Analys
The self-destructive force of unregulated solar power

Modifications

Solar and wind power production has increased rapidly over the latest years as LCOE costs have fallen sharply while government support schemes have given it an extra boost as well. Solar and wind power production is totally unregulated supply. They produce whenever they produce. Fossil power supply on the other hand is fully dispatchable to the degree that we tend to take it for granted. As such we have naturally tended to underestimate the consequences of not having dispatchability in solar and wind power.
When you start out with a large, fossil-based power system it is fairly easy to add unregulated power supply from solar and wind because it can piggyback on the dispatchability and flexibility of the fossil power system. But as the share of unregulated renewable energy rises to a larger and larger share of production, the flexibility in the fossil part of the system naturally gets smaller and smaller. This problem is accentuated further by the fact that solar power production has a very high concentration of production where 80% of production in a year is produced in only 20% of the hours in the year. Thus fossil flexibility and dispatchability is eroded much faster during these 20% hours.
Power prices typically collapse to zero or negative when demand is fully met or saturated by unregulated power supply. That again implies that solar power profitability collapse as well. And the result of that of course is that the exponential growth in solar power production which we now take for granted and which we expect will lead us all the way to zero emissions could come to a full stop as well.
This is already a rapidly increasing problem in California where more and more renewable energy is denied access to the grid because there simply isn’t enough demand for it just then or because the grid cannot handle it. But it is also becoming an increasing problem in Germany where the strong growth and high concentration of solar power increasingly is destroying the power prices just when they produce the most.
The need for biiiig, cheeeeap grid batteries are now becoming increasingly critical for the the exponential growth in solar and wind power to continue.
We fear that the self-destructive force on power prices, of exponential growth in unregulated solar power, is some kind of Solar-hara-kiri process with respect to its own profitability. And that it has the potential to develop along a curve of ”first gradually, then suddenly”. And when/if that happens the exponential growth in unregulated solar power production should naturally come to a screeching halt.
The resolution of the problem is of course the eventual arrival of biiiig, cheeeap grid batteries which then again will sett solar power production free to resume its exponential growth.
Feeding solar and wind power supply into a fossil system is easy to start with. Then very difficult. It is easy to build unregulated solar and wind power supply into a flexible fossil system. It is easy to infuse unregulated power supply (Solar and Wind) into a power system where there is lots and lots of fossil based power. Fossil supply can then back-off and make room for solar and wind power whenever the sun is shining or the wind is blowing and then ramp up again when it suddenly disappear. But when unregulated, renewable energy supply keeps growing it becomes harder and harder to infuse yet more of it into the system as the fossil flexibility is increasingly eroded. That’s when yet more supply of solar and wind is no longer pushing aside fossil supply but instead is starting to destroy their own prices.
Solar power produces 80% of its production during 20% of the hours in the year. Solar power has however a much more tightly focused production profile than wind. In Germany in 2023 some 80% of all solar power production was concentrated on only 20% of the hours of the year. For wind power the 80% share of production was spread out over 50% of the hours in the year. The reason is of course that the wind can blow both summer and winter and night and day. Solar power is instead focused during the day and during summer. It has a much higher concentration of production.
Power prices tend to collapse when demand is fully covered by unregulated power supply. When solar power production grows rapidly in a given power system then its high production concentration will eventually lead to full saturation during certain hours of the year. Demand during these hours will then be fully supplied and covered by unregulated power like solar, wind, run-of-river hydro and other unregulated supply. That is great as it means that the fossil share in these hours then are close to zero.
The problem is that power markets, more than any other commodity market in the world, are extremely sensitive to imbalances in supply and demand. A little bit too little supply and the power price can spike up to close to infinity. A little bit too much supply and the price crashes to zero or negative.
When unregulated power supply reaches full demand saturation during certain hours then power prices tend to collapse because it is so easy to get a little bit too much supply.
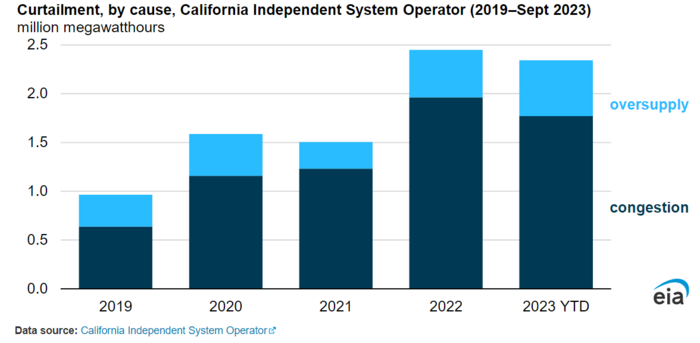
It is not a problem when power prices collapse for just a few hours per year. But the number of hours affected is growing rapidly many places. The US EIA highlighted in October 2023 (”Solar and wind power curtailments are rising in California”) that this is becoming a bigger and bigger problem in California. Since 2019 the power system operator there has been forced to curtail supply of unregulated power more and more. There simply isn’t enough demand in certain hours to meet the spikes in unregulated supply or the grid isn’t up to the task of distributing the unregulated supply in the system.
So when producers of unregulated supply produces the most they increasingly are denied access to sell it into the grid or if they are allowed to sell it into the grid the price is close to zero or even negative.
US EIA: Solar and wind power curtailments are rising in California
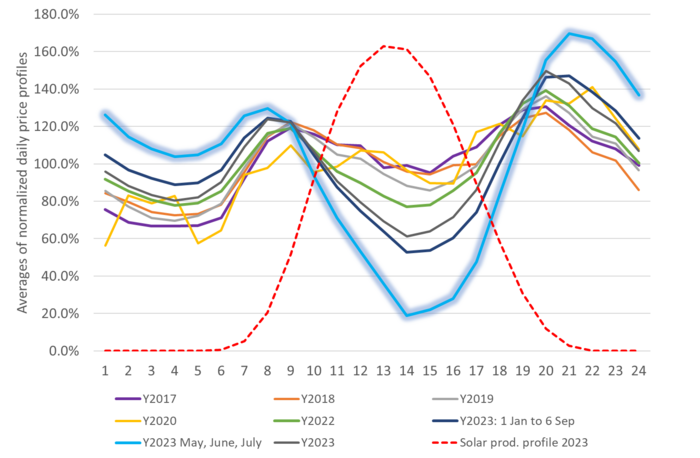
Germany is increasingly affected as booming solar production is depressing prices more and more. This is now also a rapidly increasing problem in Germany where rapid growth in supply of solar and wind power together increasingly are forcing power prices lower just when they produce the most.
Average German power prices for hour 1 to 24 for certain periods and years. Highly concentrated supply of solar power during summer and during the day is increasingly forcing power prices towards zero during these periods
It is like ”Solar hara-kiri” when increasing supply of solar power is killing its own prices and profits. It was not a big problem economically when only a few hours are affected. But as more and more hours are affected it is becoming an increasing problem. It is like ”Solar hara-kiri” where rapidly rising supply of solar power is increasingly killing its own prices. With that it is killing its profits. And if profits are killed than new-build and growth in supply will typically slow down rapidly as well.
This is probably not a big problem globally yet as the global power system is still predominantly fueled by fossil fuels which can back off when renewable energy spikes up. But in certain pockets of the world where penetration of unregulated power supply has reached high levels it is becoming an increasing problem. Like in California and in Germany.
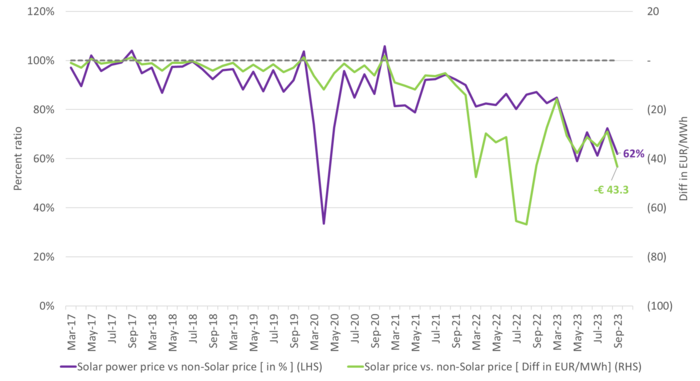
The volume weighted solar power price in September 2023 in Germany had a 38% discount to power prices during non-solar power hours. And the discount looks like it is rapidly getting bigger and bigger.
The monthly average volume weighted solar power price versus the average volume weighted non-solar power price weighted by the inverse profile. In Germany in September 2023 solar power producers only achieved 62% of the average price during hours of the day when the sun wasn’t shining.
First gradually, then suddenly. There is a clear risk here that this progresses along a process of ”first gradually, then suddenly”. This is already what we have seen over the past couple of years: The discount for what solar power earns when it produces power versus what the power price is when it is not producing is increasing rapidly as more and more unregulated power supply hits right into the ”demand ceiling”. The inflicted pain from this process so far has to a large degree been masked by incredibly high natural gas prices. So even if the profitability for solar power has been eroding, the average power price in the system has been much higher than usual due to high natural gas and CO2 prices.
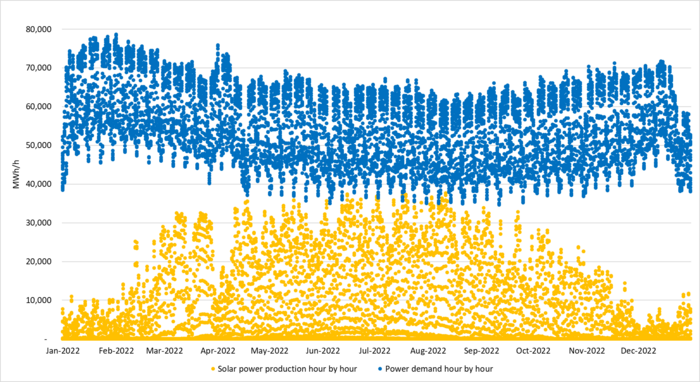
Graphing all the individual hourly data for solar power and power demand in Germany in 2022 we see that solar power alone is not yet reaching full saturation versus demand.
Germany 2022: Hourly German power demand and solar power supply in 2022. A total of 8760 hours for each in consecutive order. Her showing only Demand and Solar power production
The unregulated power supply is increasingly hitting the ”demand ceiling”. If we now add all the other sources of unregulated power supply, predominantly offshore and onshore wind and run of river, then we get the following picture where we see that unregulated German power supply increasingly is hitting right up and into the ”demand ceiling”. In those instances there will be no, flexible fossil power supply left to back off and that is typically when power prices collapse or go negative.
Germany 2022: Hourly German power demand (blue dots) and unregulated supply (solar, wind, run of river,…) in orange dots. A total of 8760 hours for each in consecutive order.
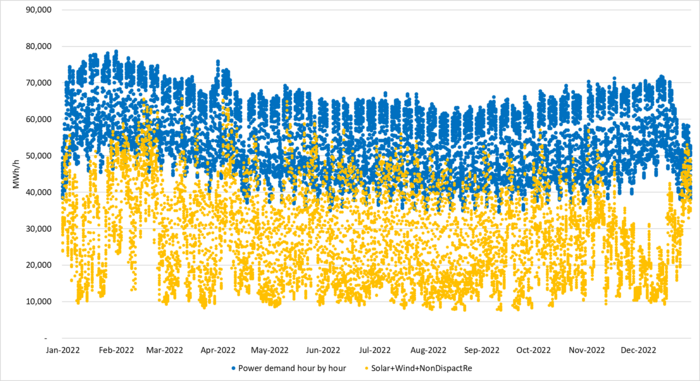
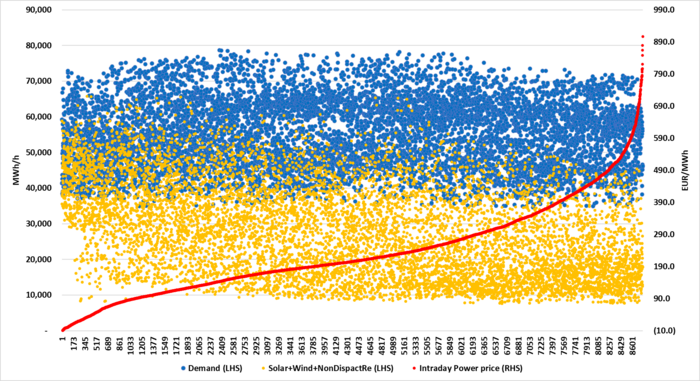
High unregulated power supply saturation vs demand implied lower power prices in 2022. Sorting 8760 individual power prices in Germany from Y2022 from lowest to highest shows that power German power prices were strongly related to the penetration of unregulated power supply. In the following graph, we have sorted the data from the lowest price to the highest price in the year 2022. Prices were ireasingly depressed when unregulated power penetrated up and into the ”demand ceiling”. Natural gas prices were extreme in 2022 and overall power prices were exceptionally high for that reason as well. But the tendency of price destruction in relation to high levels of unregulated power vs demand is clear.
Germany 2022: Hourly German power demand (blue dots) and unregulated supply (solar, wind, run of river,…) in orange dots. A total of 8760 hours. Sorted according to how hourly power prices were from lowest to highest.
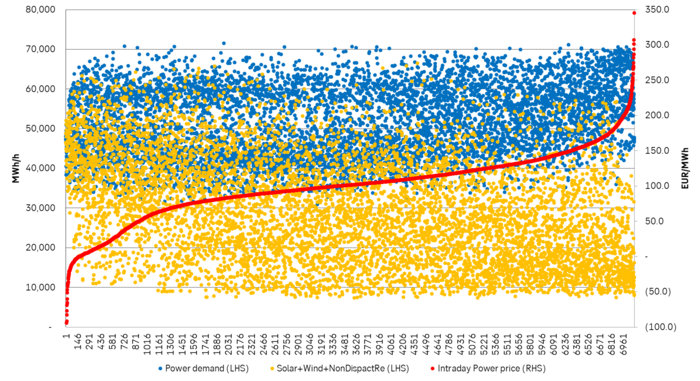
The unregulated power supply penetrating vs demand was even deeper in 2023. If we make the same graph for the year 2023 from 1 Jan to 20 Oct, we can see how the unregulated power is penetrating deeper and deeper into the power ”demand ceiling”. As a result the solar power discount vs. non-solar power hours from March to September in 2023 reached an even higher discount in 2023 than in 2022.
2023 year to 20 October: Hourly German power demand (blue dots) and unregulated supply (solar, wind, run of river,…) in orange dots. A total of 8760 hours. Sorted according to how hourly power prices were from lowest to highest. German power demand was down 8.3% YoY in H1-2023 due to the European energy crisis and still very high power prices
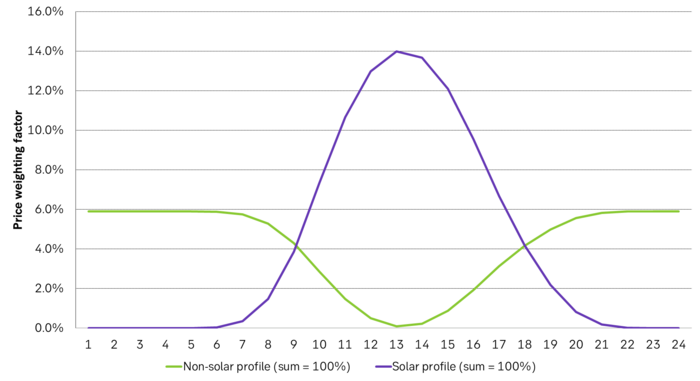
Solar power hours and non-solar power hours is not given as a clear cut-off, but a gradual one. In the following graph given as average profiles of the year from hour 1 to hour 24. First calculated explicitly for solar power production and then the inverse is calculated from that one. These solar power profiles can then be calculated for each individual day in the year giving individual inverse-curves on a daily basis.
The daily ”solar power production profiles” and the ”non-solar power production profiles” typically looks like this graph but calculated individually per day as solar power production varies from day to day and through the seasons. The solar power production profile is explicitly given by the actual solar power production that day while the non-solar power profile is derived directly from this and the inverse of it on a daily basis.
The exponential growth in solar and wind power is likely to slow down in the years to come as grid constraints and lack of power cables is holding up growth in renewable energy with waiting times for access of 5-10 years:
”Offshore wind auction’s lack of bids must be ‘wake-up call’ for UK, says RWE chief”
FT: ”Gridlock: how a lack of power lines will delay the age of renewables”
FT: ”Will there be enough cables for the clean energy transition?”
Analys
An Israeli attack on Iran moves closer as Trump’s bully-diplomacy has reach a dead end

Brent rising a meager 1% as CNN says Israel prepares to attack Iran. Brent crude traded in a narrow range of USD 64.85 – 66.0/b yesterday and ended down 0.2% to USD 65.38/b along with US equities down 0.4% while it got some support from a 0.3% softer USD. Iran’s Khamenei yesterday that it was outrageous for the US to say it won’t allow Iran to enrich uranium, that the US should not talk nonsense and that Iran’s uranium enrichment is absolutely non-negotiable. These statements did little to the oil price yesterday. But CNN reporting today that Israel is preparing to strike nuclear facilities in Iran is making Brent rise 1% to USD 66.1/b. Either the impact on the oil market in case of an attack is assumed to be low or the probability for an attack is assumed to be low. Because a 1% gain is not much when we are talking bombs in the Middle East major oil producing region.

Trump bully-diplomacy has reach a dead end as Iran clings to its nuclear capabilities. Iran will naturally never give up its ability to produce a nuclear weapon after having seen what Russia has done to Ukraine when they gave up their nuclear weapons and what the US previously has done to Iraq and Libya. Israel can never accept that Iran can have nuclear weapons. And there is the standoff. So far the market is not pricing in much risk for an Israeli strike on Iran. Trump is probably not supporting Israel with respect to an attack on Iranian nuclear facilities as it could drag the US into a wider war in the region. Israel however knows that the US will always have its back even if the US is not giving a green light for an attack. To our understanding it now takes very little time for Iran to produce weapons grade enriched uranium. That is something Israel cannot accept. Logic thus leads to the conclusion that Israel will strike Iranian nuclear facilities at some point given Khamenei’s explicit statement that Iran will continue its enrichment. The finer detail is however whether we are talking about nuclear power plant grade enrichment or weapons grade enrichment. Another close to certain point is that Iran will eventually make a nuclear bomb and there is essentially nothing Israel can do about it. Israel can either choose to accept that this will eventually be the outcome or they can try to prevent it or delay it as long as possible. The latter seems the likely first step. I.e. an eventual attack on Iranian nuclear facilities. Then the question is when. CNN reporting today that Israel is preparing an attack indicates that this could happen sooner rather than later.
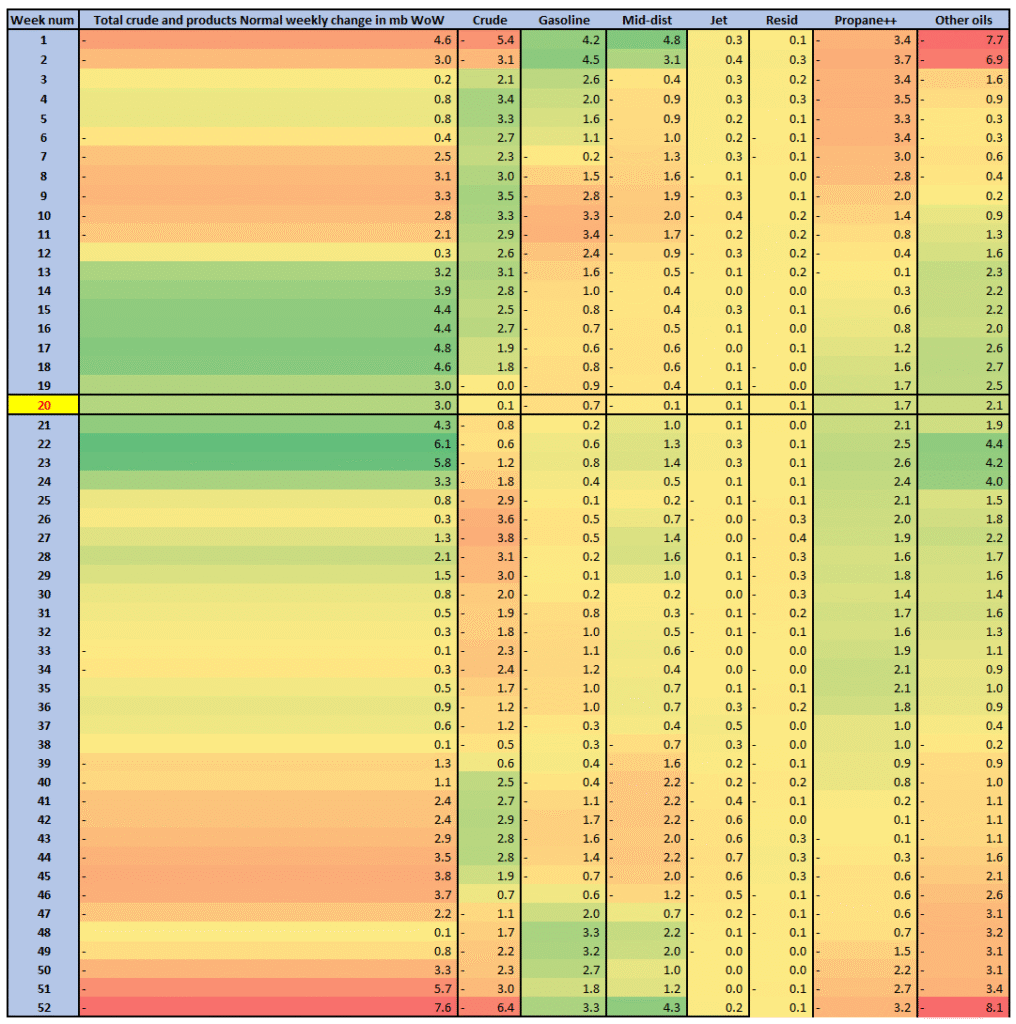
US API yesterday released data indicating that US inventories of crude and products fell 2.1 mb (Crude + 2.5 mb, Gasoline -3.2 mb and Distillates -1.4 mb). That is a seasonally counter cyclical draw when US commercial inventories normally rise 3-6 mb per week. Surplus is not yet here. Actual data later today at 16:30 CET.
Normal weekly change in US commercial crude and products in mb/week. Week 20 highlighted.
Analys
A lower oil price AND a softer USD will lift global appetite for oil

Brent starting in read after a week of 2.4% tariff relief gain. Brent crude gained 2.4% (+USD 1.5/b) last week with a close of USD 65.41/b and traded the week in a range of USD 64.53 – 66.63/b. Price gains last week aligned with dissipating tariff angst as China – US trade tariffs were lowered to 10% and 30% respectively. Down from a staggering 125% and 145% though with the risk for a snap-back after 90 days. The low of the week coincided with rumors that an Iran – US nuclear deal was near at hand. But was later downplayed. Such a deal may not add all that much more oil to the market as most of Iran’s oil probably already is in the market through different pathways. Brent crude is pulling back 0.9% this morning to USD 64.9/b while the USD index is declining 0.5% as well. That is usually a positive for the oil price as it makes oil cheaper for all non-USD based consumers. US equity futures are also down 1% this morning. Chinese new and used housing prices fell 0.12% and 0.41% respectively last month with property investments down 10.3% YTD YoY. All weaker than expected. Chinese industrial production YoY however came in at 6.1% and better than the expected 5.7%. Overall a rather weak start of the week nonetheless.

While down this morning, Brent crude is surprisingly not shedding all that much value given the rather bearish backdrop of US equity futures in the red and everyone and their grandmothers forecasting doom and gloom for the oil price.
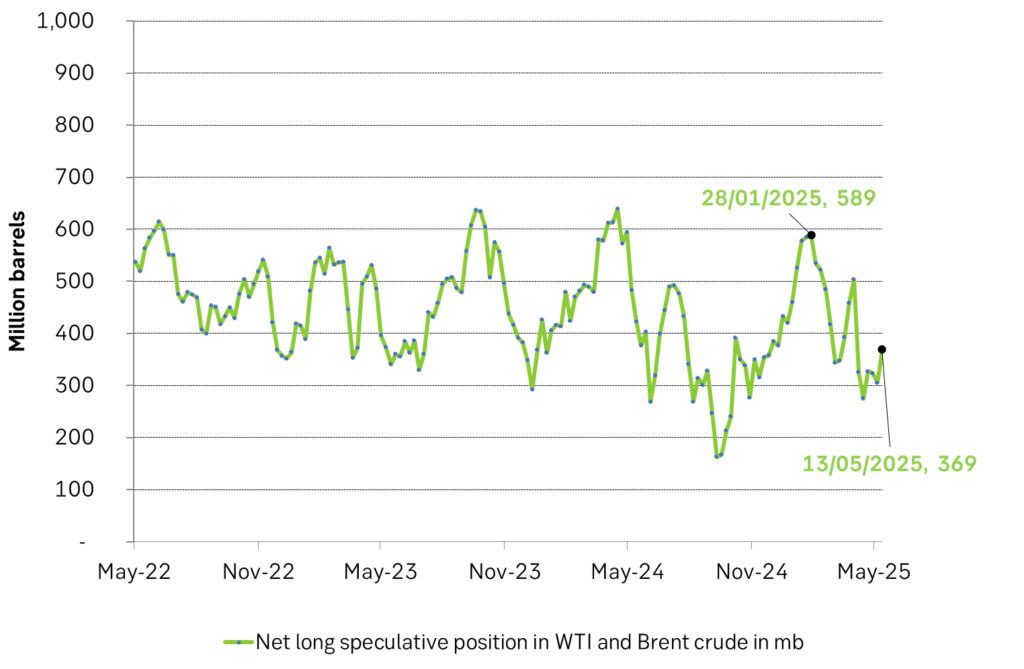
Speculators added 64 mb to net long positions in Brent crude and WTI over the week to last Tuesday. Most likely as a result of US-China tariffs being shifted down to livable levels. Most headlines and forecasts are however overall very bearish for oil. More oil from OPEC+ in the months to come coupled with expectations for a slowdown in global oil demand growth due to the US tariff trade war.
A lower oil price AND a softer USD will likely bolster global oil demand vs very bearish expectations. Global oil demand growth could surprise to the upside amid all the gloom. In EUR/b terms the the current price of Brent crude is now 22% lower than the average price in 2024. A softer oil price AND a softer USD is making oil considerably cheaper in the eyes of the global oil consumer ex-US. And that portion of global oil demand after all accounts for around 80% of global consumption. We could thus quickly see a Brent crude price down 30% versus 2024 average for 80% of the world’s consumers with a little further decline in USD-oil and the USD itself. This will likely help to boost oil demand globally. Remember also that a very important reason for why OPEC+ wanted to lift its oil production in May and June was to meet sharply stronger Middle East summer oil demand. A note on oil demand. India’s road fuel demand was up 5% YoY in April while its PMI rose to 58.2%. The IEA expects India oil demand to rise by only 2.3% to 5.77 mb/d YoY (+130 kb/d) while a 5% demand growth would yield a demand growth of 282 kb/d YoY.
OPEC+ has NOT abandoned market control. This is not 2014/15/16 or 2020. It is important to remember that the group has not abandoned its general plan of adding 2.2 mb/d from April 2025 to December 2026. The path will be decided on a monthly basis and can be moved both up AND down. The group has NOT abandoned market control. Though it is on a gradual pace to retake 2.2 mb/d of market share. US shale oil production has to stand back to make room and global consumers will respond with stronger demand growth in response to a lower oil price made additionally cheaper by a softening USD.
Brent crude forward curve in front-end backwardation. Surplus is not yet here.
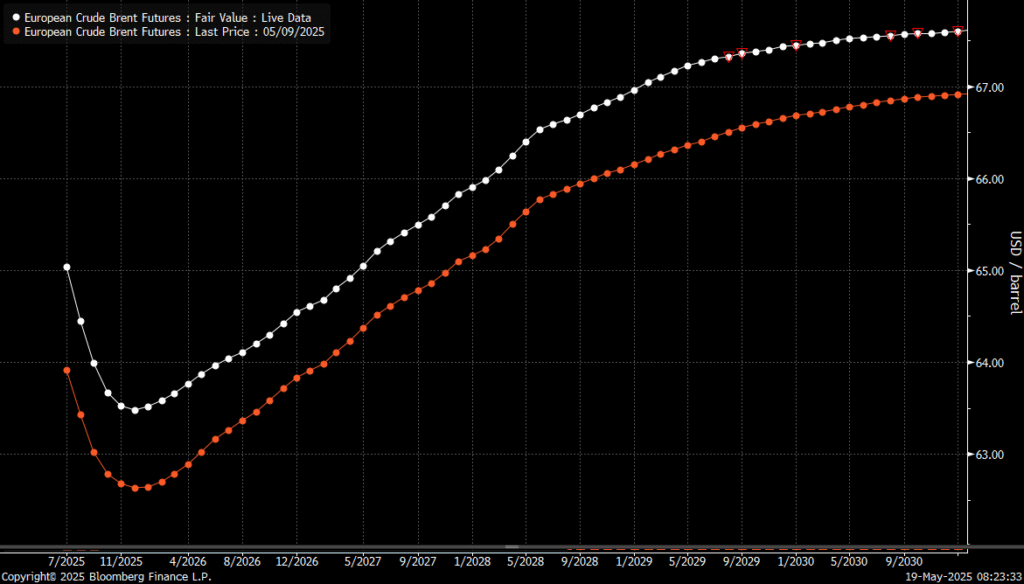
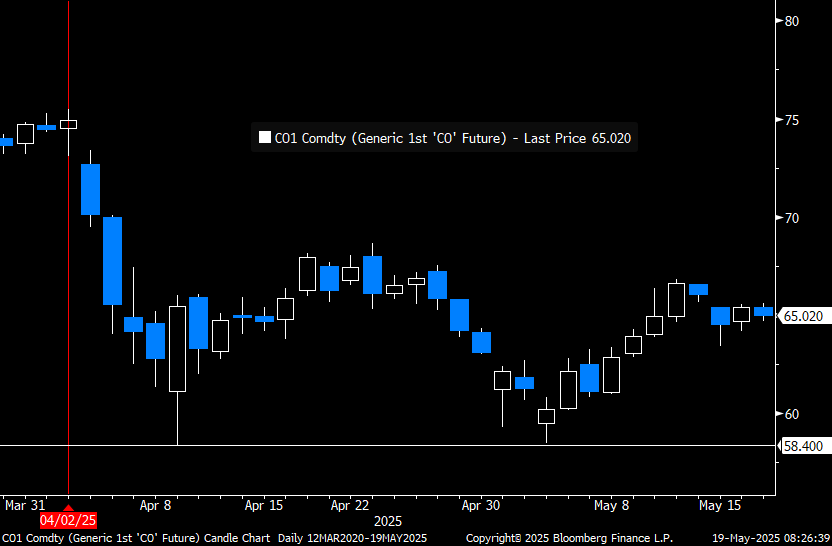
Brent crude in USD/b. Little upside conviction to be found anywhere.
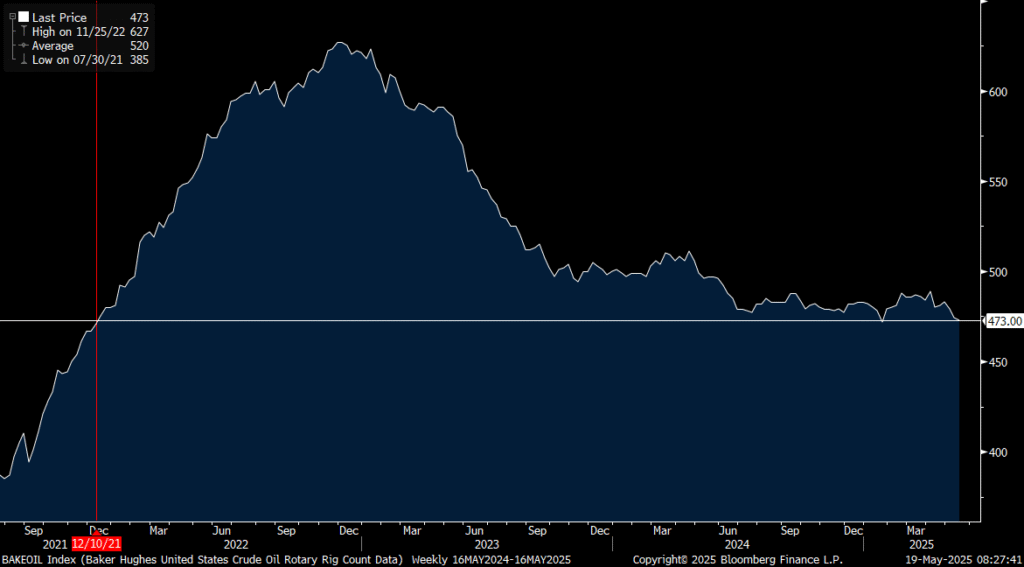
US oil drilling rig count fell by 1 last week to second lowest since December 2021. No real shedding of drilling quite yet. But we’ll likely see a drop of 5-10% over the coming months. It could drop as much as 5-10 rigs per week.
Net long speculative positions in Brent crude + WTI rebounded 64 mb to Tuesday last week.
Analys
Oil slips as Iran signals sanctions breakthrough

After a positive start to the week, crude oil prices rose on Monday and Tuesday, with Brent peaking at USD 66.8 per barrel on Tuesday evening. Since then, prices have drifted lower, declining by roughly 5% to around USD 63.5 per barrel – below where the week began during Monday’s opening.

Iran is currently in the spotlight, having signaled its willingness to sign a nuclear deal with the U.S. in exchange for lifting economic sanctions. Ali Shamkhani, a senior political, military, and nuclear adviser, spoke publicly about the ongoing negotiations. He indicated that Iran would commit to never developing nuclear weapons and could dismantle its stockpile of highly enriched uranium – provided there is immediate sanctions relief. While nothing is finalized, the rhetoric is notable and could theoretically lead to additional Iranian barrels entering the global market.
It’s worth recalling that in mid-March, Iran’s Oil Minister declared that the country’s oil exports were “unstoppable”, and that Iran would not relinquish its share of the global oil market – even in the face of new U.S. sanctions introduced earlier this year. In practice, however, this claim has proven exaggerated.
In February 2025, Iran’s crude production rose to 3.3 million barrels per day (bpd), staying above 3 million bpd since September 2023. Of this, approximately 1.74 million bpd were exported – primarily to Chinese private refiners (”teapots”). Early in the year, shipments to these teapots continued largely uninterrupted, as they have limited exposure to the U.S. financial system and remained willing buyers despite sanctions.
However, Washington’s “maximum pressure” campaign has gradually constrained Iran’s ability to ship crude to China. By March 2025, Chinese imports of Iranian oil peaked at approximately 1.8 million bpd. In April, imports dropped sharply to around 1.3 million bpd, reflecting stricter U.S. sanctions targeting Chinese refineries and port operators involved in handling Iranian crude. Preliminary data for May suggest a further decline, with Iranian oil arrivals potentially falling to 1.0–1.2 million bpd, as Chinese refiners adopt a more cautious stance.
As a result, any immediate sanctions relief stemming from a nuclear agreement could unlock an additional 0.8 million bpd of Iranian crude for the global market – an undeniably bearish development for prices.
On the other hand, failure to reach a deal would likely mean continued or even intensified U.S. pressure under the Trump administration. In a worst-case scenario – where Iran loses its remaining 1.0–1.2 million bpd of exports – and if Saudi Arabia or other major producers do not promptly step in to offset the shortfall, global oil prices could experience an immediate upside of USD 4–6 per barrel.
Meanwhile, both OPEC and the IEA expect the oil market to remain well-supplied in 2025, with supply growth exceeding demand. OPEC holds its demand growth forecast at 1.3 million bpd, driven mainly by emerging markets in Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America. In contrast, the IEA sees more modest growth of 740,000 bpd, citing macroeconomic challenges and accelerating electric vehicle adoption – particularly in China, where petrochemical demand is now the primary growth engine.
On the supply side, OPEC has revised down its non-OPEC+ growth estimate to 800,000 bpd, citing weaker prices and reduced upstream investment. The IEA, however, expects global supply to expand by 1.6 million bpd, led by the U.S., Canada, Brazil, Guyana, and Argentina. Should OPEC+ proceed with unwinding voluntary cuts, the IEA warns that the market could face a surplus of up to 1.4 million bpd in 2025 – potentially exerting renewed downward pressure on prices.
_______________
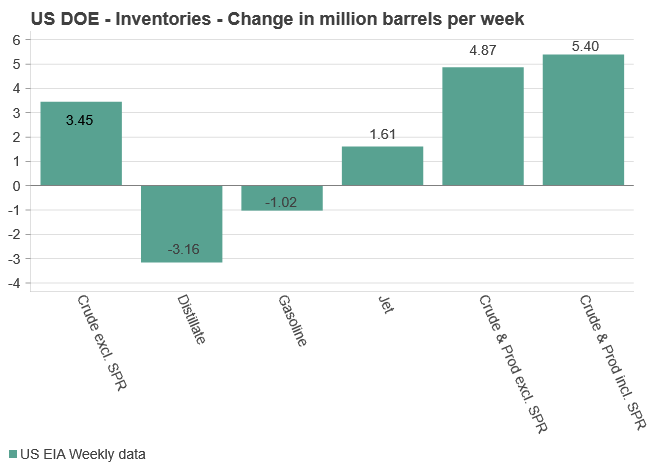
EIA data released yesterday showed U.S. Crude inventories unexpectedly rose 3.45 million barrels with a drop in exports and despite a larger than expected increase in refinery runs.
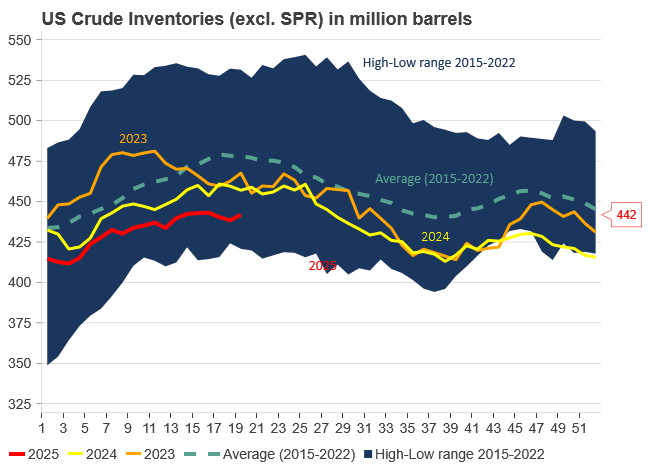
U.S. commercial crude oil inventories (excl. SPR) rose by 3.45 million barrels last week, reaching 441.8 million barrels – approximately 6% below the five-year seasonal average. Total gasoline inventories declined by 1 million barrels and now sit around 3% below the five-year average. Distillate (diesel) fuel inventories fell by 3.2 million barrels and remain roughly 16% below the seasonal norm. Meanwhile, propane/propylene inventories climbed by 2.2 million barrels but are still 9% below their five-year average. Overall, total commercial petroleum inventories rose by 4.9 million barrels over the week – overall a neutral report with limited immediate price impacts.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSamtal om läget för guld, kobolt och sällsynta jordartsmetaller
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAgnico Eagle siktar på toppen – två av världens största guldgruvor i sikte
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanLägre elpriser och många minustimmar fram till midsommar
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanJune OPEC+ quota: Another triple increase or sticking to plan with +137 kb/d increase?
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanUtbudsunderskott och stigande industriell efterfrågan av silver på marknaden
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSaudiarabien informerar att man är ok med ett lägre oljepris
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanOil demand at risk as US consumers soon will face hard tariff-realities
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanNystart för koppargruvan Viscaria i Kiruna – en av Europas största







