Analys
Crude oil comment – Surplus stored here or there?

 Crude oil comment – Surplus stored here or there?
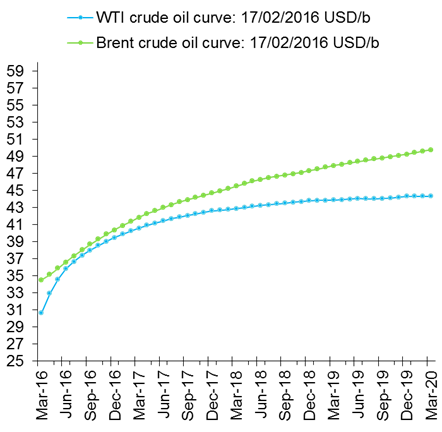
Crude oil comment – Surplus stored here or there?- Graph 1: Deep WTI contango – Costly or impractical to store oil in the US mid-continent
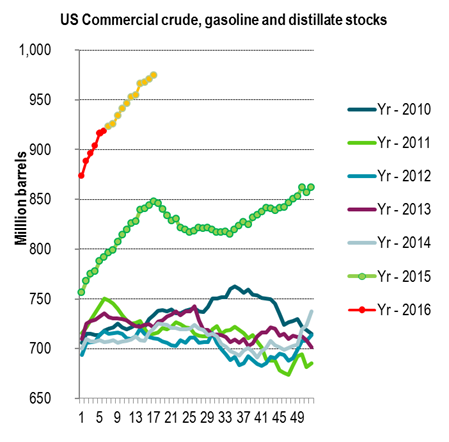
- Graph 2: US crude, gasoline and distillate stocks
Crude oil comment – Surplus stored here or there?
Today we will have the publishing of US oil inventory data at 17.00 CET. Since the start of August last year total commercial US crude and product stocks have increased by 102 million barrels. During that period we have only seen 5 weeks with declines in the net change in stocks constituted by crude + gasoline + distillates. The general take has been that the US holds a substantial capacity of the yet remaining free storage capacity for oil globally. Thus not surprisingly that has also been where we have seen the solid accumulation in oil inventories. The US is a huge net importer of oil, still the second biggest oil importer in the world. Thus when we see consistently increasing oil inventories in the US it basically means that the US is importing more oil than it needs. This has of course been impacted by logistical issues within the US regarding location of production versus consumption and crude qualities and refinery specs in combination with the earlier crude oil export ban.
In last week’s data release we saw that the net increase of crude, gasoline and distillates only came in at a +1.8 mb gain. That was the lowest gain since late December since which the average weekly gain has been running at about +10 mb per week. The Bloomberg consensus for today’s US oil inventory data released points to a total rise of 2.4 mb. The partial data set aggregated by API from its members in the US oil space did however point to a solid total decline of 4.6 mb with a significant decline in US crude stocks as well as distillates:
So what is driving this change in pattern? No more stock building in the US? On paper it looks like the US Pad II should still hold a substantial amount of free, available storage capacity for both crude and products. However, what the deep contango in the WTI curve is telling us is that it is becoming very expensive to store oil in the US mid-continent. Yes, crude stocks in Cushing Oklahoma are close to full. As such the contango in the WTI crude oil curve should be deep. However, if there was a substantial amount of storage capacity which was low cost to use, easy logistics and easily operational readily available in the vicinity of Cushing and in the Pad II region, then the close to capacity and deep contango in the WTI curve should drive oil away from Cushing and into other storage facilities in Pad II. Thus again, the deep WTI contango probably tells the market that the remaining available storage capacity in Pad II in the US may not be very cheap to utilize. This could be thus be due to several issues like cumbersome logistics or old age or that storage space is there but it is not really operationally available.
Looking at the WTI forward curve in comparison with the Brent curve the WTI curve’s accelerating, deepening contango this year is basically shouting out: It is becoming increasingly expensive to store oil in the US mid-continent. Go and store oil somewhere else.
If we today see that total US oil stocks are actually declined in the US last week as indicated by the API numbers then it is likely to have a bullish impact on oil prices. Especially if it is combined with for example a further decline in US crude oil production (data to be published together with inventory data today) in combination with the current ongoing oil price rebound on the back of the OPEC + Russia talks on production freeze. It is going to be perceived as bullish partly because it may be interpreted as if the global oil market is less in surplus now than 3-4 weeks ago. This we think is the wrong interpretation. The market is still running a surplus of some 1.5 mbpd which needs to be stored somewhere. If stocks don’t continue to rise in the US it basically means that stocks will need to rise outside of the US. It does mean that the deep contango in the WTI curve may ease a bit while the contango in the Brent curve will deepen. As such it is on the margin supportive for the WTI front month prices versus a bearish impact for the Brent front month price.
Thus do not jump on the conclusion that declining stocks in the US means that there is no global surplus. It basically means that surplus is stored somewhere else.
Graph 1: Deep WTI contango – Costly or impractical to store oil in the US mid-continent
Graph 2: US crude, gasoline and distillate stocks
Yellow line is if further inventory rise follows last year’s trende from here.
Normally total US crude, gasoline and distillate stocks don’t increase much.
Thus the increase last year and so far this year is a reflection of the global surplus
Thus if it is becoming increasingly costly to store oil in the US then the stock building has to take plase somewhere else.
Kind regards
Bjarne Schieldrop
Chief analyst, Commodities
SEB Markets
Merchant Banking
Analys
Brent crude ticks higher on tension, but market structure stays soft

Brent crude has climbed roughly USD 1.5-2 per barrel since Friday, yet falling USD 0.3 per barrel this mornig and currently trading near USD 67.25/bbl after yesterday’s climb. While the rally reflects short-term geopolitical tension, price action has been choppy, and crude remains locked in a broader range – caught between supply-side pressure and spot resilience.

Prices have been supported by renewed Ukrainian drone strikes targeting Russian infrastructure. Over the weekend, falling debris triggered a fire at the 20mtpa Kirishi refinery, following last week’s attack on the key Primorsk terminal.
Argus estimates that these attacks have halted ish 300 kbl/d of Russian refining capacity in August and September. While the market impact is limited for now, the action signals Kyiv’s growing willingness to disrupt oil flows – supporting a soft geopolitical floor under prices.
The political environment is shifting: the EU is reportedly considering sanctions on Indian and Chinese firms facilitating Russian crude flows, while the U.S. has so far held back – despite Bessent warning that any action from Washington depends on broader European participation. Senator Graham has also publicly criticized NATO members like Slovakia and Hungary for continuing Russian oil imports.
It’s worth noting that China and India remain the two largest buyers of Russian barrels since the invasion of Ukraine. While New Delhi has been hit with 50% secondary tariffs, Beijing has been spared so far.
Still, the broader supply/demand balance leans bearish. Futures markets reflect this: Brent’s prompt spread (gauge of near-term tightness) has narrowed to the current USD 0.42/bl, down from USD 0.96/bl two months ago, pointing to weakening backwardation.
This aligns with expectations for a record surplus in 2026, largely driven by the faster-than-anticipated return of OPEC+ barrels to market. OPEC+ is gathering in Vienna this week to begin revising member production capacity estimates – setting the stage for new output baselines from 2027. The group aims to agree on how to define “maximum sustainable capacity,” with a proposal expected by year-end.
While the IEA pegs OPEC+ capacity at 47.9 million barrels per day, actual output in August was only 42.4 million barrels per day. Disagreements over data and quota fairness (especially from Iraq and Nigeria) have already delayed this process. Angola even quit the group last year after being assigned a lower target than expected. It also remains unclear whether Russia and Iraq can regain earlier output levels due to infrastructure constraints.
Also, macro remains another key driver this week. A 25bp Fed rate cut is widely expected tomorrow (Wednesday), and commodities in general could benefit a potential cut.
Summing up: Brent crude continues to drift sideways, finding near-term support from geopolitics and refining strength. But with surplus building and market structure softening, the upside may remain capped.
Analys
Volatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk

Brent crude is essentially flat on the week, but after a volatile ride. Prices started Monday near USD 65.5/bl, climbed steadily to a mid-week high of USD 67.8/bl on Wednesday evening, before falling sharply – losing about USD 2/bl during Thursday’s session.

Brent is currently trading around USD 65.8/bl, right back where it began. The volatility reflects the market’s ongoing struggle to balance growing surplus risks against persistent geopolitical uncertainty and resilient refined product margins. Thursday’s slide snapped a three-day rally and came largely in response to a string of bearish signals, most notably from the IEA’s updated short-term outlook.
The IEA now projects record global oversupply in 2026, reinforcing concerns flagged earlier by the U.S. EIA, which already sees inventories building this quarter. The forecast comes just days after OPEC+ confirmed it will continue returning idle barrels to the market in October – albeit at a slower pace of +137,000 bl/d. While modest, the move underscores a steady push to reclaim market share and adds to supply-side pressure into year-end.
Thursday’s price drop also followed geopolitical incidences: Israeli airstrikes reportedly targeted Hamas leadership in Doha, while Russian drones crossed into Polish airspace – events that initially sent crude higher as traders covered short positions.
Yet, sentiment remains broadly cautious. Strong refining margins and low inventories at key pricing hubs like Europe continue to support the downside. Chinese stockpiling of discounted Russian barrels and tightness in refined product markets – especially diesel – are also lending support.
On the demand side, the IEA revised up its 2025 global demand growth forecast by 60,000 bl/d to 740,000 bl/d YoY, while leaving 2026 unchanged at 698,000 bl/d. Interestingly, the agency also signaled that its next long-term report could show global oil demand rising through 2050.
Meanwhile, OPEC offered a contrasting view in its latest Monthly Oil Market Report, maintaining expectations for a supply deficit both this year and next, even as its members raise output. The group kept its demand growth estimates for 2025 and 2026 unchanged at 1.29 million bl/d and 1.38 million bl/d, respectively.
We continue to watch whether the bearish supply outlook will outweigh geopolitical risk, and if Brent can continue to find support above USD 65/bl – a level increasingly seen as a soft floor for OPEC+ policy.
Analys
Waiting for the surplus while we worry about Israel and Qatar

Brent crude makes some gains as Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar rattles markets. Brent crude spiked to a high of USD 67.38/b yesterday as Israel made a strike on Hamas in Qatar. But it wasn’t able to hold on to that level and only closed up 0.6% in the end at USD 66.39/b. This morning it is starting on the up with a gain of 0.9% at USD 67/b. Still rattled by Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar yesterday. Brent is getting some help on the margin this morning with Asian equities higher and copper gaining half a percent. But the dark cloud of surplus ahead is nonetheless hanging over the market with Brent trading two dollar lower than last Tuesday.

Geopolitical risk premiums in oil rarely lasts long unless actual supply disruption kicks in. While Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar is shocking, the geopolitical risk lifting crude oil yesterday and this morning is unlikely to last very long as such geopolitical risk premiums usually do not last long unless real disruption kicks in.
US API data yesterday indicated a US crude and product stock build last week of 3.1 mb. The US API last evening released partial US oil inventory data indicating that US crude stocks rose 1.3 mb and middle distillates rose 1.5 mb while gasoline rose 0.3 mb. In total a bit more than 3 mb increase. US crude and product stocks usually rise around 1 mb per week this time of year. So US commercial crude and product stock rose 2 mb over the past week adjusted for the seasonal norm. Official and complete data are due today at 16:30.
A 2 mb/week seasonally adj. US stock build implies a 1 – 1.4 mb/d global surplus if it is persistent. Assume that if the global oil market is running a surplus then some 20% to 30% of that surplus ends up in US commercial inventories. A 2 mb seasonally adjusted inventory build equals 286 kb/d. Divide by 0.2 to 0.3 and we get an implied global surplus of 950 kb/d to 1430 kb/d. A 2 mb/week seasonally adjusted build in US oil inventories is close to noise unless it is a persistent pattern every week.
US IEA STEO oil report: Robust surplus ahead and Brent averaging USD 51/b in 2026. The US EIA yesterday released its monthly STEO oil report. It projected a large and persistent surplus ahead. It estimates a global surplus of 2.2 m/d from September to December this year. A 2.4 mb/d surplus in Q1-26 and an average surplus for 2026 of 1.6 mb/d resulting in an average Brent crude oil price of USD 51/b next year. And that includes an assumption where OPEC crude oil production only averages 27.8 mb/d in 2026 versus 27.0 mb/d in 2024 and 28.6 mb/d in August.
Brent will feel the bear-pressure once US/OECD stocks starts visible build. In the meanwhile the oil market sits waiting for this projected surplus to materialize in US and OECD inventories. Once they visibly starts to build on a consistent basis, then Brent crude will likely quickly lose altitude. And unless some unforeseen supply disruption kicks in, it is bound to happen.
US IEA STEO September report. In total not much different than it was in January
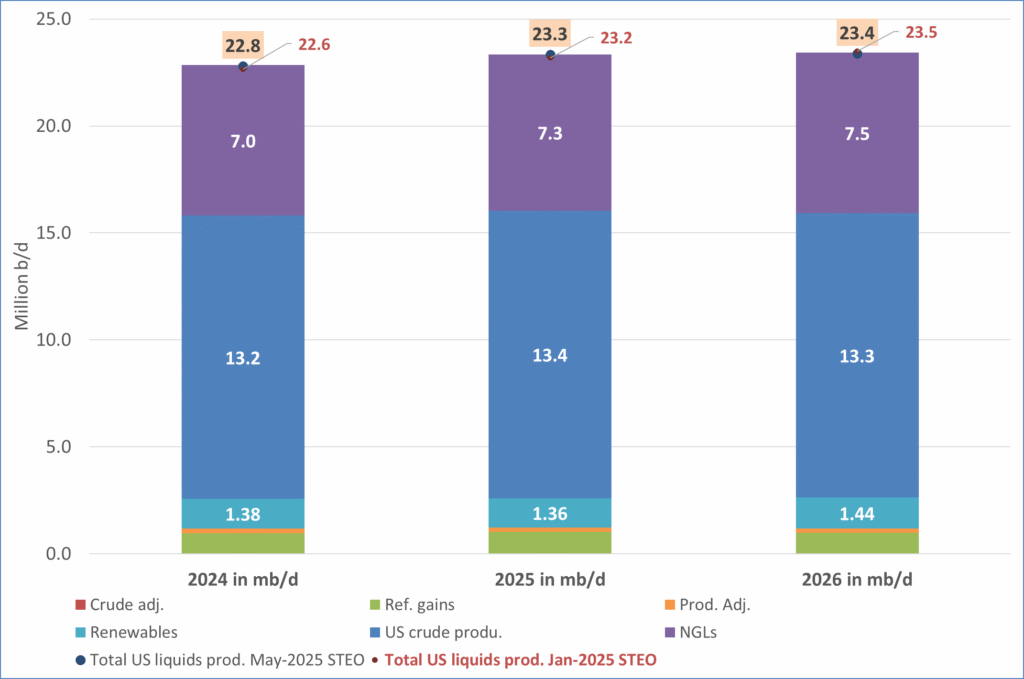
US IEA STEO September report. US crude oil production contracting in 2026, but NGLs still growing. Close to zero net liquids growth in total.
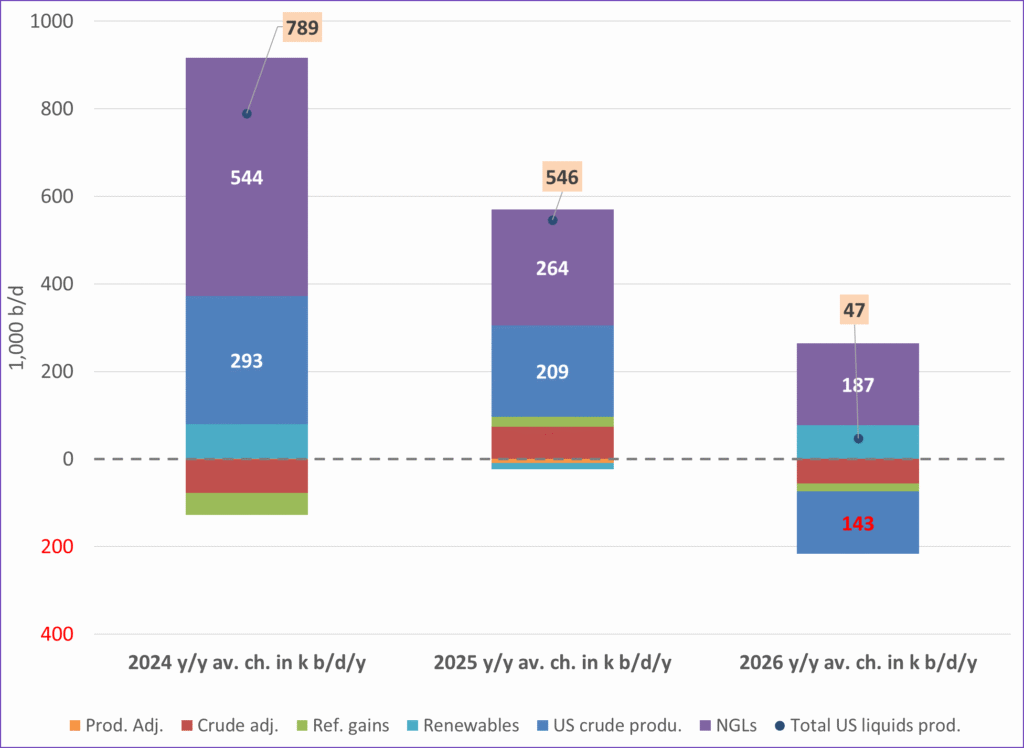
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSommarens torka kan ge högre elpriser i höst
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanBrent edges higher as India–Russia oil trade draws U.S. ire and Powell takes the stage at Jackson Hole
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals är verksamt i guldrikt område i Finland
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanIncreasing risk that OPEC+ will unwind the last 1.65 mb/d of cuts when they meet on 7 September
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanNeil Atkinson spår att priset på olja kommer att stiga till 70 USD
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanEurobattery Minerals satsar på kritiska metaller för Europas självförsörjning