Analys
Reloading the US ’oil-gun’ (SPR) will have to wait until next downturn

Brent crude traded down 0.4% earlier this morning to USD 91.8/b but is unchanged at USD 92.2/b at the moment. Early softness was probably mostly about general market weakness than anything specific to oil as copper is down 0.7% while European equities are down 0.3%. No one knows the consequences of what a ground invasion of Gaza by Israel may bring except that it will be very, very bad for Palestinians, for Middle East politics for geopolitics and potentially destabilizing for global oil markets. As of yet the oil market seems to struggle with how to price the situation with fairly little risk premium priced in at the moment as far as we can see. Global financial markets however seems to have a clearer bearish take on this. Though rallying US rates and struggling Chinese property market may be part of that.

The US has drawn down its Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR) over the latest years to only 50% of capacity. Crude oil prices would probably have to rally to USD 150-200/b before the US would consider pushing another 100-200 m b from SPR into the commercial market. As such the fire-power of its SPR as a geopolitical oil pricing tool is now somewhat muted. The US would probably happily re-load its SPR but it is very difficult to do so while the global oil market is running a deficit. It will have to wait to the next oil market downturn. But that also implies that the next downturn will likely be fairly short-lived and also fairly shallow. Unless of course the US chooses to forgo the opportunity.
The US has drawn down its Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR) to only 50% of capacity over the latest years. Most of the draw-down was in response to the crisis in Ukraine as it was invaded by Russia with loss of oil supply from Russia thereafter.
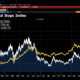
The US has however no problems with security of supply of crude oil. US refineries have preferences for different kinds of crude slates and as a result it still imports significant volumes of crude of different qualities. But overall it is a net exporter of hydrocarbon liquids. It doesn’t need all that big strategic reserves as a security of supply any more. Following the oil crisis in the early 70ies the OECD countries created the International Energy Agency where all its members aimed to have some 100 days of forward oil import coverage. With US oil production at steady decline since the 70ies the US reached a peak in net imports of 13.4 m b/d in 2006. As such it should have held an SPR of 1340 million barrels. It kept building its SPR which peaked at 727 m b in 2012. But since 2006 its net imports have been in sharp decline and today it has a net export of 2.9 m b/d.
Essentially the US doesn’t need such a sizable SPR any more to secure coverage of its daily consumption. As a result it started to draw down its SPR well before the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022. But then of course it fell fast and is today at 351 m b or about 50% of capacity.
The US is the largest oil consumer in the world. As such it is highly vulnerable to the price level of oil. The US SPR today is much more of a geopolitical tool than a security of supply tool. It’s a tool to intervene in the global oil market. To intervene in the price setting of oil. The US SPR is now drawn down to 50% but it still holds a sizable amount of oil. But it is little in comparison to the firepower of OPEC. Saudi Arabia can lower its production by 1 m b/d for one year and it will have eradicated 365 million barrels in global oil inventories. And then it can the same the year after and then the year after that again.
The US has now fired one big bullet of SPR inventory draws. It really helped to balance the global oil market last year and prevented oil prices from going sky high. With 350 m b left in its SPR it can still do more if needed. But the situation would likely need to be way more critical before the US would consider pushing yet another 100-200 m b of oil from its SPR into the global commercial oil market. An oil price of USD 150-200/b would probably be needed before it would do so.
With new geopolitical realities the US probably will want to rebuild its SPR to higher levels as it is now an important geopolitical tool and an oil price management tool. But rebuilding the SPR now while the global oil market is running a deficit is a no-go as we see it.
An oil market downturn, a global recession, a global oil market surplus where OPEC no longer want to defend the oil price with reduced supply is needed for the US to be able to refill its SPR again unless it wants to drive the oil price significantly higher.
But this also implies that the next oil price downturn will likely be short-lived and shallow as the US will have to use that opportunity to rebuild its SPR. It’s kind off like reloading its geopolitical oil gun. If it instead decides to forgo such an opportunity then it will have to accept that its geopolitical maneuverability in the global oil market stays muted.
Net US oil imports in m b/d and US Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR) in million barrels. The US doesn’t need strategic petroleum reserves for the sake of security of supply any more. But it is a great geopolitical energy-tool to intervene in the price setting of oil in the global market place.
Analys
Brent crude ticks higher on tension, but market structure stays soft

Brent crude has climbed roughly USD 1.5-2 per barrel since Friday, yet falling USD 0.3 per barrel this mornig and currently trading near USD 67.25/bbl after yesterday’s climb. While the rally reflects short-term geopolitical tension, price action has been choppy, and crude remains locked in a broader range – caught between supply-side pressure and spot resilience.

Prices have been supported by renewed Ukrainian drone strikes targeting Russian infrastructure. Over the weekend, falling debris triggered a fire at the 20mtpa Kirishi refinery, following last week’s attack on the key Primorsk terminal.
Argus estimates that these attacks have halted ish 300 kbl/d of Russian refining capacity in August and September. While the market impact is limited for now, the action signals Kyiv’s growing willingness to disrupt oil flows – supporting a soft geopolitical floor under prices.
The political environment is shifting: the EU is reportedly considering sanctions on Indian and Chinese firms facilitating Russian crude flows, while the U.S. has so far held back – despite Bessent warning that any action from Washington depends on broader European participation. Senator Graham has also publicly criticized NATO members like Slovakia and Hungary for continuing Russian oil imports.
It’s worth noting that China and India remain the two largest buyers of Russian barrels since the invasion of Ukraine. While New Delhi has been hit with 50% secondary tariffs, Beijing has been spared so far.
Still, the broader supply/demand balance leans bearish. Futures markets reflect this: Brent’s prompt spread (gauge of near-term tightness) has narrowed to the current USD 0.42/bl, down from USD 0.96/bl two months ago, pointing to weakening backwardation.
This aligns with expectations for a record surplus in 2026, largely driven by the faster-than-anticipated return of OPEC+ barrels to market. OPEC+ is gathering in Vienna this week to begin revising member production capacity estimates – setting the stage for new output baselines from 2027. The group aims to agree on how to define “maximum sustainable capacity,” with a proposal expected by year-end.
While the IEA pegs OPEC+ capacity at 47.9 million barrels per day, actual output in August was only 42.4 million barrels per day. Disagreements over data and quota fairness (especially from Iraq and Nigeria) have already delayed this process. Angola even quit the group last year after being assigned a lower target than expected. It also remains unclear whether Russia and Iraq can regain earlier output levels due to infrastructure constraints.
Also, macro remains another key driver this week. A 25bp Fed rate cut is widely expected tomorrow (Wednesday), and commodities in general could benefit a potential cut.
Summing up: Brent crude continues to drift sideways, finding near-term support from geopolitics and refining strength. But with surplus building and market structure softening, the upside may remain capped.
Analys
Volatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk

Brent crude is essentially flat on the week, but after a volatile ride. Prices started Monday near USD 65.5/bl, climbed steadily to a mid-week high of USD 67.8/bl on Wednesday evening, before falling sharply – losing about USD 2/bl during Thursday’s session.

Brent is currently trading around USD 65.8/bl, right back where it began. The volatility reflects the market’s ongoing struggle to balance growing surplus risks against persistent geopolitical uncertainty and resilient refined product margins. Thursday’s slide snapped a three-day rally and came largely in response to a string of bearish signals, most notably from the IEA’s updated short-term outlook.
The IEA now projects record global oversupply in 2026, reinforcing concerns flagged earlier by the U.S. EIA, which already sees inventories building this quarter. The forecast comes just days after OPEC+ confirmed it will continue returning idle barrels to the market in October – albeit at a slower pace of +137,000 bl/d. While modest, the move underscores a steady push to reclaim market share and adds to supply-side pressure into year-end.
Thursday’s price drop also followed geopolitical incidences: Israeli airstrikes reportedly targeted Hamas leadership in Doha, while Russian drones crossed into Polish airspace – events that initially sent crude higher as traders covered short positions.
Yet, sentiment remains broadly cautious. Strong refining margins and low inventories at key pricing hubs like Europe continue to support the downside. Chinese stockpiling of discounted Russian barrels and tightness in refined product markets – especially diesel – are also lending support.
On the demand side, the IEA revised up its 2025 global demand growth forecast by 60,000 bl/d to 740,000 bl/d YoY, while leaving 2026 unchanged at 698,000 bl/d. Interestingly, the agency also signaled that its next long-term report could show global oil demand rising through 2050.
Meanwhile, OPEC offered a contrasting view in its latest Monthly Oil Market Report, maintaining expectations for a supply deficit both this year and next, even as its members raise output. The group kept its demand growth estimates for 2025 and 2026 unchanged at 1.29 million bl/d and 1.38 million bl/d, respectively.
We continue to watch whether the bearish supply outlook will outweigh geopolitical risk, and if Brent can continue to find support above USD 65/bl – a level increasingly seen as a soft floor for OPEC+ policy.
Analys
Waiting for the surplus while we worry about Israel and Qatar

Brent crude makes some gains as Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar rattles markets. Brent crude spiked to a high of USD 67.38/b yesterday as Israel made a strike on Hamas in Qatar. But it wasn’t able to hold on to that level and only closed up 0.6% in the end at USD 66.39/b. This morning it is starting on the up with a gain of 0.9% at USD 67/b. Still rattled by Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar yesterday. Brent is getting some help on the margin this morning with Asian equities higher and copper gaining half a percent. But the dark cloud of surplus ahead is nonetheless hanging over the market with Brent trading two dollar lower than last Tuesday.

Geopolitical risk premiums in oil rarely lasts long unless actual supply disruption kicks in. While Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar is shocking, the geopolitical risk lifting crude oil yesterday and this morning is unlikely to last very long as such geopolitical risk premiums usually do not last long unless real disruption kicks in.
US API data yesterday indicated a US crude and product stock build last week of 3.1 mb. The US API last evening released partial US oil inventory data indicating that US crude stocks rose 1.3 mb and middle distillates rose 1.5 mb while gasoline rose 0.3 mb. In total a bit more than 3 mb increase. US crude and product stocks usually rise around 1 mb per week this time of year. So US commercial crude and product stock rose 2 mb over the past week adjusted for the seasonal norm. Official and complete data are due today at 16:30.
A 2 mb/week seasonally adj. US stock build implies a 1 – 1.4 mb/d global surplus if it is persistent. Assume that if the global oil market is running a surplus then some 20% to 30% of that surplus ends up in US commercial inventories. A 2 mb seasonally adjusted inventory build equals 286 kb/d. Divide by 0.2 to 0.3 and we get an implied global surplus of 950 kb/d to 1430 kb/d. A 2 mb/week seasonally adjusted build in US oil inventories is close to noise unless it is a persistent pattern every week.
US IEA STEO oil report: Robust surplus ahead and Brent averaging USD 51/b in 2026. The US EIA yesterday released its monthly STEO oil report. It projected a large and persistent surplus ahead. It estimates a global surplus of 2.2 m/d from September to December this year. A 2.4 mb/d surplus in Q1-26 and an average surplus for 2026 of 1.6 mb/d resulting in an average Brent crude oil price of USD 51/b next year. And that includes an assumption where OPEC crude oil production only averages 27.8 mb/d in 2026 versus 27.0 mb/d in 2024 and 28.6 mb/d in August.
Brent will feel the bear-pressure once US/OECD stocks starts visible build. In the meanwhile the oil market sits waiting for this projected surplus to materialize in US and OECD inventories. Once they visibly starts to build on a consistent basis, then Brent crude will likely quickly lose altitude. And unless some unforeseen supply disruption kicks in, it is bound to happen.
US IEA STEO September report. In total not much different than it was in January
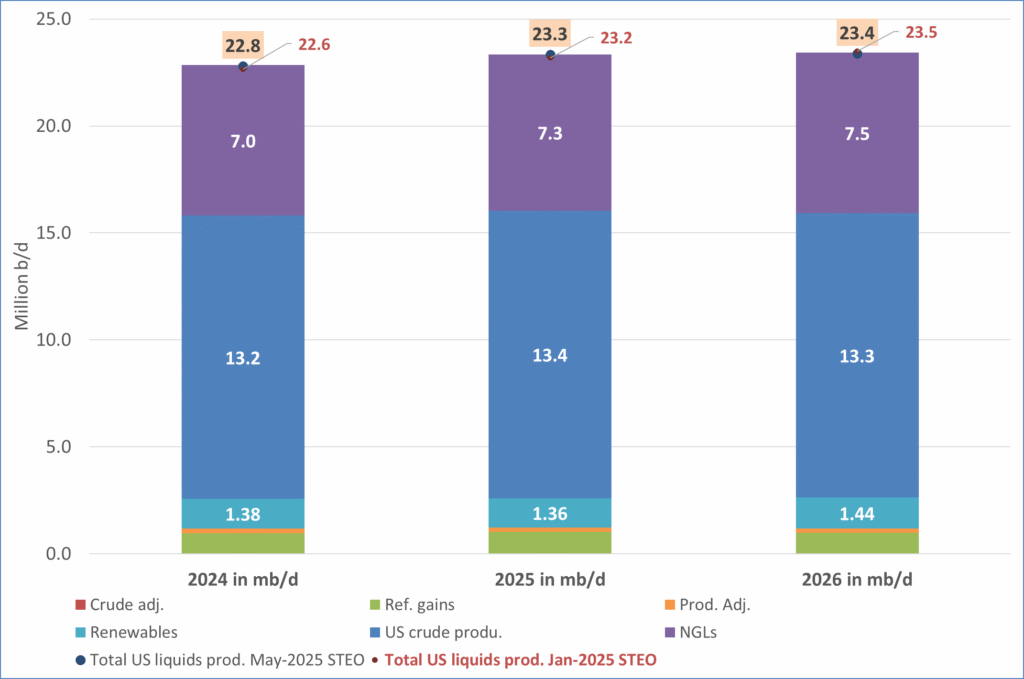
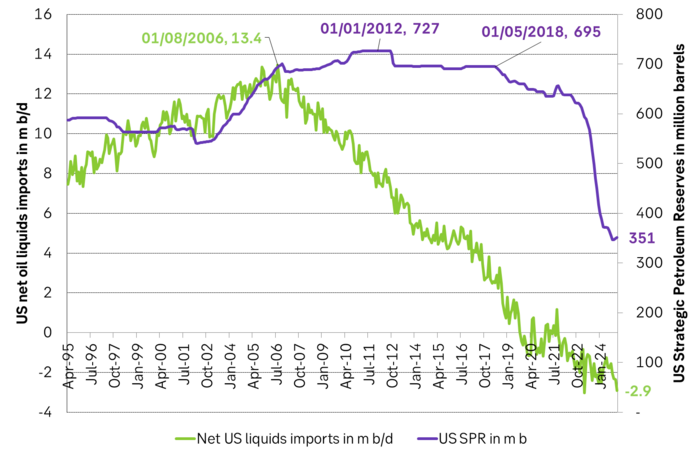
US IEA STEO September report. US crude oil production contracting in 2026, but NGLs still growing. Close to zero net liquids growth in total.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSommarens torka kan ge högre elpriser i höst
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanBrent edges higher as India–Russia oil trade draws U.S. ire and Powell takes the stage at Jackson Hole
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals är verksamt i guldrikt område i Finland
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanIncreasing risk that OPEC+ will unwind the last 1.65 mb/d of cuts when they meet on 7 September
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanNeil Atkinson spår att priset på olja kommer att stiga till 70 USD
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanOPEC+ in a process of retaking market share