Analys
The EUA price could drop to EUR 40/ton and then be picked up by Airliners, Shipping and Utilities

The EUA price is dropping hard along with a sharp decline in the front-year TTF nat gas contract. The typical last-round sell-off in EUA prices have typically been a final sell-off of 10-20-30%. From EUR 60/ton level it implies a price decline down to EUR 54; 48; 42/ton. The front-year nat gas price and the front-year Coal-to-Gas (C-t-G) differential is what has held the EUA price above EUR 60/ton. But if the TTF 2025 price falls down to EUR 27/ton the front-year C-t-G differential will fall all the way towards EUR 40/ton. That TTF 2025 falls to EUR 27/ton or lower seems likely to happen and the risk is high that the EUA price will be sucked down along with it. But nat gas demand is starting to come back with a lag in nat gas price declines in the EU but probably also in Asia. Thus first an over-sell in nat gas prices, then demand revival and then a rebound in both nat gas prices and EUA prices. Airliners, shipping companies and Utilities will probably buy as much EUAs they can get if the EUA price fall down towards EUR 40/ton.

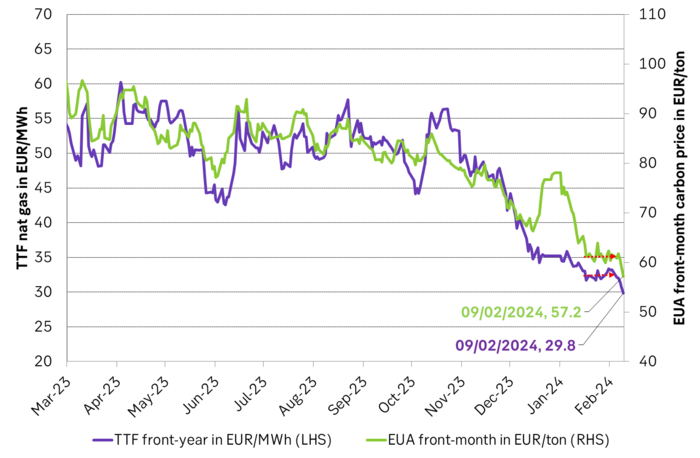
Front-year 2025 TTF nat gas price falls hard and so does the EUA price. The front-month EUA price dropped 2.7% yesterday to EUR 58.97/ton and thus broke out of the sideways trend around EUR 61/ton since 18 January. Today it has sold off another 3.2% to EUR 57.1/ton.
Again it is the nat gas price which is leading the way and more specifically it is about the front-year nat gas which lost 1.9% on Wednesday and another 2.5% again ydy to a close of EUR 30.65/MWh and today it has solf off 2.8% to EUR 29.8/ton.
The EUA price has very clearly been balancing on the front-year Coal-to-Gas (C-t-G) differentials. The C-t-G differentials have been significantly lower than EUR 60/ton both at the front-end of the curve (1-2-3 month) and for calendars 2026 and 2027. But the front-year nat gas price has held up at around EUR 31/MWh quite well since around mid January.
How far down will the EUA price go? The final sell-off could be down towards EUR 40/ton. With these dynamics the big question then becomes: How far down will the front-year nat gas contract sell? It will of course sell off too far as commodities always do. The reason commodities do this is the natural reactive chain of events which normally comes with a lag: First the price goes down before dropping hard in the final round of the sell-off. Then demand comes back with a lag to the price action. This again drives the price back up and off from the lows to a level consistent with the revival in demand. If demand instead had reacted immediately to lower prices then the hard drop at the end of the sell-off might not have happened.
Looking at previous hard, final sell-off-drops in the EUA price we can see that final drops typically have been 10-20-30% as the last final drop. If we take the EUR 60/ton as the starting point of this final drop, then we are talking an EUA price bottom of somewhere in the range of EUR 54; 48; 42/ton.
Global nat gas demand destruction in the face of very high nat gas prices solved the energy crisis. Let’s link this back to price action in nat gas. The reason why Europe has managed the recent energy crisis (Russia/Ukraine, nat gas,…) so surprisingly well is 1) Large reduction in nat gas demand in EU due to exceptionally high prices and 2) Significant demand destruction in Asia freeing up nat gas to flow to the EU. I.e. it was global demand destruction of nat gas in response to extremely high prices globally which solved the energy crisis. It was solved by the global market.
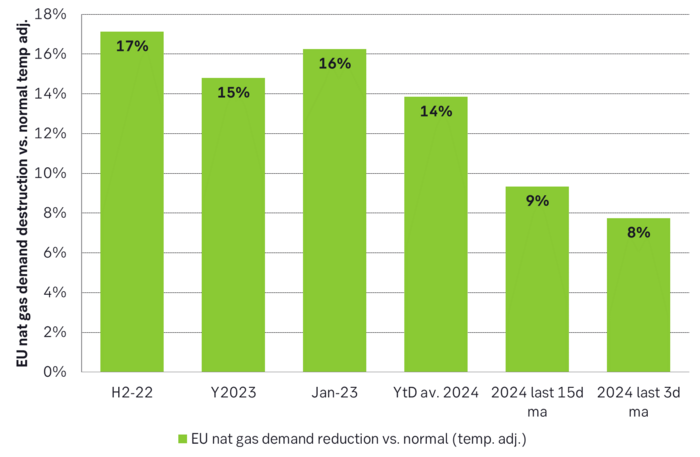
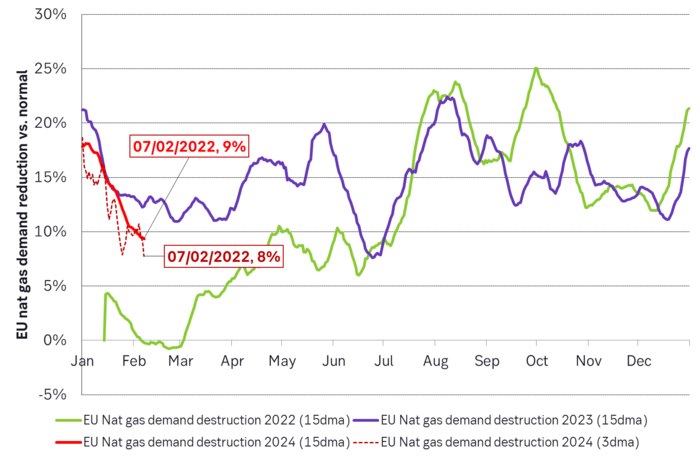
Demand for nat gas is starting to come back as the price falls. The nominal historical average nat gas TTF price was EUR 20/MWh from 2010 to 2019. But the real average was EUR 26/MWh. So seen from the eyes of consumers in both Europe and Asia, a price of EUR 26/MWh is an historically absolutely normal price. Demand for nat gas should thus naturally accelerate back towards normal levels at current nat gas prices. Not just in Europe, but also globally in all regions exposed to nat gas prices set by global LNG prices. This is already happening in the EU. Temp. adj. demand destruction vs. normal has typically been running at around 16% from mid-2022 to December 2023. Average ytd is 14% while the last 15 days is 9%. Demand destruction is fading as the price of nat gas is falling. But do remember that this is also happening in Asia but it is harder to track.
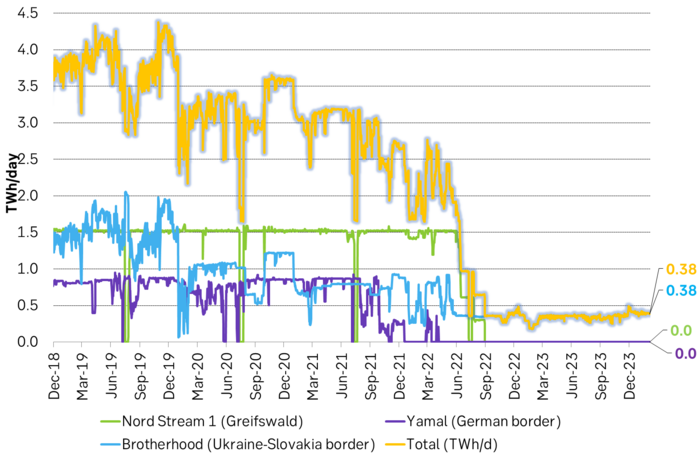
Normal nat gas demand AND normal gas prices is not consistent as Russian nat gas exports still down 1100 TWh/yr. There is however an inconsistency here in expecting normal prices and normal demand for natural gas now onward. The inconsistency is that the EU and thus the world is still robbed of the normal flow of nat gas on pipelines to Europe. This amounts to a loss of 3 TWh/day and thus close to 1100 TWh/year. When this gas is no longer flowing to the EU it isn’t flowing anywhere. It is lost to both the EU and the world. Until that is, Russia has built loads of new pipes to Asia and new LNG terminals. And that takes years.
A return to normal prices and normal demand while the world still is missing 1100 TWh/year of Russian nat gas isn’t really a consistent outcome in our view.
Demand for nat gas will continue to revive as the price of nat gas keeps falling. But both the EU and the world still need of a nat gas price at above normal levels to induce a certain amount of demand destruction until the point in time when new LNG export facilities globally has managed to replace the 1100 TWh/year we have lost from Russia.
Front-end TTF nat gas down to EUR 27/MWh could drive the EUA price to EUR 40/ton. The dynamic sell-off nat gas, prices will likely move lower than to the level which over time is consistent with continued need for some demand destruction globally. This because demand revival will come with a lag to the decline in prices. It is thus fully plausible that the TTF 2025 contract moves all the way down to EUR 27/MWh (or maybe even lower). If so it would imply a 2025 C-t-G differential of only EUR 40/ton for the EUA price to balance on and reference to. That could be the final hard drop in the EUA price. That’s a 30% drop from EUR 60/ton. But it won’t last because that nat gas price is likely too low vs. what is needed globally to maintain some level of demand destruction for a while longer.
An EUA price of EUR 40/ton would also be too cheap to resist for a range of market participants and they’d likely jump in and purchase with both hands. Airliners and shipping companies which will have difficulties of shifting away from fossil fuels and will need EUAs for years to come. Also utilities could step in and purchase large amounts of EUAs even if forward margins are negative. Some EU based utilities with large fossil-based assets bought truckloads of EUAs from 2011 to 2017 when the EUA price ranged from EUR 3/ton to EUR 9/ton. For them the EUA certificate is not only a marginal cost. It is also a licence to operate. The EUA price will of course not return to that level again. But if we move to EUR 40-50/ton, then it will probably trigger strategic buying by shipping companies, airliners as well as utilities.
Front-year TTF nat gas TTF price is dropping and leading the EUA price lower after a period of sideways action since mid-Jan
But the EU and the world is still missing some 3 TWh/d or 1100 TWh/yr of piped nat gas from Russia. When Russian nat gas is no longer flowing on pipes to Europe, it is flowing nowhere.
Nat gas demand destruction in the EU has been running at 15% to 17% since mid-2022 in the face of high nat gas prices. But demand destruction is now fading down to 8%. Demand has started to come back as nat gas prices fall. Demand is probably also coming back in Asia, but not so easily to see.
EU nat gas demand destruction has started to fade.
Forward Coal to Gas (C-t-G) differentials vs EUA market prices. The EUA price has balanced on the front-year differential. But that has now fallen like a rock along with the fall in front-year TTF nat gas price. Lead the EUA into a free-fall
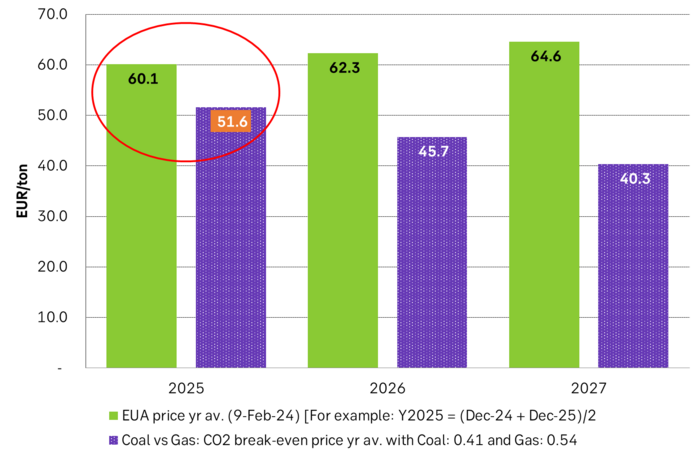
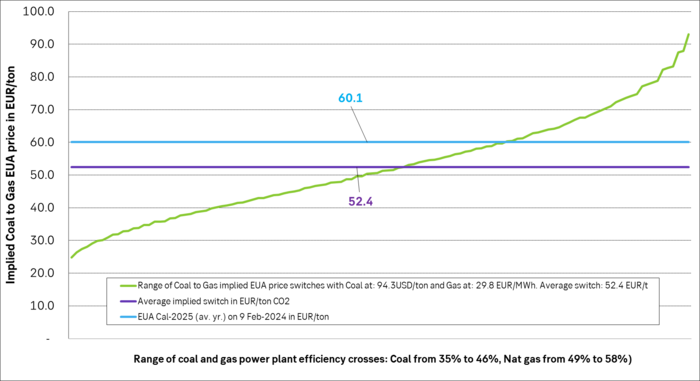
The front-year Coal-to-Gas differential is a distribution of crosses between many different levels of efficiencies for coal and nat gas power plants. Averages of these are EUR 52.4/ton with Coal at USD 94.3/ton and Nat gas at EUR 29.8/MWh (both front-year 2025 prices). So EUA price is still hanging high.
Analys
Brent needs to fall to USD 58/b to make cheating unprofitable for Kazakhstan

Brent jumping 2.4% as OPEC+ lifts quota by ”only” 411 kb/d in July. Brent crude is jumping 2.4% this morning to USD 64.3/b following the decision by OPEC+ this weekend to lift the production cap of ”Voluntary 8” (V8) by 411 kb/d in July and not more as was feared going into the weekend. The motivation for the triple hikes of 411 kb/d in May and June and now also in July has been a bit unclear: 1) Cheating by Kazakhstan and Iraq, 2) Muhammed bin Salman listening to Donald Trump for more oil and a lower oil price in exchange for weapons deals and political alignments in the Middle East and lastly 3) Higher supply to meet higher demand for oil this summer. The argument that they are taking back market share was already decided in the original plan of unwinding the 2.2 mb/d of V8 voluntary cuts by the end of 2026. The surprise has been the unexpected speed with monthly increases of 3×137 kb/d/mth rather than just 137 kb/d monthly steps.

No surplus yet. Time-spreads tightened last week. US inventories fell the week before last. In support of point 3) above it is worth noting that the Brent crude oil front-end backwardation strengthened last week (sign of tightness) even when the market was fearing for a production hike of more than 411 kb/d for July. US crude, diesel and gasoline stocks fell the week before last with overall commercial stocks falling 0.7 mb versus a normal rise this time of year of 3-6 mb per week. So surplus is not here yet. And more oil from OPEC+ is welcomed by consumers.
Saudi Arabia calling the shots with Russia objecting. This weekend however we got to know a little bit more. Saudi Arabia was predominantly calling the shots and decided the outcome. Russia together with Oman and Algeria opposed the hike in July and instead argued for zero increase. What this alures to in our view is that it is probably the cheating by Kazakhstan and Iraq which is at the heart of the unexpectedly fast monthly increases. Saudi Arabia cannot allow it to be profitable for the individual members to cheat. And especially so when Kazakhstan explicitly and blatantly rejects its quota obligation stating that they have no plans of cutting production from 1.77 mb/d to 1.47 mb/d. And when not even Russia is able to whip Kazakhstan into line, then the whole V8 project is kind of over.
Is it simply a decision by Saudi Arabia to unwind faster altogether? What is still puzzling though is that despite the three monthly hikes of 411 kb/d, the revival of the 2.2 mb/d of voluntary production cuts is still kind of orderly. Saudi Arabia could have just abandoned the whole V8 project from one month to the next. But we have seen no explicit communication that the plan of reviving the cuts by the end of 2026 has been abandoned. It may be that it is simply a general change of mind by Saudi Arabia where the new view is that production cuts altogether needs to be unwinded sooner rather than later. For Saudi Arabia it means getting its production back up to 10 mb/d. That implies first unwinding the 2.2 mb/d and then the next 1.6 mb/d.
Brent would likely crash with a fast unwind of 2.2 + 1.6 mb/d by year end. If Saudi Arabia has decided on a fast unwind it would meant that the group would lift the quotas by 411 kb/d both in August and in September. It would then basically be done with the 2.2 mb/d revival. Thereafter directly embark on reviving the remaining 1.6 mb/d. That would imply a very sad end of the year for the oil price. It would then probably crash in Q4-25. But it is far from clear that this is where we are heading.
Brent needs to fall to USD 58/b or lower to make it unprofitable for Kazakhstan to cheat. To make it unprofitable for Kazakhstan to cheat. Kazakhstan is currently producing 1.77 mb/d versus its quota which before the hikes stood at 1.47 kb/d. If they had cut back to the quota level they might have gotten USD 70/b or USD 103/day. Instead they choose to keep production at 1.77 mb/d. For Saudi Arabia to make it a loss-making business for Kazakhstan to cheat the oil price needs to fall below USD 58/b ( 103/1.77).
Analys
All eyes on OPEC V8 and their July quota decision on Saturday

Tariffs or no tariffs played ping pong with Brent crude yesterday. Brent crude traded to a joyous high of USD 66.13/b yesterday as a US court rejected Trump’s tariffs. Though that ruling was later overturned again with Brent closing down 1.2% on the day to USD 64.15/b.

US commercial oil inventories fell 0.7 mb last week versus a seasonal normal rise of 3-6 mb. US commercial crude and product stocks fell 0.7 mb last week which is fairly bullish since the seasonal normal is for a rise of 4.3 mb. US crude stocks fell 2.8 mb, Distillates fell 0.7 mb and Gasoline stocks fell 2.4 mb.
All eyes are now on OPEC V8 (Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Kuwait, UAE, Algeria, Russia, Oman, Kazakhstan) which will make a decision tomorrow on what to do with production for July. Overall they are in a process of placing 2.2 mb/d of cuts back into the market over a period stretching out to December 2026. Following an expected hike of 137 kb/d in April they surprised the market by lifting production targets by 411 kb/d for May and then an additional 411 kb/d again for June. It is widely expected that the group will decide to lift production targets by another 411 kb/d also for July. That is probably mostly priced in the market. As such it will probably not have all that much of a bearish bearish price impact on Monday if they do.
It is still a bit unclear what is going on and why they are lifting production so rapidly rather than at a very gradual pace towards the end of 2026. One argument is that the oil is needed in the market as Middle East demand rises sharply in summertime. Another is that the group is partially listening to Donald Trump which has called for more oil and a lower price. The last is that Saudi Arabia is angry with Kazakhstan which has produced 300 kb/d more than its quota with no indications that they will adhere to their quota.
So far we have heard no explicit signal from the group that they have abandoned the plan of measured increases with monthly assessments so that the 2.2 mb/d is fully back in the market by the end of 2026. If the V8 group continues to lift quotas by 411 kb/d every month they will have revived the production by the full 2.2 mb/d already in September this year. There are clearly some expectations in the market that this is indeed what they actually will do. But this is far from given. Thus any verbal wrapping around the decision for July quotas on Saturday will be very important and can have a significant impact on the oil price. So far they have been tightlipped beyond what they will do beyond the month in question and have said nothing about abandoning the ”gradually towards the end of 2026” plan. It is thus a good chance that they will ease back on the hikes come August, maybe do no changes for a couple of months or even cut the quotas back a little if needed.
Significant OPEC+ spare capacity will be placed back into the market over the coming 1-2 years. What we do know though is that OPEC+ as a whole as well as the V8 subgroup specifically have significant spare capacity at hand which will be placed back into the market over the coming year or two or three. Probably an increase of around 3.0 – 3.5 mb/d. There is only two ways to get it back into the market. The oil price must be sufficiently low so that 1) Demand growth is stronger and 2) US shale oil backs off. In combo allowing the spare capacity back into the market.
Low global inventories stands ready to soak up 200-300 mb of oil. What will cushion the downside for the oil price for a while over the coming year is that current, global oil inventories are low and stand ready to soak up surplus production to the tune of 200-300 mb.
Analys
Brent steady at $65 ahead of OPEC+ and Iran outcomes

Following the rebound on Wednesday last week – when Brent reached an intra-week high of USD 66.6 per barrel – crude oil prices have since trended lower. Since opening at USD 65.4 per barrel on Monday this week, prices have softened slightly and are currently trading around USD 64.7 per barrel.

This morning, oil prices are trading sideways to slightly positive, supported by signs of easing trade tensions between the U.S. and the EU. European equities climbed while long-term government bond yields declined after President Trump announced a pause in new tariffs yesterday, encouraging hopes of a transatlantic trade agreement.
The optimisms were further supported by reports indicating that the EU has agreed to fast-track trade negotiations with the U.S.
More significantly, crude prices appear to be consolidating around the USD 65 level as markets await the upcoming OPEC+ meeting. We expect the group to finalize its July output plans – driven by the eight key producers known as the “Voluntary Eight” – on May 31st, one day ahead of the original schedule.
We assign a high probability to another sizeable output increase of 411,000 barrels per day. However, this potential hike seems largely priced in already. While a minor price dip may occur on opening next week (Monday morning), we expect market reactions to remain relatively muted.
Meanwhile, the U.S. president expressed optimism following the latest round of nuclear talks with Iran in Rome, describing them as “very good.” Although such statements should be taken with caution, a positive outcome now appears more plausible. A successful agreement could eventually lead to the return of more Iranian barrels to the global market.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanUtbudsunderskott och stigande industriell efterfrågan av silver på marknaden
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanNystart för koppargruvan Viscaria i Kiruna – en av Europas största
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanRebound to $65: trade tensions ease, comeback in fundamentals
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanOil slips as Iran signals sanctions breakthrough
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanFörenade Arabemiraten siktar på att bygga ett datacenter på 5 GW, motsvarande fem stora kärnkraftsreaktorer
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanWhipping quota cheaters into line is still the most likely explanation
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanA lower oil price AND a softer USD will lift global appetite for oil
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanStark affär för Pan American – men MAG Silvers aktieägare kan bli förlorare











