Analys
SEB Jordbruksprodukter – Vecka 46
 Marknaderna för jordbruksprodukter har hållit sig väldigt lugna den senaste veckan. Det är endast priset på potatis som rört sig, minus 9%. Däremot sker det saker i bakgrunden, framförallt på etanolmarknaden, men även på exportmarknaden för vete och inte minst, i ekonomin i stort.
Marknaderna för jordbruksprodukter har hållit sig väldigt lugna den senaste veckan. Det är endast priset på potatis som rört sig, minus 9%. Däremot sker det saker i bakgrunden, framförallt på etanolmarknaden, men även på exportmarknaden för vete och inte minst, i ekonomin i stort.
Att byta namn på premiärministrarna i Grekland och Italien skulle lösa några problem gick marknaden på i några minuter. Angela Merkels tyska CDU träffades i förrgår och det kom starka uttalanden därifrån om att hålla fast vid EU-projektet som det viktigaste för den här generationen.
Det är helt uppenbart att läxan från 1992 års uppgörelse med fasta växelkurser inte har fastnat. Läxan var att en för hög växelkurs som försvaras med allt högre räntor, leder till att räntorna slår ihjäl ekonomin i landet, vilket gör landet ännu mindre värt – dvs växelkursen borde vara ÄNNU lägre, och trycket på växelkursen blir ännu hårdare. Det är en spiral som endast kan ha flera lösningar, varav bankrutt är en av dem.
 För några dagar sedan var räntan på italienska obligationer under 6%. Det var OK. Sedan gick räntan över och ligger nu på 7%. Förändringen av läge är som natt och dag. Länder som har så höga skulder byter spår i växeln från destination ”helt ok”, till destination ”bankrutt”.
För några dagar sedan var räntan på italienska obligationer under 6%. Det var OK. Sedan gick räntan över och ligger nu på 7%. Förändringen av läge är som natt och dag. Länder som har så höga skulder byter spår i växeln från destination ”helt ok”, till destination ”bankrutt”.
EU-politikernas lätthet att snacka om skuldavskrivning för Grekland, har gjort att allt fler inser att ”skuldavskrivning” är slutdestinationen för länder med för höga skulder, att klara sig. Skuldavskrivning gör att banker i Frankrike, Tyskland, med flera länder, får det svårt. Krisen flyttas norrut, eftersom bankernas skulder blir Frankrikes och Tysklands statsskulder. Därför steg räntorna på franska statsobligationer och belgiska, t ex, i tisdags.
Varför är det här av intresse i ett brev om jordbruksprodukter? Jo, därför att lagren av spannmål i Frankrike, som dessutom inte sjunker som de ska, blir allt dyrare att finansiera. Det contango som finns på Matif måste bort. Lagren måste likvideras.
Detta om inte ECB tillåts genomföra en europeiska version av det amerikanska QE2 – dvs att trycka pengar och pumpa in dem i ekonomin. I vilket, fall borde euron falla mot dollarn. Men väljer man inflationsvägen för att bli av med de ohanterligt stora statsskulderna får man en boom i råvarupriser och markpriser. Till den punkten är det nog ändå en tid kvar. Till dess blir det nog en orolig färd.
Vete
Terminspriset på Matif-vete håller sig alltjämt över den psykologiskt viktiga 180-euro-nivån, men orosmolnen hopar sig. Ryssland och Ukrainas återinträde på världsmarknaden spelar en stor roll nu. Dessa exportländers volymer påverkar i synnerhet europeiska länders exportmarknad, som är Mellanöstern och Nordafrika. Särskilt märks detta för Frankrike, som är ett av världens största exportländer när det gäller vete. Frankrike har hittills på säsongen förlorat mer än ett dussin av Egyptens tenders; Egypten är världens viktigaste importland med ca 9 mt som årlig importvolym. Vete från Ryssland, Ukraina och Kazakstan väller ut över marknaden. Egypten har de senaste 17 gångerna valt vete från Svartahavsregionen. Exporten från Rouen, som är Europas största export-hub, noterade den 2 november fyra månaders lägsta nivå. Franska myndigheter räknar med 23% lägre export i perioden juli 2011 – juni 2012, jämfört med förra året. Det blir då den lägsta nivån på 10 år. Egypten har endast stått för 4% av Frankrikes export utanför EU sedan juli, mot 18% förra året.
Algeriet är ett land som gärna har köpt franskt vete. Algeriet vann självständighet från Frankrike år 1962. Brödet man äter är baguetter och det franska vetet passar utmärkt för detta. Enligt FAO äter den genomsnittlige algeriern 212 kg vete om året, en klar andraplats i världsligan efter grannlandet Tunisien. Förra året gick 24% av Frankrikes export till Algeriet, som är världens näst största importland efter Egypten. Algeriet har hårda krav på insektsskador och svartahavsregionen drabbas ofta av sköldskinnbaggar (eurygaster integricepts), som suger ur sädeskornen. Därför kan Frankrike känna sig ganska säker än så länge där.
Rysslands skörd blir enligt USDA:s WASDE den tredje största på 10 år och erbjuder vete ca 10 dollar per ton under franska priser. Rysslands export påverkar främst, men inte bara Europa. Enligt USDA kommer USA:s export att minska med 24% till 26.5 mt den här säsongen. -24% är det största fallet på ett kvartssekel.
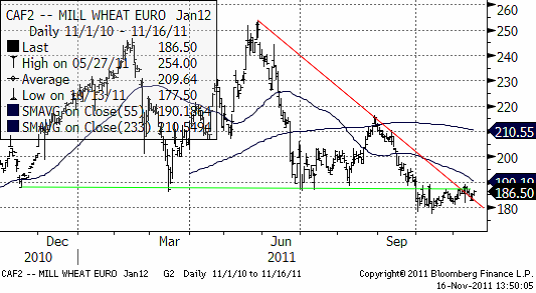
Nedan ser vi januarikontraktet på Matif. Den tekniska, dvs psykologiskt viktiga stödnivån på 180 euro utgår allt jämt ett starkt stöd. Vi bedömer ändå, med tanke på den minskning av konsumtion som lär komma i spåren av alla sparprogram i EU, och överväldigande bevis på att priset är för högt för att vinna exportordrar, att 180 euro lär brytas.
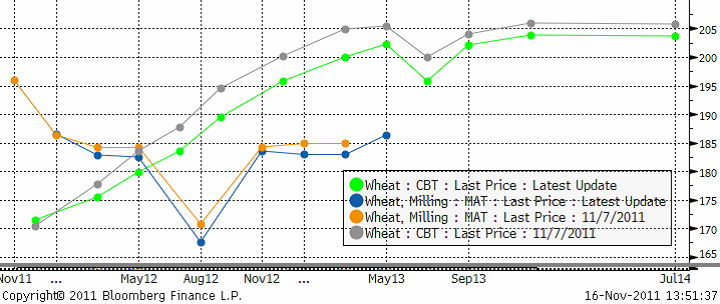
Nedan ser vi terminskurvan för Chicagovete och Matif nu och för en vecka sedan.
Allt talar för att Matif-vete faller ner i första hand till 150 – 160 – euro-nivån.
Maltkorn
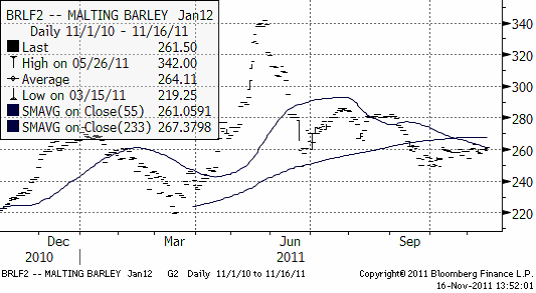
Maltkornsmarknaden följer vetet och det finns inga speciella nyheter att rapportera. Tekniskt ligger priset under glidande medelvärden. Den tekniska trenden är alltså nedåtriktad.
Potatis
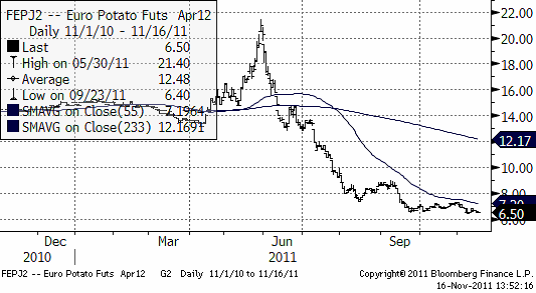
Priset på potatis av årets skörd har fallit med 9% den senaste veckan. Det är den enda råvara som rört sig mer än någon procentenhet.
Nedan ser vi kursdiagrammet på europeisk potatis, som handlas på Eurex; terminen avser leverans april nästa år.
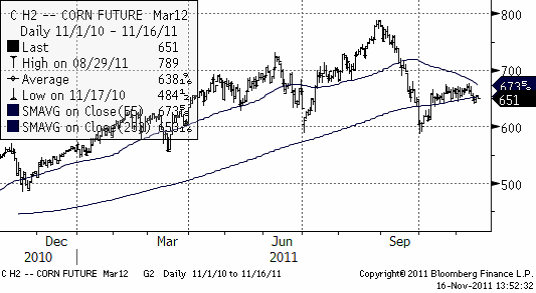
Majs
Liksom på vetemarknaden, vinner Ryssland och Ukraina exportordrar. Igår köpte Japan 800,000 ton majs från Ukraina istället för att köpa den dyrare amerikanska produkten. Japan är världens största importör av majs, som används i djurhållningen.
Nedan ser vi marskontraktet på CBOT, där priset backat under 233-dagars glidande medelvärde, något av en negativ teknsisk signal.
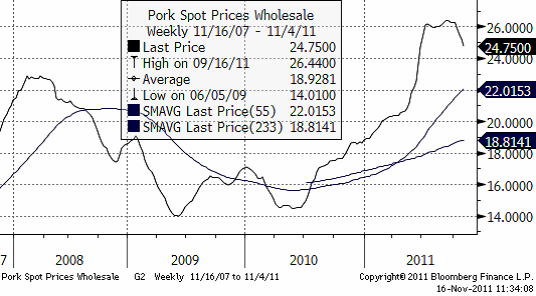
Det händer intressanta saker i bakgrunden till majsmarknaden. För det första handlar det om amerikansk etanolproduktion och för det andra om kinesisk fläskkonsumtion. Vi ser priserna i yuan per kilo (senast 24.75 yuan) i diagrammet nedan – notera det stora prisfallet som just pågår (två glidande medelvärden är också inritade):
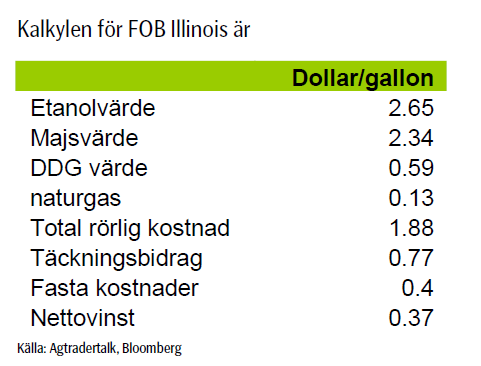
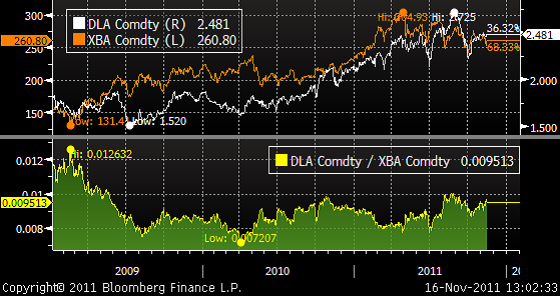
När det gäller etanol är det boom i USA. Firman Agtradertalk som sammanställer statistik visar följande nettovinst per gallon på att producera etanol, baserat på spotpriser FOB Illinois.
Nu är det så att det finns en skatterabatt på 45 cent per gallon i USA, som ges till den som blandar etanol i bensin. Den heter Volumetric Ethanol Excise Tax Credit och introducerades av George W Bush år 2004 och trädde i kraft 2005. Skatten syftade till att minska importberoendet av råolja, men kostar i dagsläget 5.7 miljarder dollar för skattebetalarna.
Etanol borde kosta 70% av bensin, eftersom etanol har ett energivärde som ligger på 70% av bensinens, men i diagrammet nedan ser vi att etanol nu kostar 95% av bensinen. DLA är kortnamnet för etanolterminer i dollar per gallon och bensin som handlas i cent per gallon, heter XBA.
Särskilt märkligt blir det höga priset när USA:s 209 destillerier producerar mer än vad som förbrukas i USA. USA exporterar etanol till Kanada, Europa och till och med till Brasilien! Brasiliens skörd av sockerrör blir i år 459.6 mt mot 501.2 förra året och den brasilianska regeringen har minskat inblandningen av etanol från 25 till 20%. Industrin producerar också mer socker och mindre etanol.
EU:s krav på etanolinblandning har också lett till brist. En gallon etanol kostar 3.21 dollar i Rotterdams hamn och 2.94 dollar i New Yorks hamn.
Situationen är intressant eftersom skatterabatten på 45 cent går ut vid årsskiftet. Det gjorde den även förra året, men då fick branschen en förlängning. En republikansk senator försökte i juni ta bort subventionen men förlaget gick nätt och jämt inte igenom. Samtidigt noterar jordbruksmark i USA rekordpriser, vilket väl är de enda fastighetspriserna i USA som inte kraschar. Markpriserna tog ett skutt uppåt 2004-2005 (gissa varför…).
Nedan ser aktuell terminskurva (grön) och för en vecka sedan (blå). Vi ser att tendensen till mer backwardation.
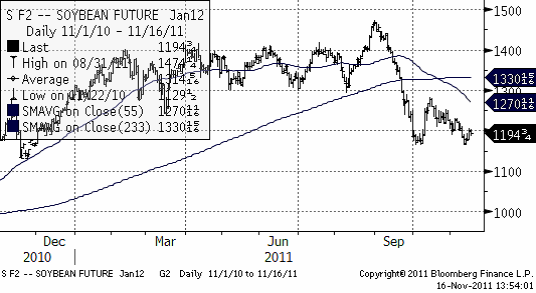
Sojabönor
Priset på sojabönor befinner sig i sjunkande trend. Vi har redan sett de sjunkande priserna på fläskkött i Kina. Å andra sidan, China National Grain & Oils Information Center släppte en rapport i förrgår där de menar att Kinas import av sojabönor för marknadsföringsåret 2011-12 kan öka med 7% till 56 mt.
Nedan ser vi terminskurvorna (nu, grön) och för en vecka sedan.
Det mest sannolika är nog ett test nedåt på sojabönorna, men fundamenta ger stöd just nu. Vi väntar oss nog ändå att säljarna kommer in – från Brasilien om inte annat – och säljer ner sojabönorna under stödet på 1167. På tre månaders sikt är vi negativa.
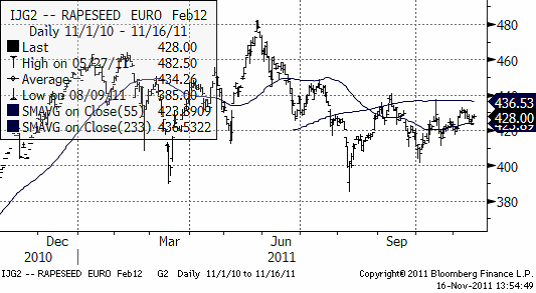
Raps
Rapspriset håller sig högt pga den svaga euron, inget annat. Raps är dyrt i förhållande till sojabönor och ”borde” falla ner mot 400 euro i första hand.
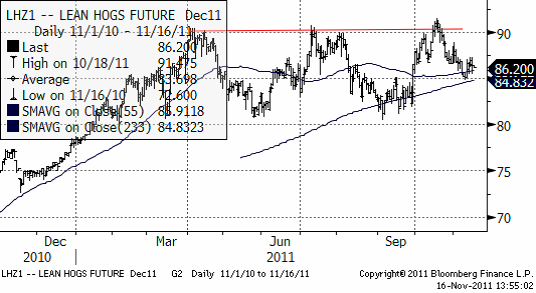
Gris
Tekniskt vilar priset på lean hogs på de glidande medelvärdena, vilket kan ge visst stöd. Test av dessa ger viktig information om rörelsen på kort sikt. Det falska brottet uppåt i oktober, ger en stark varning om att ”bulls” håller på att förlora kriget. Det är ganska vanligt att marknaden faller av kraftigt efter att den visat en falsk köpsignal. Ytterligare säljasignal ges när de glidande medelvärdena bryts. Just nu ger de glidande medelvärdena stöd. Nedan ser vi decemberkontraktet på CME, där priset fortsatt har varit i rekyl från den falska köpsignalen för två veckor sedan.
På en veckas sikt är vi negativa till lean hogs, men priset står och väger, ännu.
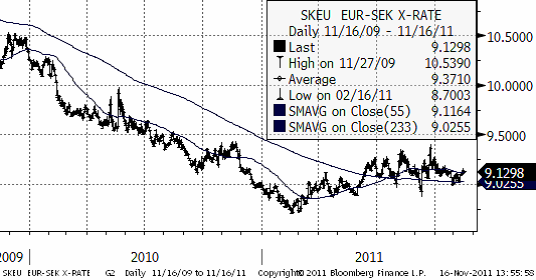
Valutor
EURSEK handlas i ett volatilt brett intervall. Det finns inga signaler att utläsa alls.
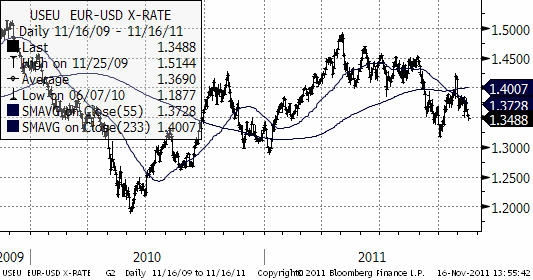
EURUSD tycks slutligen bryta nedåt. Det korta besöket över de glidande medelvärdena (som båda säjer ”sälj”), stärker den negativa vyn. All fundamenta talar för att euron ska falla och det ordentligt.
Tekniskt är läget en klar säljsignal. I första hand är nästa stöd 1.3145 dollar. I andra hand är det botten nere vid 1.2 dollar.
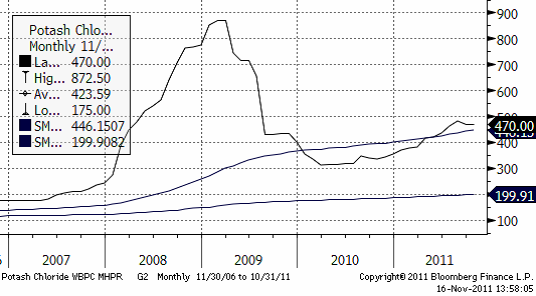
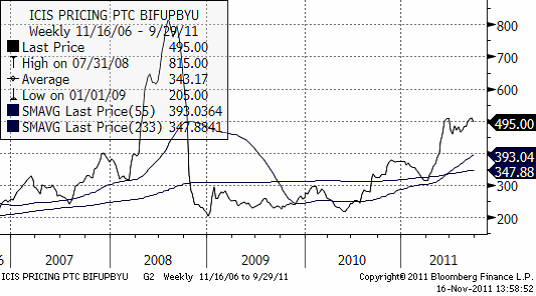
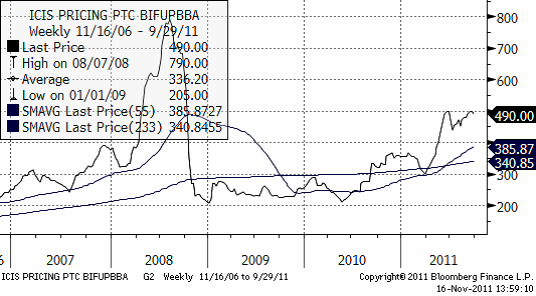
Gödsel
Kalium
Priset på kalium ligger kvar på samma nivå som för ett par veckor sedan.
Kväve
Nedan ser vi prisutvecklingen på Urea FOB Yuzhny i dollar per ton.
Fosfor
Nedan ser vi prisutvecklingen på Diammoniumfosfat FOB Baltic i dollar per ton.
[box]SEB Veckobrev Jordbruksprodukter är producerat av SEB Merchant Banking och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been compiled by SEB Merchant Banking, a division within Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) (“SEB”).
Opinions contained in this report represent the bank’s present opinion only and are subject to change without notice. All information contained in this report has been compiled in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. However, no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made with respect to the completeness or accuracy of its contents and the information is not to be relied upon as authoritative. Anyone considering taking actions based upon the content of this document is urged to base his or her investment decisions upon such investigations as he or she deems necessary. This document is being provided as information only, and no specific actions are being solicited as a result of it; to the extent permitted by law, no liability whatsoever is accepted for any direct or consequential loss arising from use of this document or its contents.
About SEB
SEB is a public company incorporated in Stockholm, Sweden, with limited liability. It is a participant at major Nordic and other European Regulated Markets and Multilateral Trading Facilities (as well as some non-European equivalent markets) for trading in financial instruments, such as markets operated by NASDAQ OMX, NYSE Euronext, London Stock Exchange, Deutsche Börse, Swiss Exchanges, Turquoise and Chi-X. SEB is authorized and regulated by Finansinspektionen in Sweden; it is authorized and subject to limited regulation by the Financial Services Authority for the conduct of designated investment business in the UK, and is subject to the provisions of relevant regulators in all other jurisdictions where SEB conducts operations. SEB Merchant Banking. All rights reserved.
Analys
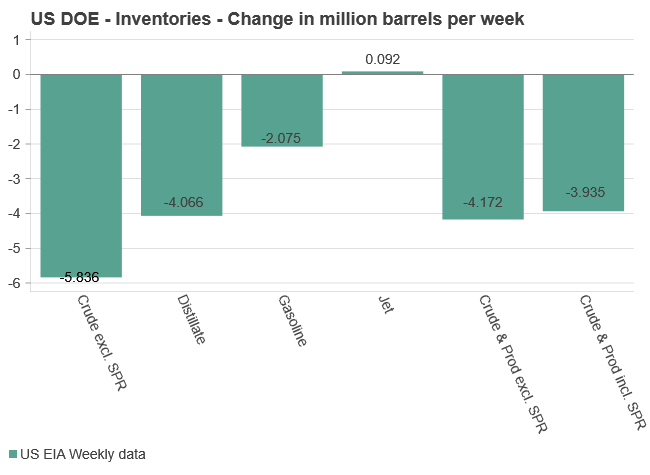
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

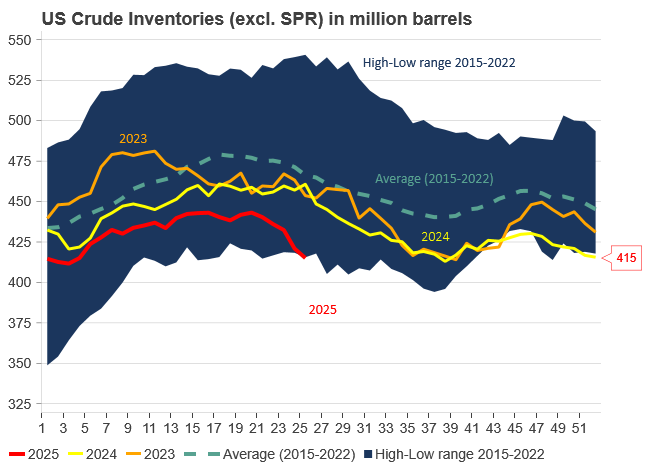
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanA muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanJonas Lindvall är tillbaka med ett nytt oljebolag, Perthro, som ska börsnoteras
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanOljan, guldet och marknadens oroande tystnad
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanDomstolen ger klartecken till Lappland Guldprospektering
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanTightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanRyska staten siktar på att konfiskera en av landets största guldproducenter
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanLundin Mining ska bli en av de tio största kopparproducenterna i världen