Analys
OPEC meeting May 25th – Give me a premium!

 OPEC members and some non-OPEC producers including Russia are most likely going to decide to maintain current production cuts for another six to nine months. Inventories are likely to draw down towards normal at the end of 2017. It will be supportive for oil prices in H2-17 and would likely lift the front month Brent crude oil contract to $60/b by the end of 2017. The risk is however that US shale oil production is stimulated to grow yet more driving both 2018 and 2019 into strict surplus. It may thus be increasingly difficult to exit the cuts further down the road. It thus poses a downside price risk to 2018 unless some cuts are kept all through 2018 as well as 2019.
OPEC members and some non-OPEC producers including Russia are most likely going to decide to maintain current production cuts for another six to nine months. Inventories are likely to draw down towards normal at the end of 2017. It will be supportive for oil prices in H2-17 and would likely lift the front month Brent crude oil contract to $60/b by the end of 2017. The risk is however that US shale oil production is stimulated to grow yet more driving both 2018 and 2019 into strict surplus. It may thus be increasingly difficult to exit the cuts further down the road. It thus poses a downside price risk to 2018 unless some cuts are kept all through 2018 as well as 2019.
“We think that we have everybody on board” said Saudi Arabia’s energy minister Khalid al-Falih (Bloomberg) following a meeting in Vienna on Friday in preparation for the ministerial OPEC meeting on May 25th this week. Both OPEC and some non-OPEC producers were present. He stated that everybody he had talked to viewed a nine months extension of the cuts in H1-17 as a wise decision. Apparently there thus seems to be a unanimous support for an extension of the current cuts. There still seems to be some discussion whether to extend the cuts to Dec 2017 or to Mar 2018.
On November 30th last year individual OPEC members decided to cut production by 1.17 mb/d versus their October production level while a group of non-OPEC producers joined in with a promised cut of 0.6 mb/d. Thus a pledged cut from both OPEC and non-OPEC members of close to 1.8 mb/d. Both OPEC and Russia have delivered on their pledges with OPEC’s production down 1.14 mb/d averaging 32.1 mb/d so far this year while Russia’s production was down 0.3 mb/d in April versus November.
Oil demand will jump seasonally by close to 2% (close to 2 mb/d) from H1-17 to H2-17. Thus production cuts will get a tailwind help by this seasonal jump in demand. If OPEC keeps its production at 32 mb/d in H2-17 we expect global oil inventories to draw down some 350 mb. OECD’s commercial crude and product inventories are today some 300 mb above normal. Some of the draw down may however take place in unspecified non-OECD inventories.
When OPEC decided to cut production last November it did talk about prices. An oil price of $60/b was mentioned many times. That was probably a mistake as it helped to shift forward crude curves higher and helped to stimulate US shale oil rig activation unnecessary.
Now there is no talk about an oil price level. The whole focus is on inventories. When oil inventories are above normal and rising then the crude curves are in deep contango which means a large spot price discount to longer dated crude contracts. Last year the front month Brent crude oil contract had an average discount of $12/b versus the five year contract. Since OPEC mostly sells its oil in the spot market it lost some $150 – 200bn last year solely due to this spot price discount of $12/b. When oil inventories are below normal and the market is tight then the forward curve is instead backwardated with spot prices at a premium to longer dated prices. That is what OPEC desires and long for.
OPEC knows that it cannot control the oil price over time. Especially it cannot place it at an artificially high level over time without having to accept a continuous decline in market share which over time is of course unsustainable. OPEC can however intervene in the market in the short term. The goal now is to draw down oil inventories. To move away from a contango market with a spot price discount which has been the situation since mid-2014 and instead hoping for a backwardated market with a spot price premium over longer dated crude prices. “Give me a premium!” is basically what OPEC is asking.
Over the last year we have learned that when the WTI 18 months forward crude oil contract is below $47.5/b then the number of US shale oil rigs is declining. When it is above it is increasing. This rig count inflection point is of course not cut in stone. It rises with cost inflation and declines with volume productivity growth. Over the last year the oil price has stimulated US shale oil to expand continuously. The number of oil rigs is still rising, but productivity growth has lately halted to zero on the margin while cost inflation has accelerated. The inflection point may thus start to rise if US shale oil production is stimulated to expand yet more in response to a positive price signal following further production cuts.
Three examples of price settings and dynamics in a global oil market with US shale oil on the margin:
1)US shale oil at neutral with normal inventories:
WTI crude 18 month contract = $47.5/b (no expansion or contraction in US oil rig count)
Brent crude 18 month contract = $50.0/b (Brent crude trades at a $2.5/b premium to WTI)
Brent crude 1 month contract = $50.0/b (Brent crude oil curve is flat)
2)US shale oil accelerating in a deficit market with below normal OECD inventories:
WTI crude 18 month contract = $55.0/b (Solid expansion in US oil rig count)
Brent crude 18 month contract = $57.5/b (Brent crude trades at a $2.5/b premium to WTI)
Brent crude 1 month contract = $65.0/b (Brent 1 mth at a $7.5/b premium to the 18 mth)
3)US shale oil is slowing in a surplus oil market with above normal OECD inventories:
WTI crude 18 month contract = $40.0/b (Solid contraction in US oil rig count)
Brent crude 18 month contract = $42.5/b (Brent crude trades at a $2.5/b premium to WTI)
Brent crude 1 month contract = $35.0/b (Brent 1 mth at a $7.5/b discount to the 18 mth)
Thus even if we assume that the US shale oil rig count inflection point is fixed at $47.5/b in the above three different exemplified states it still leaves the Brent crude oil front month contract to range within a large span of ranging from $35/b to $65/b. Then add cost inflation/deflation on top of the expansionary and contractionary phases and the span becomes even larger.
If production cuts are maintained for another six to nine months we expect it to drive OECD inventories down to normal or below by year end 2017. It is also likely to hold oil prices at such a level that it stimulates US shale oil rig activation yet further. The market will thus move towards a state depicted in example two above: A market in deficit due to production cuts with inventories below normal and a crude oil curve in backwardation. That is of course as long as the market is still in deficit.
The big question is what will happen when the cuts end in six to nine months. Rosneft’s CEO, Igor Sechin, has asked the Russian government to draw up a plan for an orderly exit from the ongoing production cuts. He sees a clear risk for a renewed competitive battle and price war if US production growth is not contained and production cuts ends uncontrolled.
It is clear that the likely decision to cut for another six to nine months will stimulate US crude oil production to grow yet more. Our projection is that US crude oil production will grow by 0.52 mb/d y/y in 2017 and by 1.51 mb/d y/y in 2018. However, if the oil price stimulates the US shale oil rig count to grow by 30 rigs/month (its current pace of expansion) from July 2017 to March 2018 then we project that US crude production will grow 2.3 mb/d y/y in 2018 driving the market into strict surplus for both 2018 and 2019 (assuming sufficient labor, materials and services capacities in the US shale oil space).
The risk is thus that if cuts are extended (as now seems likely), then there is likely going to be a need for cuts all through 2018 and 2019. Else the market is likely to shift into surplus, growing inventories, a crude curve which shifts from backwardation to contango again and a price level which needs to move down again in order to send a signal to US shale oil producers to reduce the number of oil rigs in operation again. I.e. the oil market could possibly shift back to phase 3) above again for a while.
If production cuts are extended and OECD inventories are drawn down towards normal by year end we expect the Brent crude oil curve to flip into backwardation by some $5/b versus the 18 month contract. It also seems reasonable to expect the the US rig count inflection point to shift up $5/b from $47.5/b to $52.5/b. Since Brent crude trades at a $2.5/b premium to WTI it places the Brent 18 mth contract at $55/b by year end. Adding a backwardation premium of $5/b to this means that the front month Brent crude oil contract would trade at $60/b by the end of 2017. The head-scratching problem is then that 2018 and 2019 may have shifted into surplus if 30 rigs are added per month from Jul-17 to Mar-18.
Kind regards
Bjarne Schieldrop
Chief analyst, Commodities
SEB Markets
Merchant Banking
Analys
Waiting for the surplus while we worry about Israel and Qatar

Brent crude makes some gains as Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar rattles markets. Brent crude spiked to a high of USD 67.38/b yesterday as Israel made a strike on Hamas in Qatar. But it wasn’t able to hold on to that level and only closed up 0.6% in the end at USD 66.39/b. This morning it is starting on the up with a gain of 0.9% at USD 67/b. Still rattled by Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar yesterday. Brent is getting some help on the margin this morning with Asian equities higher and copper gaining half a percent. But the dark cloud of surplus ahead is nonetheless hanging over the market with Brent trading two dollar lower than last Tuesday.

Geopolitical risk premiums in oil rarely lasts long unless actual supply disruption kicks in. While Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar is shocking, the geopolitical risk lifting crude oil yesterday and this morning is unlikely to last very long as such geopolitical risk premiums usually do not last long unless real disruption kicks in.
US API data yesterday indicated a US crude and product stock build last week of 3.1 mb. The US API last evening released partial US oil inventory data indicating that US crude stocks rose 1.3 mb and middle distillates rose 1.5 mb while gasoline rose 0.3 mb. In total a bit more than 3 mb increase. US crude and product stocks usually rise around 1 mb per week this time of year. So US commercial crude and product stock rose 2 mb over the past week adjusted for the seasonal norm. Official and complete data are due today at 16:30.
A 2 mb/week seasonally adj. US stock build implies a 1 – 1.4 mb/d global surplus if it is persistent. Assume that if the global oil market is running a surplus then some 20% to 30% of that surplus ends up in US commercial inventories. A 2 mb seasonally adjusted inventory build equals 286 kb/d. Divide by 0.2 to 0.3 and we get an implied global surplus of 950 kb/d to 1430 kb/d. A 2 mb/week seasonally adjusted build in US oil inventories is close to noise unless it is a persistent pattern every week.
US IEA STEO oil report: Robust surplus ahead and Brent averaging USD 51/b in 2026. The US EIA yesterday released its monthly STEO oil report. It projected a large and persistent surplus ahead. It estimates a global surplus of 2.2 m/d from September to December this year. A 2.4 mb/d surplus in Q1-26 and an average surplus for 2026 of 1.6 mb/d resulting in an average Brent crude oil price of USD 51/b next year. And that includes an assumption where OPEC crude oil production only averages 27.8 mb/d in 2026 versus 27.0 mb/d in 2024 and 28.6 mb/d in August.
Brent will feel the bear-pressure once US/OECD stocks starts visible build. In the meanwhile the oil market sits waiting for this projected surplus to materialize in US and OECD inventories. Once they visibly starts to build on a consistent basis, then Brent crude will likely quickly lose altitude. And unless some unforeseen supply disruption kicks in, it is bound to happen.
US IEA STEO September report. In total not much different than it was in January
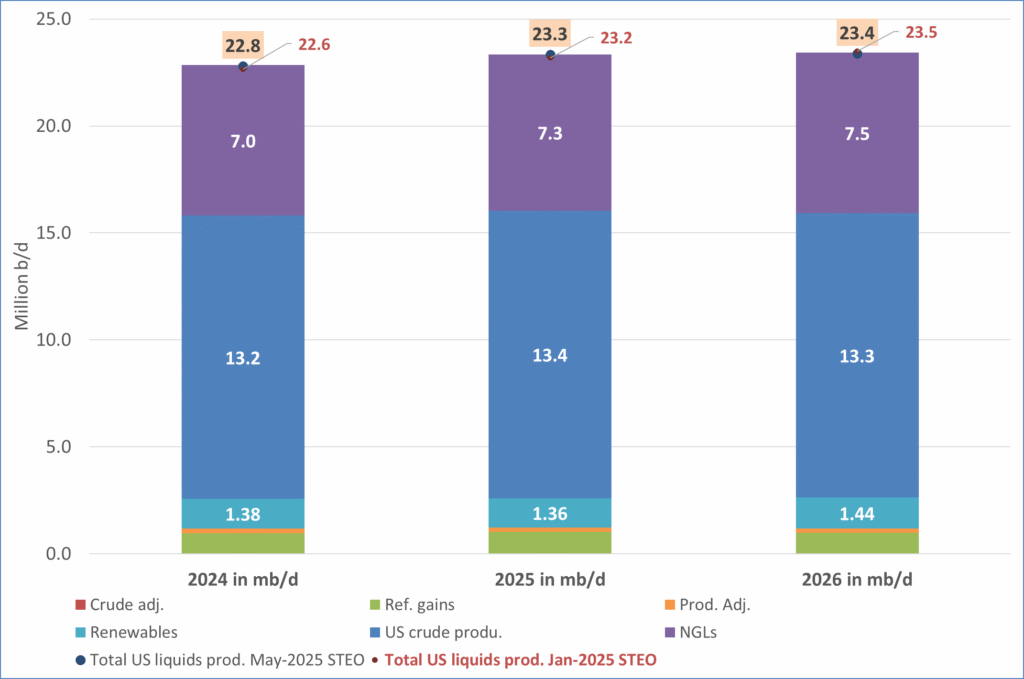
US IEA STEO September report. US crude oil production contracting in 2026, but NGLs still growing. Close to zero net liquids growth in total.
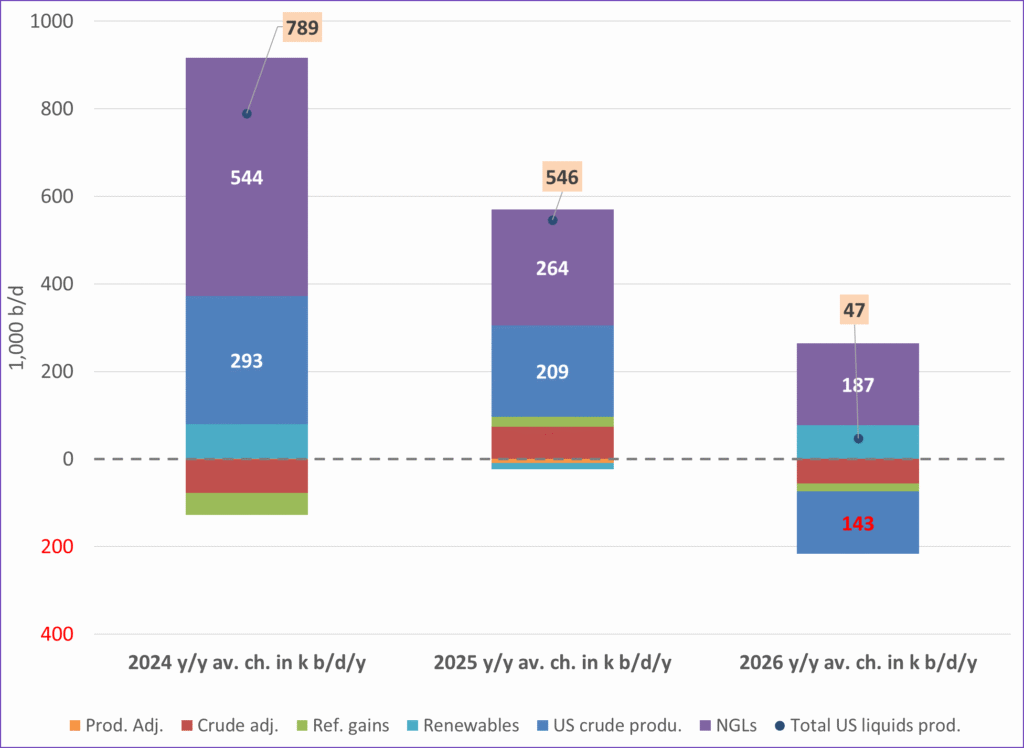
Analys
Brent crude sticks around $66 as OPEC+ begins the ’slow return’

Brent crude touched a low of USD 65.07 per barrel on Friday evening before rebounding sharply by USD 2 to USD 67.04 by mid-day Monday. The rally came despite confirmation from OPEC+ of a measured production increase starting next month. Prices have since eased slightly, down USD 0.6 to around USD 66.50 this morning, as the market evaluates the group’s policy, evolving demand signals, and rising geopolitical tension.

On Sunday, OPEC+ approved a 137,000 barrels-per-day increase in collective output beginning in October – a cautious first step in unwinding the final tranche of 1.66 million barrels per day in voluntary cuts, originally set to remain off the market through end-2026. Further adjustments will depend on ”evolving market conditions.” While the pace is modest – especially relative to prior monthly hikes – the signal is clear: OPEC+ is methodically re-entering the market with a strategic intent to reclaim lost market share, rather than defend high prices.
This shift in tone comes as Saudi Aramco also trimmed its official selling prices for Asian buyers, further reinforcing the group’s tilt toward a volume-over-price strategy. We see this as a clear message: OPEC+ intends to expand market share through steady production increases, and a lower price point – potentially below USD 65/b – may be necessary to stimulate demand and crowd out higher-cost competitors, particularly U.S. shale, where average break-evens remain around WTI USD 50/b.
Despite the policy shift, oil prices have held firm. Brent is still hovering near USD 66.50/b, supported by low U.S. and OECD inventories, where crude and product stocks remain well below seasonal norms, keeping front-month backwardation intact. Also, the low inventory levels at key pricing hubs in Europe and continued stockpiling by Chinese refiners are also lending resilience to prices. Tightness in refined product markets, especially diesel, has further underpinned this.
Geopolitical developments are also injecting a slight risk premium. Over the weekend, Russia launched its most intense air assault on Kyiv since the war began, damaging central government infrastructure. This escalation comes as the EU weighs fresh sanctions on Russian oil trade and financial institutions. Several European leaders are expected in Washington this week to coordinate on Ukraine strategy – and the prospect of tighter restrictions on Russian crude could re-emerge as a price stabilizer.
In Asia, China’s crude oil imports rose to 49.5 million tons in August, up 0.8% YoY. The rise coincides with increased Chinese interest in Russian Urals, offered at a discount during falling Indian demand. Chinese refiners appear to be capitalizing on this arbitrage while avoiding direct exposure to U.S. trade penalties.
Going forward, our attention turns to the data calendar. The EIA’s STEO is due today (Tuesday), followed by the IEA and OPEC monthly oil market reports on Thursday. With a pending supply surplus projected during the fourth quarter and into 2026, markets will dissect these updates for any changes in demand assumptions and non-OPEC supply growth. Stay tuned!
Analys
The path of retaking market share goes through a lower price

OPEC+ on Sunday decided to lift production caps by an additional 137 kb/d in October. Thereby starting to unwind the last tranche of voluntary cuts of 1.66 mb/d. It will unwind this last tranche gradually until the end of 2026 depending on market conditions it said.

Brent closed on Friday at USD 65.5/b. The market is up at USD 66.7/b this morning. That is below the high on Friday and USD 2.4/b below where it closed on Tuesday last week. So while the decision by the group was less aggressive than the market feared on Friday afternoon, it was still a very different from the group than what most market participants expected at the beginning of last week.
Our expectation last week was for the group to unwind the remaining 1.66 mb/d of voluntary cuts over only three months to the end of this year and get done with it. But the group decided on a slower path. It will not shock its way back to a larger market share like it tried without much luck in 2014/15/16. It will instead push steadily, steadily and take it back. Allowing US shale oil players time to step aside. But step aside they must.
The implied message from the group this weekend was 1) They are in the process of retaking market share and 2) As long as the price is USD 65.5/b (close on Friday) the group will revive more production.
What we know is that this process of retaking market share by OPEC+ goes through a lower oil price. And that lower price is below USD 65.5/b. A lower price to stimulate more demand. A lower price to hamper supply by non-OPEC+ (predominantly US shale oil).
The fact that Brent crude is still trading at USD 66.6/b despite this very explicit message from the group this weekend is down to still low US and OECD crude and product inventories. The front-end backwardation of the Brent futures curve is a reflection of this tightness. But this tightness will ease along with more oil from OPEC+ over the coming months. The Brent crude oil forward curve will then flip into full contango all along the curve. We then expect the front-end of the Brent curve to trade around USD 55/b with WTI close to USD 50/b.
At the beginning of this year BNEF estimated US shale oil cost break even levels to be in a range from USD 40/b to USD 60/b with a volume weighted average of USD 50/b. The latter our calculation. So a WTI price at the middle of that range is probably what is needed to force activity in US shale oil activity yet lower.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanBrent sideways on sanctions and peace talks
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanEtt samtal om koppar, kaffe och spannmål
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSommarens torka kan ge högre elpriser i höst
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanBrent edges higher as India–Russia oil trade draws U.S. ire and Powell takes the stage at Jackson Hole
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals är verksamt i guldrikt område i Finland
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanIncreasing risk that OPEC+ will unwind the last 1.65 mb/d of cuts when they meet on 7 September







