Analys
SEB Jordbruksprodukter, 4 november 2013


 Det var en generellt lite svagare vecka för jordbruksprodukter förra veckan. De skiljde inte ut sig från resten av råvarumarknaden, som generellt sett utvecklades svagt. Bland jordbruksprodukterna märktes särskilt stora prisfall för sojamjöl och smör. Dollarn steg och euron föll och det ganska mycket, 3%. Naturligtvis förklarar detta till stor del prisnedgångarna på de amerikanska terminsmarknaderna. Chicagovetet gick ner (i dollar räknat), men Matifvetet steg. Den svenska kronan följde i princip eurons rörelser mot dollarn. Förklaringen till valutakursförändringen var dels starkare inköpschefsindex i USA, som signalerar en snabb konjunkturåterhämtning, och en rapport om närmast deflation i Eurozonen. Förväntningar om att ECB ska sänka styrräntan i Eurozonen tändes omedelbart, vilket fick euron att falla.
Det var en generellt lite svagare vecka för jordbruksprodukter förra veckan. De skiljde inte ut sig från resten av råvarumarknaden, som generellt sett utvecklades svagt. Bland jordbruksprodukterna märktes särskilt stora prisfall för sojamjöl och smör. Dollarn steg och euron föll och det ganska mycket, 3%. Naturligtvis förklarar detta till stor del prisnedgångarna på de amerikanska terminsmarknaderna. Chicagovetet gick ner (i dollar räknat), men Matifvetet steg. Den svenska kronan följde i princip eurons rörelser mot dollarn. Förklaringen till valutakursförändringen var dels starkare inköpschefsindex i USA, som signalerar en snabb konjunkturåterhämtning, och en rapport om närmast deflation i Eurozonen. Förväntningar om att ECB ska sänka styrräntan i Eurozonen tändes omedelbart, vilket fick euron att falla.
Vi tror att prisuppgången i euro / svenska kronor – termer fortsätter för vete. För raps går vi tillbaka till neutral rekommendation från en (försiktig) köprekommendation för två veckor sedan. I övrigt gör vi inte heller några förändringar av rekommendationerna.
På fredag klockan 18 publicerar USDA sin första WASDE-rapport på två månader. Förra månadens frös inne på grund av budgetbråket i USA.
Odlingsväder
Väderprognoser för USA indikerar gynnsamt väder för sådden och utvecklingen av det amerikanska höstvetet. Det finns en del analytiker som redan nu säger att höstvetet kommer att vara i det bästa tillståndet sedan 2010 när det går in i vintervila.
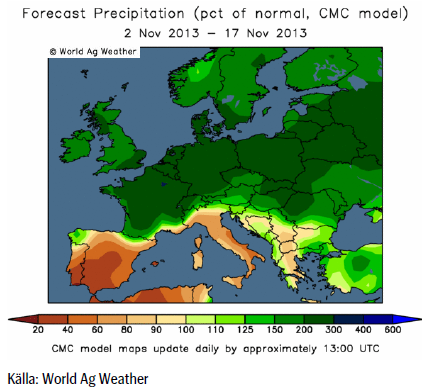
Europa har som bekant varit ovanligt regnigt. Prognosen fram till mitten av månaden visar att detta väntas fortsätta med väsentligt mycket mer regn än normalt över norra Kontinentaleuropa. Södra Europa väntas däremot vara torrare än normalt.
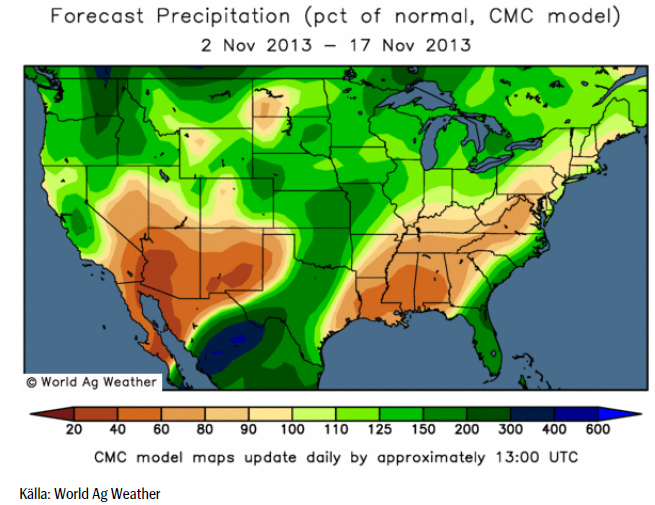
Även i USA väntas det vara mer nederbörd än normalt, utom i områden som normalt är torra, som t ex New Mexico och Arizona.
Vete
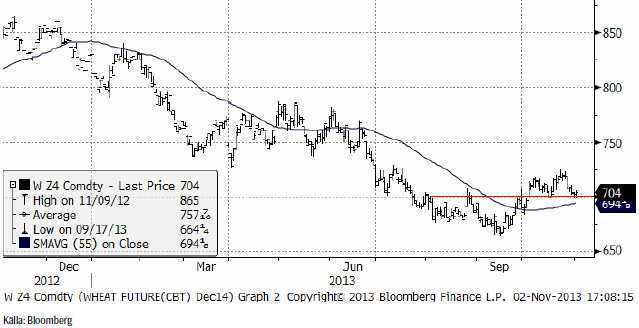
November 2014 fann stöd i veckan och ser ut att vara på väg mot ett nytt test av 200 euro. Prisutvecklingen på Matif stöds av den svagare valutan. ECB väntas sänka sin viktigaste styrränta den kommande veckan. Inflationen i Eurozonen lyser med sin frånvaro och ekonomin är i behov av monetär stimulans.
Decemberkontraktet 2014 på CBOT visar inte samma bild, därför att dollarn stärktes på eurons bekostnad. Priset i fredags stängde precis över det tekniska motståndet på 700 cent.
Nedan ser vi terminskurvorna för Chicagovete och Matif. Matif gick ännu mer in i backwardation för årets skörd, vilket visar på vilket akut behov det finns hos EU:s bönder att lära sig mer om terminer och affärsmässighet när det gäller marknadsföring av spannmål.
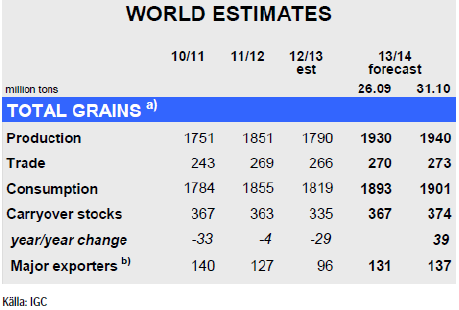
IGC (International Grains Council) kom med sin rapport i förra veckan och har ökat sitt estimat för den globala spannmålsproduktionen 2013/14 med 10 mt till 1940 mt. Tack vare gynnsamma väderförhållanden hos de stora producenterna, framförallt i USA och OSS, så bidrar detta till en förväntad ökning med 8% på årsbasis från 2012 års produktion då torka drabbade stor del av grödorna. Utgående lager justeras upp sedan förra månaden med 7 mt till ett fyra-års-högsta på 367 mt.
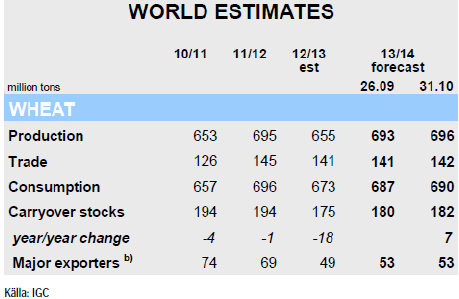
För vete indikeras en global produktion på 696 mt, vilket är en ökning med nästan 4 mt från förra månaden. Revideringen återspeglar framförallt en återhämtning av produktionen i OSS-länderna, vilket skulle ge en ökning med 6% på årsbasis.
Utgående lager förväntas öka med 7 mt på årsbasis till 182 mt som en följd av högre lager hos de stora exportländerna samt Kina.
Måndagens Crop Progress från USDA – den andra efter att USDA återupptagit publiceringen efter ”the U.S. government shutdown” – visar att sådden av amerikanskt höstvete nu börjar närma sig sitt slut då 86% var avklarad per den 27 oktober vilket är i linje med förra årets 87% vid den här tiden liksom det femåriga genomsnittet på 85%.
Uppkomsten av höstvete ligger på 65% – vilket är något högre än förra årets 61% men i linke med det femåriga genomsnittet på 64%.
Intressant är också andelen grödor klassade som ”good/excellent”. Visserligen justeras siffran ner med 4% från veckan innan till 61%, men det är betydligt högre än förra årets 40% vid den här tiden.
Vi fortsätter att tro på högre pris på vete basis Matif och rekommenderar köp.
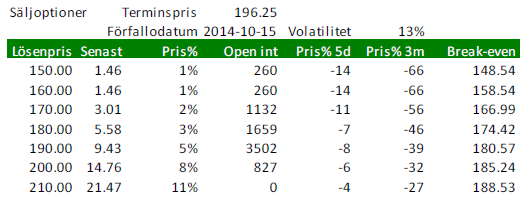
Optioner på vete
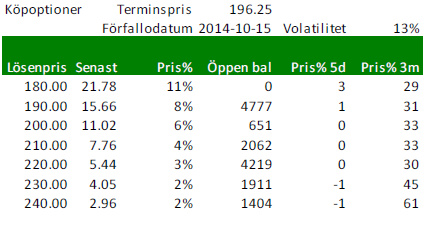
Nedan ser vi priserna på köpoptioner på Matif på November-2014 (Matif vete). Notera att volatiliteten 13% är ganska låg. Volatiliteten brukar vara låg när priserna är låga. Eftersom terminen gått upp lite har köpoptioner ökat lite i värde och säljoptioner fallit i värde.
Nedanstående optioner är köpoptioner, priser per stängning i fredags.
 Nedanstående är priser på säljoptioner.
Nedanstående är priser på säljoptioner.
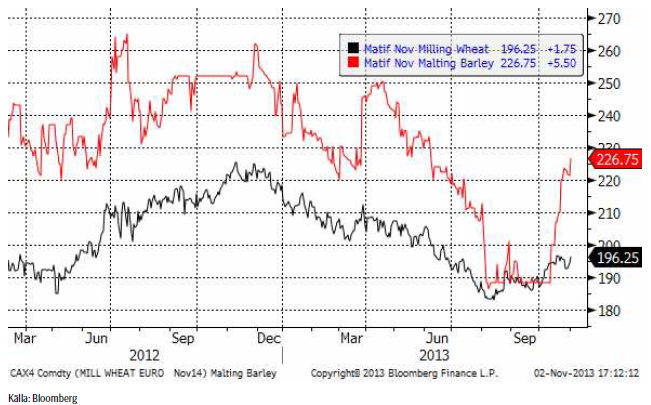
Maltkorn
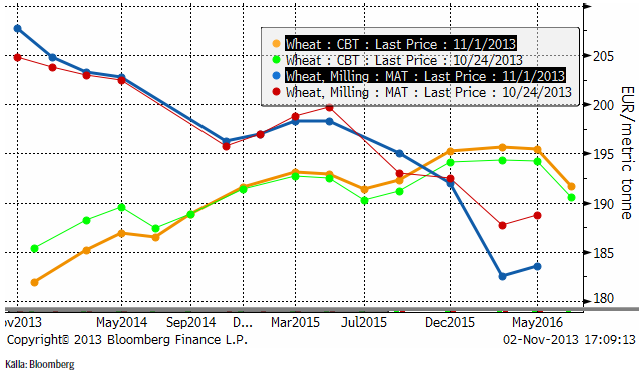
Vi har nu gått över till att studera 2014 års terminskontrakt för vete och maltkorn. Prisutvecklingen på dessa kontrakt ser vi nedan. Notera hur kraftigt terminskontraktet på maltkorn har återhämtat sig i oktober! Priset har gått upp från 190 euro per ton till 226.75 euro. Som vi sagt tidigare ser det ut att kunna bli lönsamt att odla maltkorn nästa år. Den som tycker att det är ett vågspel kan alltid prissäkra till 226.75 euro.
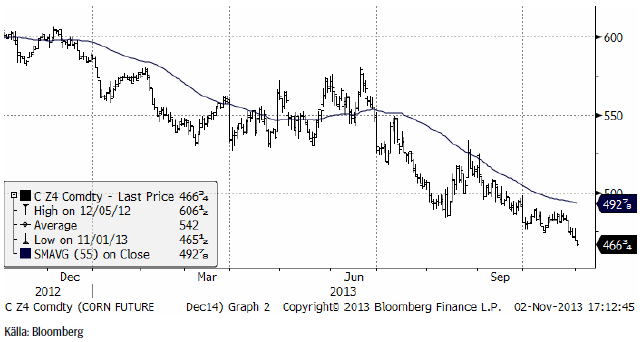
Majs
Majspriset – och nu tittar vi på nästa års skörd, december 2014-kontraktet har återtagit sin fallande trend. Förväntningarna inför WASDE-rapporten som kommer i veckan är att avkastningen per acre ska vara högre än tidigare beräknat.
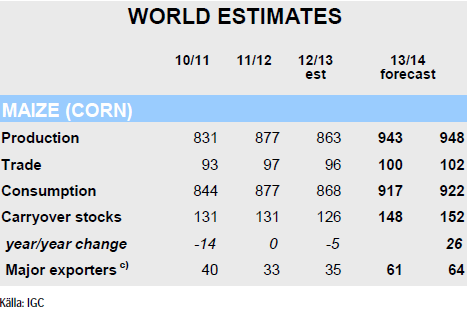
IGC rapporterade i veckan som gick. Den globala produktionen av majs beräknas uppgå till rekordhöga 948 mt, vilket är en ökning med 5 mt sedan IGC’s förra rapport vilket framförallt drivs av en återhämtning i USA. Detta göra också att utgående lager justeras upp med 4 mt jämfört med september och lagren hos de största exportörerna (Argentina, Brasilien, Ukraina och USA) estimeras till ett 26-års högsta.
Måndagens Crop Progress från USDA visade ett rejält uppsving i skörden av majs från 39% per den 20 oktober till 59% en vecka senare. Marknadens förväntningar låg runt 50-55%. Tar man en närmare titt på ”Istaterna” så är skörden avklarad till 74% respektive 59% i Illinois och Indiana. Iowa ligger nu på 55%, vilket är strax under genomsnittet på 60% men visar på att lantbrukarna varit aktiva då detta trots allt är en ökning med 20% från veckan innan. Den största veckovisa ökningen står dock lantbrukare i Minnesota för, från 19% till 48%.
Tillståndet för den amerikanska majsen har också förbättrats i de flesta stater under veckan och andelen grödor klassade som ”good/excellent” justeras upp med 2% till 62%. Tillståndet för grödorna i Illinois lämnades oförändrat och andelen ”good/excellent” ligger på 68%. Tillståndet för grödorna i Indiana förbättrades marginellt med 1% till 74% medan Iowa ’s grödor klassade som ”godd/excellent” justerades upp med 4% till 49%.
Vi väljer att hålla fast vid köprekommendationen.
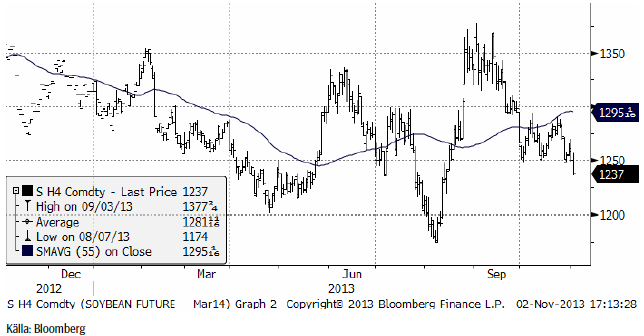
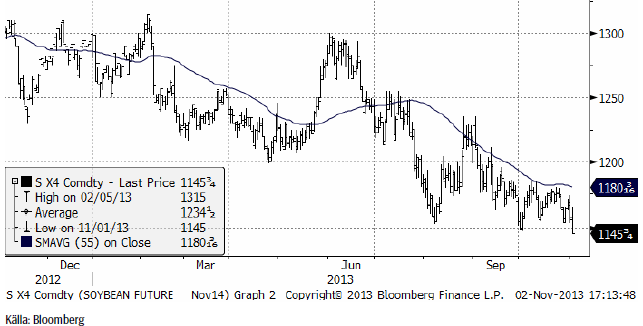
Sojabönor
Marskontraktet 2014 föll i fredags under det tekniska stödet på 1250, vilket ger möjlighet till fritt fall ner till 1200.
Vi ser också att November 2014 bröt under sitt tekniska stöd på 1150.
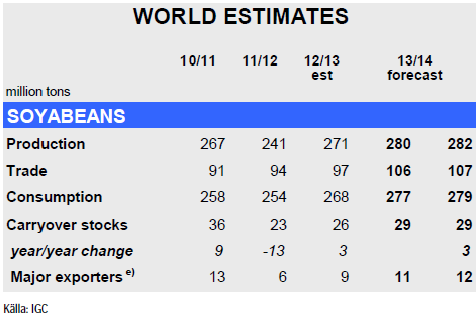
IGC rapporterade i veckan som gick. För sojabönor förväntas den globala produktionen att stiga för andra året i rad till rekordhöga 282 mt för 2013/14, en ökning med 4% på årsbasis, framförallt tack vare estimerade jätteskördar i Sydamerika. Globala utgående lager lämnas oförändrade från förra månaden på 29 mt men beräknas öka med 12% på årsbasis med de stora exportörerna Argentina och Brasilien i täten. Den globala handeln med sojabönor väntas öka med 10% på årsbasis drivet av en fortsatt stark efterfrågan från Kina med en ökad import.
Måndagens Crop Progress från USDA visar att skörden av sojabönor i USA avancerar och nu ligger i linje med det femåriga genomsnittet på 77%, en ökning från 63% veckan innan. Minnesota och South Dakota ligger strax över genomsnittet liksom Iowa och Illinois med 87% respektive 85% av skörden avklarad.
Förra veckans Crop Progress rapport var också den sista som visade tillståndet för sojabönorna där USDA avslutade säsongen med att konstatera att 57% klassades som ”good/excellent”, vilket var något lägre än snittet på 61% vid samma tid.
62% av grödorna i Illinois klassades som ”good/excellent” och för Indiana låg siffran på 68%. För Iowa stannade siffran på blygsamma 42%.
Vi behåller säljrekommendation.
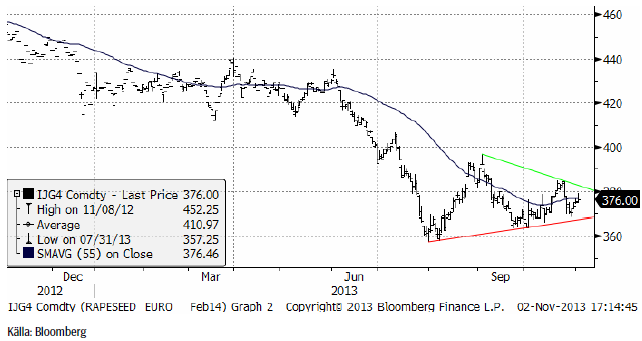
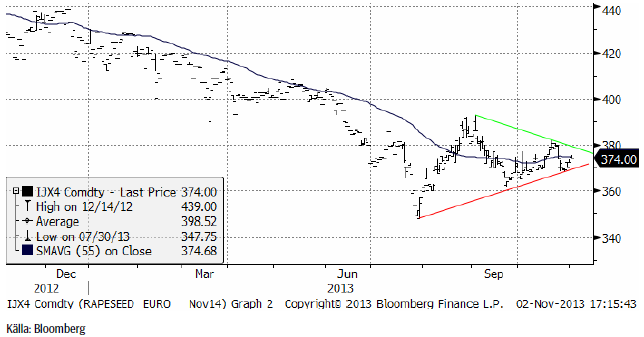
Raps
Rapspriset (februari 2014) gick inte under det tekniska stödet på 360 euro i början av oktober och har sedan dess stigit på ett sätt som inte riktigt kan förväntas av en marknad som ska vara i fallande trend. Priset ligger nu strax under 380 euro. Om priset går över 380 euro förändras bilden ytterligare. Det kan vara en trendvändning uppåt på gång. Det återstår att se.
November 2014-kontraktet uppvisar liksom februarikontraktet en formation som inom den tekniska analysen kallas för en triangelformation. Sådana karaktäriseras av lägre toppar och högre bottnar. Utbrott ur ”triangeln” brukar följas av ytterligare rörelse i utbrottets riktning. I skrivande stund finns inget annat att göra än att avvakta och se åt vilket håll utbrottet sker.
För två veckor sedan gick vi över till en försiktig köprekommendation, men som läget är nu tycker vi det är bättre att avvakta med en neutral position.
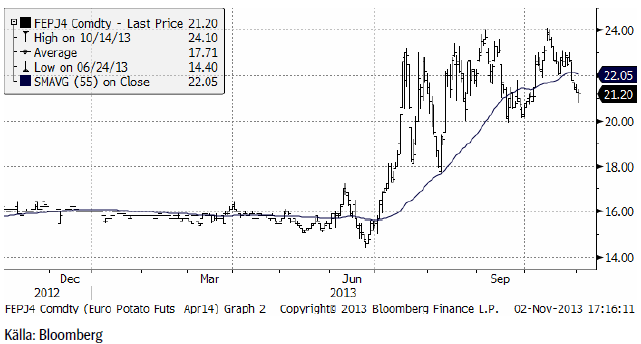
Potatis
Potatispriset av årets skörd, föll tillbaka från toppnoteringen 24 euro och stängde förra veckan på 21.20 euro per deciton.
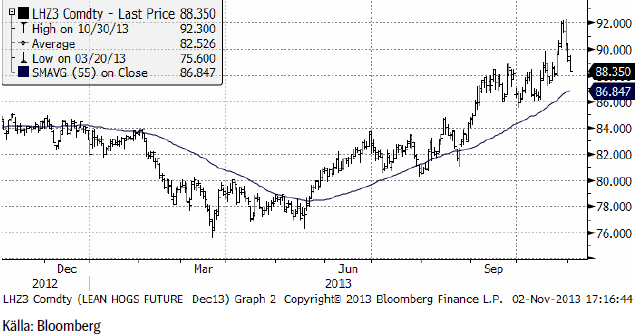
Gris
Lean hogs gick upp till ny toppnotering på 92.3 cent per pund innan priset föll tillbaka och stängde veckan på 88.35.
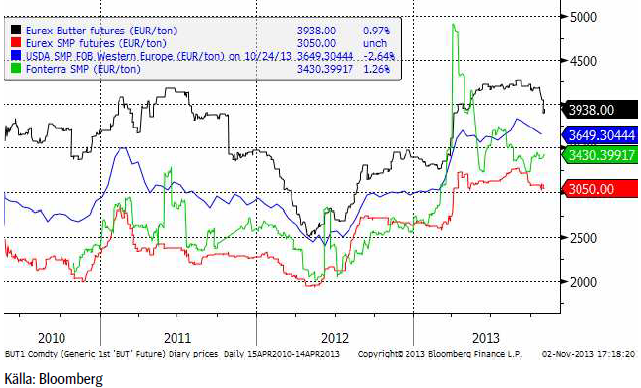
Mjölk
Terminerna på smör och skummjölkspulver vid Eurex-börsen var påtagligt svaga under veckan. Terminerna på smör föll med 3% för det kortaste kontraktet och med 2% för de lite längre. Priset på skummjölkspulver backade även det, men lite mindre.
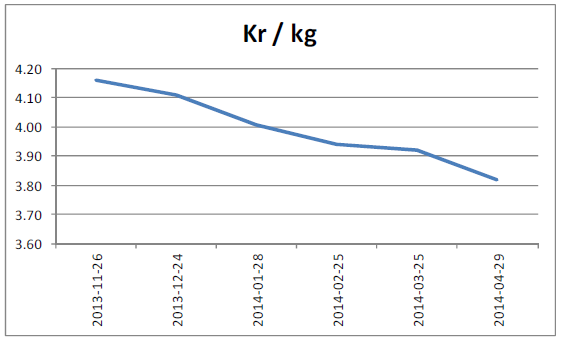
Om vi utgår från terminspriserna på smör och SMP och aktuell växelkurs eursek, får vi följande terminskurva i kronor per kilo svensk mjölkråvara. Notera dock att dessa priser alltid bör ligga över ett pris för råvaran i Sverige (och på andra ställen också) eftersom SMP och smör är produkter och inte råvaror.
Socker
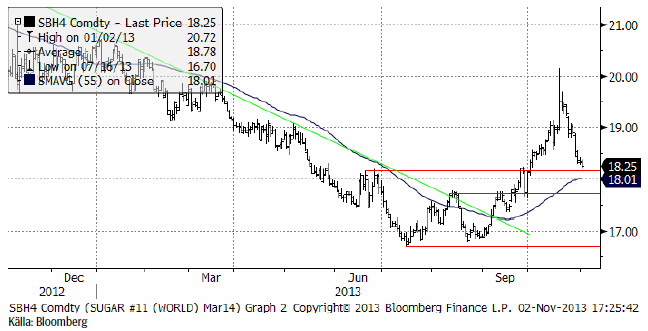
Marskontraktet på råsocker har rekylerat tillbaka till en teknisk stödnivå. Det är en nivå där en vändning uppåt skulle kunna ske. Vi upprepar därför vår köprekommendation på socker.
Det råder inget tvivel om att trenden för sockerpriset har vänts från att vara fallande de senaste åren, till att bli stigande.
Gödsel
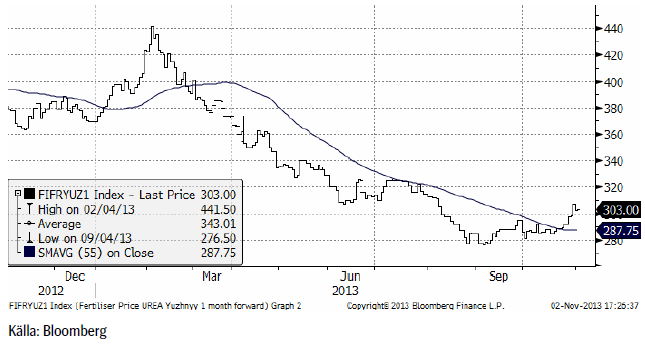
Priset på kväve / urea steg i veckan som gick och ligger nu på 303 dollar per ton. Botten noterades den 4 september på 276.50 dollar per ton. Priset ligger ändå en bra bid under förra årets toppnotering på 441.50.
[box]SEB Veckobrev Jordbruksprodukter är producerat av SEB Commodities Sales desk och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Detta marknadsföringsmaterial, framtaget av SEB’s Commodities Sales desk, har upprättats enbart i informationssyfte.
Även om innehållet är baserat på källor som SEB bedömt som tillförlitliga ansvarar SEB inte för fel eller brister i informationen. Den utgör inte oberoende, objektiv investeringsanalys och skyddas därför inte av de bestämmelser som SEB har infört för att förebygga potentiella intressekonflikter. Yttranden från SEB’s Commodities Sales desk kan vara oförenliga med tidigare publicerat material från SEB, då den senare hänvisas uppmanas du att läsa den fullständiga rapporten innan någon åtgärd vidtas.
Dokumentationen utgör inte någon investeringsrådgivning och tillhandahålls till dig utan hänsyn till dina investeringsmål. Du uppmanas att självständigt bedöma och komplettera uppgifterna i denna dokumentation och att basera dina investeringsbeslut på material som bedöms erforderligt. Alla framåtblickande uttalanden, åsikter och förväntningar är föremål för risker, osäkerheter och andra faktorer och kan orsaka att det faktiska resultatet avviker väsentligt från det förväntade. Historisk avkastning är ingen garanti för framtida resultat. Detta dokument utgör inte ett erbjudande att teckna några värdepapper eller andra finansiella instrument. SEB svarar inte för förlust eller skada – direkt eller indirekt, eller av vad slag det vara må – som kan uppkomma till följd av användandet av detta material eller dess innehåll.
Observera att det kan förekomma att SEB, dess ledamöter, dess anställda eller dess moder- och/eller dotterbolag vid olika tillfällen innehar, har innehaft eller kommer att inneha aktier, positioner, rådgivningsuppdrag i samband med corporate finance-transaktioner, investment- eller merchantbankinguppdrag och/eller lån i de bolag/finansiella instrument som nämns i materialet.
Materialet är avsett för mottagaren, all spridning, distribuering mångfaldigande eller annan användning av detta meddelande får inte ske utan SEB:s medgivande. Oaktat detta får SEB tillåta omfördelning av materialet till utvald tredje part i enlighet med gällande avtal. Materialet får inte spridas till fysiska eller juridiska personer som är medborgare eller har hemvist i ett land där sådan spridning är otillåten enligt tillämplig lag eller annan bestämmelse.
Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) är ett [publikt] aktiebolag och står under tillsyn av Finansinspektionen samt de lokala finansiella tillsynsmyndigheter i varje jurisdiktionen där SEB har filial eller dotterbolag.
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

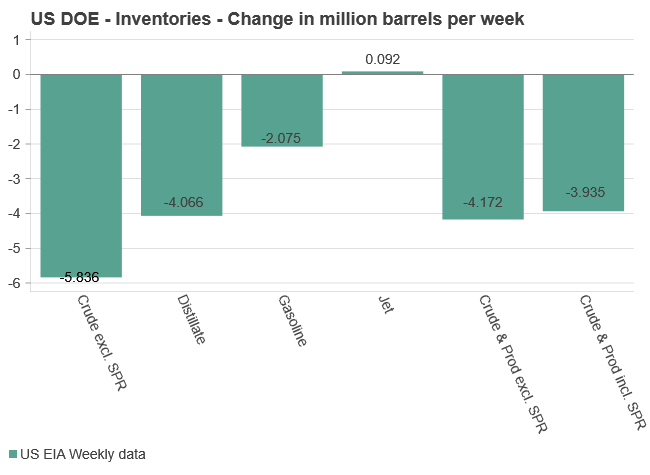
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

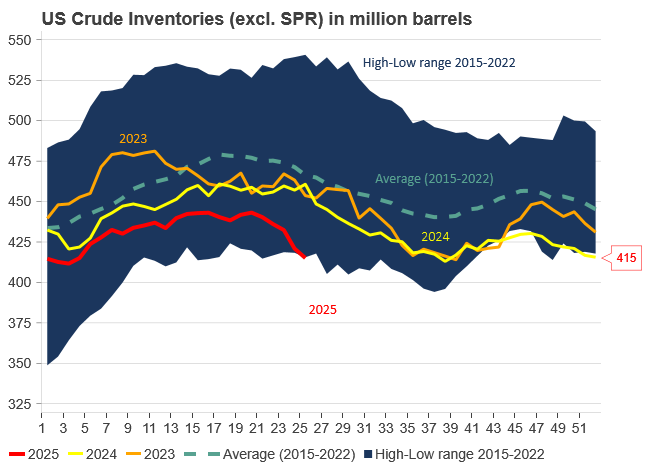
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBrookfield ska bygga ett AI-datacenter på hela 750 MW i Strängnäs
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanTradingfirman XTX Markets bygger datacenter i finska Kajana för 1 miljard euro
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter1 vecka sedan
Nyheter1 vecka sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld