Analys
From surge to slump for natural gas: Navigating the new normal in Europe

Over the past 4-5 months, EU natural gas prices, indicated by the TTF benchmark, have plummeted by 50% from an October high of EUR 56/MWh to the current EUR 28/MWh for the front-month contract, defying expectations of seasonal price increases. This downturn can be attributed to robust EU inventories at 59% capacity and persistently subdued natural gas demand, down by 11% compared to historical norms. Mild weather in Northwest Europe and a prolonged industrial recession have suppressed consumption, resulting in a significant gas surplus despite nearing the end of the winter heating season (90% complete). These factors collectively exert downward pressure on prices.

The correlation between Brent and TTF prices remains from times partly “fluid”. In our December 2023 natural gas price update, we predicted a constrained global natural gas market, anticipating a swift resurgence in demand following a decline in gas prices. Our projections were underpinned by a robust Brent Crude price outlook, set at USD 85/bl, USD 87.5/bl, and USD 90/bl for 2024, 2025, and 2026 respectively, with a Crude-to-gas rate of 80%. However, this scenario has yet to materialize as the anticipated demand recovery has been notably delayed, requiring even lower prices than initially predicted for its realization—a phenomenon unique in recent memory.
Achieving a global natural gas price convergence towards levels more aligned with Brent Crude appears plausible, signaling a return to a measure of normalcy. The absence of a winter premium during the 2023/24 winter season suggests a healthier outlook for Q2-24, mitigating the risk of substantial short-term price spikes in European gas markets. The sporadic spikes witnessed in 2022 and partially in 2023 are now a thing of the past, indicating a change from the volatility experienced in recent years.
Short-term EU gas prices hinge heavily on immediate weather patterns and industrial gas demand, both exerting considerable influence on inventory levels, which serve as a critical gauge of supply and demand dynamics. Looking further ahead, the trajectory of prices is linked with the global LNG balance, particularly contingent upon factors such as projected US natural gas production and the capacity of US LNG exports to the global market.
Moreover, the declining influence of Russia on the European gas market is notable, with sporadic gas export halts from the former energy powerhouse carrying reduced impact. Global market recalibrations indicate a sustained elevation in price levels, with EUR 30/MWh emerging as a feasible benchmark for the foreseeable future. We also call “the end of the energy crisis”, as the worst is history. Reflecting on the current year, EU TTF prices hit the lowest point in late February, with expectations of a potential slide/climb from current prices at EUR 28/MWh.
In essence, our current natural gas price forecast hinges on a delicate equilibrium among three pivotal factors. Firstly, the TTF price must strike a balance, remaining sufficiently low to stimulate a resurgence in demand. For context, the historical average real price hovers around EUR 27/MWh, with EUR 30/MWh anticipated to gradually encourage demand recovery, thereby mitigating the effects of demand destruction. Secondly, the TTF price should maintain a relatively ”normal” relationship with Crude prices, as historical trends indicate a natural correlation between the two. A notably low rate would invariably attract heightened interest from Asian markets, as LNG emerges as a cost-effective alternative to oil in terms of energy content. Lastly, the TTF price must also exhibit a level of elevation to cover the expenses associated with producing and transporting US natural gas to the European market. This entails factoring in costs related to Henry Hub, tolling fees, liquefaction, transportation, and regasification, among other associated expenses. Achieving a delicate equilibrium among these factors is vital for ensuring the stability and sustainability of natural gas pricing dynamics in the European market.
Consequently, our current stance reflects a delicate balancing act among these three critical factors. Settling on EUR 30/MWh, we predict that prices lower than this threshold would catalyze a swifter demand resurgence, while simultaneously enhancing the appeal of natural gas against oil as the spread widens. Moreover, importation from the USA would encounter mounting challenges as prices decline, particularly approaching the EUR 25/MWh mark when landed in ARA.
The TTF market has been complexly interlinked with the global LNG market at the margins since 2015, many years before the energy crisis. While the proportion of LNG consumed in Europe has surged significantly, the concept of LNG prices influencing TTF prices at the margin is not new. However, in terms of volume, the current situation declares us notably more vulnerable than in previous years.
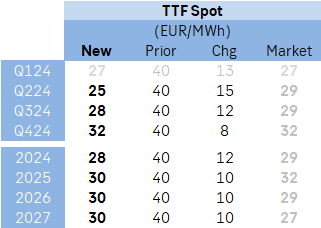
In our updated projections, we have revised our price forecasts downward, particularly notable at the front end, encompassing Q2-24, Q3-24, and the Full-year (FY) 2024. Other adjustments, though marginally smaller, remain for FY 2025, 2026, and 2027. Despite these reductions, we anticipate a trajectory of increasing European natural gas prices from their current levels. Notably, Q1-24 is now expected to average EUR 27/MWh, followed by predictions of EUR 25/MWh, EUR 28/MWh, and EUR 32/MWh for Q2-24, Q3-24, and Q4-24 respectively. Consequently, the average for FY 2024 is forecasted at EUR 28/MWh, marking a notable decline from the previous estimate of EUR 40/MWh.
In our outlook for longer-term pricing, we anticipate an average of EUR 30/MWh for the years 2025, 2026, and 2027—a reduction of EUR 10/MWh compared to our previous update in December 2023, which projected EUR 40/MWh. This long-term forecast only sits marginally higher, by EUR 3-4/MWh, than the historical average real price of approximately EUR 27/MWh. Such pricing aligns intending to stimulate further demand recovery and maintain consumer affordability within the European economy. Reflecting on historical trends, previous price levels in the European market might be seen as reliant on potentially risky agreements with Russia. Consequently, the era of exceptionally low-cost energy is drawing to a close, indicating a new paradigm where European gas and power are priced slightly higher, establishing a ”new normal” for the foreseeable future.
PRICE ACTION
The absence of a winter premium for global natural gas is notable. Our longer-term natural gas price projection, set at EUR 30/MWh, demonstrates resilience compared to historical market norms. Last quarter (Q4-23) closed at EUR 43/MWh for the front-month contract, a figure approximately EUR 10/MWh lower than our recent expectations. Noteworthy market adjustments have transpired not only within the European gas market but also on a global scale. This ongoing adaptation is expected to continue influencing the gas market into 2024, resulting in fewer severe price spikes and a return to more normal price differentials.
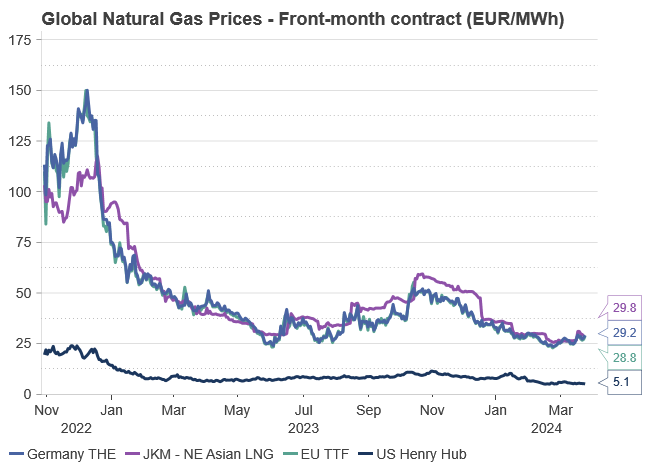
Maintaining our gas price forecast at EUR 30/MWh for 2025 suggests an expectation for European natural gas prices to stabilize at current market rates. This projection extends to 2026 and 2027, which stand roughly 30% higher than historical norms – a contrast to the previous era of favorable deals with Russia flooding European consumers with low-cost piped natural gas.
Considerable attention is drawn to the relationship between gas and oil prices. With our oil market outlook projecting USD 85/bl, USD 87.5/bl, and USD 90/bl for 2024, 2025, and 2026 respectively, the convergence of gas prices to more normal circumstances implies a corresponding alignment with oil prices. Historically, EU natural gas prices have traded at 0.55-0.6 times Brent crude prices, a figure that is expected to converge closer to historical norms. However, our forecasts for 2024, 2025, and 2026 slightly exceed historical norms, at 0.62 x Brent, 0.65 x Brent, and 0.62 x Brent respectively, reflecting a tighter natural gas balance in the coming years.
The transformation of global LNG trade, from roughly 5% spot and short-term LNG trade in 2000 to roughly 30% in 2023, underscores a higher degree of flexibility in negotiating spot and short-term LNG contracts. This evolution suggests a shift towards contracts potentially decoupled from Brent indexations, challenging the conventional reliance on oil prices as a benchmarking tool for global natural gas prices.
US LNG
A significant surge in global liquefaction (export) capacity is anticipated from the US and Qatar starting in 2026 and beyond. These large-scale liquefaction projects typically entail long-term contracts with predefined off-takers or demand centers, primarily serving power plants or industrial applications. The transportation of substantial LNG volumes from the US to Europe underscores strategic economic and energy considerations. The US, propelled by abundant shale gas resources and extensive LNG liquefaction infrastructure, has emerged as a major LNG exporter. Europe, seeking to diversify energy sources and reduce dependence on Russia, offers an attractive market for American LNG. Additionally, LNG’s flexibility as a cleaner-burning fuel aligns with Europe’s environmental sustainability objectives and transition away from coal.
The transatlantic LNG trade between the US and Europe capitalizes on arbitrage opportunities driven by regional gas price variations and demand-supply imbalances. This flow not only enhances energy security for European nations but also aids NE Asia in meeting environmental obligations.
The US-Europe netback for LNG cargo depends on various economic factors, including global natural gas prices, US regional supply and demand dynamics, and fluctuations in shipping costs.
The competitiveness of US LNG in the European market is influenced by several factors, including the US benchmark price for domestic natural gas (Henry Hub), source gas costs, voyage costs, shipping costs, and regasification costs at the destination.
In more detail the competitiveness of US LNG in the European market is influenced by factors such as the US benchmark price for domestic natural gas (Henry Hub); Source gas cost (Henry Hub + Tolling fee and liquefaction fee); voyage cost (Insurance, port, canal, boil-off, and fuel cost); shipping cost at day rate; and regasification cost in the other end.
A simplified calculation demonstrates the US-EU arbitrage opportunity. At current market figures, the total cost of delivering LNG from the US to Europe is roughly USD 7.05/MMBtu or approximately EUR 22/MWh. Comparatively, the EU TTF front-month contract trades at EUR 28/MWh, indicating an average EUR 6/MWh arbitrage opportunity and an equal profit margin for traders. However, with state-of-the-art LNG vessels, the total cost could decrease significantly, resulting in a substantial profit margin for traders.
The calculation (with current market figures all in USD per MMBtu as a standard unit):
Front-month Henry Hub (1.65) + 15% tolling fee (0.25) and liquefaction fee for conventional LNG ships (2.5) + Insurance, port, and canal (on average 0.33) + boil-off and fuel cost (on average 1.2) + regasification (0.5) + shipping cost at current day rate (0.62).
i.e., for total cost from the US to Europe we get 1.65 + 0.25 + 2.5 + 0.33 + 1.2 + 0.5 + 0.62 = USD 7.05/MMBtu – or roughly EUR 22/MWh. At the time of writing, the EU TTF front-month contract is trading at EUR 28/MWh. Hence, in the current spot market, the US-EU arbitrage is at roughly on average EUR 6/MWh and equally EUR 6/MWh profit to trader. However, this is a conservative estimate. In a situation with a state-of-the-art MEGI / X-DF LNG vessel, we would have a lower liquefaction fee and per unit insurance, boil-off, and fuel cost, which would imply a total cost of USD 6.0/MMBtu (EUR 18.5/MWh) – consequently, a massive EUR 9.5/MWh profit to the trader. Understating the massive economic argument in shipping LNG from the US to the EU (at current market rates).
But even though a substantial arrival of LNG export capacity in the US is approaching, it is not like the US has unlimited natural gas production, or unlimited LNG capacity to feed the global thirst for LNG. Hence, it is not like the EU TTF will plunge to levels comparable to the US Henry Hub + all associated costs for delivering to the EU.
A substantial surge in LNG export capacity is imminent, fueled by significant investments totaling USD 235 billion directed towards upcoming super-chilled fuel projects since 2019. The majority of these projects are slated to come online from the second half of 2025 onward, with an additional USD 55 billion investment expected by 2025, driving a remarkable 45% surge in LNG liquefaction capacity by the end of the decade.
Currently, the global LNG export market boasts a total capacity of approximately 420 million tonnes, projected to expand significantly to 610 million tonnes by 2030. The bulk of this expansion will stem from Qatar, Russia, and the US, with capacities increasing by roughly 23, 26, and 117 million tonnes respectively from 2024 to 2030.
However, it’s worth noting that on January 26, 2024, the Biden Administration paused LNG exports to non-FTA countries, awaiting updated analyses by the DOE. This affects 4 major projects and risks WTO challenges. The DOE cites outdated assessments, signaling a policy shift and raising market uncertainties.
This pause could have significant geopolitical and trade implications, as it also becomes an election issue. Stakeholders, including exporters and developers, now face uncertainties and must review agreements. Overall, the pause prompts a broader review of LNG export policies, impacting domestic and international markets. However, it’s too early to fully assess its impact, so the aforementioned capacity forecast remains firm for now.
The industry’s confidence is underpinned by the anticipation of rising LNG demand, driven by Europe’s efforts to reduce reliance on Russian gas and Asia’s shift away from coal, particularly in China. Yet, this expansion is not merely speculative; it represents a long-term commitment between suppliers and off-takers. These projects typically entail long-term contracts of 20+ years, often supplying power plants or industrial applications. Consequently, the new LNG export capacity is expected to match a similar scale of demand.
The significant export ventures from the United States to Qatar will further cement LNG’s role in the global energy landscape, with contracts extending well into the 2050s, even surpassing some carbon-neutral targets.
Moreover, there remains ample room for natural gas in the long run. The COP28 acknowledged that transitional fuels like LNG can facilitate the energy transition, signaling implicit support for LNG over dirtier fossil fuels.
Critics argue that natural gas isn’t the most environmentally friendly fossil fuel due to potential methane leakage along the supply chain. However, such concerns arise belatedly as the wave of new facilities is already underway. With oil demand reaching its peak and coal declining gradually, gas is expected to maintain its prominence in the energy mix.
SUPPLY & DEMAND
In the short term, the winter wildcard/premium is gone, pointing to a healthier Q2 2024. We have, a while back, pinpointed that the European natural gas market is in a limbo state between supply uncertainties and demand uncertainties. With a consequence of a winter wildcard largely being balanced by the short/medium-term weather and withdrawal rate of European natural gas inventories.
Recent weather forecasts predict slightly colder temperatures in early April across Northwest Europe, but the preceding winter months saw normal to milder conditions, resulting in lower-than-expected inventory drawdowns and weak price trends.
Looking ahead, forecasts for April to June 2024 suggest above-normal temperatures in Northwest Europe, reducing heating and power demand and maintaining subdued gas consumption. Prices in Q2-24 are forecasted to average around EUR 25/MWh.
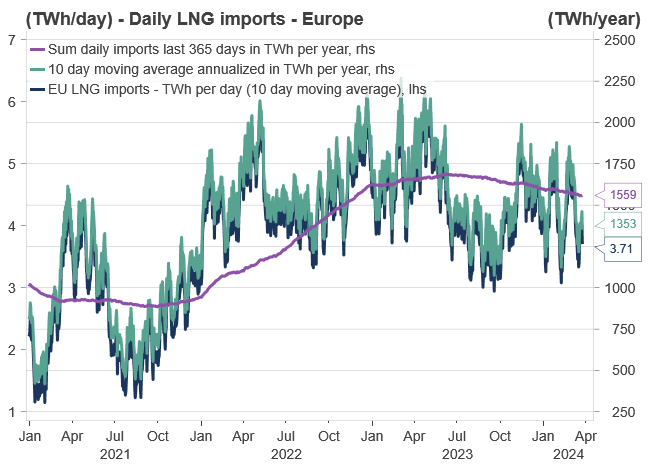
Furthermore, it is easy to think of the faded energy crisis as a European crisis. But the adaptation for global gas markets has been equally/more important. Very high global gas prices have resulted in adaption in all corners of the globe, consequently, easing the global natural gas balance and freeing more gas volumes to the highest bidder at more “reasonable” prices. During the peak of the crisis, the highest bidder was naturally Europe which was sucking up all excess global LNG volumes. However, at the current price levels, the “three importing giants”, namely China, South Korea, and Japan have finally woken up, and are no longer “re-routing” their LNG cargos, while also actively participating in the short-term/spot market.
Russia’s grip over the EU is expected to weaken in the spring/summer of 2024. Since February/March 2022, President Putin sought to balance revenue generation and geopolitical pressure by controlling the energy supply to the EU. This strategy faced challenges: reducing exports to zero would jeopardize revenue, while high exports would alleviate the EU’s energy crisis, as seen in winter 2022/23. Despite efforts, Putin’s goal of using natural gas as a strategic tool faltered in winter 2023/24.
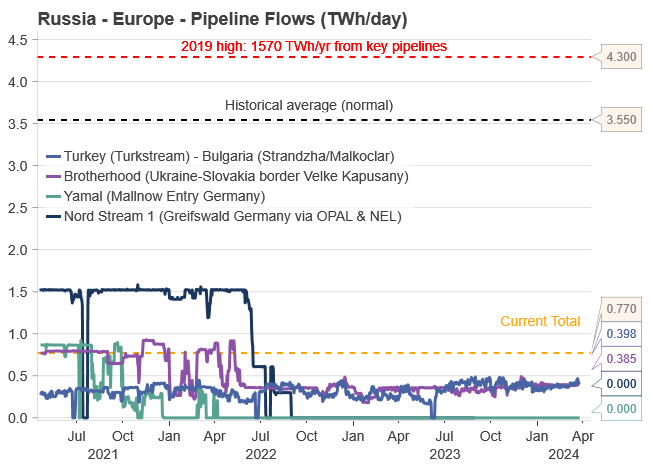
Market adaptation ensued. Since December 2022, Russian piped gas supply to Europe has fluctuated between 10-25% of historical averages, currently nearing 20%. To intensify geopolitical pressure, Russia may need to further reduce flows, possibly to around 10% in winter 2024/25. Despite the distant outlook, the market has already factored in potential price increases for next winter.
Two main pipelines deliver Russian gas to Europe: ”Turkstream,” to Turkey, and the ”Brotherhood,” through Ukraine to Slovakia. These pipelines each contribute roughly 50% of the 0.75 TWh per day flow. The pipeline via Ukraine faces physical risks, and a supply halt is likely next winter as the transit agreement between Gazprom and Naftogaz expires in December 2024, with little chance of renewal.
EU INVENTORIES
The trajectory of EU natural gas inventories for the upcoming summer is primarily influenced by both the global LNG market and European natural gas demand. In Q2-23 (one year ago), inventories commenced the injection season at an all-time high, leading to the current record-high inventory status. These comfortable inventories suggest the EU has the situation under control as it emerges from the winter season. Currently, inventories stand at 59%, a substantial 25% above the 2015-2022 average.
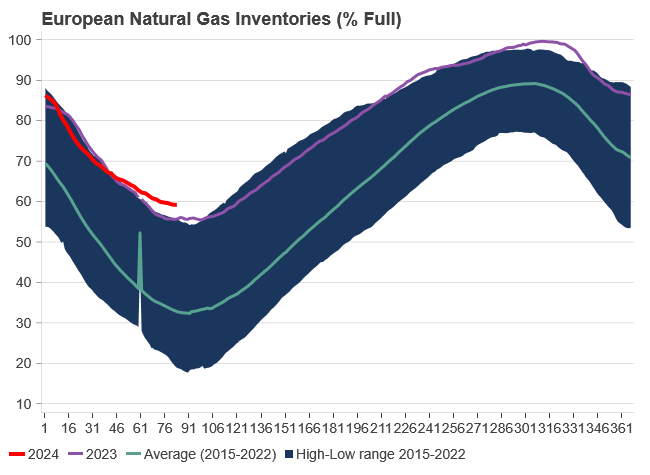
Despite missing out on over 1,000 TWh of natural gas imports from Russia compared to historical levels, the mild winter of 2022/23, reduced demand due to high prices, and increased LNG imports compensated with an additional 1,400 TWh. This over-compensation of 400 TWh in Q1-23 facilitated an unprecedented injection rate into European inventories during Q1 and Q2 2023. As a result, European inventories shifted from a deficit of 180 TWh in January 2022 to a surplus of 259 TWh in April 2023, leading to the current record-high levels.
However, if NE Asia, predominantly led by China, continues to outbid the EU for LNG cargo and industrial gas demand increases due to favorable long-term hedging levels, current comfortable inventory levels will gradually return to normal. This suggests EU TTF prices will slowly climb towards over EUR 30/MWh by the next heating season, a trend partly factored into current pricing.
While the crisis urgency has faded, market adjustments now activate at lower price thresholds. Nonetheless, we anticipate slightly higher long-term price levels (EUR 30/MWh) due to increasing LNG bids from China (+NE Asia), a rebound in EU demand, and reduced LNG imports influenced by lower prices. This will result in a slower inventory build during Q2-24 and Q3-24 compared to last year. Despite diminishing supply from Russia, the EU remains focused on maintaining preparedness for future winters, leading to a new normal in natural gas inventory levels throughout the year.
The European energy crisis has significantly eased during 2023 and Q1-24. Softened front-end prices influence longer-dated prices, with the winter premium/seasonality fully washed out during the ongoing heating season. Healthy EU natural gas inventories, currently at 59% capacity (675 TWh) and surpassing the European Commission’s target of reaching 90% storage fullness by 1 November, contribute to this subsiding crisis. Continued subdued European consumption (11% below historical averages) and robust LNG imports set a ceiling on short-term prices, although increased EU demand could quickly alter this scenario, as EU demand has proven stickier than anticipated.
DEMAND RECOVERY
Reduced uncertainty and lower prices are expected to lead to more long-term hedging. Since the start of Q1 2024 (year-to-date), the TTF spot has averaged EUR 27/MWh, approximately USD 50/boe, only marginally below the ’historical norm’ when adjusted for inflation. Despite these price levels, a resurgence in European industrial gas consumption during the winter is not straightforward.
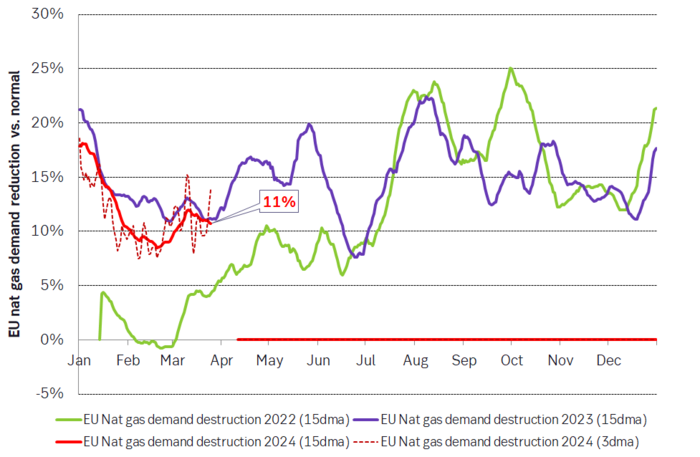
Industrial gas demand remains subdued, sitting 11% below historical averages. While this marks an improvement from the 25-30% drop experienced in mid-summer 2022 – a period characterized as the ”peak of the crisis” – when spot prices consistently traded at EUR 150/MWh (USD 255/boe).
The slower-than-expected recovery is largely attributed to industries hesitating to commit to longer-term prices. For example, during Q4 2023, despite tumbling spot prices, futures prices remained strong. In mid-October, gas for delivery in January 2024 was priced at EUR 55/MWh (USD 103/boe). Thus, during Q4 2023, peak-winter prices maintained a considerable premium over spot prices to a large extent.
However, the current landscape has changed. The winter premium has diminished as we exit the heating season, and weak spot prices predominantly drive forward. This reflects a market that is more certain and willing to forecast futures during a less turbulent phase. The convergence and narrowing gap between spot and long-term prices signify that ”peak natural gas has passed.” Major consumers in Europe are expected to adopt more long-term hedging for longer-term prices, ideally hedging these futures close to current spot prices. This suggests that current market prices will likely trigger increased consumption compared to Q3 and Q4 2023, although a full-scale comeback will take time.
As previously noted, substantial demand destruction occurred not only in Europe but also globally, particularly in Asia. Over the last couple of years, demand destruction amounted to approximately 800 TWh per year, while the normal growth rate in the global LNG market is 200 TWh per annum. This indicates that most of the demand will eventually return, although the timing remains uncertain.
NE ASIAN LNG
EUR 25/MWh presents a favorable ”buy opportunity,” and prices are expected to either slide or climb from this point. The decline in prices can be attributed to sustained low demand and high inventories. We anticipate prices to either slide or increase from here, with minimal downside, as prices are likely to find support around EUR 25/MWh.
Forward prices for both JKM and TTF indicate that the NE Asian LNG market will remain a preferred destination for marginal LNG cargo in the near term. While the EU previously heavily relied on NE Asia, the European market can no longer solely depend on the economic vulnerabilities of NE Asia or China.
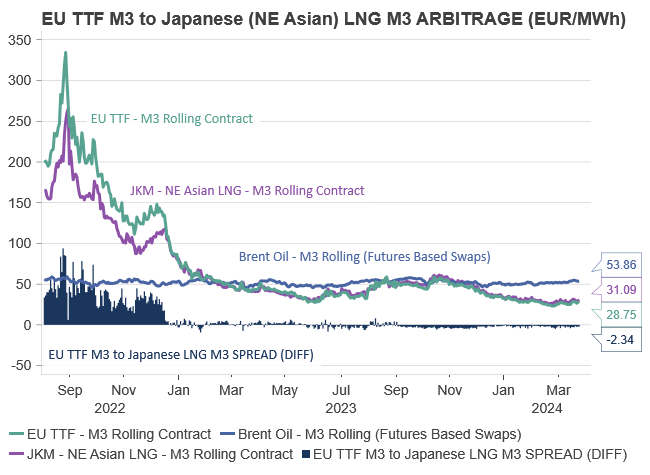
A long-awaited pent-up demand for energy in China would lead to increased demand for goods and services, consequently boosting energy consumption, particularly natural gas, primarily in the form of LNG. In such a scenario, the JKM may command a larger premium over the TTF than the existing EUR 2.5/MWh (3-month rolling contract). This would divert LNG spot cargoes away from Europe, further reducing the EU’s natural gas surplus. Thus, the ongoing recovery in China’s economy is likely to stimulate Asia’s demand for natural gas, potentially resulting in EU LNG purchasers paying a premium to secure essential LNG imports in the future.
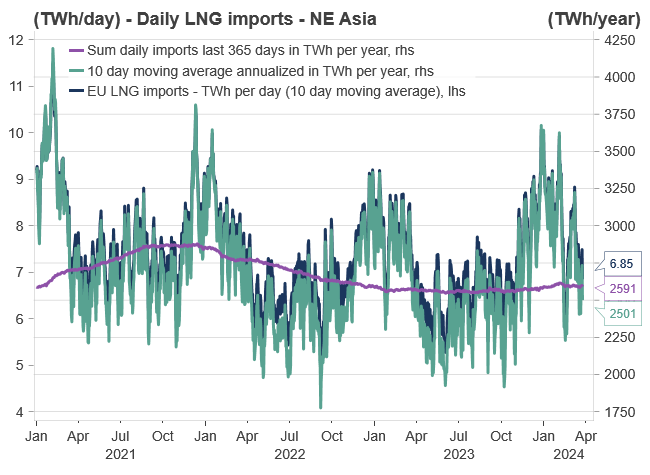
With current prices, we anticipate an increase in EU demand coupled with a decrease in EU LNG imports. This trend may persist until we observe a slight shortfall in compensation relative to the natural gas deficit from Russia, which could drive prices upward during the summer.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
The ongoing transition from coal to natural gas signifies a significant shift in the global energy landscape. Natural gas emerges as a crucial bridging technology, offering a cleaner alternative to coal and facilitating the transition toward widespread adoption of renewable energy sources. This transition underscores the environmental benefits of natural gas, positioning it as a pivotal component in mitigating climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Despite challenges such as the reduction in Russian gas supply, the natural gas market is adapting rapidly. Europe, in particular, faces competition for global LNG volumes, primarily sourced from the US and Qatar. The market’s ability to swiftly adjust reflects its adaptability and resilience on a global scale, highlighting the importance of diversifying energy sources and supply routes.
Our current natural gas price forecast relies on achieving a delicate equilibrium among key factors. This includes stimulating demand, maintaining a correlation with crude prices, and ensuring cost coverage for US natural gas transportation. Striking this balance is essential for maintaining stability and sustainability in European gas pricing dynamics, ensuring energy security.
In response to changing market conditions, we have revised our price outlook downward for the short term, notably for Q2-24, Q3-24, and FY 2024. Specifically, Q1-24 is forecasted to average EUR 27/MWh, followed by predictions of EUR 25/MWh for Q2-24, EUR 28/MWh for Q3-24, and EUR 32/MWh for Q4-24. However, prices are expected to gradually increase over the longer term, with an average forecast of EUR 30/MWh for the years 2025, 2026, and 2027, slightly higher than historical averages.
This revised outlook reflects the evolving nature of the natural gas market and the need for flexibility in response to changing geopolitical landscapes and supply dynamics. Looking ahead, natural gas remains a crucial bridge over coal, facilitating the transition towards cleaner energy sources.
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

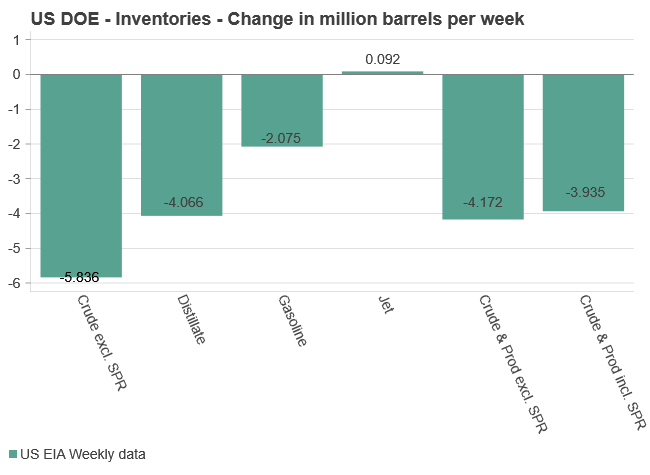
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

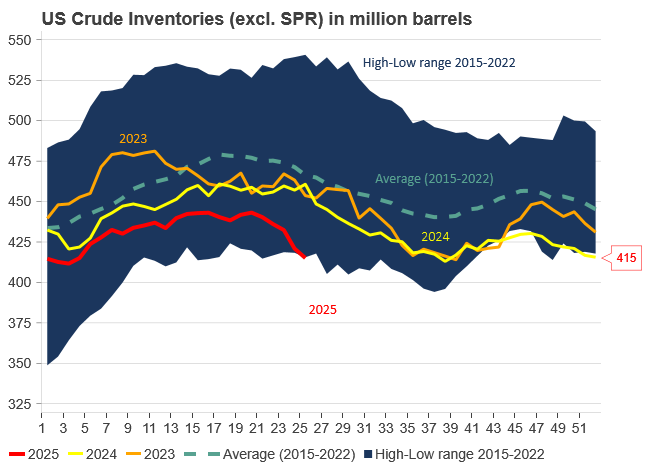
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBrookfield ska bygga ett AI-datacenter på hela 750 MW i Strängnäs
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanTradingfirman XTX Markets bygger datacenter i finska Kajana för 1 miljard euro
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld









