Analys
SEB – Råvarukommentarer vecka 31 2012
Sammanfattning av rekommendationer
Råvara – Rekommendation
Råolja – Köp OLJA S
Guld – Köp BULL GULD X4 S (hög risk) eller GULD S (låg risk)
Silver – Ingen rekommendation
Koppar – Köp KOPPAR S
Zink – Ingen rekommendation
Kaffe – Köp KAFFE S
Socker – Köp SHORT SOCKE A S
Vete – Köp VETE S
Majs – Köp MAJS S
Sojabönor – Köp SOJABO S
Inledning
Efter den positiva avslutningen förra veckan, efter Drahgis ”löften” om ett kraftfullt penningpolitiskt agerande, började handeln avvaktande i måndags. Centralbanksmöten både i USA, England och ECB:s under veckan och det var upplagt för prisrörelser. Det var det vi fick se idag torsdag, men på nedsidan.
Drahgis uttalande diskonterade in alltför positiva utsikter. FED vilar på hanen ännu en månad och ECB redovisade inget nytt. Eurodollarn föll kraftigt och så gjorde metallerna. De större basmetallerna koppar, aluminium, zink och nickel är ned 2-3 %.
Marknaderna för jordbruksprodukter har varit avvaktande efter de stora prisuppgångarna. Kortsiktig brist måste ransoneras, men när är det dags för priset att vända ner igen?
Guld och socker har fått nya tekniska signaler. Köpsignal för guld och säljsignal för socker.
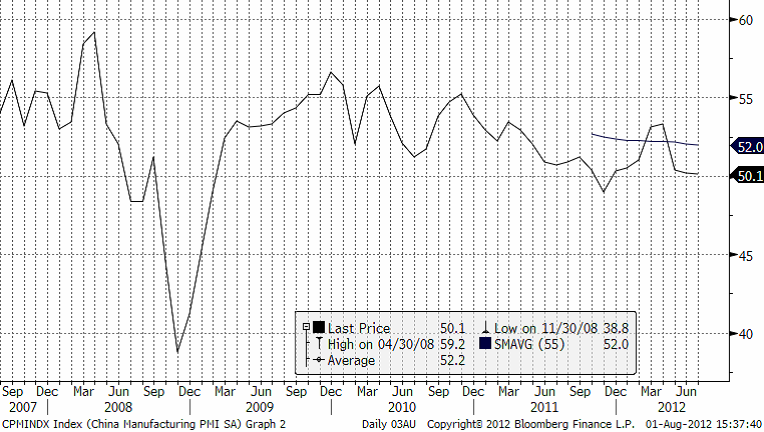
Brent tycker vi att man bör köpa på ”dippar” under 100 dollar. Iran försöker peddla sin olja till dem som vågar trotsa EU.s och USA:s köpförbud. OPEC producerar på sin lägsta nivå sedan 2008 pga detta. Kina bromsar in, men försöker stimulera ekonomin på olika sätt. Frågar än när dessa stimulanser biter. Kinesiskt PMI (inköpschefsindex) kom in på 50.1. Det är lite lägre än förra månadens 50.2. Ett värde över 50 indikerar att ekonomin växer och ett värde under 50 indikerar att ekonomin krymper.
Eurokrisen
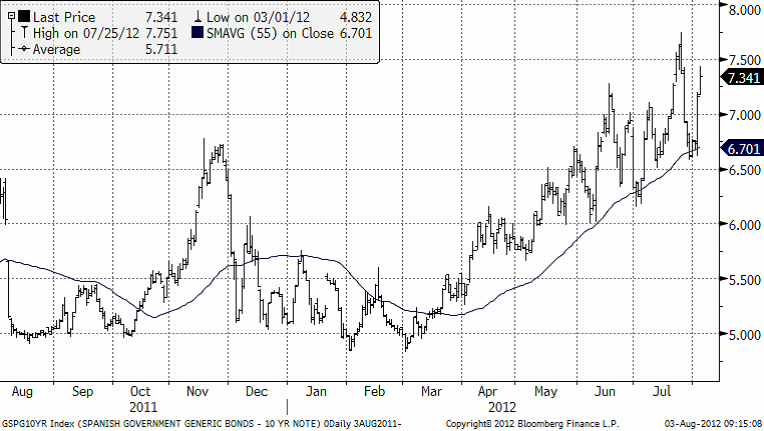
Vad som sker i EU är att det finns en social acceptans att banker tas över av staten därför att man inte vill uppleva obehaget av att bankerna går under var och en för sig, Detta gör att det är rimligt att anta att staternas i fråga egentliga skulder är deras egen statsskuld + bankernas skulder. När man studerar den typen av skuldberg i förhållande till de här ländernas skatteintäkter, får man en skrämmande bild. Än så länge försöker man skjuta upp det oundvikliga. ECB:s satsning på att få ner räntorna i Spanien är det senaste och främsta exemplet på detta. Vi ser nedan hur räntorna har på deras tioårs statsobligation föll från 7.75 till 6.68. Efter Draghis tal igår steg räntorna återigen upp till 7.34% i skrivande stund.
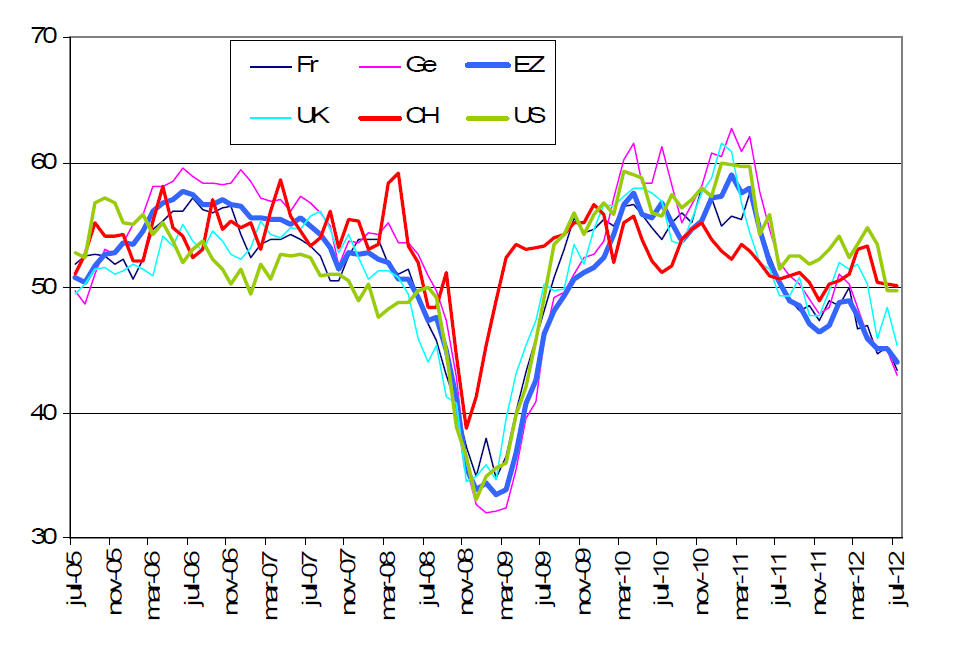
Inköpschefsindex, PMI, för de stora ekonomierna har sjunkit stadigt det senaste året. Tysklands PMI för tillverkningsindustrin ligger nu under Frankrikes, på 43 mot 43.4. Eurozonen ligger på 44. Storbritannien har bromsat in fort de senaste tre månaderna och har sjunkit från 50.2 i april till 45.4 i juli. USA har halkat under 50. Endast Kina ligger över 50. Gårdagens kinesiska PMI kom in på 50.1, vilket är en tiondel lägre än i juni (50.2). PMI anses vara en ”ledande indikator” för ekonomins utveckling.
PMI, som är en ledande indikator, är för Eurozonen på samma nivå som månaden före Lehmankraschen 2008. Folk verkar inte göra någonting och det märks när t ex Dagens Industri varnar för ”döda aktier”, aktier med bristfällig likviditet. Vad gick bra under hösten 2008? Det var nästan guld och guldet steg ordentligt det året. Om det vill sig illa är råvaror och då främst guld den tillgång man vill ha i sin portfölj när det skakar på värde-pappers-marknaderna.
Råolja – Brent
Nedan ser vi kursdiagrammet på spotkontraktet på Brent. 90 – 100 dollar tycks Brent vara köpvärt. Samtidigt finns ett kortsiktigt tekniskt motstånd på ca 110 dollar. SEB:s prognos är 115 dollar per fat under det fjärde kvartalet i år.
Råvarucertifikat får sin avkastning inte endast från stigande priser, utan också på att över tiden tillgodogöra sig rabatter på terminer i förhållande till spot. Vi ser i diagrammet nedan att terminer är billigare än spot på Brent. Genom att över tiden köpa billigt och sälja till spot (dyrt), samlar man på sig vinster. Råvarucertifikat gör just detta genom sin konstruktion. De hämtar sin avkastning från terminskontrakt, som ”rullas” in i längre kontrakt när tiden gjort att det gamla kontraktet är nära förfall.
Att köpa t ex OLJA S, och sitta på det, kan därför ge ganska hög avkastning, även om priset på råolja väntar med att stiga.
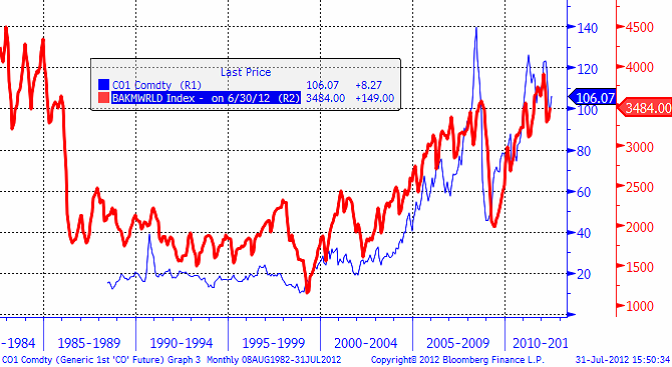
Nedan ser vi antalet borr-riggar i världen de senaste 30 åren enligt Baker Hughes Inc. Blå linje är priset på Brent.
Nedan ser vi hur antalet oljeriggar i USA har utvecklat sig. Sedan 2009 är det en ökning på 1200 riggar. Det betyder att en stor del av prospekteringen och produktionsökningen sker i det fria landet USA.
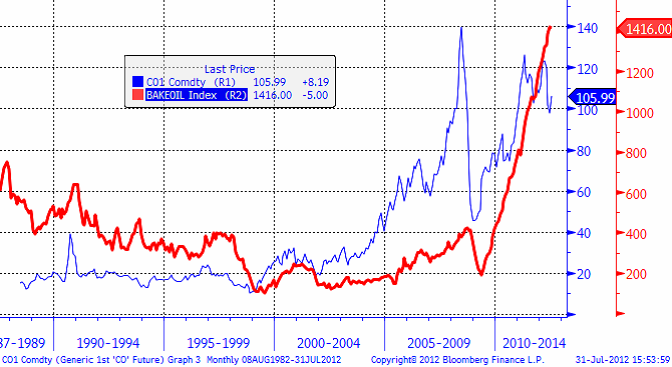
För gasriggar ser det helt annorlunda ut. Från en toppnotering på 1600 borr-riggar i drift 2008 är det nu bara 505 riggar i drift. Frackingtekniken har ökat utbudet och pressat ner priset, så det är inte lönsamt att borra efter gas på samma sätt som förut. Omställningen till konsumtion av den billiga gasen har inte gått lika fort som teknikutvecklingen.
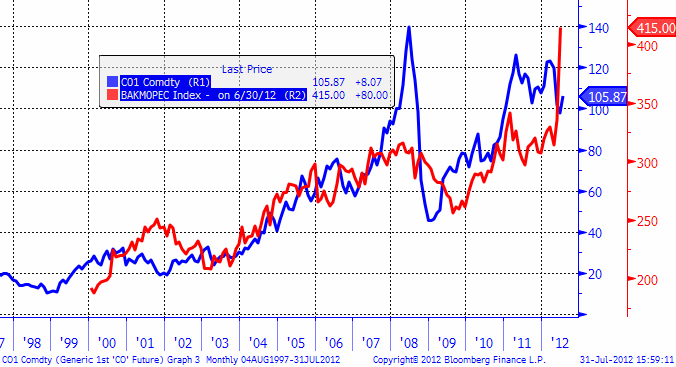
Antalet oljeriggar i alla OPEC-länder uppgår till relativt blygsamma 415 stycken. Men det är ändå en ökning på 100 riggar sedan början av året, som vi ser i diagrammet nedan.
Guld
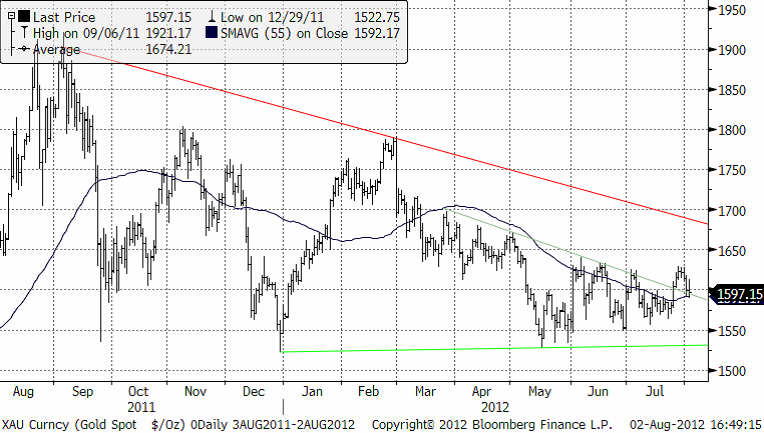
Guldpriset i dollar har brutit den kortsiktiga nedåtgående trendlinjen och rekylerat tillbaka till denna. Det brukar vara ett bra köptillfälle när detta sker.
Den fundamentala kraften som verkar positivt på guldpriset är naturligtvis finanskrisen i Europa och skuldbergen runtom i världens stater. Men som vi ser nedan under jordbruksprodukter är momsunen (nederbörden) i Indien 21% sämre den här säsongen och torka råder. Det gör att guldefterfrågan från Indien, det största enskilda konsumentlandet, sannolikt kommer att minska. GFMS släppte en rapport om detta den 16 juli. GFMS har också sänkt efterfrågeestimatet för Kina till 870 ton på helåret. Tidigare trodde man att efterfrågan skulle nå upp till 1000 ton. Samtidigt fortsätter såväl Kina som Indien att stimulera, liksom ECB som för en tid sedan sänkte korträntan till 0.75%. Räntesänkningar brukar innebära högre guldpris.
Den som är lite modig kan försöka sig på att köpa ett certifikat med hög hävstång och hög förlustrisk om priset vänder ner. Ett sådant är BULL GULD X4 S. Det ger 4 gångers utväxling på prisuppgångar (och till nackdel om priset istället faller). Den som är mindre modig och mer saktmodig kanske, kanske föredrar GULD S, vars värdeförändringar i kronor är desamma som värdeförändringen på en guldtacka i svenska kronor.
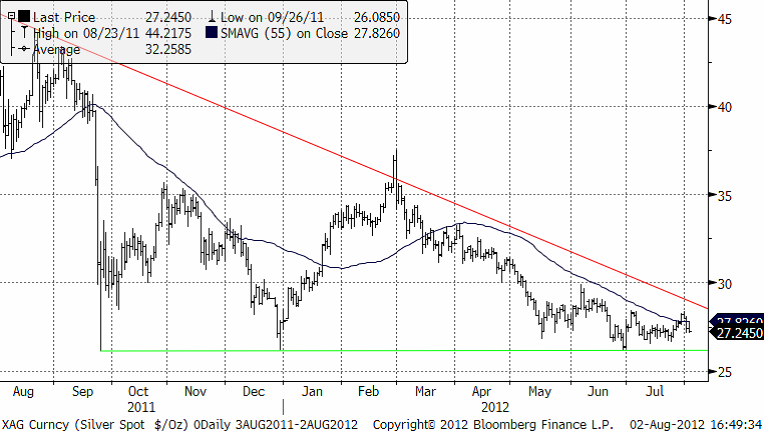
Silver
Silver har ännu inte brutit några tekniska köpsignaler. Med sjunkande industriproduktion i världen, sjunker efterfrågan på silver. Scenariot just nu med sjunkande PMI för tillverkningsindustrin innebär alltså att silver inte alls har en lika positiv uppbackning som guld.
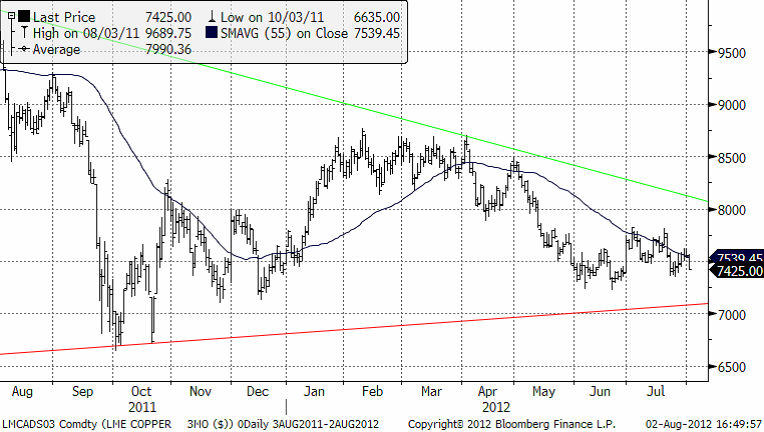
Koppar
Den fundamentala situationen är stark. Utbudet har under flera år överraskat på nedsidan, och ser ut att göra så även i år. Kopparhalterna är så pass låga i Chile att de inte mäktar med att öka enligt tidigare prognoser. Det mesta tyder på en produktionsökning globalt på endast 2-3 % mot prognostiserat 6-7 %.
Lagren utanför Kina har kontinuerligt minskat det senaste året – till stor del med destination Kina, som står för 40 % av den globala konsumtionen. Enligt International Copper Study Group noterades ett underskott om 384 tton för årets fyra första månader (ca 5 % av årsproduktionen).
Svagare konsumtion i Europa och USA de senaste månaderna indikerar en marknad närmare balans på årsbasis. Allt hänger på Kina. Hu Jintao aviserade i veckan kommande finans- och penningpolitiska stimulanser under hösten. Det kinesiska analyshuset Antaike prognostiserar en konsumtionsökning med 5 % i Kina 2012, till stor del baserat på fortsatt utbyggnad av elnätet.
Som en anekdot producerade Kina 1,8 millioner mil kraftkabel första halvåret (430 varv runt jorden), innebärande en ökning med 13,7 % jämfört med samma period förra året. Kina kommer att konsumera mycket koppar även i framtiden, så mycket är klart, samtidigt som risken är stor att utbudet inte räcker till. Kina har utnyttjat varje större korrigering i marknaden till köp och ökad import. Mycket tyder på att det kommer att upprepas. Fråga är bara hur långt ner man ”släpper” marknaden. Den tekniska bilden kan ge oss viss vägledning. Den långsiktigt uppåtgående trenden kommer in ungefär vid $7000/ton (motsvaras av $3,18/lbs för Comex-kontraktet), ca 4,5 % under dagens nivå på $7330.
Bara att äga råvarucertifikat på koppar gör att man tjänar pengar, även om priset på koppar står still.
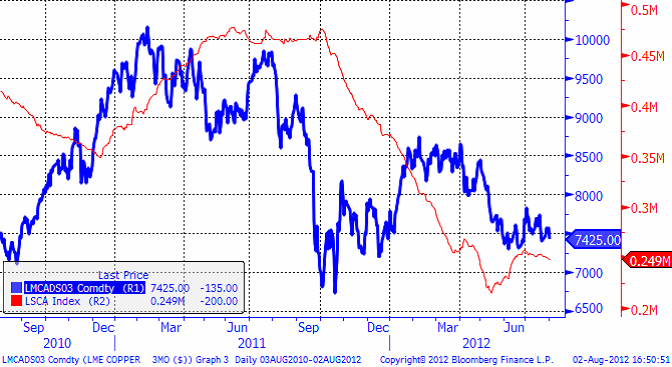
Anledningen till detta är att kopparmarknaden är i backwardation, som vi ser i nedanstående diagram. När det är backwardation köper man terminer billigare än spot. Den rabatten blir en vinst över tiden.
Koppar är en råvara som konsekvent över tiden ofta för att inte säga, nästan alltid, handlats med rabatt på terminerna. Trots att prisuppgången på t ex guld har varit så stor, har ändå en råvarucertifikatinvestering i koppar gett imponerande avkastning.
I nedanstående diagram ser vi kopparpriset och lagren i antal ton i LME:s lagerhus. Vi ser att lagernivåerna har fallit sedan mitten av 2011. Konsumtionen är alltså större än produktionen. Det är ingen mekanisk sanning, men allt annat lika ”borde” sjunkande lager i vart fall ge stöd åt priset.
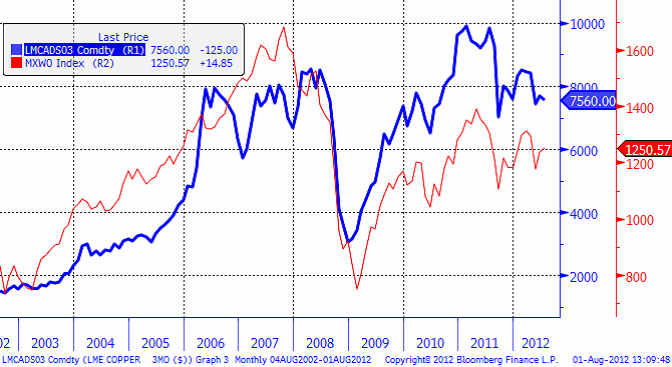
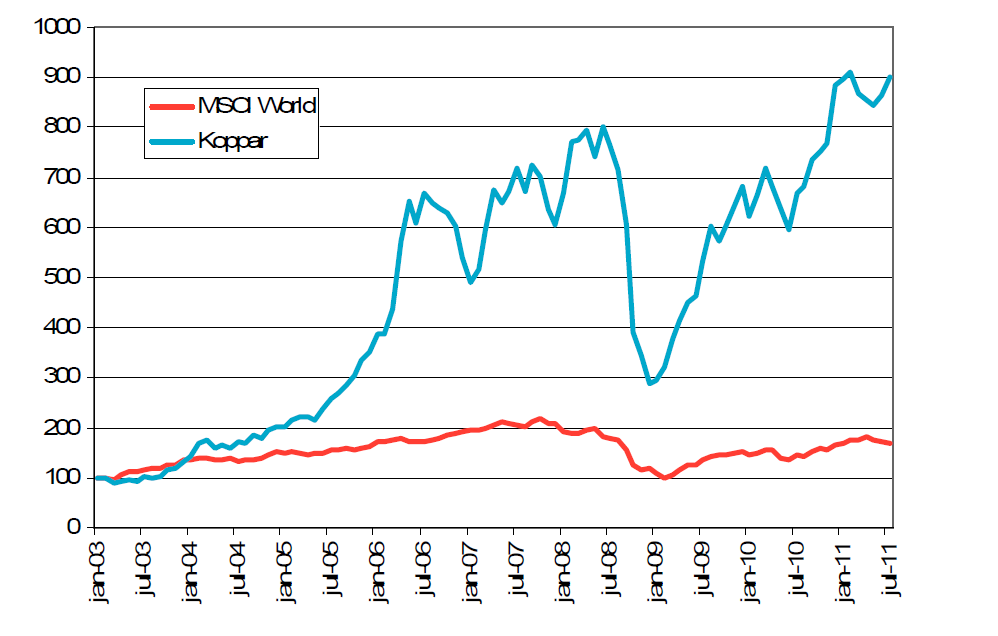
Vi rekommenderar köp av koppar, via ett råvarucertifikat utan hävstång och då är KOPPAR S ett sådant som skulle kunna placeras i. Koppar har en hög korrelation med konjunkturen och kallas ibland för ”Dr Copper” för dess roll som ekonomiskt ledande indikator (inte bara elektriskt alltså). Nedan ser vi 3-månaders kopparterminspris och MSCI World aktieindex.
Vilket har varit den bästa placeringen för att spekulera i konjunkturcykeln under den här tiden? Ja, i diagrammet nedan ser vi hur 100 dollar investerat i koppar (blå linje) och 100 dollar investerat i MSCI World (inkl utdelningar, röd linje) har utvecklat sig.
Den intelligente läsaren invänder kanske att koppar ser ut att ha högre risk. Det stämmer. Volatiliteten har legat på 30% i koppar och bara 16% i MSCI World. Så… med samma risknivå, hade 100 dollar i koppar bara blivit 450 dollar idag. Mot 170 dollar i MSCI World aktieindex. Så varför ska man spekulera i konjunkturcykler i aktier, när det finns ”Dr Koppar” som är mycket mer rätt på vad gäller konjunkturen och dessutom via ständig rabatt på terminerna erbjuder en förutsägbar riskpremie till investeraren?
Det säger inget om framtiden, men en placering på det här sättet, som man får via KOPPAR S, har under lång tid varit bättre än en placering i aktier.
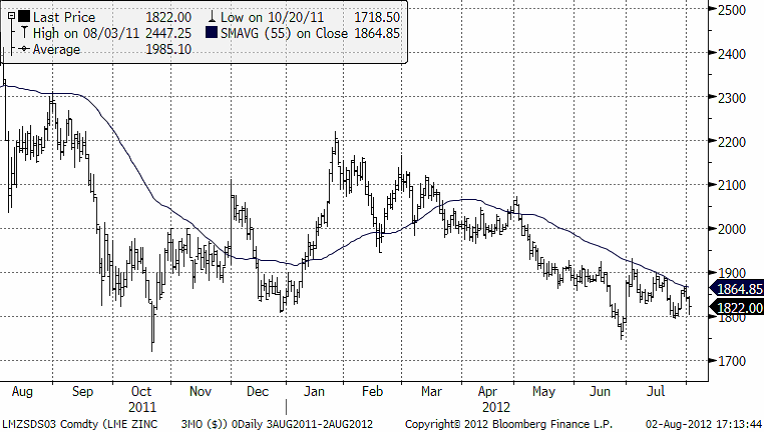
Zink
Zinkpriset ligger på bottennivåer i det prisintervall som etablerats sedan 2009. Produktionskostnaden för zink ligger på dessa nivåer. I råvarumarknaden brukar man kalla detta för råvarans ”fundamentala golv”. Vi ser därför inte några stora kursfallsrisker i zink.
Vi är positiva till zink, men inte lika mycket så som för koppar.
Kaffe
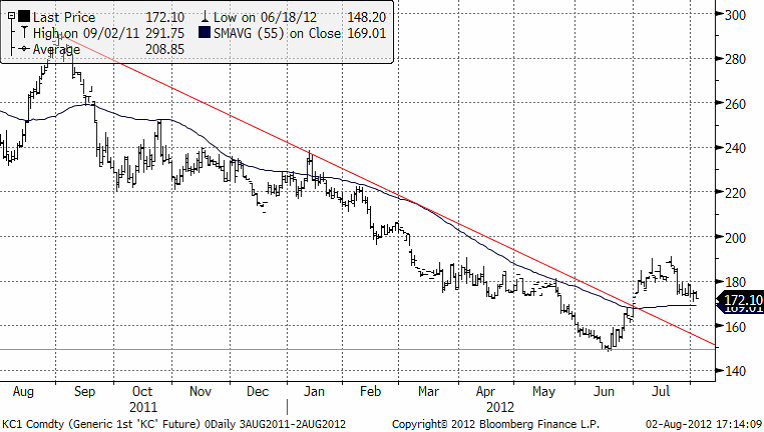
Priset på Arabica, som handlas i New York, har brutit sin nedåtgående trend, efter att ha varit nere på 150 cent per pund. 150 cent var toppnoteringen från slutet av 2009 och var därför för många en naturlig nivå att lägga in köpordrar på.
Vi tycker att man kan börja köpa på sig certifikat på kaffe, på rekyler. Den rekyl vi har haft de senaste dagarna kan t ex vara ett sådant tillfälle. Om man inte önskar ta så hög risk kan råvarucertifikatet KAFFE S vara ett bra val.
Socker
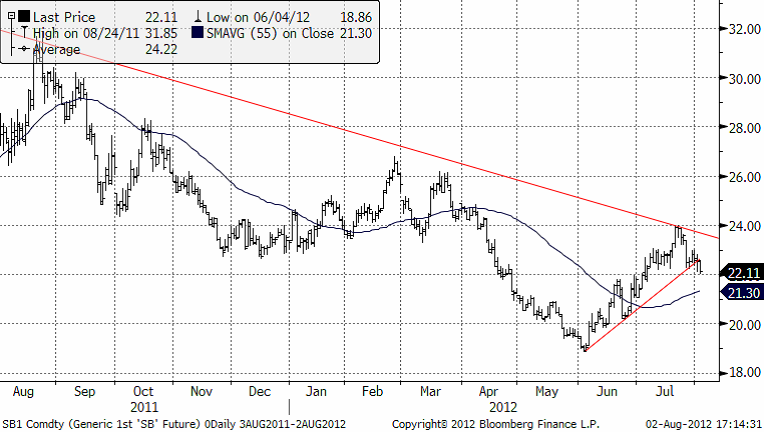
Priset på socker har precis brutit den kortsiktiga stigande trenden och vi är därför negativa till kaffeprisutvecklingen såväl på lång som kort sikt.
Vi rekommenderar köp av certifikatet SHORT SOCKE A S med en hävstång på – 1.2 för den som vill ta position i enlighet med vår vy. Stöd finns på 20 cent och det finns alltså en vinstpotential på ca 12% för en placering i certifikatet. Vi antar att man kliver ur positionen vid ett sockerpris på 20 cent.
För att läsa mer om SEBs syn på spannmål så rekommenderar vi en genomläsning av gårdagens utskick, Jordbruksprodukter från SEB.
[box]SEB Veckobrev Veckans råvarukommentar är producerat av SEB Merchant Banking och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been compiled by SEB Merchant Banking, a division within Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) (“SEB”).
Opinions contained in this report represent the bank’s present opinion only and are subject to change without notice. All information contained in this report has been compiled in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. However, no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made with respect to the completeness or accuracy of its contents and the information is not to be relied upon as authoritative. Anyone considering taking actions based upon the content of this document is urged to base his or her investment decisions upon such investigations as he or she deems necessary. This document is being provided as information only, and no specific actions are being solicited as a result of it; to the extent permitted by law, no liability whatsoever is accepted for any direct or consequential loss arising from use of this document or its contents.
About SEB
SEB is a public company incorporated in Stockholm, Sweden, with limited liability. It is a participant at major Nordic and other European Regulated Markets and Multilateral Trading Facilities (as well as some non-European equivalent markets) for trading in financial instruments, such as markets operated by NASDAQ OMX, NYSE Euronext, London Stock Exchange, Deutsche Börse, Swiss Exchanges, Turquoise and Chi-X. SEB is authorized and regulated by Finansinspektionen in Sweden; it is authorized and subject to limited regulation by the Financial Services Authority for the conduct of designated investment business in the UK, and is subject to the provisions of relevant regulators in all other jurisdictions where SEB conducts operations. SEB Merchant Banking. All rights reserved.
Analys
More weakness and lower price levels ahead, but the world won’t drown in oil in 2026

Some rebound but not much. Brent crude rebounded 1.5% yesterday to $65.47/b. This morning it is inching 0.2% up to $65.6/b. The lowest close last week was on Thursday at $64.11/b.

The curve structure is almost as week as it was before the weekend. The rebound we now have gotten post the message from OPEC+ over the weekend is to a large degree a rebound along the curve rather than much strengthening at the front-end of the curve. That part of the curve structure is almost as weak as it was last Thursday.
We are still on a weakening path. The message from OPEC+ over the weekend was we are still on a weakening path with rising supply from the group. It is just not as rapidly weakening as was feared ahead of the weekend when a quota hike of 500 kb/d/mth for November was discussed.
The Brent curve is on its way to full contango with Brent dipping into the $50ies/b. Thus the ongoing weakening we have had in the crude curve since the start of the year, and especially since early June, will continue until the Brent crude oil forward curve is in full contango along with visibly rising US and OECD oil inventories. The front-month Brent contract will then flip down towards the $60/b-line and below into the $50ies/b.
At what point will OPEC+ turn to cuts? The big question then becomes: When will OPEC+ turn around to make some cuts? At what (price) point will they choose to stabilize the market? Because for sure they will. Higher oil inventories, some more shedding of drilling rigs in US shale and Brent into the 50ies somewhere is probably where the group will step in.
There is nothing we have seen from the group so far which indicates that they will close their eyes, let the world drown in oil and the oil price crash to $40/b or below.
The message from OPEC+ is also about balance and stability. The world won’t drown in oil in 2026. The message from the group as far as we manage to interpret it is twofold: 1) Taking back market share which requires a lower price for non-OPEC+ to back off a bit, and 2) Oil market stability and balance. It is not just about 1. Thus fretting about how we are all going to drown in oil in 2026 is totally off the mark by just focusing on point 1.
When to buy cal 2026? Before Christmas when Brent hits $55/b and before OPEC+ holds its last meeting of the year which is likely to be in early December.
Brent crude oil prices have rebounded a bit along the forward curve. Not much strengthening in the structure of the curve. The front-end backwardation is not much stronger today than on its weakest level so far this year which was on Thursday last week.
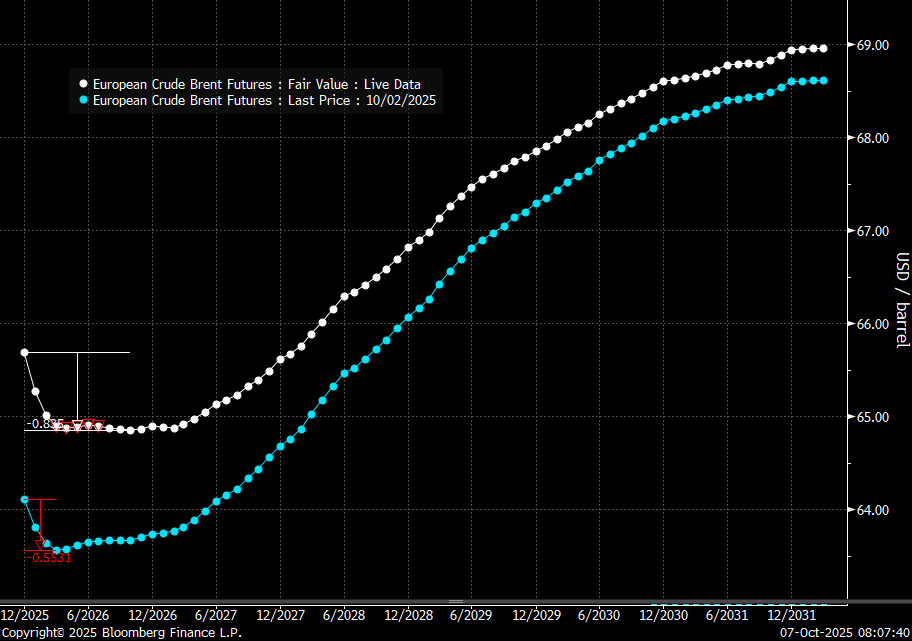
The front-end backwardation fell to its weakest level so far this year on Thursday last week. A slight pickup yesterday and today, but still very close to the weakest year to date. More oil from OPEC+ in the coming months and softer demand and rising inventories. We are heading for yet softer levels.
Analys
A sharp weakening at the core of the oil market: The Dubai curve

Down to the lowest since early May. Brent crude has fallen sharply the latest four days. It closed at USD 64.11/b yesterday which is the lowest since early May. It is staging a 1.3% rebound this morning along with gains in both equities and industrial metals with an added touch of support from a softer USD on top.

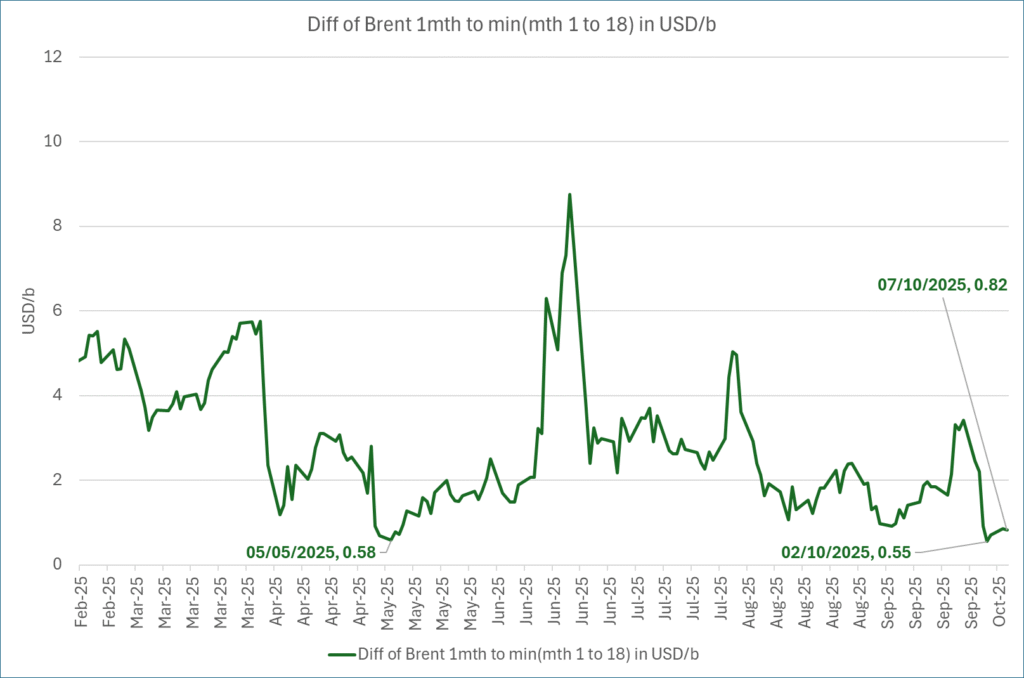
What stands out the most to us this week is the collapse in the Dubai one to three months time-spread.
Dubai is medium sour crude. OPEC+ is in general medium sour crude production. Asian refineries are predominantly designed to process medium sour crude. So Dubai is the real measure of the balance between OPEC+ holding back or not versus Asian oil demand for consumption and stock building.
A sharp weakening of the front-end of the Dubai curve. The front-end of the Dubai crude curve has been holding out very solidly throughout this summer while the front-end of the Brent and WTI curves have been steadily softening. But the strength in the Dubai curve in our view was carrying the crude oil market in general. A source of strength in the crude oil market. The core of the strength.
The now finally sharp decline of the front-end of the Dubai crude curve is thus a strong shift. Weakness in the Dubai crude marker is weakness in the core of the oil market. The core which has helped to hold the oil market elevated.
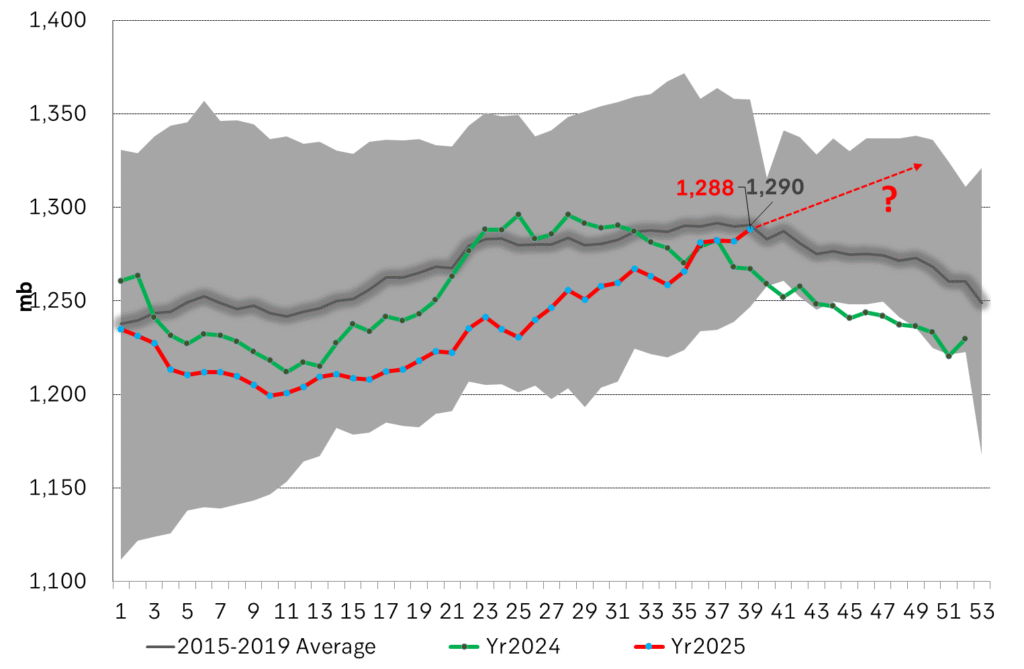
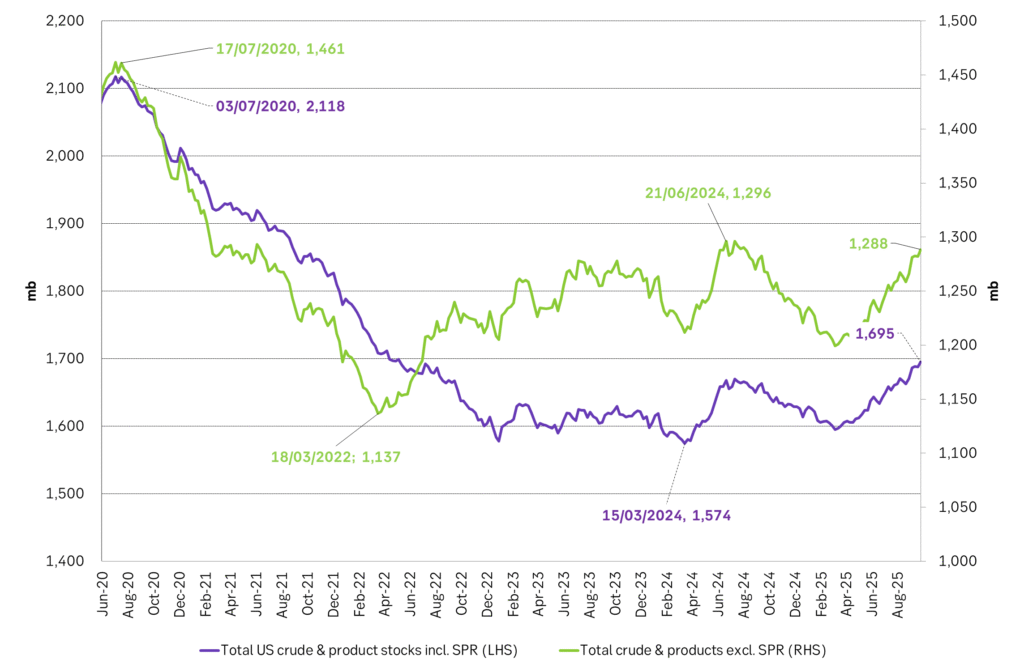
Facts supports the weakening. Add in facts of Iraq lifting production from Kurdistan through Turkey. Saudi Arabia lifting production to 10 mb/d in September (normal production level) and lifting exports as well as domestic demand for oil for power for air con is fading along with summer heat. Add also in counter seasonal rise in US crude and product stocks last week. US oil stocks usually decline by 1.3 mb/week this time of year. Last week they instead rose 6.4 mb/week (+7.2 mb if including SPR). Total US commercial oil stocks are now only 2.1 mb below the 2015-19 seasonal average. US oil stocks normally decline from now to Christmas. If they instead continue to rise, then it will be strongly counter seasonal rise and will create a very strong bearish pressure on oil prices.
Will OPEC+ lift its voluntary quotas by zero, 137 kb/d, 500 kb/d or 1.5 mb/d? On Sunday of course OPEC+ will decide on how much to unwind of the remaining 1.5 mb/d of voluntary quotas for November. Will it be 137 kb/d yet again as for October? Will it be 500 kb/d as was talked about earlier this week? Or will it be a full unwind in one go of 1.5 mb/d? We think most likely now it will be at least 500 kb/d and possibly a full unwind. We discussed this in a not earlier this week: ”500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d”
The strength in the front-end of the Dubai curve held out through summer while Brent and WTI curve structures weakened steadily. That core strength helped to keep flat crude oil prices elevated close to the 70-line. Now also the Dubai curve has given in.
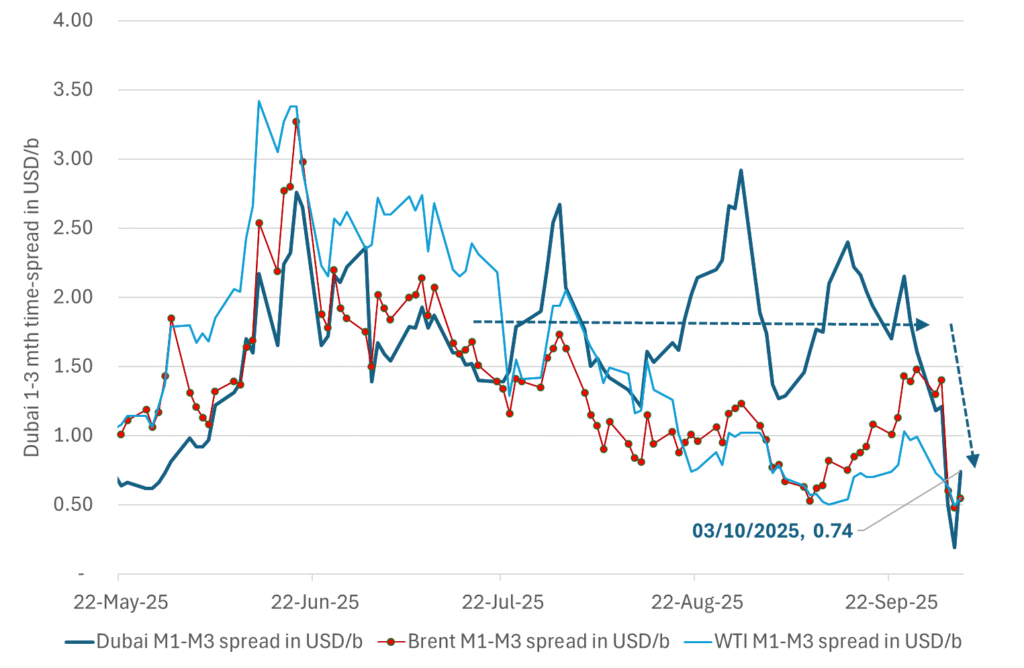
Brent crude oil forward curves
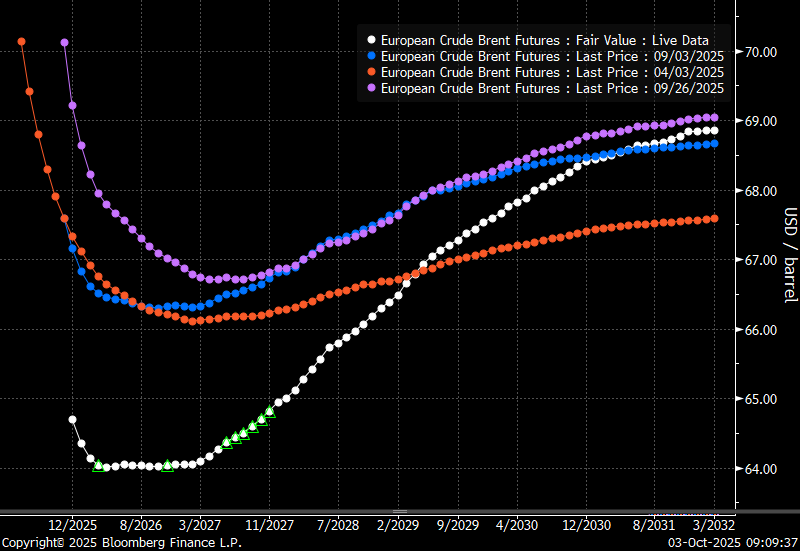
Total US commercial stocks now close to normal. Counter seasonal rise last week. Rest of year?
Total US crude and product stocks on a steady trend higher.
Analys
OPEC+ will likely unwind 500 kb/d of voluntary quotas in October. But a full unwind of 1.5 mb/d in one go could be in the cards

Down to mid-60ies as Iraq lifts production while Saudi may be tired of voluntary cut frugality. The Brent December contract dropped 1.6% yesterday to USD 66.03/b. This morning it is down another 0.3% to USD 65.8/b. The drop in the price came on the back of the combined news that Iraq has resumed 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan with exports through Turkey while OPEC+ delegates send signals that the group will unwind the remaining 1.65 mb/d (less the 137 kb/d in October) of voluntary cuts at a pace of 500 kb/d per month pace.

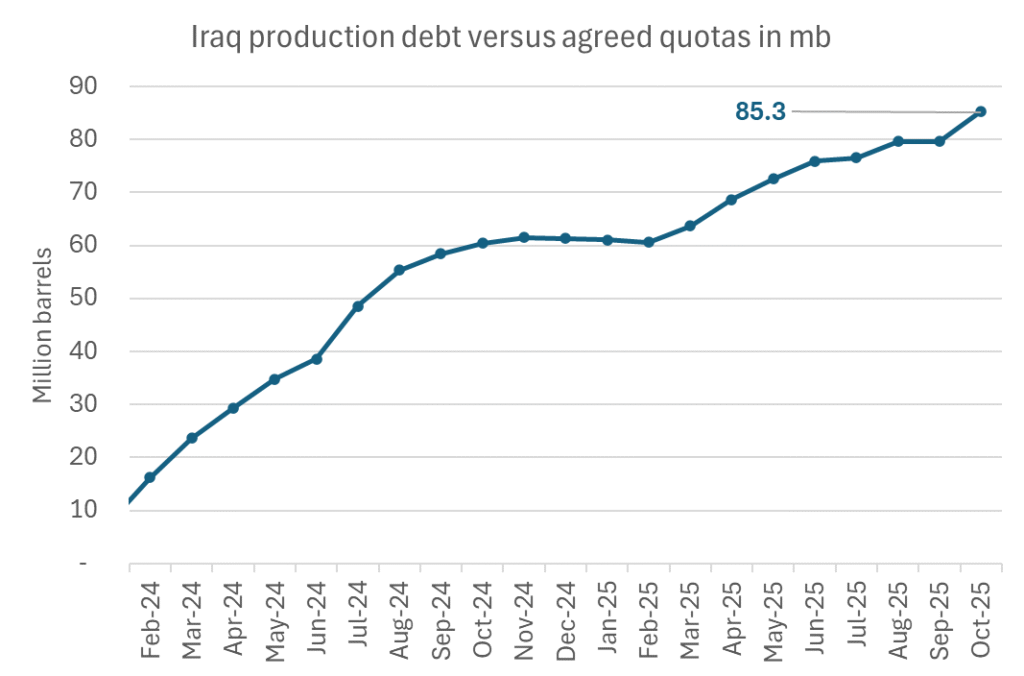
Signals of accelerated unwind and Iraqi increase may be connected. Russia, Kazakhstan and Iraq were main offenders versus the voluntary quotas they had agreed to follow. Russia had a production ’debt’ (cumulative overproduction versus quota) of close to 90 mb in March this year while Kazakhstan had a ’debt’ of about 60 mb and the same for Iraq. This apparently made Saudi Arabia angry this spring. Why should Saudi Arabia hold back if the other voluntary cutters were just freeriding? Thus the sudden rapid unwinding of voluntary cuts. That is at least one angle of explanations for the accelerated unwinding.
If the offenders with production debts then refrained from lifting production as the voluntary cuts were rapidly unwinded, then they could ’pay back’ their ’debts’ as they would under-produce versus the new and steadily higher quotas.
Forget about Kazakhstan. Its production was just too far above the quotas with no hope that the country would hold back production due to cross-ownership of oil assets by international oil companies. But Russia and Iraq should be able to do it.
Iraqi cumulative overproduction versus quotas could reach 85-90 mb in October. Iraq has however steadily continued to overproduce by 3-5 mb per month. In July its new and gradually higher quota came close to equal with a cumulative overproduction of only 0.6 mb that month. In August again however its production had an overshoot of 100 kb/d or 3.1 mb for the month. Its cumulative production debt had then risen to close to 80 mb. We don’t know for September yet. But looking at October we now know that its production will likely average close to 4.5 mb/d due to the revival of 190 kb/d of production in Kurdistan. Its quota however will only be 4.24 mb/d. Its overproduction in October will thus likely be around 250 kb/d above its quota with its production debt rising another 7-8 mb to a total of close to 90 mb.
Again, why should Saudi Arabia be frugal while Iraq is freeriding. Better to get rid of the voluntary quotas as quickly as possible and then start all over with clean sheets.
Unwinding the remaining 1.513 mb/d in one go in October? If OPEC+ unwinds the remaining 1.513 mb/d of voluntary cuts in one big go in October, then Iraq’s quota will be around 4.4 mb/d for October versus its likely production of close to 4.5 mb/d for the coming month..
OPEC+ should thus unwind the remaining 1.513 mb/d (1.65 – 0.137 mb/d) in one go for October in order for the quota of Iraq to be able to keep track with Iraq’s actual production increase.
October 5 will show how it plays out. But a quota unwind of at least 500 kb/d for Oct seems likely. An overall increase of at least 500 kb/d in the voluntary quota for October looks likely. But it could be the whole 1.513 mb/d in one go. If the increase in the quota is ’only’ 500 kb/d then Iraqi cumulative production will still rise by 5.7 mb to a total of 85 mb in October.
Iraqi production debt versus quotas will likely rise by 5.7 mb in October if OPEC+ only lifts the overall quota by 500 kb/d in October. Here assuming historical production debt did not rise in September. That Iraq lifts its production by 190 kb/d in October to 4.47 mb/d (August level + 190 kb/d) and that OPEC+ unwinds 500 kb/d of the remining quotas in October when they decide on this on 5 October.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals i en guldtrend
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanVolatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk
-
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAktier i guldbolag laggar priset på guld
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanKinas elproduktion slog nytt rekord i augusti, vilket även kolkraft gjorde
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanTyskland har så höga elpriser att företag inte har råd att använda elektricitet
-
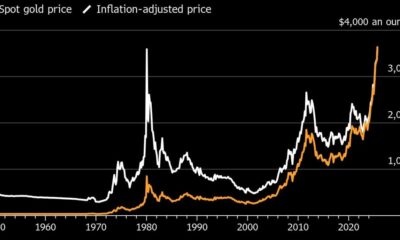
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanGuld når sin högsta nivå någonsin, nu även justerat för inflation
-
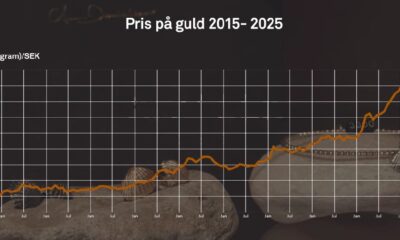
 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanDet stigande guldpriset en utmaning för smyckesköpare
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanBrent crude ticks higher on tension, but market structure stays soft