Analys
Peak oil-teorin har peakat – men har priset gjort det?

 International Petroleum Week London
International Petroleum Week London
“Peak oil theory has peaked – but has the price peaked too?”
Under veckan besökte vi den årliga internationella petroleum konferensen i London. Vårt första intryck var lika starkt som tydligt; för sex år sedan pratade alla ”peak oil”, i år pratar alla ”shale revolution”. Nedan sammanfattar vi de fundamentala förutsättningarna på oljemarknaden inför konferensen samt de diskussioner som fördes såväl på podiet som i annexen över kaffe, snacks och drinkar.
Oljemarknadens hörnpelare skakar
Vi reste till London med bilden av en oljemarknad som på pappret ser ut att möta svåra prövningar under 2014. Brent, den nya globala standarden, har snittat 110 USD under de tre senaste åren, ett väldigt högt pris med historisk blick. Under 25 år fram till 2011 snittade brent 33 USD. På kort tid har konsensus långsiktiga syn med ett brentpris över 100 USD växt sig så starkt att man kan tro att vi alla föds med den vyn. Bloombergs konsensus-undersökning visar just nu 105 USD för december 14. Goda nyheter för oljeproducenter – mindre goda för oljeimporterande länder, speciellt de lidande i Europa som med en svag euro betalar mer för sin oljenota under eurokrisen än under prisspiken på 147 USD 2008. ”That´s the Europeans´ problem isn´t it?”, som en amerikansk producent kommenterade den saken.
Emerging Markets
Första och största utmaningen för året är Kina och de övriga snabbväxande icke OECDländerna. Detta kluster ska skapa väldens ökade oljekonsumtion under året genom att kompensera för fallande konsumtion i OECD orsakad av energieffektiviseringar. Kina står för 25 % av gruppens oljekonsumtion men landets ekonomi skakar. Sista kvartalet 2013 växte drakens revir med 7,7 %, den lägsta nivån på 14 år och vår prognos är att inbromsningen fortsätter till 7,5 % under 2014. Zoomar vi in på drakens aptit för olja har den mättats oroväckande fort. Under 2013 växte den bara med 1,6 % klart under IEA:s förväntning på 3,8%. Det gjorde faktiskt att USA blev världens snabbast växande oljekonsument i fat räknat 2013. Det gör också att Kina inte längre kan axla rollen som hörnpelaren på efterfrågesidan i ekvationen som ger ett oljepris över 100 USD.
Big Ben
Det slutar inte med Kina, icke OECD blocket har problem även utöver drakens matvanor. Västvärldens maniska stimulanser efter finanskrisen har gett EM ett lyft när investerare sökt bättre avkastning utanför sina hemmamarknader och på så vis gett EM-länderna tillgång till billig finansiering. Denna rörelse har triggat ett starkt behov av råvaror – däribland olja – till EM. När nu västvärldens fanbärare, Fed har vänt på klacken och börjat strypa tillgången på ”hot money” till EM så har det skakat om EM ordentligt, både i år när tapering började och i maj 2013 när tapering påkallades av Ben Bernanke.
Geopolitiken och OPEC
Den tredje skakande hörnpelaren är den geopolitiska oron. Oron kring Iran, oljetjuvar i Nigeria, sönderfallet i Irak och inbördeskriget i Libyen har alla eldat på oljepriset under de tre senaste åren. Omkring 3 millioner fat per dag i export ligger idag nere i dessa länder. Denna förlust kompenseras ganska precist av USA:s stigande produktion vilket skapat ett status quo för oljepriset trots den dramatiska omfördelningen i produktion de senaste åren. Nu börjar emellertid dessa problem att lätta. Irak har redan ökat exporten från de södra delarna med 0,3 Mbpd och landet säger sig kunna addera 1 Mbpd under året totalt.
Förhandlingarna med Iran har däremot klappat ihop och motsvarar inte längre förväntansbilden. Lättnader i sanktionerna innefattar ännu inte olja men om de fortsätter borde oljesanktionerna släppas i mitten av året och Irans oljeexport kan då påbörja en långsam återhämtning. Om det överhuvudtaget händer.
Libyen ser däremot hoppfullt ut. Exporten är uppdämd av strejker och hot från östra delarna av landet om att sälja olja oberoende av Tripoli. Det vore osannolikt att 2014 slutar utan en lösning och möjlighet för Libyen att säkra väl behövda exportinkomster från olja. Av de tre oroshärdarna är Libyen den som snabbast kan åstadkomma en prispåverkande export och därför den främste att hålla ögonen på.
OPEC:s situation kommer därmed försämras radikalt. De icke drabbade medlemmarna i kartellen har kunnat åtnjuta hög produktion till högt pris då tre av medlemmarnas export ofrivilligt legat nere. Återvänder Libyen, Iran och Irak till export återstår det att se hur intresserade Saudi är av att skära ner på produktionen för att lämna över inkomsterna till Irak (som ännu officiellt står utanför OPEC:s gemensamma produktionskvot) och Iran?
Vad tyckte folk på IP Week?
Enklast kan man dela upp diskussionspunkterna i vad som deltagarna generellt tycktes vara
väl överrens om:
- Brent som benchmark fungerar dåligt. Den underliggande produktionen är nu under 1 Mbpd och 60-70 % av den går till Asien. Ska Brent som benchmark överleva när Nordsjöns produktion faller måste kvalitéer från Afrika eller Ryssland inkluderas.
- Energiefterfrågan kommer att öka med icke OECD-ländernas framväxt.
- Elproduktion kommer ta en allt större del av oljekonsumtionen när EM får utökad tillgång till el.
- Energikonsumtionen är mättad i OECD och kommer minska i takt med energieffektiviseringar.
- Kina kommer öka energikonsumtionen fram till 2020 och sedan plana ut.
- Konceptet med ”peak oil” är utdött, var är Aleklett nu?
- Fossila bränslen kommer att dominera under en horisont fram till 2040
- Naturgas har växt fram som den mest prisvärda energiråvaran i kontexten av ett pris på CO2 utsläpp.
…och de områden där åsikterna starkt gick isär:
- Kommer kolanvändningen öka eller minska (beror på Kinas vägval för att lösa luftproblemen)
- Hur kommer efterfrågan på energi att påverkas av OECD:s allt effektivare energianvändande? (potentialen är enorm, energiförlusten innan den slutar som användbar värme eller kyla, ljus eller rörelse är förvånansvärt stor) .
- Kommer gas ersätta oljan i transportsektorn?
- Kommer el och/eller vätgasbilar ta betydelsefulla marknadsandelar från olja i transportsektorn?
Man kan konstatera att transportsektorns ökade andel av oljekonsumtionen förde sektorn högt på agendan. Utvecklingspotentialen i sektorn skapade diskussioner. Så gjorde även de nu inte lika aktuella klimatmålen. Osäkerheten kring hur mycket koldioxid som krävs för en grad uppvärmning divergerar mer än någonsin och gör diskussionerna hypotetiska. 2 gradsmålet verkar energiindustrin inte längre ta på allvar.
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

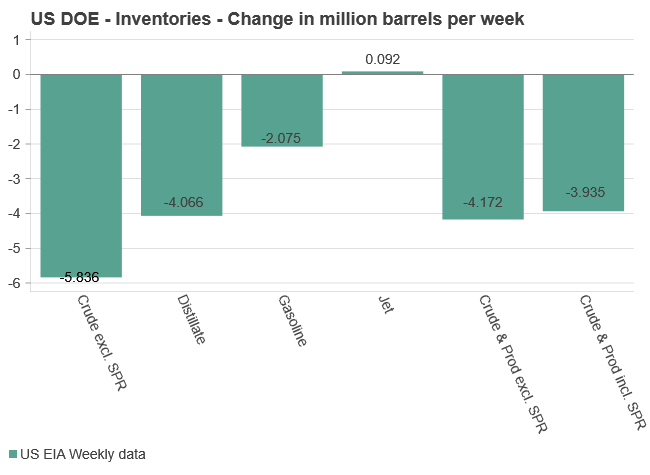
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

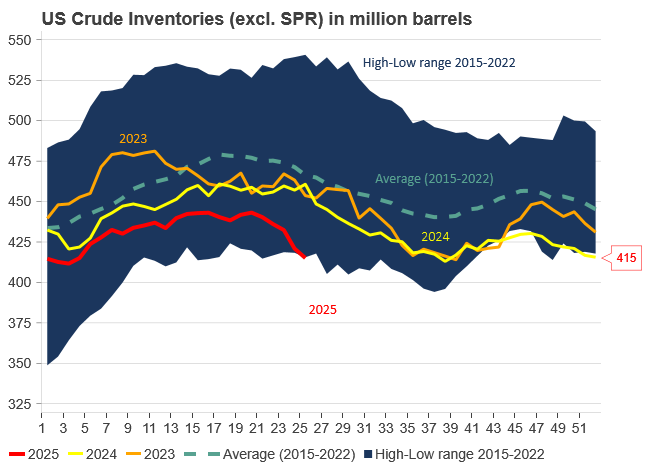
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals växlar spår – satsar fullt ut på guld
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLåga elpriser i sommar – men mellersta Sverige får en ökning
-

 Analys3 veckor sedan
Analys3 veckor sedanA muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanJonas Lindvall är tillbaka med ett nytt oljebolag, Perthro, som ska börsnoteras
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanOljan, guldet och marknadens oroande tystnad
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanVery relaxed at USD 75/b. Risk barometer will likely fluctuate to higher levels with Brent into the 80ies or higher coming 2-3 weeks
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanDomstolen ger klartecken till Lappland Guldprospektering















