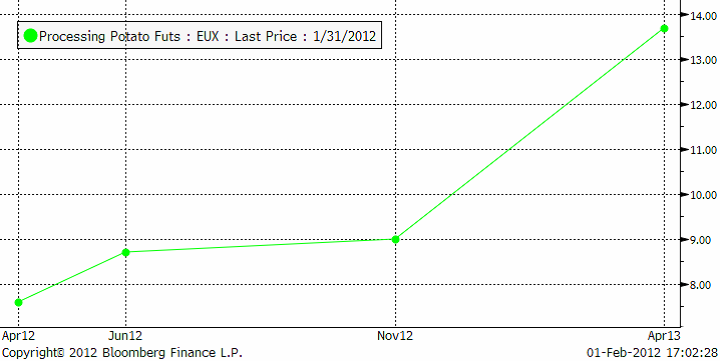
Nedan ser vi terminskurvan framåt i tiden. Årets låga priser väntas alltså inte bestå.
Majs
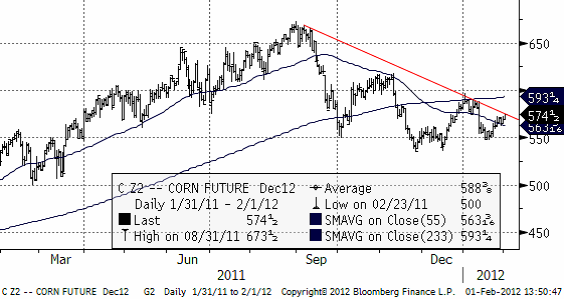
Väntad skörd i Argentina håller på att stabilisera sig på 18-21 mt, som är lägre än vad USDA förutspådde i januari-WASDE. Nedan ser vi att priset på decemberkontraktet ligger precis under en motståndslinje. Brott upp genom den är ett tecken på styrka och att vi i så fall skulle kunna få se en fortsatt prisuppgång.
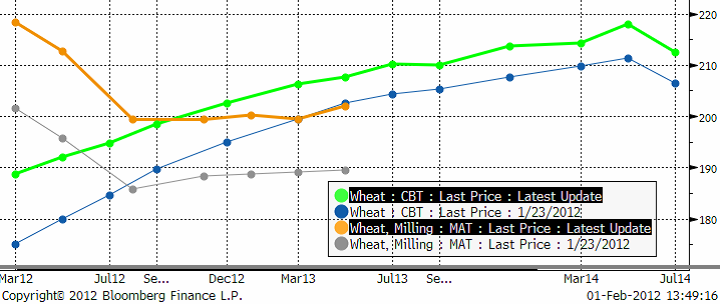
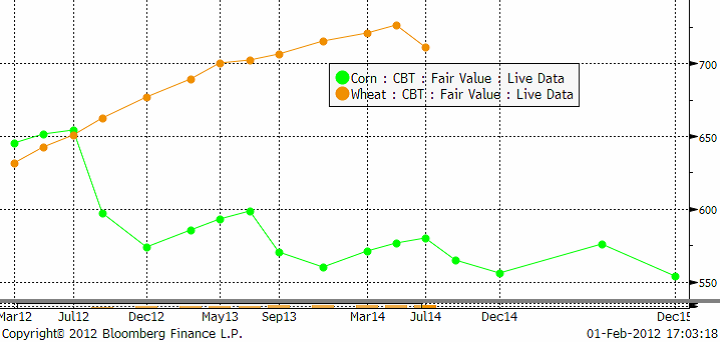
Nedan ser vi terminskurvorna för vete (contango) och majs (backwardation).
Vete är 60 punds bushel, men här har jag räknat om priserna så att de båda är uttryckta som majsens 56 punds bushels.
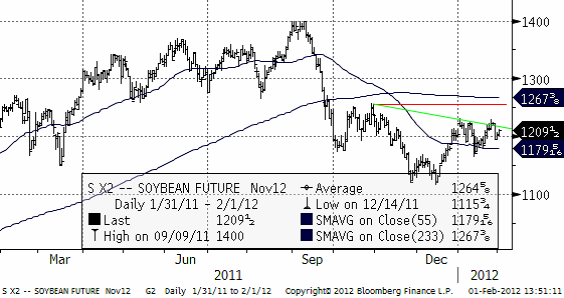
Sojabönor
Sodrugestvo och Grain Ukraine förutspår en rekordskörd av sojabönor i Ukraina under 2012/13. Lönsamheten är 100-150% på grödan. Bara solrosor och majs har högre lönsamhet. Det finns gott om utsäde. Förfruktsfördelarna har ett högt värde för korn och vete. Tekniskt ser finns ingen signal ännu.
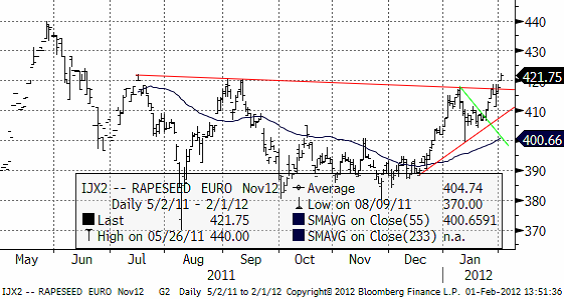
Raps
Novemberkontraktet har brutit motståndet, men ännu inte gått över pristoppen i juli. Så länge det inte sker, har vi inte någon stor trendvändning.
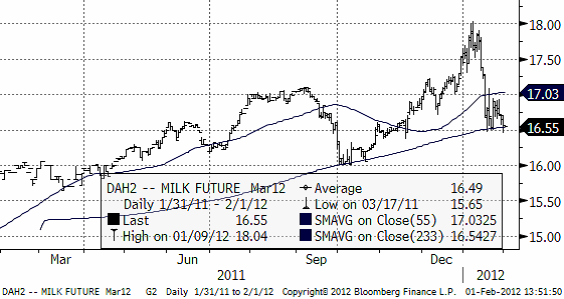
Mjölk
Nedan ser vi priset på marskontraktet på flytande mjölk (kontakt avräknat mot USDA:s prisindex). Vi tror fortfarande att priset kan gå ner till 16 och att prisnedgången är ”halvvägs”.
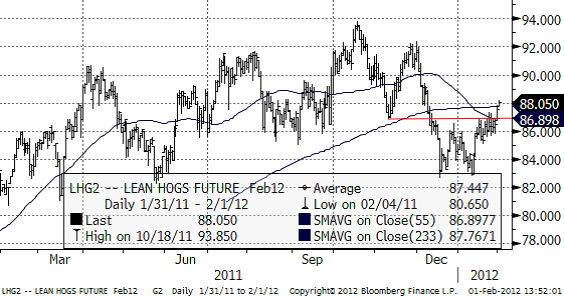
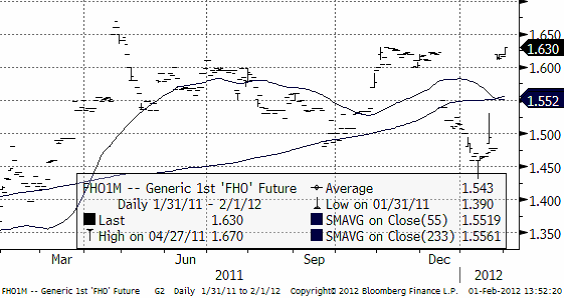
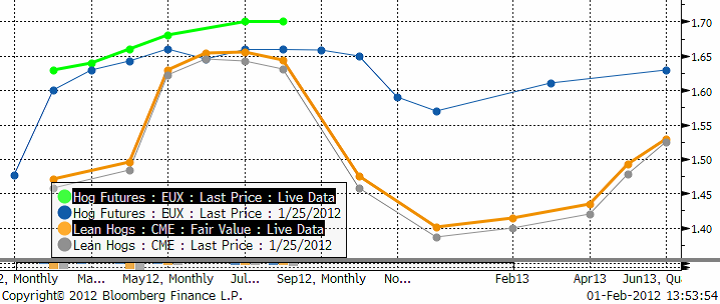
Gris
Priset på lean hogs har brutit uppåt, och befinner sig därmed fortfarande i det breda intervall som priset pendlat inom det senaste året.
Priset i Europa har betett sig på samma sätt. Nedan ser vi det vid var tid kortaste terminskontraktet (närmast spot). Det ser ut som om priset stigit kraftigt, men det beror bara på att det kontrakt som var kortast tidigare förfallit och att det kortaste nu, ligger på en högre nivå pga säsongseffekten.
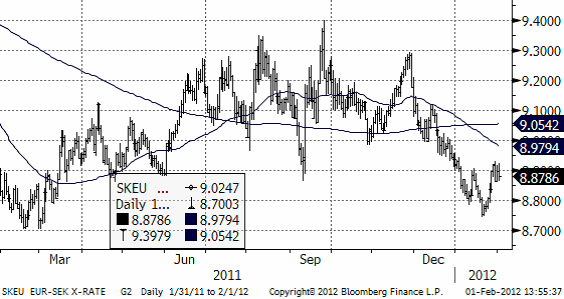
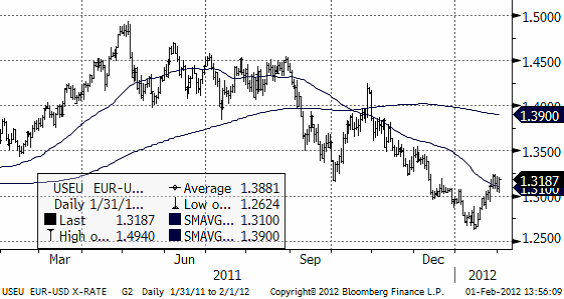
Valutor
EURSEK – försöker korrigera nedgången. Vi har en neutral rekommendation på både en veckas sikt och tre månaders.
EURUSD – i rekyl fortfarande Rekommendation: Neutral på en veckas sikt. Negativ på tre månader.
USDSEK – söker efter en botten i korrektionen nedåt Vi har en neutral rekommendation på en veckas sikt, men är positive på tre månader.
[box]SEB Veckobrev Jordbruksprodukter är producerat av SEB Merchant Banking och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been compiled by SEB Merchant Banking, a division within Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) (“SEB”).
Opinions contained in this report represent the bank’s present opinion only and are subject to change without notice. All information contained in this report has been compiled in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. However, no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made with respect to the completeness or accuracy of its contents and the information is not to be relied upon as authoritative. Anyone considering taking actions based upon the content of this document is urged to base his or her investment decisions upon such investigations as he or she deems necessary. This document is being provided as information only, and no specific actions are being solicited as a result of it; to the extent permitted by law, no liability whatsoever is accepted for any direct or consequential loss arising from use of this document or its contents.
About SEB
SEB is a public company incorporated in Stockholm, Sweden, with limited liability. It is a participant at major Nordic and other European Regulated Markets and Multilateral Trading Facilities (as well as some non-European equivalent markets) for trading in financial instruments, such as markets operated by NASDAQ OMX, NYSE Euronext, London Stock Exchange, Deutsche Börse, Swiss Exchanges, Turquoise and Chi-X. SEB is authorized and regulated by Finansinspektionen in Sweden; it is authorized and subject to limited regulation by the Financial Services Authority for the conduct of designated investment business in the UK, and is subject to the provisions of relevant regulators in all other jurisdictions where SEB conducts operations. SEB Merchant Banking. All rights reserved.
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

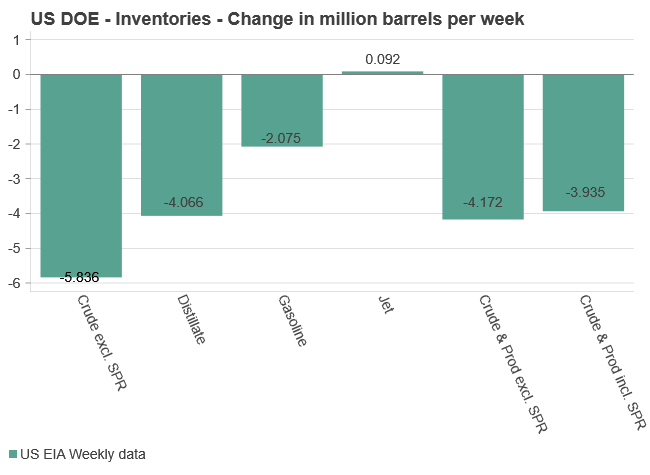
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

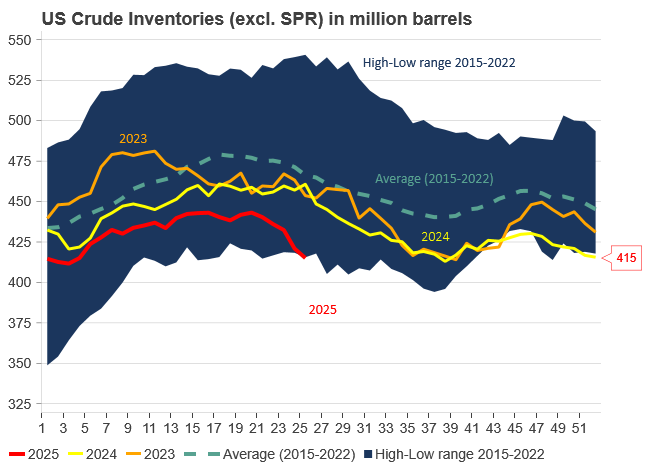
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBrookfield ska bygga ett AI-datacenter på hela 750 MW i Strängnäs
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanOljan, guldet och marknadens oroande tystnad