Analys
SEB – Jordbruksprodukter, vecka 3
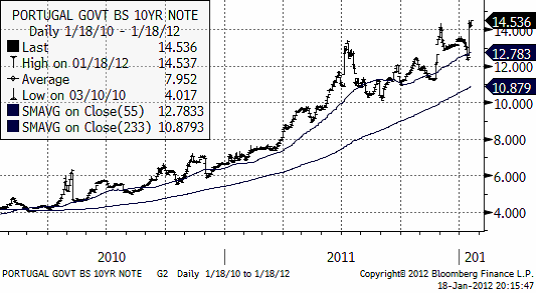
 Torkan i Argentina och södra Brasilien och effekten på soja- och majsskörden är i fokus i nyhetsflödet. Kanske är det eurokris-utmattning som gjort att Portugals nedgradering till ”skräp” passerat obemärkt förbi. Marknaden räknar med en 65% chans att landet går i konkurs inom fem år. Staten lånar nu till över 14.5% ränta, som vi ser i diagrammet nedan.
Torkan i Argentina och södra Brasilien och effekten på soja- och majsskörden är i fokus i nyhetsflödet. Kanske är det eurokris-utmattning som gjort att Portugals nedgradering till ”skräp” passerat obemärkt förbi. Marknaden räknar med en 65% chans att landet går i konkurs inom fem år. Staten lånar nu till över 14.5% ränta, som vi ser i diagrammet nedan.
 Kina rapporterade en tillväxt på låga 8.9%, vilket är närmast chockerande lågt när landet legat på 10% i nästan tio år. Samtidigt noterar vi att tillväxten på landsbygden i Kina ligger på 11% och att halva Kinas befolkning bor där. Kina är också ett land som rapporterar högre veteskörd för 2011, trots minskad areal. Mycket tyder på att Kina släppt på monetär stimulans under december och att detta – tillsammans med solid tillväxt på landsbygden, bidrar till att ge landet en mjuklandning. Den monetära stimulansen – att staten släpper på likviditet – brukar slå igenom med ett maximum av effekt efter ca 6 månader.
Kina rapporterade en tillväxt på låga 8.9%, vilket är närmast chockerande lågt när landet legat på 10% i nästan tio år. Samtidigt noterar vi att tillväxten på landsbygden i Kina ligger på 11% och att halva Kinas befolkning bor där. Kina är också ett land som rapporterar högre veteskörd för 2011, trots minskad areal. Mycket tyder på att Kina släppt på monetär stimulans under december och att detta – tillsammans med solid tillväxt på landsbygden, bidrar till att ge landet en mjuklandning. Den monetära stimulansen – att staten släpper på likviditet – brukar slå igenom med ett maximum av effekt efter ca 6 månader.
Vete
USA var stängt i måndags och det är ovanlig nyhetstorka. Det är relativt torrt i USA och det saknas snötäcke på sina håll. Det är också kallare än normalt, så utvintring kan möjligen bli ett tema framöver. Ukraina har samma situation. En uppgift finns om att så mycket som 35% av vetet skulle kunna vara i dåligt skick. Ryskt vete har snötäcke. Nederbörden i Europa har varit normal, utom i Spanien.
Lagren av vete är höga i världen och om det inte uppstår stora problem under våren borde vetet kunna falla från de här nivåerna.
Nedan ser vi kursdiagrammet för novemberkontraktet på Matif.
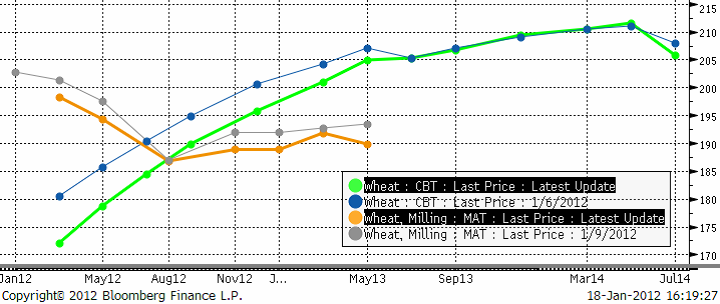
Nedan ser vi terminskurvan för Chicagovete och Matif nu och för en vecka sedan. De ”feta” kurvorna är de aktuella. De ”smala” är förra veckans. Det fortsätter att vara ”backwardation” på Matif, dvs terminspriserna för längre löptid är lägre än för korta. I USA är det däremot ”contango”, högre terminspriser ju längre ut i tiden man kommer. Det är lagringskostnaden som orsakar contangot.
Vi fortsätter att tro på en nedgång i vetepriset under året.
Maltkorn
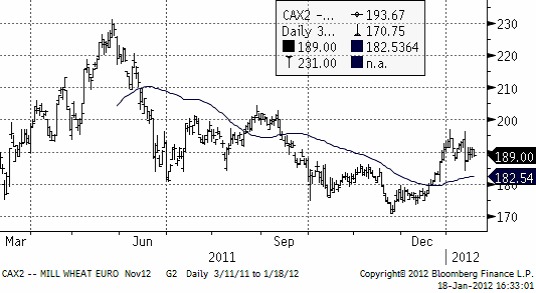
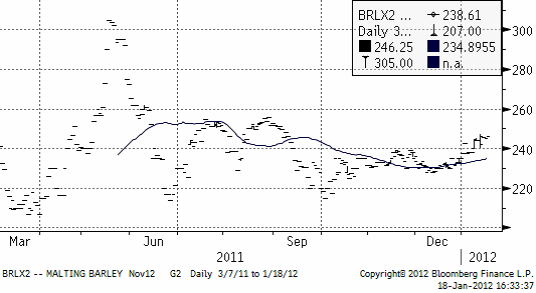
Maltkornsmarknaden har behållit sin styrka relativt andra spannmål med novemberleverans på Matif på 246.25, upp från 242 euro per ton förra veckan.
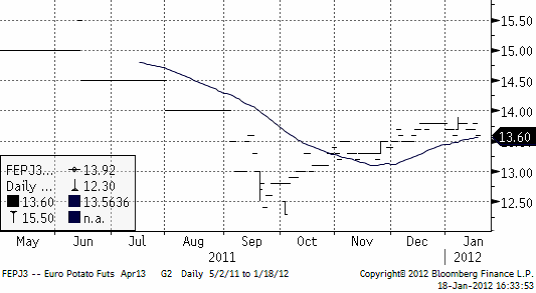
Potatis
Priset på potatis har fortsatt att stiga, för leverans nästa år (av sommarens skörd), men uppgången har förlorat lite av sin kraft.
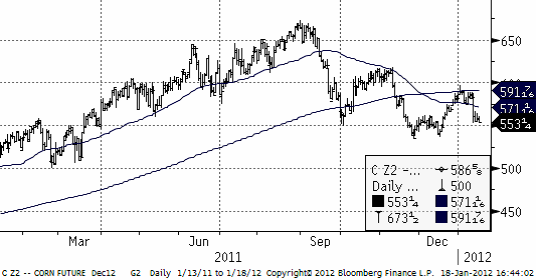
Majs
Förra året producerade Argentina 23 mt majs och inför sommaren (i Argentina) hade man hoppats kunna nå 28 – 29 mt. USDA förutspådde förra veckan att skörden blir 26 mt (en sänkning med 3 mt).
Maizar, som representerar majsodlarna i Argentina rapporterar att 20% av majssådden inte blev av och att 10% av det som såddes gått förlorat. Man kan så om och man kan så en andra gröda, safrinha, men om den blir för sen kan den skadas av tidig frost i mars och april. Oftast är det sojabönor man sår som andra gröda.
Det finns två väderleksprognoser för norra Argentina / södra Brasilien. En säger regn till helgen och sedan torrt igen. Den andra har mer generell nederbörd i prognosen.
Enligt en rapport från Global Weather Monitoring på onsdagseftermiddagen ska det regna 25 mm från 21 januari. Förra veckan regnade det 50 mm, efter att det varit torrt i 40 dagar. Nedan ser vi decemberkontraktet på CBOT, där priset just fallit ner från 600-cent-nivån.
Tekniskt ser det ut som om priset skulle kunna falla ner mot 500 cent, men 550 cent är ett starkt stöd, där det funnits starka köpintressen tidigare.
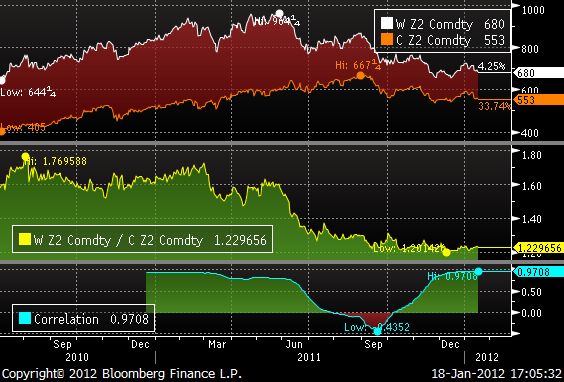
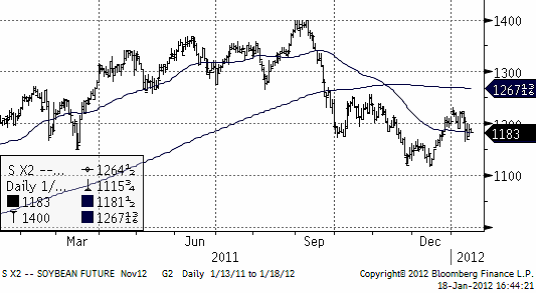
Sojabönor
Conab, som gör skördeprognoserna inom det brasilianska jordbruksdepartementet estimerar att landet kommer att bärga en skörd på 71.75 mt i år. Det är 4.7% mindre än förra året. Att det blir en så liten minskning trots torkan i Parana (15 mt normal produktion) i söder, beror på att det vuxit frodigt i den väldiga delstaten Mato Grosso (där det knappt finns någon skog kvar, bara till namnet). Privata analysfirmor i Brasilien, som t ex Agroconsult förutspår en nedgång på 2% totalt till 73.52 mt och AgRural väntar sig en skörd på 73.06 mt.
I Argentina sänkte USDA skörden förra veckan från 52 mt till 50.5 mt. Förra året skördades 49 mt soja, så det är ändå en uppgång. Jordbrukare i Argentina kan fortfarande så ”andrasojan”. I delstaten Cordoba, som vi skrev om förra veckan, och som är näst största producenten av majs, utlystes katastroftillstånd den här veckan. Det betyder att nödhjälp kan betalas ut till jordbrukarna. Hela landet Paraguay gjordet detsamma.
Tekniskt står priset och väger. Vädret håller på att förbättras i Sydamerika. Å andra sidan tyder det mesta på att Kina har startat monetär stimulans och det kan öka efterfrågan senare under året.
Enligt USDA kommer Brasilien att gå om USA som världens största exportör av sojabönor i år, året som slutar den 30 september 2012.
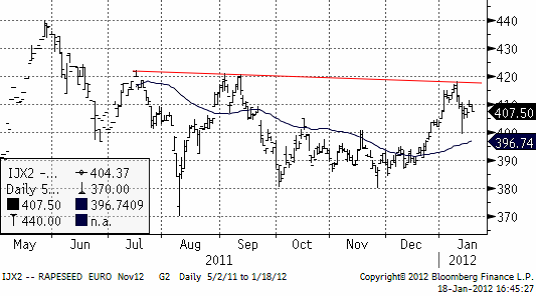
Raps
Priset på rapsfrö har varit förbluffande starkt på Matif. Tekniskt ser vi i diagrammet nedan att det finns en motståndslinje precis ovanför. Det skulle förvåna mycket om raps, som är mycket dyrare än kandensisk canola och sojabönor skule lyckas bryta upp över 420 euro per ton.
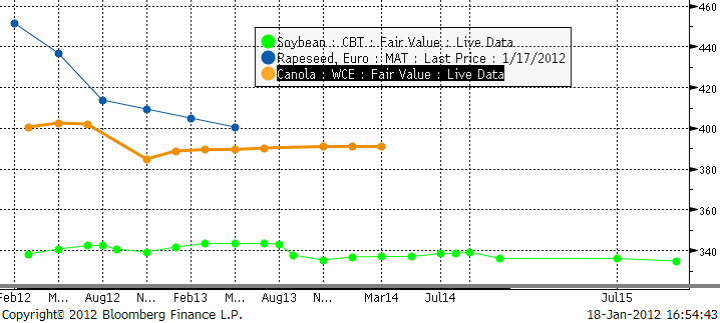
Nedan ser vi terminspriserna framåt i tiden för Matif raps, kanadensisk canola och för CBOT sojabönor, allt uttryckt i euro per metriskt ton.
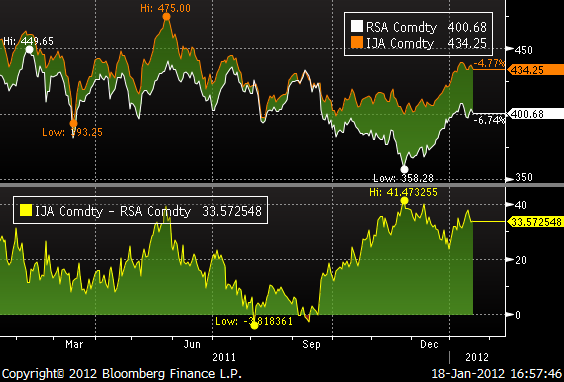
I diagrammet nedan ser vi att rapsfrö är ovanligt dyrt i förhållande till kanadensisk canola (IJA=raps, RSA=canola).
Vi har en negativ vy på Matif raps.
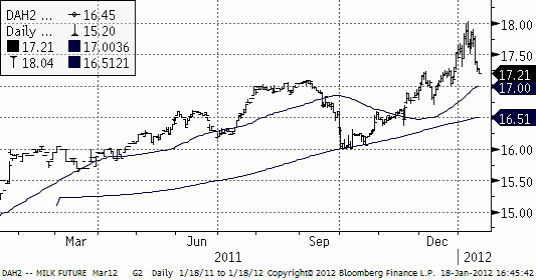
Mjölk
Nedan ser vi priset på marskontraktet på flytande mjölk (kontant avräknat mot USDA:s prisindex). Marknaden stötte på säljare på 18 och priset föll tillbaka kraftigt ner till 17.21.
Gris
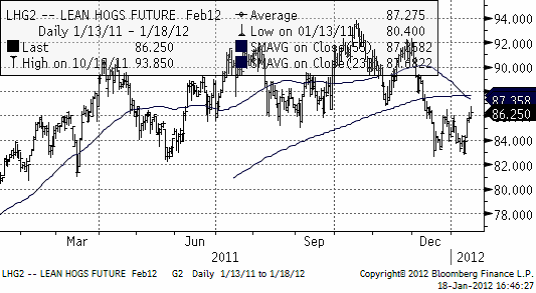
Priset på lean hogs rekylerade upp kraftigt de senaste dagarna, vilket gör att priset fortfarande ligger kvar i det breda prisintervall som etablerades redan under förra våren.
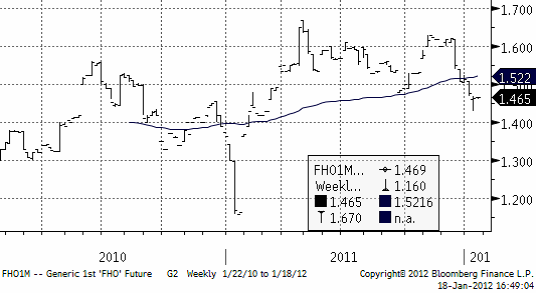
Priset i Europa har betett sig på samma sätt. Nedan ser vi det vid var tid kortaste terminskontraktet (närmast spot):
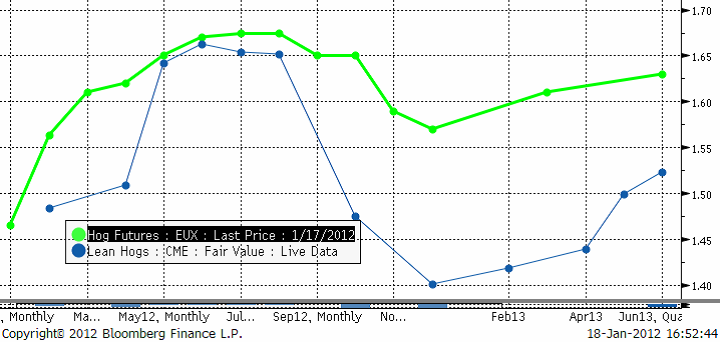
Nedan ser vi terminspriserna med förfall framåt i tiden. Amerikanska Lean Hogs-priserna är omräknade till euro per kilo. Vi ser att Lean Hogs ligger lägre i pris och att skillnaden är riktigt stor från oktober och framåt.
Valutor
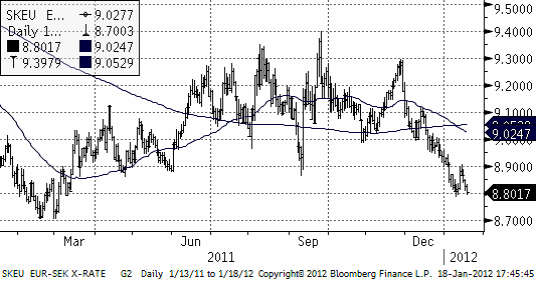
EURSEK har helt naturligt noterat lägre priser och borde fortsätta att falla.
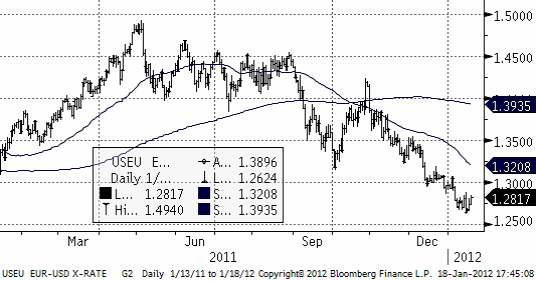
EURUSD är i en tydlig negativ trend.
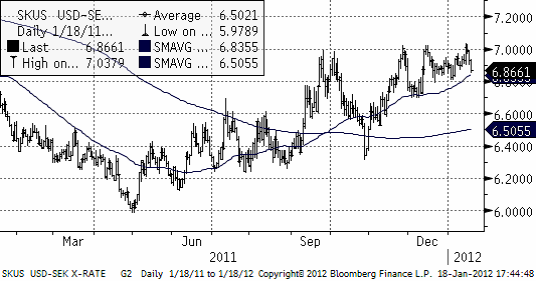
USDSEK har en stigande trend och har nått upp till heltalet 7 kr per dollar, varifrån det återigen vänt ner. 7 kronor verkar vara ett starkt motstånd. Köpsignal torde vi ta på allvar om kursen noteras över 7.05 kr, väl över motståndsnivån.
Gödsel
Kväve
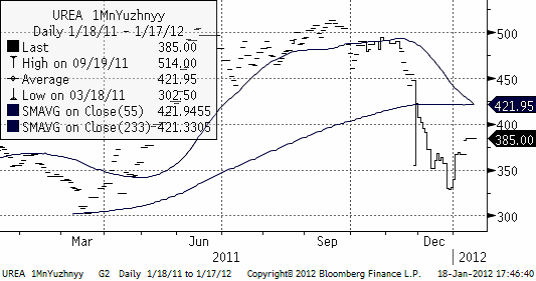
Nedan ser vi 1 månads terminspris på Urea fob Uyzhnyy. Priset har inte rört sig från den nivån den senaste veckan.
[box]SEB Veckobrev Jordbruksprodukter är producerat av SEB Merchant Banking och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been compiled by SEB Merchant Banking, a division within Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) (“SEB”).
Opinions contained in this report represent the bank’s present opinion only and are subject to change without notice. All information contained in this report has been compiled in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. However, no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made with respect to the completeness or accuracy of its contents and the information is not to be relied upon as authoritative. Anyone considering taking actions based upon the content of this document is urged to base his or her investment decisions upon such investigations as he or she deems necessary. This document is being provided as information only, and no specific actions are being solicited as a result of it; to the extent permitted by law, no liability whatsoever is accepted for any direct or consequential loss arising from use of this document or its contents.
About SEB
SEB is a public company incorporated in Stockholm, Sweden, with limited liability. It is a participant at major Nordic and other European Regulated Markets and Multilateral Trading Facilities (as well as some non-European equivalent markets) for trading in financial instruments, such as markets operated by NASDAQ OMX, NYSE Euronext, London Stock Exchange, Deutsche Börse, Swiss Exchanges, Turquoise and Chi-X. SEB is authorized and regulated by Finansinspektionen in Sweden; it is authorized and subject to limited regulation by the Financial Services Authority for the conduct of designated investment business in the UK, and is subject to the provisions of relevant regulators in all other jurisdictions where SEB conducts operations. SEB Merchant Banking. All rights reserved.
Analys
Brent crude ticks higher on tension, but market structure stays soft

Brent crude has climbed roughly USD 1.5-2 per barrel since Friday, yet falling USD 0.3 per barrel this mornig and currently trading near USD 67.25/bbl after yesterday’s climb. While the rally reflects short-term geopolitical tension, price action has been choppy, and crude remains locked in a broader range – caught between supply-side pressure and spot resilience.

Prices have been supported by renewed Ukrainian drone strikes targeting Russian infrastructure. Over the weekend, falling debris triggered a fire at the 20mtpa Kirishi refinery, following last week’s attack on the key Primorsk terminal.
Argus estimates that these attacks have halted ish 300 kbl/d of Russian refining capacity in August and September. While the market impact is limited for now, the action signals Kyiv’s growing willingness to disrupt oil flows – supporting a soft geopolitical floor under prices.
The political environment is shifting: the EU is reportedly considering sanctions on Indian and Chinese firms facilitating Russian crude flows, while the U.S. has so far held back – despite Bessent warning that any action from Washington depends on broader European participation. Senator Graham has also publicly criticized NATO members like Slovakia and Hungary for continuing Russian oil imports.
It’s worth noting that China and India remain the two largest buyers of Russian barrels since the invasion of Ukraine. While New Delhi has been hit with 50% secondary tariffs, Beijing has been spared so far.
Still, the broader supply/demand balance leans bearish. Futures markets reflect this: Brent’s prompt spread (gauge of near-term tightness) has narrowed to the current USD 0.42/bl, down from USD 0.96/bl two months ago, pointing to weakening backwardation.
This aligns with expectations for a record surplus in 2026, largely driven by the faster-than-anticipated return of OPEC+ barrels to market. OPEC+ is gathering in Vienna this week to begin revising member production capacity estimates – setting the stage for new output baselines from 2027. The group aims to agree on how to define “maximum sustainable capacity,” with a proposal expected by year-end.
While the IEA pegs OPEC+ capacity at 47.9 million barrels per day, actual output in August was only 42.4 million barrels per day. Disagreements over data and quota fairness (especially from Iraq and Nigeria) have already delayed this process. Angola even quit the group last year after being assigned a lower target than expected. It also remains unclear whether Russia and Iraq can regain earlier output levels due to infrastructure constraints.
Also, macro remains another key driver this week. A 25bp Fed rate cut is widely expected tomorrow (Wednesday), and commodities in general could benefit a potential cut.
Summing up: Brent crude continues to drift sideways, finding near-term support from geopolitics and refining strength. But with surplus building and market structure softening, the upside may remain capped.
Analys
Volatile but going nowhere. Brent crude circles USD 66 as market weighs surplus vs risk

Brent crude is essentially flat on the week, but after a volatile ride. Prices started Monday near USD 65.5/bl, climbed steadily to a mid-week high of USD 67.8/bl on Wednesday evening, before falling sharply – losing about USD 2/bl during Thursday’s session.

Brent is currently trading around USD 65.8/bl, right back where it began. The volatility reflects the market’s ongoing struggle to balance growing surplus risks against persistent geopolitical uncertainty and resilient refined product margins. Thursday’s slide snapped a three-day rally and came largely in response to a string of bearish signals, most notably from the IEA’s updated short-term outlook.
The IEA now projects record global oversupply in 2026, reinforcing concerns flagged earlier by the U.S. EIA, which already sees inventories building this quarter. The forecast comes just days after OPEC+ confirmed it will continue returning idle barrels to the market in October – albeit at a slower pace of +137,000 bl/d. While modest, the move underscores a steady push to reclaim market share and adds to supply-side pressure into year-end.
Thursday’s price drop also followed geopolitical incidences: Israeli airstrikes reportedly targeted Hamas leadership in Doha, while Russian drones crossed into Polish airspace – events that initially sent crude higher as traders covered short positions.
Yet, sentiment remains broadly cautious. Strong refining margins and low inventories at key pricing hubs like Europe continue to support the downside. Chinese stockpiling of discounted Russian barrels and tightness in refined product markets – especially diesel – are also lending support.
On the demand side, the IEA revised up its 2025 global demand growth forecast by 60,000 bl/d to 740,000 bl/d YoY, while leaving 2026 unchanged at 698,000 bl/d. Interestingly, the agency also signaled that its next long-term report could show global oil demand rising through 2050.
Meanwhile, OPEC offered a contrasting view in its latest Monthly Oil Market Report, maintaining expectations for a supply deficit both this year and next, even as its members raise output. The group kept its demand growth estimates for 2025 and 2026 unchanged at 1.29 million bl/d and 1.38 million bl/d, respectively.
We continue to watch whether the bearish supply outlook will outweigh geopolitical risk, and if Brent can continue to find support above USD 65/bl – a level increasingly seen as a soft floor for OPEC+ policy.
Analys
Waiting for the surplus while we worry about Israel and Qatar

Brent crude makes some gains as Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar rattles markets. Brent crude spiked to a high of USD 67.38/b yesterday as Israel made a strike on Hamas in Qatar. But it wasn’t able to hold on to that level and only closed up 0.6% in the end at USD 66.39/b. This morning it is starting on the up with a gain of 0.9% at USD 67/b. Still rattled by Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar yesterday. Brent is getting some help on the margin this morning with Asian equities higher and copper gaining half a percent. But the dark cloud of surplus ahead is nonetheless hanging over the market with Brent trading two dollar lower than last Tuesday.

Geopolitical risk premiums in oil rarely lasts long unless actual supply disruption kicks in. While Israel’s attack on Hamas in Qatar is shocking, the geopolitical risk lifting crude oil yesterday and this morning is unlikely to last very long as such geopolitical risk premiums usually do not last long unless real disruption kicks in.
US API data yesterday indicated a US crude and product stock build last week of 3.1 mb. The US API last evening released partial US oil inventory data indicating that US crude stocks rose 1.3 mb and middle distillates rose 1.5 mb while gasoline rose 0.3 mb. In total a bit more than 3 mb increase. US crude and product stocks usually rise around 1 mb per week this time of year. So US commercial crude and product stock rose 2 mb over the past week adjusted for the seasonal norm. Official and complete data are due today at 16:30.
A 2 mb/week seasonally adj. US stock build implies a 1 – 1.4 mb/d global surplus if it is persistent. Assume that if the global oil market is running a surplus then some 20% to 30% of that surplus ends up in US commercial inventories. A 2 mb seasonally adjusted inventory build equals 286 kb/d. Divide by 0.2 to 0.3 and we get an implied global surplus of 950 kb/d to 1430 kb/d. A 2 mb/week seasonally adjusted build in US oil inventories is close to noise unless it is a persistent pattern every week.
US IEA STEO oil report: Robust surplus ahead and Brent averaging USD 51/b in 2026. The US EIA yesterday released its monthly STEO oil report. It projected a large and persistent surplus ahead. It estimates a global surplus of 2.2 m/d from September to December this year. A 2.4 mb/d surplus in Q1-26 and an average surplus for 2026 of 1.6 mb/d resulting in an average Brent crude oil price of USD 51/b next year. And that includes an assumption where OPEC crude oil production only averages 27.8 mb/d in 2026 versus 27.0 mb/d in 2024 and 28.6 mb/d in August.
Brent will feel the bear-pressure once US/OECD stocks starts visible build. In the meanwhile the oil market sits waiting for this projected surplus to materialize in US and OECD inventories. Once they visibly starts to build on a consistent basis, then Brent crude will likely quickly lose altitude. And unless some unforeseen supply disruption kicks in, it is bound to happen.
US IEA STEO September report. In total not much different than it was in January
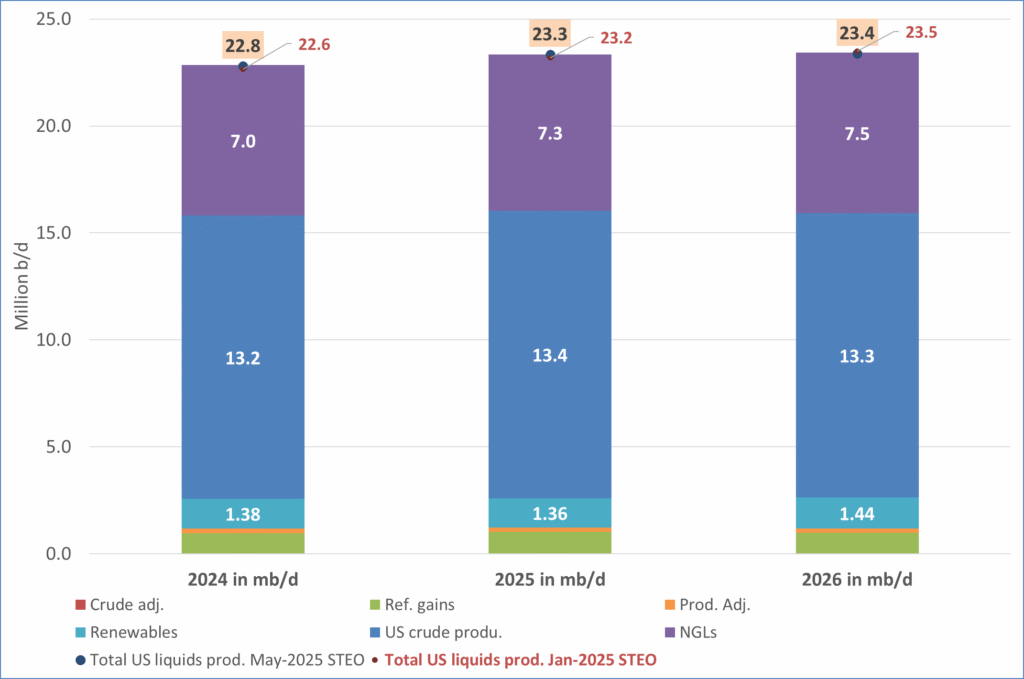
US IEA STEO September report. US crude oil production contracting in 2026, but NGLs still growing. Close to zero net liquids growth in total.
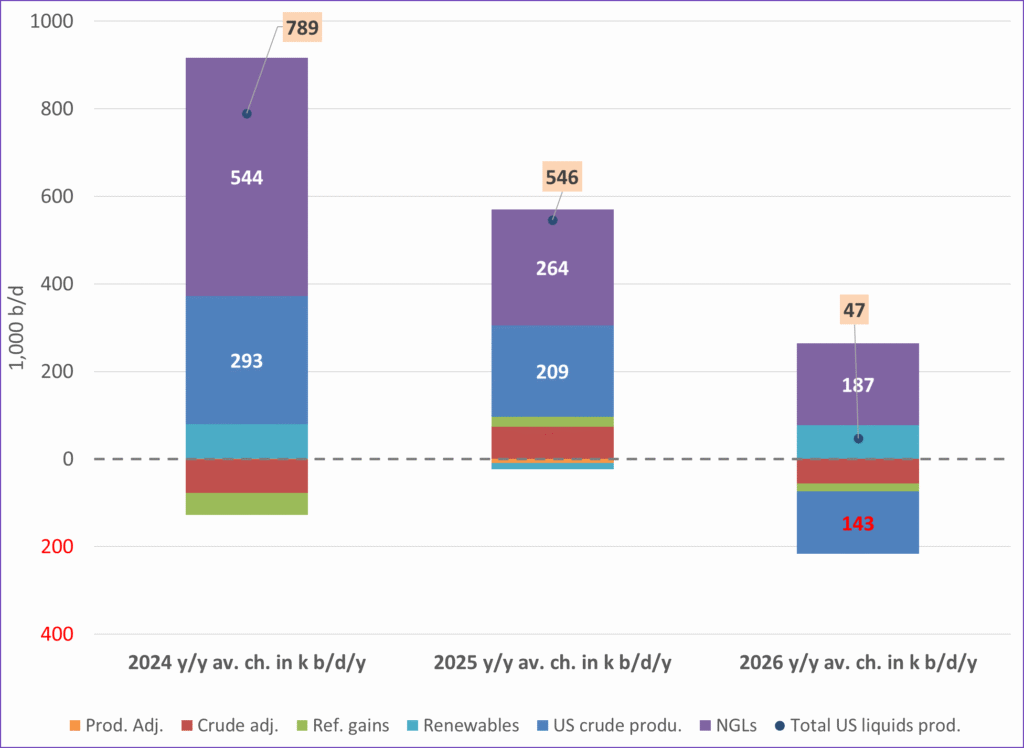
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanMeta bygger ett AI-datacenter på 5 GW och 2,25 GW gaskraftverk
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanAker BP gör ett av Norges största oljefynd på ett decennium, stärker resurserna i Yggdrasilområdet
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSommarens torka kan ge högre elpriser i höst
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanBrent edges higher as India–Russia oil trade draws U.S. ire and Powell takes the stage at Jackson Hole
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanMahvie Minerals är verksamt i guldrikt område i Finland
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanIncreasing risk that OPEC+ will unwind the last 1.65 mb/d of cuts when they meet on 7 September
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanNeil Atkinson spår att priset på olja kommer att stiga till 70 USD
-

 Analys2 veckor sedan
Analys2 veckor sedanOPEC+ in a process of retaking market share