Analys
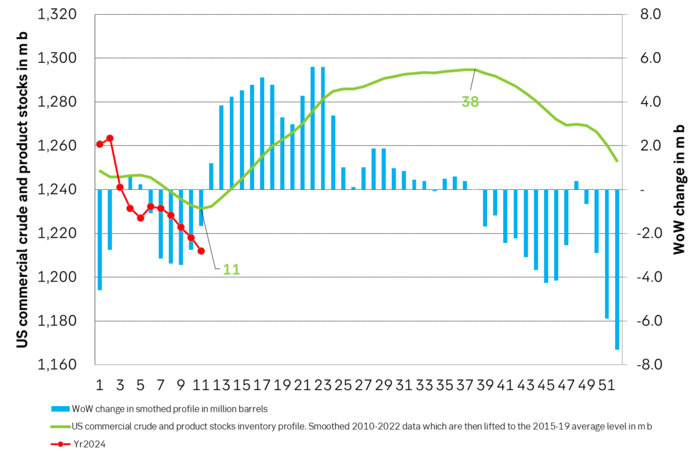
US inventories will likely rise less than normal in mths ahead and that is bullish

US commercial crude and product stocks will now most likely start to rise on a weekly basis and not really start to decline again before in week 38. We do however expect US inventories to rise less than normal in reflection of a global oil market in a slight deficit. This will likely hand support to the Brent crude oil price going forward.

Shedding some value along with bearish metals and China/HK equity losses. Brent crude has trailed lower since it jumped to an intraday high of USD 87.7/b on 19. March spurred by Ukrainian drone attacks on Russian refineries. Ydy if fell back 0.6% and today it is pulling back another 1% to USD 85.4/b. But the decline today is accompanied by declines in industrial metals together with a 1.3% decline in Chinese and Hong Kong equities. Thus more broad based forces are helping to pull the oil price lower.
US API indicated a 5.4 m b rise in US oil stocks last week. But rising stocks are normal now onwards. The US API ydy indicated that US crude stocks rose 9.3 m b last week while gasoline stocks declined 4.4 m b while distillates rose 0.5 m b. I.e. a total rise in crude and products of 5.4 m b (actual EIA data today at 15:30 CET). That may have helped to push Brent crude lower this morning. It is however very important to be aware that US inventories seasonally tend to rise from week 12 to week 38. And from week 12 to 24 the average weekly rise is 4.1 m b per week. The increase indicated by the US API ydy is thus not at all way out of line with what is normally taking place in the months to come. What really matters is how US commercial inventories do versus what is normal at the time of year.
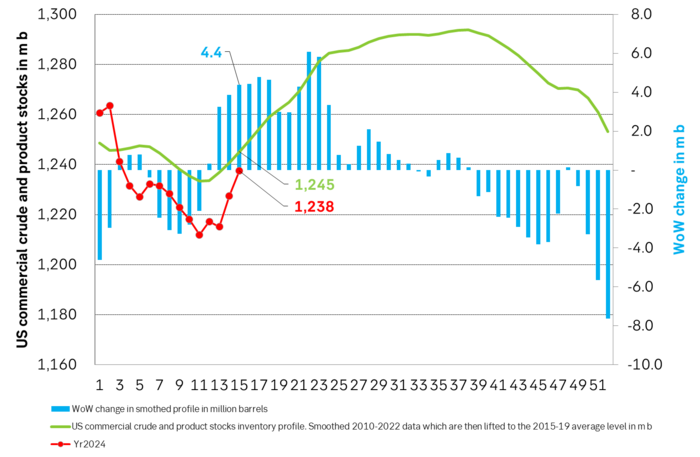
US commercial stocks have fallen 17 m b more than normal since end of 2023. So far this year we have seen a draw of 39 m b vs the last week of 2023. The normal draw over this period is only -22 m b. I.e. US commercial inventories have drawn down 17 m b more than normal over this period. This has been the gradual, bullish nudge on oil prices. US commercial stocks should normally rise 63.5 m b from week 12 to week 38. What matters to oil prices is thus whether US inventories rise more or less than that over this period.
Drone attacks on Russian refineries was a catalyst to release Brent to higher levels. Brent crude broke out to the upside on 13 March along with the Ukrainian drone attacks on Russian refineries. Some 800 k b/d of refining capacity was hurt and probably went off line. But in the global scheme of things this is a mere 1% or so of total global refining capacity. And if we assume that it is off line for say 3 months, then it equates to maybe 0.25% impact on global refining activity in 2024 which is easy to adapt to. Refining margins have not moved much at all. ARA spot diesel cracks are now USD 2.25/b lower than it was in 12 March 2024. Thus no crisis for refined products at all.
We’ll probably not return to pre-drone attack price level of USD 82/b any time soon. Though a dip to that price level is of course not at all out of the question. The oil market may send the oil price lower in the short term since very little material impact in the global scope of things seems to follow from the drone attacks on Russian refineries. Our view is however that the attacks were more like a catalyst to release the oil price to the upside following a steady and stronger than normal decline in US commercial inventories. I.e. the latest price gains in our view is not so much about an added risk premium in the oil price but more about oil price finally adjusting higher according to the fundamentals which have played out since the start of the year with stronger than normal declines in US commercial inventories. We thus see no immediate return to pre-drone-attack price level of USD 82/b. Rather we expect to see continued support to the upside through steady, gradual inventory erosion versus normal like we have seen so far this year.
Voluntary cuts by Russia in Q2-24 could be bullish if delivered as promised. Earlier in March we saw Russia’n willingness to cut back supply in Q2-24 in a mix of production restraints and export restraints. Saudi Arabia and Russia are equal partners in OPEC+ with equal magnitudes of production. In a reflection of this they set equal baselines in May 2020 of 11.0 m b/d. Saudi Arabia produced 9.0 m b/d in February while Russia produced 9.4 m b/d. This is probably why Russia in early March stated that they were willing to cut back in Q2-24. To align more with what Saudi Arabia is producing. It has been of huge importance that Saudi Arabia last year cut its production down to 9.0 m b/d and thus below Russian production. This reactivated Russia as a dynamic, proactive participant in OPEC+. The actual effect of proclaimed production/export cuts by Russia in Q2-24 remains to be seen, but calls for USD 100/b as a consequence of such cuts have surfaced.
So far we haven’t lost a single drop of oil due to Houthie attacks in the Red Sea. We have lost some up-time in Russia refining due to Ukrainian drone strikes lately. But nothing more than can be compensated elsewhere in the world. Temporarily reduced volumes of refined hydrocarbons from Russian will instead lead to higher exports of unrefined molecules (crude oil).
For now OPEC+ is comfortably controlling the oil market and the market will likely be running a slight deficit as a result with inventories getting a continued gradual widening, negative difference versus normal levels thus nudging the oil price yet higher. SEB’s forecast for Brent crude average 2024 is USD 85/b. This means that we’ll likely see both USD 90/b and maybe also USD 100/b some times during the year. But do make sure to evaluate changes in US oil inventories versus what is normal at the time of year. Rising inventories are bullish if they rise less than what is normal from now to week 38.
US commercial crude and product stocks will likely rise going forward. But since the global oil market is likely going to be in slight deficit we’ll likely see slower than normal rise in US inventories with an increasing negative difference to normal inventory levels.
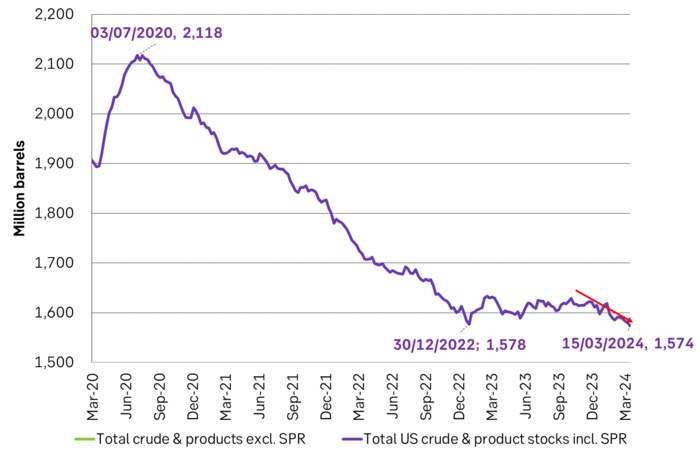
Total US crude and product stocks incl. SPR are now 4 m b below the low-point from December 2022
Analys
’wait and see’ mode

So far this week, Brent Crude prices have strengthened by USD 1.3 per barrel since Monday’s opening. While macroeconomic concerns persist, they have somewhat abated, resulting in muted price reactions. Fundamentals predominantly influence global oil price developments at present. This week, we’ve observed highs of USD 89 per barrel yesterday morning and lows of USD 85.7 per barrel on Monday morning. Currently, Brent Crude is trading at a stable USD 88.3 per barrel, maintaining this level for the past 24 hours.

Additionally, there has been no significant price reaction to Crude following yesterday’s US inventory report (see page 11 attached):
- US commercial crude inventories (excluding SPR) decreased by 6.4 million barrels from the previous week, standing at 453.6 million barrels, roughly 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
- Total motor gasoline inventories decreased by 0.6 million barrels, approximately 4% below the five-year average.
- Distillate (diesel) inventories increased by 1.6 million barrels but remain weak historically, about 7% below the five-year average.
- Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude + products) decreased by 3.8 million barrels last week.
Regarding petroleum products, the overall build/withdrawal aligns with seasonal patterns, theoretically exerting limited effect on prices. However, the significant draw in commercial crude inventories counters the seasonality, surpassing market expectations and API figures released on Tuesday, indicating a draw of 3.2 million barrels (compared to Bloomberg consensus of +1.3 million). API numbers for products were more in line with the US DOE.
Against this backdrop, yesterday’s inventory report is bullish, theoretically exerting upward pressure on crude prices.
Yet, the current stability in prices may be attributed to reduced geopolitical risks, balanced against demand concerns. Markets are adopting a wait-and-see approach ahead of Q1 US GDP (today at 14:30) and the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, “core PCE prices” (tomorrow at 14:30). A stronger print could potentially dampen crude prices as market participants worry over the demand outlook.
Geopolitical “risk premiums” have decreased from last week, although concerns persist, highlighted by Ukraine’s strikes on two Russian oil depots in western Russia and Houthis’ claims of targeting shipping off the Yemeni coast yesterday.
With a relatively calmer geopolitical landscape, the market carefully evaluates data and fundamentals. While the supply picture appears clear, demand remains the predominant uncertainty that the market attempts to decode.
Analys
Also OPEC+ wants to get compensation for inflation

Brent crude has fallen USD 3/b since the peak of Iran-Israel concerns last week. Still lots of talk about significant Mid-East risk premium in the current oil price. But OPEC+ is in no way anywhere close to loosing control of the oil market. Thus what will really matter is what OPEC+ decides to do in June with respect to production in Q3-24 and the market knows this very well. Saudi Arabia’s social cost-break-even is estimated at USD 100/b today. Also Saudi Arabia’s purse is hurt by 21% US inflation since Jan 2020. Saudi needs more money to make ends meet. Why shouldn’t they get a higher nominal pay as everyone else. Saudi will ask for it

Brent is down USD 3/b vs. last week as the immediate risk for Iran-Israel has faded. But risk is far from over says experts. The Brent crude oil price has fallen 3% to now USD 87.3/b since it became clear that Israel was willing to restrain itself with only a muted counter attack versus Israel while Iran at the same time totally played down the counterattack by Israel. The hope now is of course that that was the end of it. The real fear has now receded for the scenario where Israeli and Iranian exchanges of rockets and drones would escalate to a point where also the US is dragged into it with Mid East oil supply being hurt in the end. Not everyone are as optimistic. Professor Meir Javedanfar who teaches Iranian-Israeli studies in Israel instead judges that ”this is just the beginning” and that they sooner or later will confront each other again according to NYT. While the the tension between Iran and Israel has faded significantly, the pain and anger spiraling out of destruction of Gaza will however close to guarantee that bombs and military strifes will take place left, right and center in the Middle East going forward.
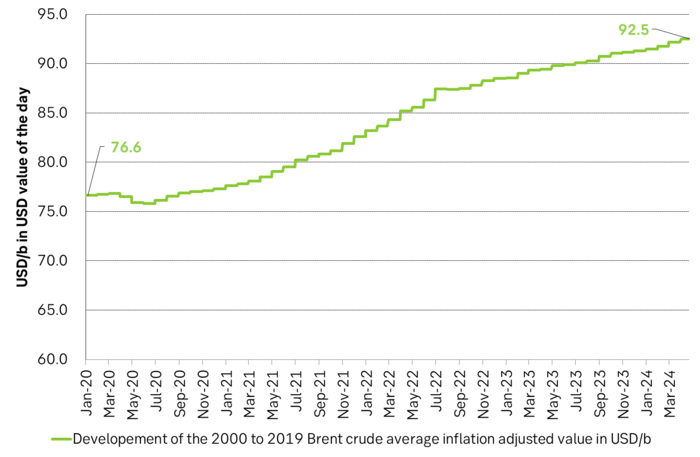
Also OPEC+ wants to get paid. At the start of 2020 the 20 year inflation adjusted average Brent crude price stood at USD 76.6/b. If we keep the averaging period fixed and move forward till today that inflation adjusted average has risen to USD 92.5/b. So when OPEC looks in its purse and income stream it today needs a 21% higher oil price than in January 2020 in order to make ends meet and OPEC(+) is working hard to get it.
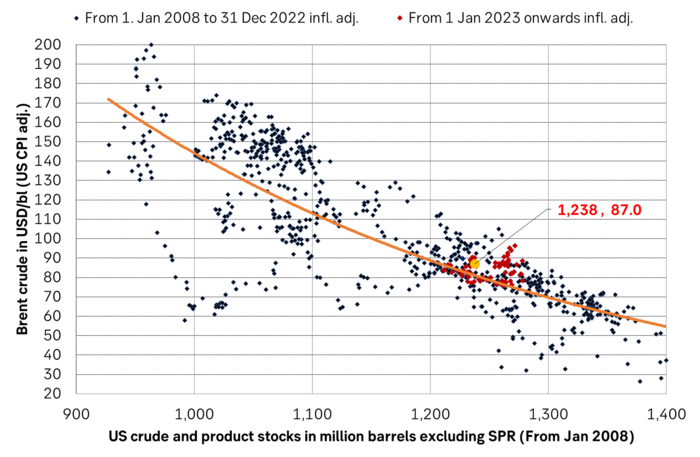
Much talk about Mid-East risk premium of USD 5-10-25/b. But OPEC+ is in control so why does it matter. There is much talk these days that there is a significant risk premium in Brent crude these days and that it could evaporate if the erratic state of the Middle East as well as Ukraine/Russia settles down. With the latest gains in US oil inventories one could maybe argue that there is a USD 5/b risk premium versus total US commercial crude and product inventories in the Brent crude oil price today. But what really matters for the oil price is what OPEC+ decides to do in June with respect to Q3-24 production. We are in no doubt that the group will steer this market to where they want it also in Q3-24. If there is a little bit too much oil in the market versus demand then they will trim supply accordingly.
Also OPEC+ wants to make ends meet. The 20-year real average Brent price from 2000 to 2019 stood at USD 76.6/b in Jan 2020. That same averaging period is today at USD 92.5/b in today’s money value. OPEC+ needs a higher nominal price to make ends meet and they will work hard to get it.
Inflation adjusted Brent crude price versus total US commercial crude and product stocks. A bit above the regression line. Maybe USD 5/b risk premium. But type of inventories matter. Latest big gains were in Propane and Other oils and not so much in crude and products
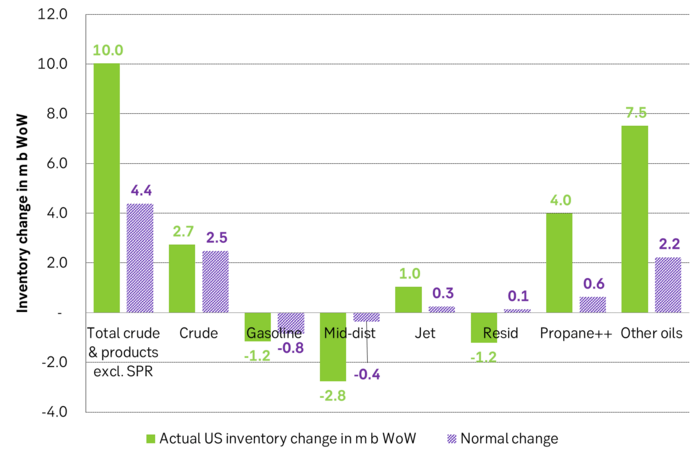
Total US commercial crude and product stocks usually rise by 4-5 m b per week this time of year. Gains have been very strong lately, but mostly in Propane and Other oils
Last week’s US inventory data. Big rise of 10 m b in commercial inventories. What really stands out is the big gains in Propane and Other oils
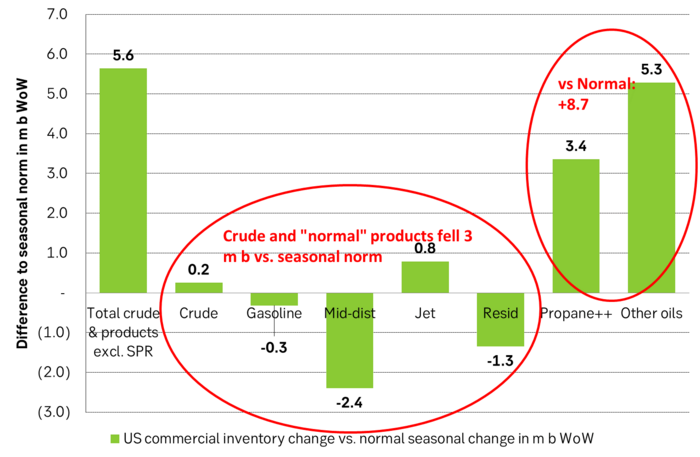
Take actual changes minus normal seasonal changes we find that US commercial crude and regular products like diesel, gasoline, jet and bunker oil actually fell 3 m b versus normal change.
Analys
Nat gas to EUA correlation will likely switch to negative in 2026/27 onward

Historically positive Nat gas to EUA correlation will likely switch to negative in 2026/27 onward

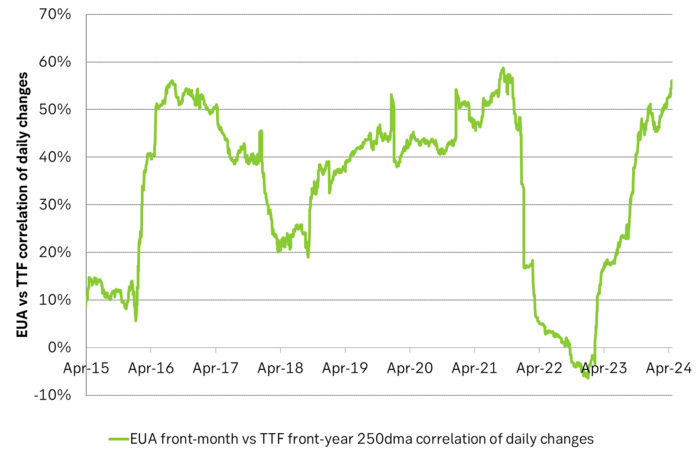
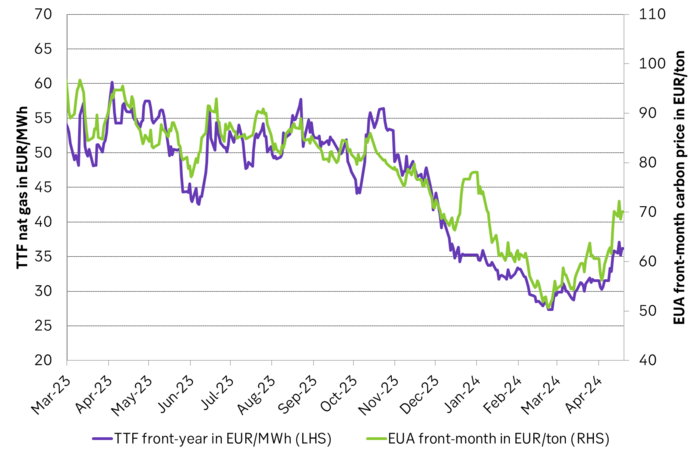
Historically there has been a strong, positive correlation between EUAs and nat gas prices. That correlation is still fully intact and possibly even stronger than ever as traders increasingly takes this correlation as a given with possible amplification through trading action.
The correlation broke down in 2022 as nat gas prices went ballistic but overall the relationship has been very strong for quite a few years.
The correlation between nat gas and EUAs should be positive as long as there is a dynamical mix of coal and gas in EU power sector and the EUA market is neither too tight nor too weak:
Nat gas price UP => ”you go black” by using more coal => higher emissions => EUA price UP
But in the future we’ll go beyond the dynamically capacity to flex between nat gas and coal. As the EUA price moves yet higher along with a tightening carbon market the dynamical coal to gas flex will max out. The EUA price will then trade significantly above where this flex technically will occur. There will still be quite a few coal fired power plants running since they are needed for grid stability and supply amid constrained local grids.
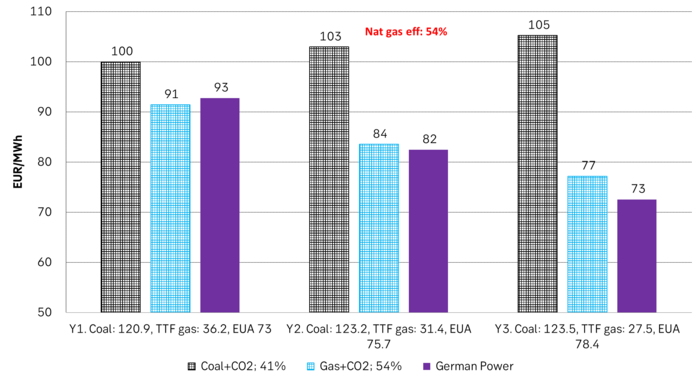
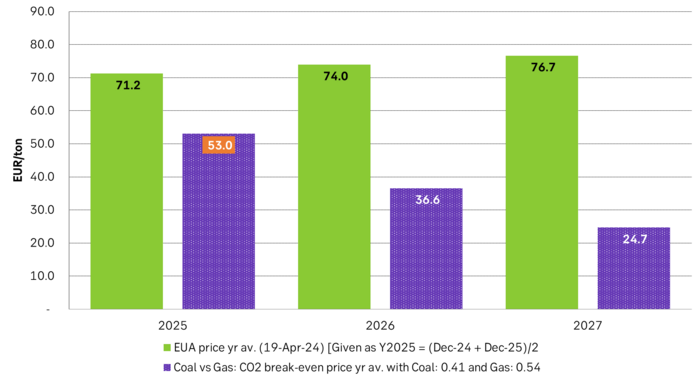
As it looks now we still have such overall coal to gas flex in 2024 and partially in 2025, but come 2026 it could be all maxed out. At least if we look at implied pricing on the forward curves where the forward EUA price for 2026 and 2027 are trading way above technical coal to gas differentials. The current forward pricing implications matches well with what we theoretically expect to see as the EUA market gets tighter and marginal abatement moves from the power sector to the industrial sector. The EUA price should then trade up and way above the technical coal to gas differentials. That is also what we see in current forward prices for 2026 and 2027.
The correlation between nat gas and EUAs should then (2026/27 onward) switch from positive to negative. What is left of coal in the power mix will then no longer be dynamically involved versus nat gas and EUAs. The overall power price will then be ruled by EUA prices, nat gas prices and renewable penetration. There will be pockets with high cost power in the geographical points where there are no other alternatives than coal.
The EUA price is an added cost of energy as long as we consume fossil energy. Thus both today and in future years we’ll have the following as long as we consume fossil energy:
EUA price UP => Pain for consumers of energy => lower energy consumption, faster implementation of energy efficiency and renewable energy => lower emissions
The whole idea with the EUA price is after all that emissions goes down when the EUA price goes up. Either due to reduced energy consumption directly, accelerated energy efficiency measures or faster switch to renewable energy etc.
Let’s say that the coal to gas flex is maxed out with an EUA price way above the technical coal to gas differentials in 2026/27 and later. If the nat gas price then goes up it will no longer be an option to ”go black” and use more coal as the distance to that is too far away price vise due to a tight carbon market and a high EUA price. We’ll then instead have that:
Nat gas higher => higher energy costs with pain for consumers => weaker nat gas / energy demand & stronger drive for energy efficiency implementation & stronger drive for more non-fossil energy => lower emissions => EUA price lower
And if nat gas prices goes down it will give an incentive to consume more nat gas and thus emit more CO2:
Cheaper nat gas => Cheaper energy costs altogether, higher energy and nat gas consumption, less energy efficiency implementations in the broader economy => emissions either goes up or falls slower than before => EUA price UP
Historical and current positive correlation between nat gas and EUA prices should thus not at all be taken for granted for ever and we do expect this correlation to switch to negative some time in 2026/27.
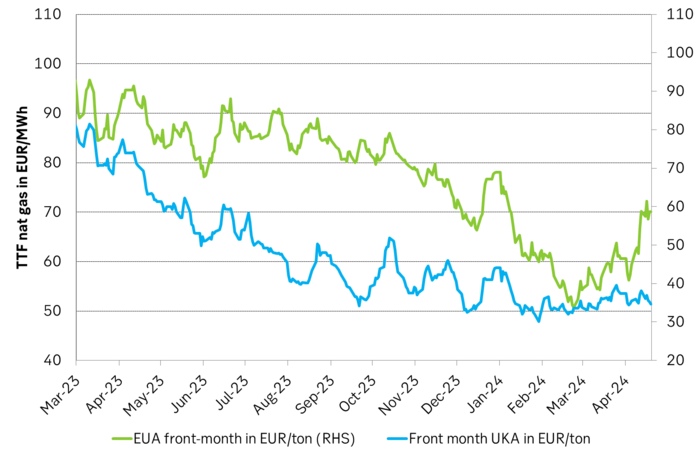
In the UK there is hardly any coal left at all in the power mix. There is thus no option to ”go black” and burn more coal if the nat gas price goes up. A higher nat gas price will instead inflict pain on consumers of energy and lead to lower energy consumption, lower nat gas consumption and lower emissions on the margin. There is still some positive correlation left between nat gas and UKAs but it is very weak and it could relate to correlations between power prices in the UK and the continent as well as some correlations between UKAs and EUAs.
Correlation of daily changes in front month EUA prices and front-year TTF nat gas prices, 250dma correlation.
EUA price vs front-year TTF nat gas price since March 2023
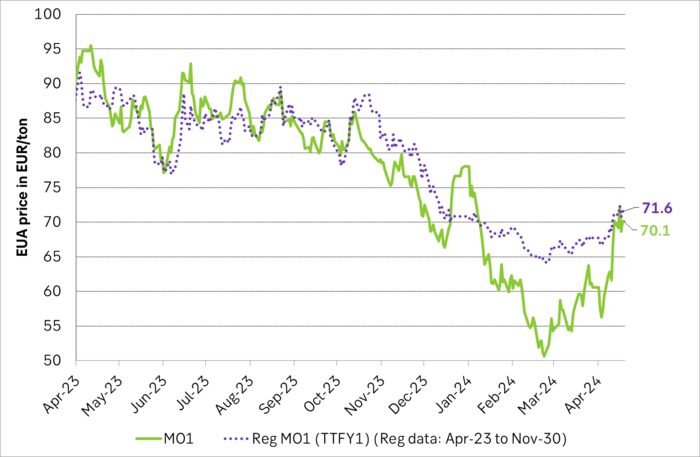
Front-month EUA price vs regression function of EUA price vs. nat gas derived from data from Apr to Nov last year.
The EUA price vs the UKA price. Correlations previously, but not much any more.
Forward German power prices versus clean cost of coal and clean cost of gas power. Coal is totally priced out vs power and nat gas on a forward 2026/27 basis.
Forward price of EUAs versus technical level where dynamical coal to gas flex typically takes place. EUA price for 2026/27 is at a level where there is no longer any price dynamical interaction or flex between coal and nat gas. The EUA price should/could then start to be negatively correlated to nat gas.
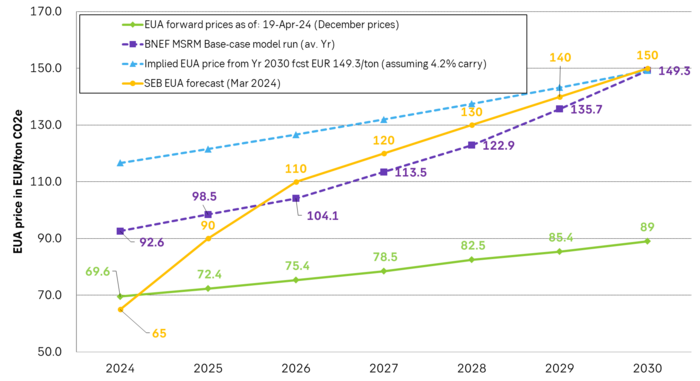
Forward EAU price vs. BNEF base model run (look for new update will come in late April), SEB’s EUA price forecast.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGuldpriset når nytt all time high och bryter igenom 2300 USD
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanUSAs stigande konsumtion av naturgas
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanCentralbanker fortsatte att köpa guld under februari
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanKakaomarknaden är extrem för tillfället
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanHur mår den svenska skogsbraschen? Två favoritaktier
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBoliden på 20 minuter
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanBetydande underskott i utbudet av olja kan få priset att blossa upp
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMyten om guld – Den magiska metallen född från stjärnstoft









