Analys
German solar power prices are collapsing as market hits solar saturation

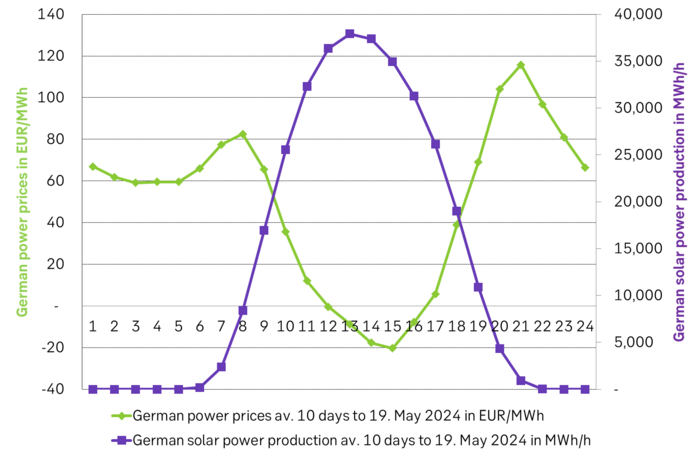
German solar power producers got a price haircut of 87% over the past 10 days. German solar power producers have over the past 10 days received a volume weighted power price of only EUR 9.1/MWh. The average power price during non-solar-power-hours was in comparison EUR 70.6/MWh. Solar power producers thus got an 87% cut in the power price they get when they produce vs. the power price during non-solar-power-hours. This is what happens to power prices when the volume of unregulated power becomes equally big or bigger than demand: Prices collapse when unregulated power produces the most.

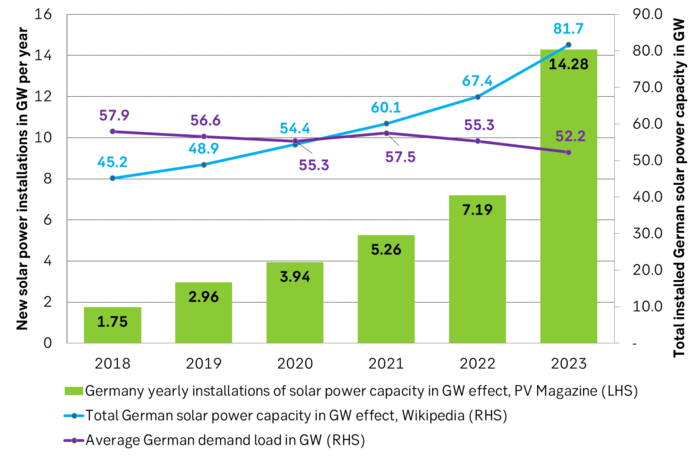
Massive growth in solar power installations in Germany in 2023 is leading to destruction of solar hour prices and solar profitability. Germany installed a record 14,280 MW of solar power capacity According to ’PV Magazine International’. That is close to twice as much as in 2022. Total installed solar capacity reached 81.7 GW at the end of 2023 according to ’Renewables Now’. Average German demand load was in comparison 52.2 GW. So total solar capacity reached almost 30 GW above average demand. Solar power produces the most during summer when demand is lower. The overshoot is thus much larger than the 30 GW mentioned when it matters.
The collapse in solar-hour-power-prices implies a collapse in solar power producer earnings unless the earnings of the installations are secured with subsidies or by PPAs. It also means that there is a sharp reduction in the earnings potential for new solar power projects. The exponential growth in new installations of solar capacity we have seen to date is likely to come to an abrupt halt. There is however most likely still a large range of solar power projects under construction in Germany which will be finalized before growth in new capacity comes to a halt. The problem of solar power production curbs (you are not allowed to produce at all) and solar power price destruction is likely to escalate yet higher before new growth in supply comes to a halt.
Focus will now shift from solar production capacity growth to grid improvements, batteries and adaptive demand. All consumers are of course happy for cheap power as long as they are able to consume it when it is cheap. At the moment they can’t. But the incentive to be inventive is now super high. The focus will now likely shift from solar power production growth to grids, batteries, adaptive demand and all possible ways to utilize ”free power”. This will over time exhaust the availability of ”free power” and drive solar-hour-power-prices back up. This again will then eventually open for renewed growth in solar power capacity growth.
It is probably much worse down in the grid. What is worth noting is that these numbers are for all of Germany average. Solar power congestion is much worse in the local grids all around Germany along with local grid capacity constraints ect.
The problem of solar power is high concentration of production: 80% of German solar production was produced during 22.3% of the hours in the year in 2023. What is also worth mentioning is that solar power production is extremely concentrated in relatively few hours per year. It produces in the middle of the day and during summer. In 2023 German solar power produced 80% of its production in only 22.3% of the hours of the year. This basically implies that once solar power production reaches 22.3% of total power supply (without batteries), then solar-hour-power-prices will likely collapse. Solar power production reached 55 TWh in 2023. That’s a lot but it is still only 12% of total demand of 458 TWh in 2023. What it means is that the acute problem of solar-hour-power-price-destruction sets in much before the ”theoretical 22.3%” mentioned above.
On the 21 Feb 2024 we wrote the following note on this issue: ”The self-destructive force of unregulated solar power” where we highlighted these issues and warned that this will likely be a process of ”First gradually. Then suddenly”.
German solar power capacity makes a big leap upwards in 2023 as the energy crisis hurt everybody. Demand went down. Now there is a large overcapacity in installed solar effect vs. demand load.
German solar power producers got an 87% price haircut on average during last 10 days vs. those who produced during non-solar-power hours.
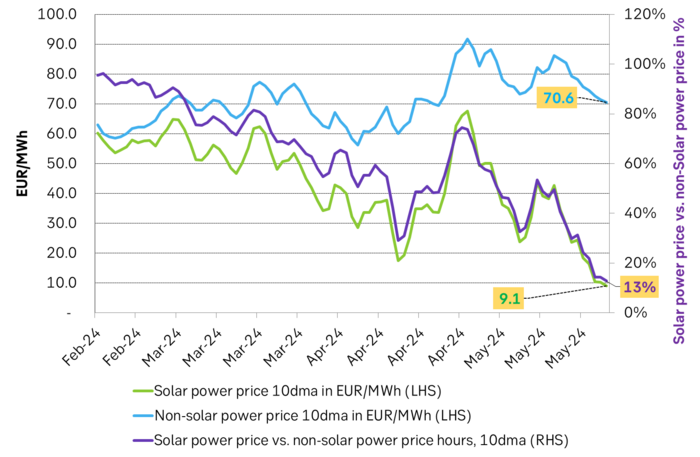
Volume weighted solar power prices vs. non-solar-hours. Bigger and bigger discount.
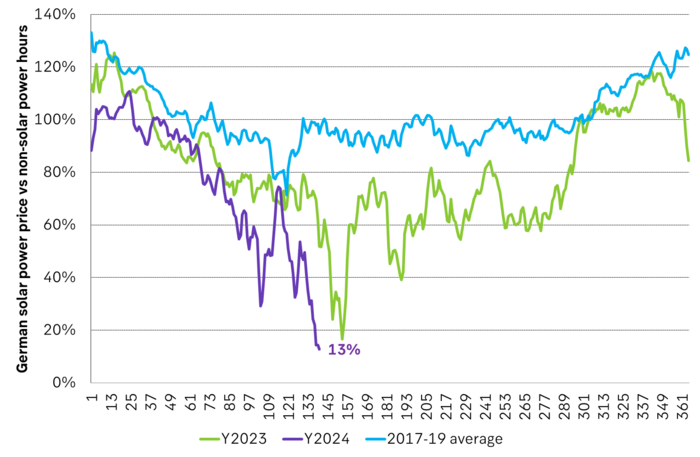
Volume weighted solar power prices vs. non-solar-hours. Bigger and bigger discount.
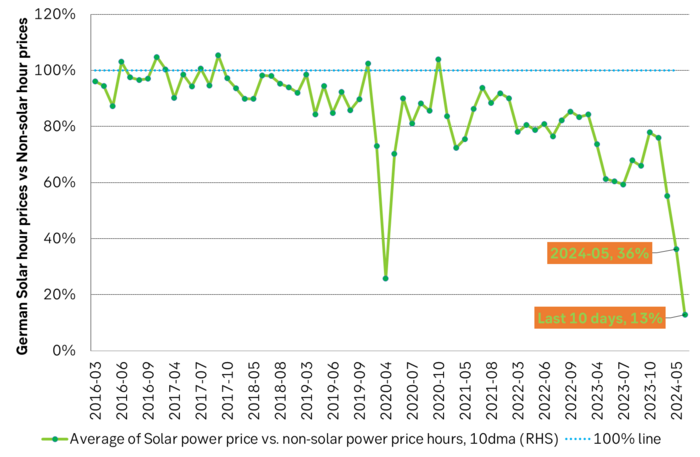
Solar power production and German power prices over the past 10 days.
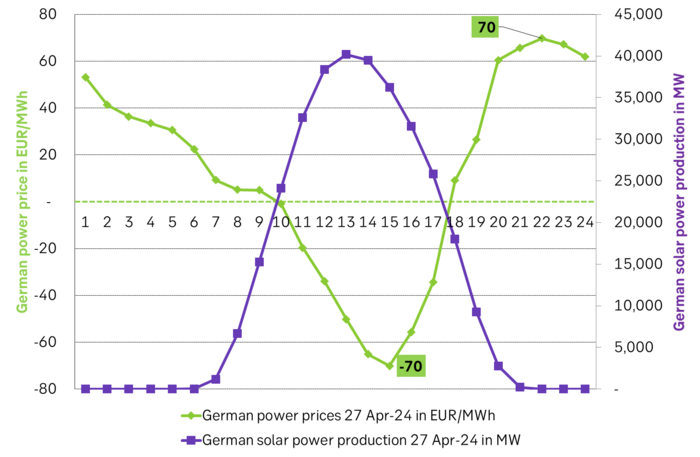
Solar power production and German power prices on 27 April 2024.
Analys
Physical easing. Iran risk easing. But Persian Gulf risk cannot fully fade before US war ships are pulled away

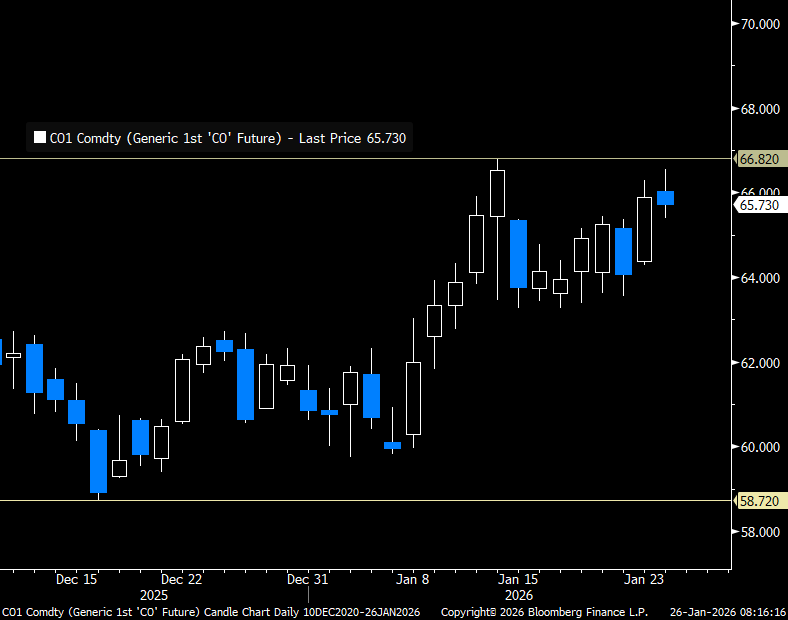
Traded down 3.7% last week as Iranian risk faded a bit. Brent crude traded in a range of $65.19 – 69.76/b last week. In the end it traded down 3.7% with a close of $68.05/b. It was unable to challenge the peak of $71.89/b from the previous week when the market got its first nervous shake as Trump threatened Iran with an armada of US war ships.

The market has started to cool down a bit with US and Iran in talks in Oman on Friday and Brent crude is easing 0.9% this morning to $67.4/b in an extension of that. As we have stated before we think the probability is very low for a scenario where the US attacks Iran in such a way that it risks an uncontrollable escalation with possible large scale disruption of oil out of the Strait of Hormuz and thus a massive spike in the oil price. That would endanger Trump’s mid-term election which is already challenged with unhappy US voters complaining about affordability and that Trump is spending too much time on foreign issues.
A statement by Trump last week that India had agreed not to buy Russian crude turns out to have little substance as India has agreed to no such thing on paper. The statement last week naturally supported oil prices as the market is already struggling with a two tire market with legal versus illegal barrels. There is a lot of friction in the market for sanctioned crude oil barrels from Iran and Russia. If India had agreed not to buy Russian crude oil then the market for legal barrels would have been tighter.
The physical market has been tighter than expected. And the recent concerns over Iranian risk has come on top of that. The market is probably starting calm down regarding the Iranian risk. But the physical tightness is also going to ease gradually over the coming couple of weeks. CPC blend exports averaged 1.5 mb/d last year, but were down to less than 1 mb/d in January due to a combination of factors. Drone attacks by Ukraine in late November. The Tengiz field has been disrupted by fires. Adverse winter weather has also been a problem. US crude oil production has also been disrupted by a fierce winter storm. But these issues are fading with supply reviving over the next couple of weeks.
The physical tightness is likely going to ease over the next couple of weeks. The market may also have started to get used to the Iranian situation. But the Iranian risk premium cannot be fully defused as long as US warships are located where they are with their guns and rockets pointing towards Iran.
Analys
Brent crude will pull back if the US climbs down its threats towards Iran

Brent crude rose 2.7% last week to $65.88/b with a gain on Friday of 2.8%. Unusually cold US winter weather with higher heating oil demand and likely US oil supply outages was probably part of the bullish drive at the end of last week. But US threats towards Iran with USS Abraham Lincoln being deployed to the Middle East was probably more important.

Brent crude has maintained the gains it got from 8 January onwards when it rose from the $60/b-line and up to around $65/b on the back of Iranian riots where the US added fuel to the fire by threatening to attack Iran in support of the rioters. This morning Brent has tested the upside to $66.54/b. That is short of the $66.82/b from 14 January and Brent has given back part of the early gains this morning and is currently trading close to unchanged versus Friday’s close with a dollar decline of 0.4% not enough to add much boost to the price yet at least.
Brent crude front-month prices in USD/b
The rally in Brent crude from the $60/b-line to its current level of $65-66/b seems to be tightly linked to an elevated risk of the US attacking Iran in support of the rioters. Bloomberg reported on Saturday that the US has dispatched the USS Abraham Lincoln aircraft carrier and its associated strike group to the Middle East. It is a similar force which the US deployed to the Caribbean Sea just weeks before the 3 January operation where Maduro was captured. The probability of a US/Israeli attack on Iran is pegged at 65-70% by geopolitical risk assessment firms Eurasia Group and Rapidan Energy Group. Such a high probability explains much of the recent rally in Brent crude.
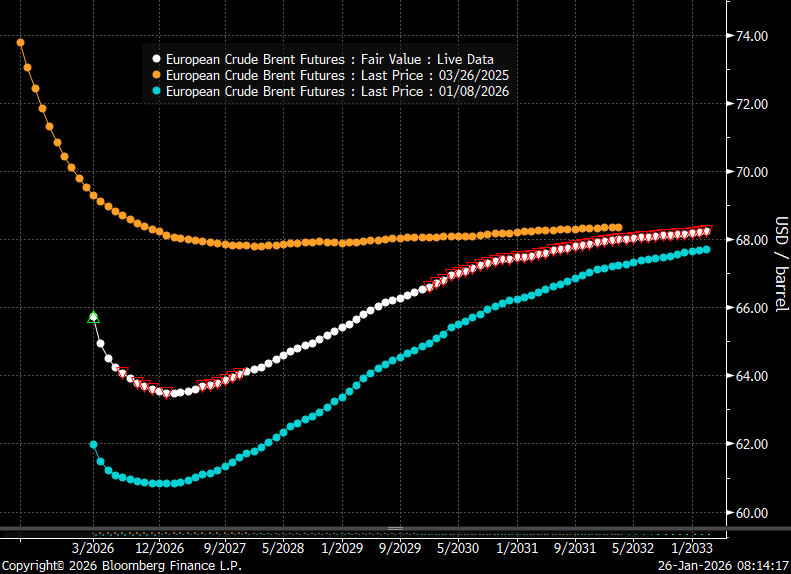
The recent rally in Brent crude is not a signal from the oil market that the much discussed global surplus has been called off. If we look at the shape of the Brent crude oil curve it is currently heavily front-end backwardated with the curve sloping upwards in contango thereafter. It signals front-end tightness or near term geopolitical risk premium followed by surplus. If the market had called off the views of a surplus, then the whole Brent forward curve would have been much flatter and without the intermediate deep dip in the curve. The shape of the Brent curve is telling us that the market is concerned right now for what might happen in Iran, but it still maintains and overall view of surplus and stock building unless OPEC+ cuts back on supply.
It also implies that Brent crude will fall back if the US pulls back from its threats of attacking Iran.
Brent crude forward curves in USD/b.
Analys
Oil market assigns limited risks to Iranian induced supply disruptions

Falling back this morning. Brent crude traded from an intraday low of $59.75/b last Monday to an intraday high of $63.92/b on Friday and a close that day of $63.34/b. Driven higher by the rising riots in Iran. Brent is trading slightly lower this morning at $63.0/b.

Iranian riots and risk of supply disruption in the Middle East takes center stage. The Iranian public is rioting in response to rapidly falling living conditions. The current oppressive regime has been ruling the country for 46 years. The Iranian economy has rapidly deteriorated the latest years along with the mismanagement of the economy, a water crisis, encompassing corruption with the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps at the center and with US sanctions on top. The public has had enough and is now rioting. SEB’s EM Strategist Erik Meyersson wrote the following on the Iranian situation yesterday: ”Iran is on the brink – but of what?” with one statement being ”…the regime seems to lack a comprehensive set of solutions to solve the socioeconomic problems”. That is of course bad news for the regime. What can it do? Erik’s takeaway is that it is an open question what this will lead to while also drawing up different possible scenarios.
Personally I fear that this may end very badly for the rioters. That the regime will use absolute force to quash the riots. Kill many, many more and arrest and torture anyone who still dare to protest. I do not have high hopes for a transition to another regime. I bet that Iranian’s telephone lines to its diverse group of autocratic friends currently are running red-hot with ”friendly” recommendations of how to quash the riots. This could easily become the ”Tiananmen Square” moment (1989) for the current Iranian regime.
The risks to the oil market are:
1) The current regime applies absolute force. The riots die out and oil production and exports continue as before. Continued US and EU sanctions with Iranian oil mostly going to China. No major loss of supply to the global market in total. Limited impact on oil prices. Current risk premium fades. Economically the Iranian regime continues to limp forward at a deteriorating path.
2) The regime applies absolute force as in 1), but the US intervenes kinetically. Escalation ensues in the Middle East to the point that oil exports out of the Strait of Hormuz are curbed. The price of oil shots above $150/b.
3) Riots spreads to affect Iranian oil production/exports. The current regime does not apply sufficient absolute force. Riots spreads further to affect oil production and export facilities with the result that the oil market loses some 1.5 mb/d to 2.0 mb/d of exports from Iran. Thereafter a messy aftermath regime wise.
Looking at the oil market today the Brent crude oil price is falling back 0.6% to $63/b. As such the oil market is assigning very low risk for scenario 2) and probably a very high probability for scenario 1).
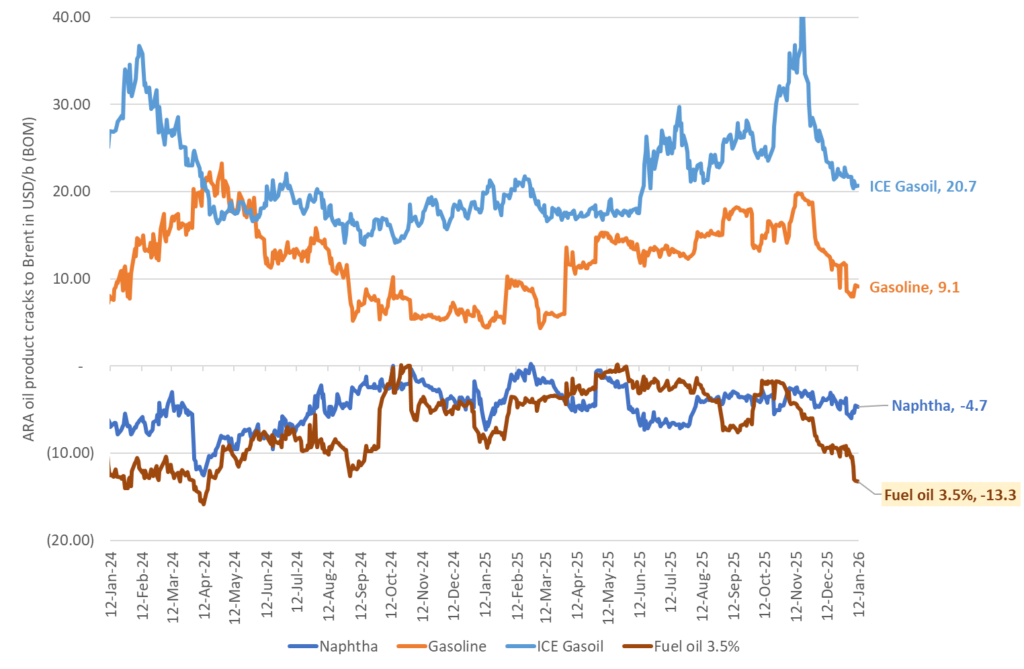
Venezuela: Heavy sour crude and product prices falls sharply on prospect of reduced US sanctions on Venezuelan oil exports. The oil market take on Venezuela has quickly shifted from fear of losing what was left of its production and exports to instead expecting more heavy oil from Venezuela to be released into the market. Not at least easier access to Venezuelan heavy crude for USGC refineries. The US has started to partially lift sanctions on Venezuelan crude oil exports with the aim of releasing 30mn-50mn bl of Venezuelan crude from onshore and offshore stocks according to the US energy secretary Chris Wright. But a significant increase in oil production and exports is far away. It is estimated that it will take $10bn in capex spending every year for 10 years to drive its production up by 1.5 mb/d to a total of 2.5 mb/d. That is not moving the needle a lot for the US which has a total hydrocarbon liquids production today of 23.6 mb/d (2025 average). At the same time US oil majors are not all that eager to invest in Venezuela as they still hold tens of billions of dollars in claims against the nation from when it confiscated their assets in 2007. Prices for heavy crude in the USGC have however fallen sharply over the prospect of getting easier access to more heavy crude from Venezuela. The relative price of heavy sour crude products in Western Europe versus Brent crude have also fallen sharply into the new year.
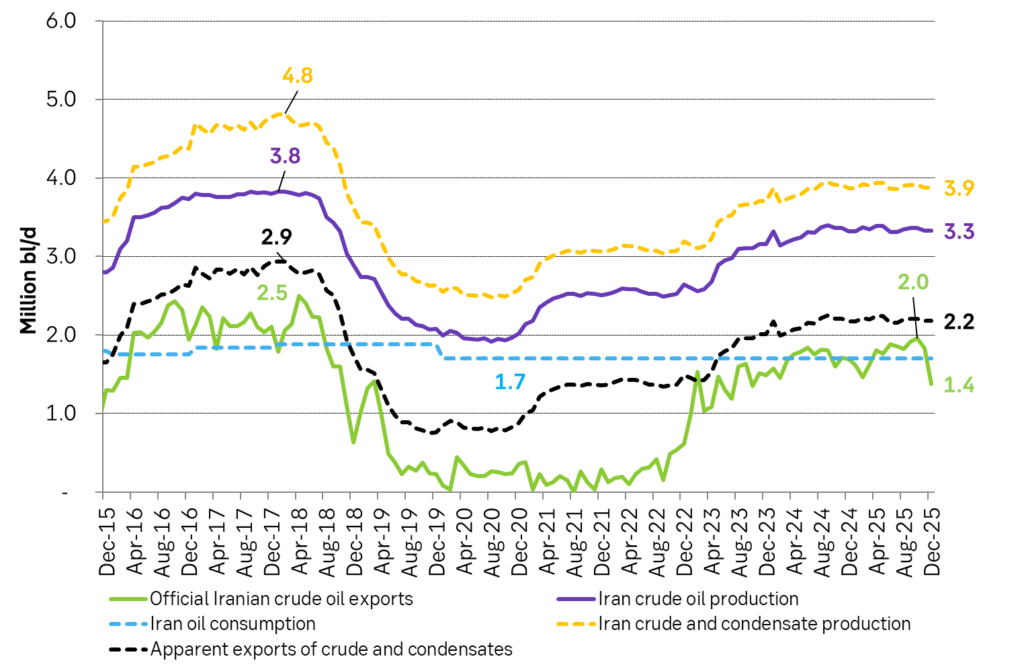
Iran officially exported 1.75 mb/d of crude on average in 2025 falling sharply to 1.4 mb/d in December. But it also produces condensates. Probably in the magnitude of 0.5-0.6 mb/d. Total production of crude and condensates probably close to 3.9 mb/d.
The price of heavy, sour fuel oil has fallen sharply versus Brent crude the latest days in response to the prospect of more heavy sour crude from Venezuela.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSilverpriset stiger över 100 USD per uns
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGuldpriset stiger till över 5000 USD per uns
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSamtal om guld och andra råvaror när flera priser rusar i höjden
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanChristian Kopfer om marknadens olika råvaror
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSilver utgör nu 30 procent av kostnaden för att producera solcellspaneler
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanKall och nederbördsfattig månad driver upp elpriset
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanIndien kommer inte att göra slut med kol
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanKylan lyfter elpriset i vinter, minst 40 procent högre än väntat








