Analys
SEB Jordbruksprodukter, 20 maj 2013


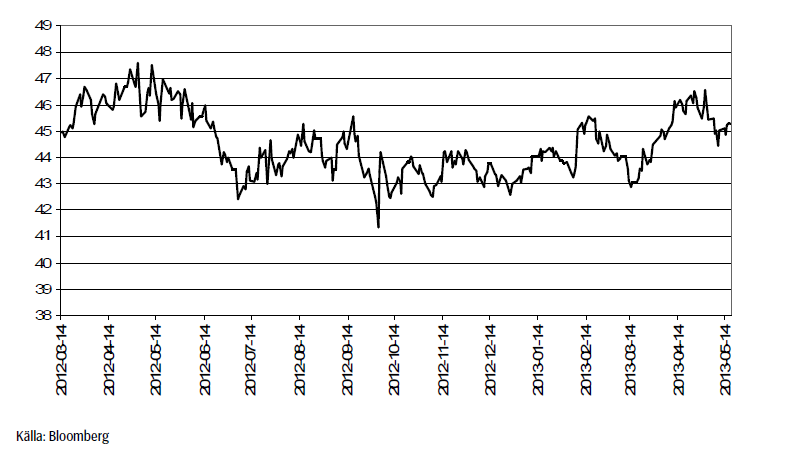
 Statistiken hamrar på marknaderna. Ur vinterns torka blandas massiva rapporter som WASDE-rapporten för en vecka sedan med sin prognostiserade rekordskörd av spannmål – så stor att många först inte kunde tro den, med rapporter om den sena såddens allt snabbare takt. Global ekonomi står samtidigt och stampar. Trots att centralbanker håller räntan på rekordlåg nivå och förser ekonomin med pengar, vill inte tillväxten ta fart. Pengarna hamnar istället på aktiebörsen. Anledningen är att Kina faktiskt kommit ganska långt upp på utvecklingsstegen. En inkomstökning leder inte som förr till en stor ökning av köttkonsumtionen. Att Kina börjar växa in som ett väsentligt mycket mer konkurrenskraftigt alternativ till Europas och Japans äldre delar av industrin innebär också att problemet inte är pengar, utan konkurrens från tillväxtländer.
Statistiken hamrar på marknaderna. Ur vinterns torka blandas massiva rapporter som WASDE-rapporten för en vecka sedan med sin prognostiserade rekordskörd av spannmål – så stor att många först inte kunde tro den, med rapporter om den sena såddens allt snabbare takt. Global ekonomi står samtidigt och stampar. Trots att centralbanker håller räntan på rekordlåg nivå och förser ekonomin med pengar, vill inte tillväxten ta fart. Pengarna hamnar istället på aktiebörsen. Anledningen är att Kina faktiskt kommit ganska långt upp på utvecklingsstegen. En inkomstökning leder inte som förr till en stor ökning av köttkonsumtionen. Att Kina börjar växa in som ett väsentligt mycket mer konkurrenskraftigt alternativ till Europas och Japans äldre delar av industrin innebär också att problemet inte är pengar, utan konkurrens från tillväxtländer.
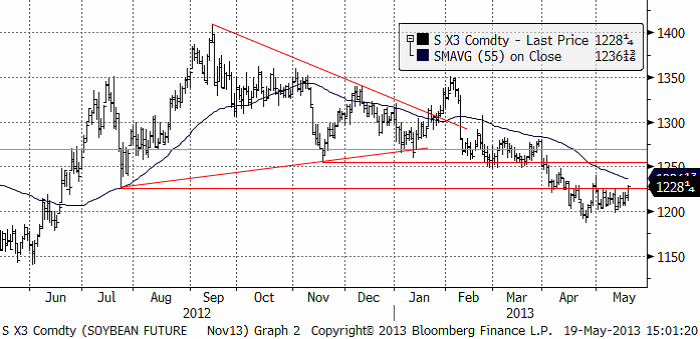
Pristrenden på spannmål är definitivt nedåtriktad. Sojabönor (Chicago) handlades upp, till stor del beroende på den tighta situationen för amerikanska sojabönor. Sydamerika har gott om dem.
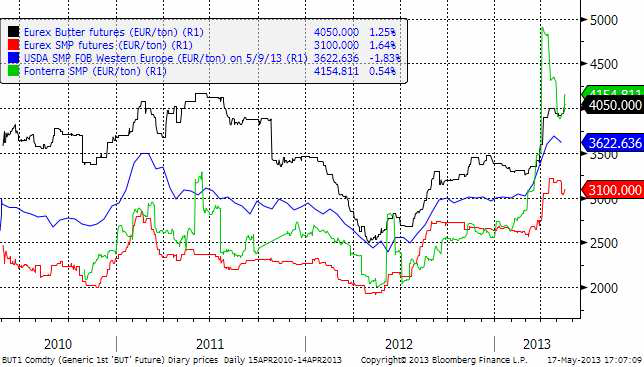
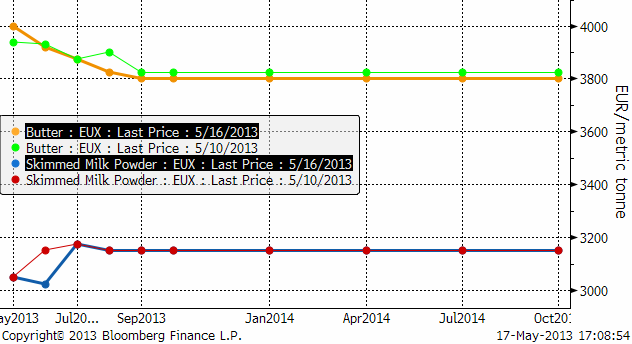
Mjölkmarknaden fortsätter falla, Fonterra lite mindre, men den kom från hög höjd. Eurex terminer på smör och mjölkpulver ligger fortfarande på hög nivå.
Odlingsväder
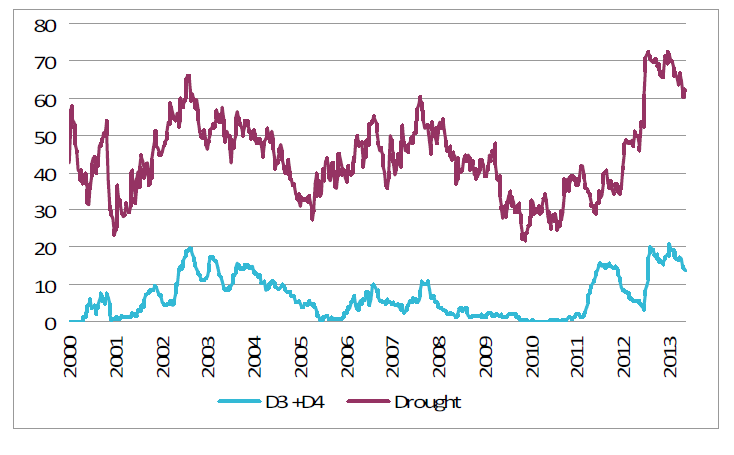
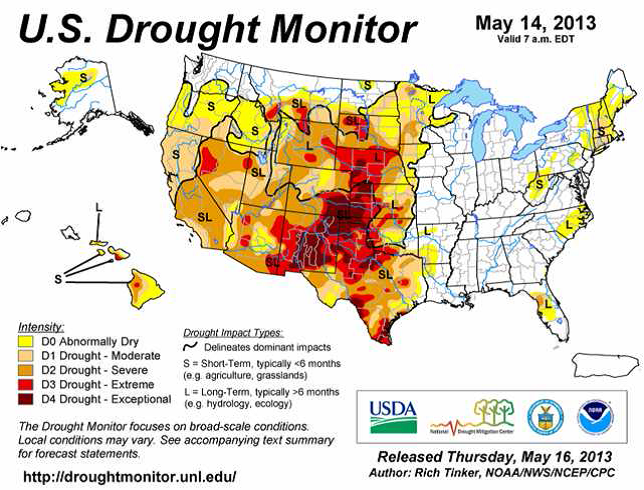
Torkan i USA har fortsatt att avta, i allt raskare takt. Det är nu 61.7% av USA som är torrare än normalt. Som mest på Juldagen var det 72% som var drabbat av torka. De två allra mest extrema graderna av torka lider 13.64% av landet av. Andelen minskade med 0.5% sedan förra veckan.
Som vi ser i kartbilden nedan är det västra delen av prärien och längs Klippiga bergen som det råder torka. Mellanvästern är praktiskt taget fri från torka. Östra delarna av Kansas och andra delstater hör dock till de som är hårdast drabbade av de svåraste typerna av torka.
Vete
Vetepriset började falla i torsdags och kursfallet accelererade under fredagens sista timmar. Bakom ligger sannolikt de spekulationer om att sådden av majs ska ha tagit ett rekordkliv framåt i måndagkvällens statistik. Siffror på att 70% (28% förra veckan) skulle vara sått. Det tror inte jag, men att sådden kommer att ha tagit ett stort kliv framåt ska man vänta sig. Innebörden av WASDE-rapporten kanske också börjar sjunka in. De flesta jag talat med om WASDE-rapporten har inte reagerat, helt enkelt för att den stora skörden av spannmål som prognosticeras är så enorm. En reaktion på ett seminarium i Malmö var ”Men hur ska det då gå med lönsamheten!?”. Jag tror dock att ju förr man fattar att priset kommer att gå ner rejält, desto bättre är det. För då kan man raskt göra något åt det.
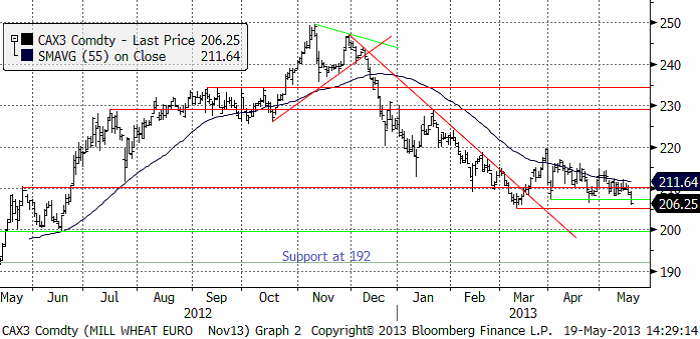
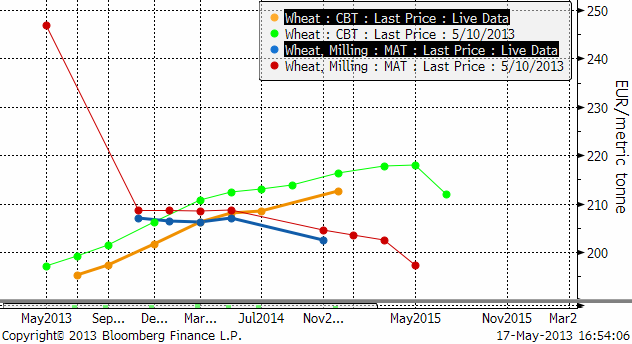
Priset på novemberterminen på Matif stängde på 206.25 euro per ton. Det är lägre än föregående botten. Nästa tekniska stöd ligger på 205.25 och under det förstås 200. Trenden är nedåtriktad och dessa stöd ska testas.
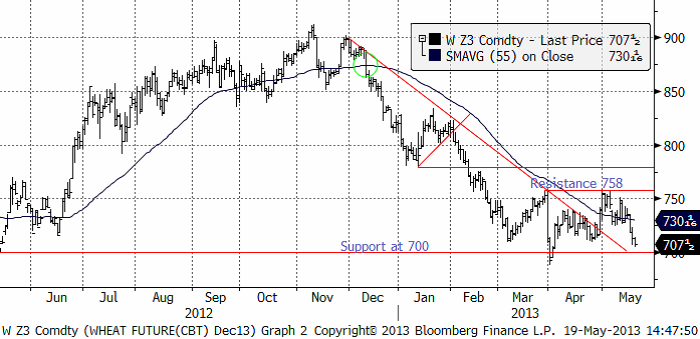
Decemberkontraktet på CBOT fortsatte falla och är nu nära stödet på 700 cent, som jag tror det är hög sannolikhet att marknaden till slut faller genom.
Nedan ser vi förändringen i terminskurvorna fredag till fredag. Maj-kontraktet på Matif är nu borta ur leken.
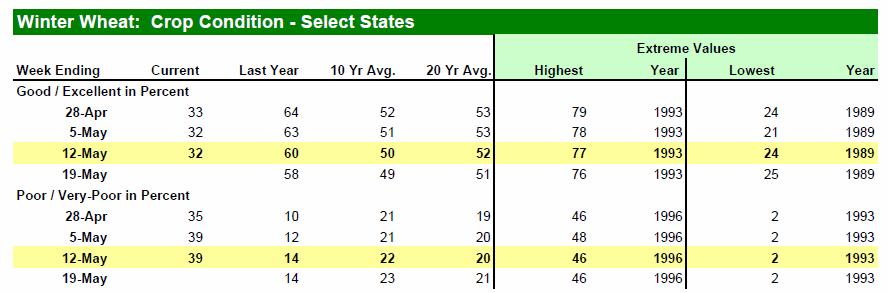
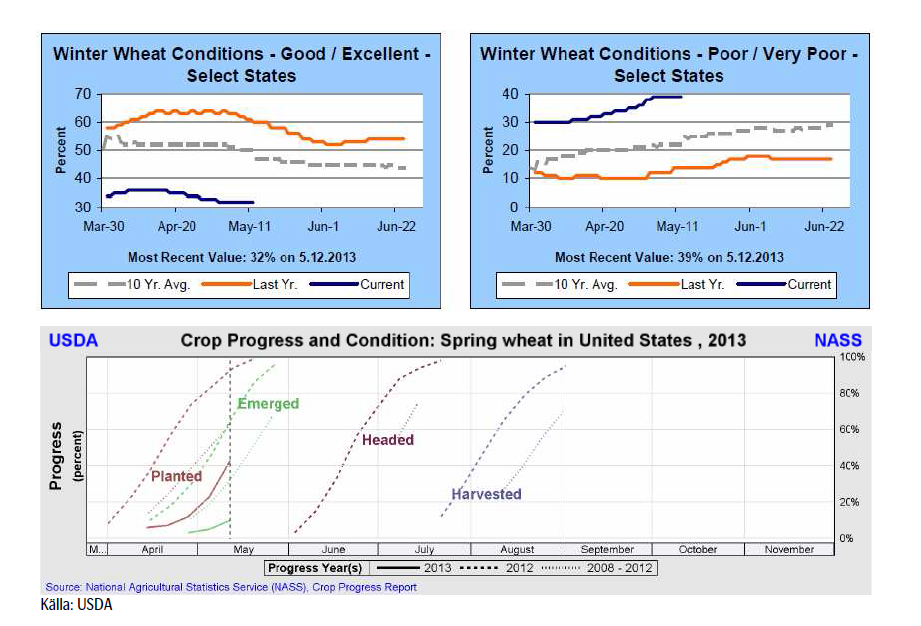
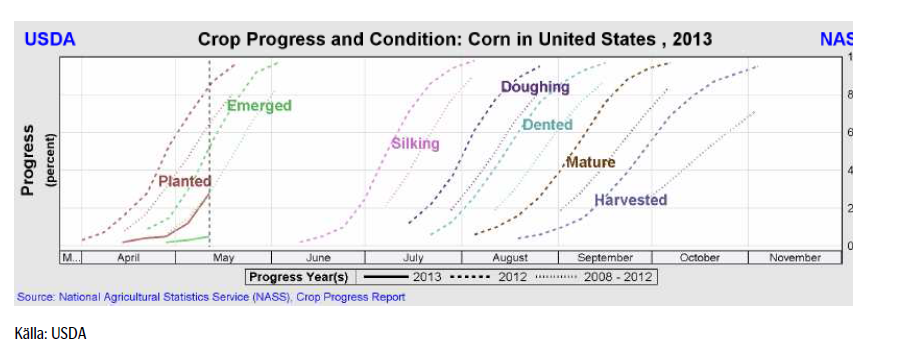
Måndagens Crop Progress rapport från USDA visar att tillståndet för det amerikanska höstvetet i stort sett var oförändrat i de 18 stater som rapporterar. Vete i merparten av de HRW producerande staterna klassas fortfarande som ”poor/very poor”, medan vete i de SRW producerande staterna mestadels klassas som ”good/excellent”. För de 18 staterna sammantaget så klassas 32% som ”good/excellent”, oförändrat från förra veckan men väl under förra årets 60% vid samma tid. Höstvete klassat som ”poor/very poor” uppgår till 39%, också oförändrat från förra veckan men väl över förra årets 14% vid samma tid.
Totalt har endast 29% av höstvetet gått i ax, vilket är långt efter förra årets 73% vid samma tid och det femåriga genomsnittet på 51% vid denna tidpunkt.
Sådden av vårvete i de 6 största staterna gjorde framsteg i veckan som gick och avancerade till 43%, upp rejält från 23% en vecka innan men fortfarande väl efter förra årets 92% och det femåriga genomsnittet på 63%.
Slutsatsen är att vi behåller vår säljrekommendation på vete.
Maltkorn
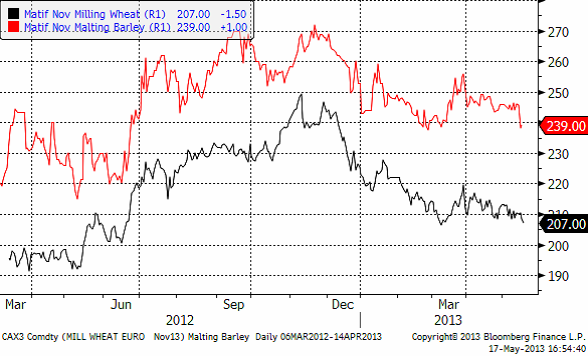
Maltkorn föll relativt kraftigt i veckan vilket gjorde att prisskillnaden mellan maltkorn och kvarnvete fick en ”återställare”. Relationen mellan maltkorn och vete har historiskt varit väldigt stabil.
Majs
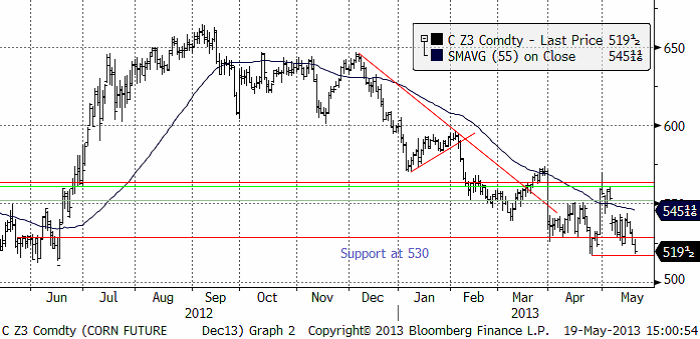
Majspriset (december 2013) är nu nere och testar årets bottennotering från april. Det ser ut att kunna bli ett brott nedåt. Det beror sannolikt på ”planting progress”-rapporten på måndag kväll klockan 22:00, eller på spekulationer om att sådden har varit rekordsnabb i det gynnsamma vädret.
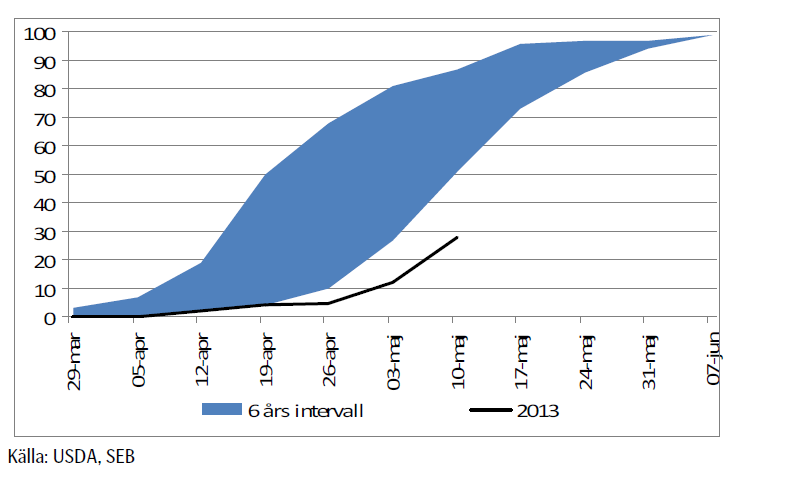
Sådden ligger efter i USA, men hade i måndags tagit sig upp till 28% färdigt.
Spekulationerna går just nu varma om vad måndagens siffra kommer att bli. Den mest optimistiska siffran är att 70% ska vara sått. Det skulle vara en ökning med 42 procentenheter. Den största veckovisa ökningstakten som lantbrukarna har mäktat med är 30% sedan 2007 är 30%. Det skedde mellan 26 mars och 3 maj. Om lantbrukarna lyckas så 30% igen, hamnar vi på 58% sått. Det gör att sådden hamnar strax under den lägre delen av intervallet för 2007 – 2012, där sådden år 2008 utgör botten. Att det är just 2008 får oss naturligtvis att minnas att priserna på spannmål det året föll kraftigt.
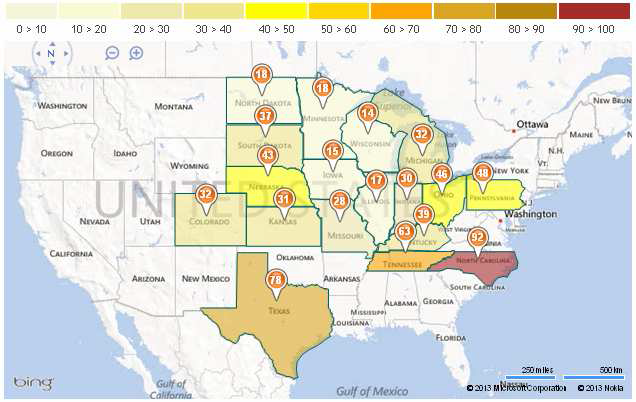
Sådden i Iowa, den största producenten, är nu avklarad till 15% – långt efter det femåriga genomsnittet på 79% – medan sådden hos den näst största producenten, Illinois, nu är avklarad till 17% – även det långt efter det femåriga genomsnittet på 64%.
En studie från University of Illinois visat att sådden av majs som görs efter den 10 maj riskerar att ge 8% lägre avkastning i Illinois. Sådd efter den 20 maj kan ge en 15% lägre avkastning och efter den 1 juni så riskerar lantbrukarna en 25% lägre avkastning.
I kartan nedan ser vi hur mycket som var sått för en vecka sedan, i delstat för delstat.
Det ligger dock en hel del ”luft” i efterfrågeprognosen från USDA, som vi skrev om förra veckan. Farmdoc har som vi tidigare skrivit om, beräknat att även en 14% lägre majsskörd än väntat ger högre utgående lager. Slutsatsen är att vi behåller vår säljrekommendation på majs.
Sojabönor
Sojabönorna visade förvånande styrka i fredags. Samtidigt som sådden väntas gå framåt för majs, faller förhoppningarna om att det som inte blir sått med majs blir besått med sojabönor. Starkare import från Kina bidrog också till att få upp sojabönspriset.
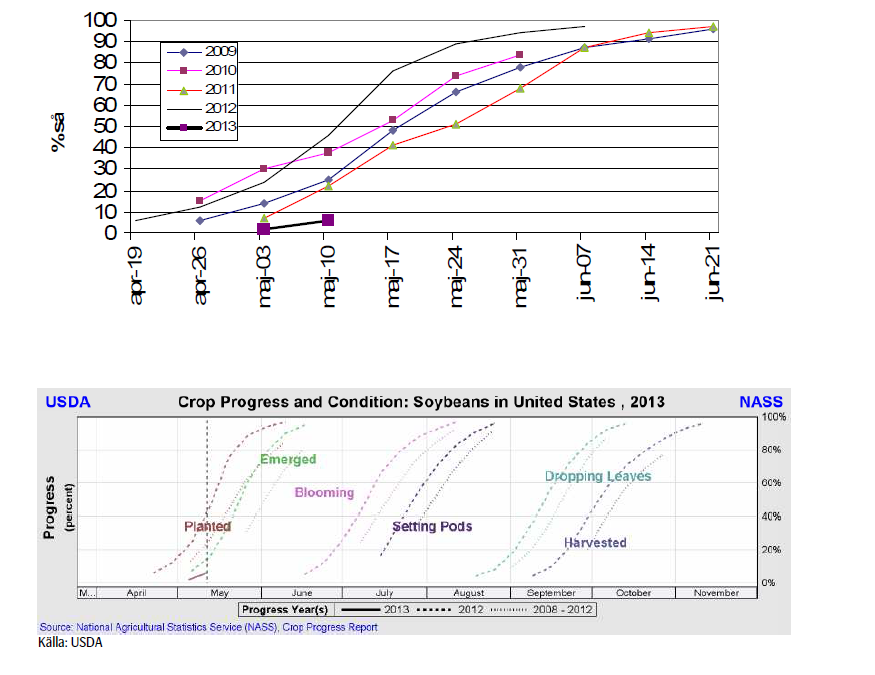
Måndagens Crop Progess visar att sådden av sojabönor nu är avklarad till 6%, vilket kan jämföras med 43% vid den här tiden förra året och det femåriga genomsnittet på 24%.
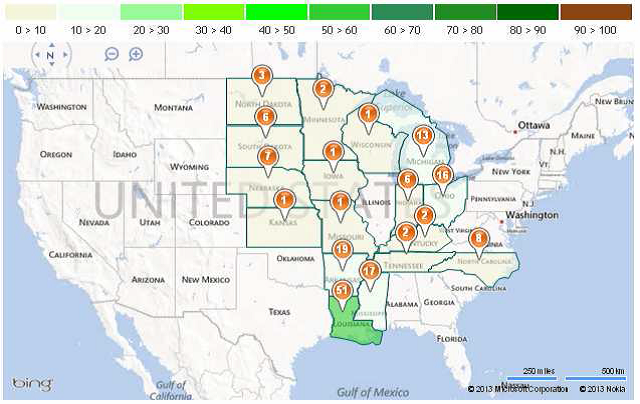
I Iowa, den största producenten, är sådden endast avklarad till 1% – vilket är långt efter det femåriga genomsnittet på 30% vid denna tid – samtidigt som sådden hos den näst största producenten, Illinois, inte ens har påbörjats. Det femåriga genomsnittet för Illinois vid den här tiden ligger på 19%.
Nedan ser vi en karta som visar såddens framåtskridande i delstat för delstat.
Samtidigt som exporten från USA är stark, håller exporten från Brasilien på att ta fart. Det har bland annat (till och med) gått tre fartyg med USA som destination.
Jag tror att det vi ser nu är en rekyl mot den fallande trenden och alltså ett tillfälle att sälja.
Slutsatsen är att vi behåller och upprepar vår säljrekommendation på sojabönor.
Raps
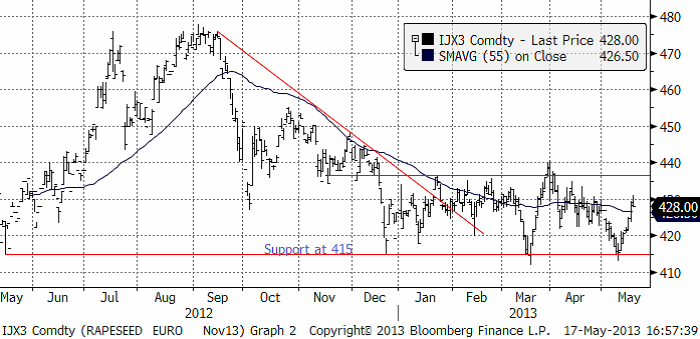
Rapspriset som förra veckan hade studsat på det tekniska stödet, rekylerade uppåt, men orkade inte hålla sig över 430 euro per ton. Under inflytande av sojamarknaden, kan priset hålla sig på den här nivån, men jag tror annars att det är ett bra tillfälle att sälja raps på.
Nedanför ser vi kvoten mellan rapsterminspriset (nov) mot sojabönspriset (nov). Vi ser att raps fram till maj månads början handlades allt dyrare i förhållande till sojabönor, men att detta, som vi påpekat börjat normaliseras genom ett större prisfall på raps än på sojabönor. Ännu finns det extra fallhöjd i rapspriset, eftersom rapsen fortfarande är dyr i ett historiskt perspektiv, i förhållande till sojabönor.
Skulle det tekniska stödet på 415 euro brytas, är detta en rejäl säljsignal. Jag tror att rapspriset kommer att falla. Dels för att sojabönorna bör ha en lång tid av fallande priser framför sig och dels för att rapsen är ovanligt dyr i förhållande till sojabönor.
Mjölk
Fonterras notering fortsatte ner på deras Global Dairy Trade auktion i onsdags.
Nedan ser vi terminspriserna framåt i tiden i fredags och veckan innan. Det är ett litet nedställ på SMP, men smöret ligger i princip på samma nivå som förra veckan.
[box]SEB Veckobrev Jordbruksprodukter är producerat av SEB Merchant Banking och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been compiled by SEB Merchant Banking, a division within Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) (“SEB”).
Opinions contained in this report represent the bank’s present opinion only and are subject to change without notice. All information contained in this report has been compiled in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. However, no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made with respect to the completeness or accuracy of its contents and the information is not to be relied upon as authoritative. Anyone considering taking actions based upon the content of this document is urged to base his or her investment decisions upon such investigations as he or she deems necessary. This document is being provided as information only, and no specific actions are being solicited as a result of it; to the extent permitted by law, no liability whatsoever is accepted for any direct or consequential loss arising from use of this document or its contents.
About SEB
SEB is a public company incorporated in Stockholm, Sweden, with limited liability. It is a participant at major Nordic and other European Regulated Markets and Multilateral Trading Facilities (as well as some non-European equivalent markets) for trading in financial instruments, such as markets operated by NASDAQ OMX, NYSE Euronext, London Stock Exchange, Deutsche Börse, Swiss Exchanges, Turquoise and Chi-X. SEB is authorized and regulated by Finansinspektionen in Sweden; it is authorized and subject to limited regulation by the Financial Services Authority for the conduct of designated investment business in the UK, and is subject to the provisions of relevant regulators in all other jurisdictions where SEB conducts operations. SEB Merchant Banking. All rights reserved.
Analys
’wait and see’ mode

So far this week, Brent Crude prices have strengthened by USD 1.3 per barrel since Monday’s opening. While macroeconomic concerns persist, they have somewhat abated, resulting in muted price reactions. Fundamentals predominantly influence global oil price developments at present. This week, we’ve observed highs of USD 89 per barrel yesterday morning and lows of USD 85.7 per barrel on Monday morning. Currently, Brent Crude is trading at a stable USD 88.3 per barrel, maintaining this level for the past 24 hours.

Additionally, there has been no significant price reaction to Crude following yesterday’s US inventory report (see page 11 attached):
- US commercial crude inventories (excluding SPR) decreased by 6.4 million barrels from the previous week, standing at 453.6 million barrels, roughly 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
- Total motor gasoline inventories decreased by 0.6 million barrels, approximately 4% below the five-year average.
- Distillate (diesel) inventories increased by 1.6 million barrels but remain weak historically, about 7% below the five-year average.
- Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude + products) decreased by 3.8 million barrels last week.
Regarding petroleum products, the overall build/withdrawal aligns with seasonal patterns, theoretically exerting limited effect on prices. However, the significant draw in commercial crude inventories counters the seasonality, surpassing market expectations and API figures released on Tuesday, indicating a draw of 3.2 million barrels (compared to Bloomberg consensus of +1.3 million). API numbers for products were more in line with the US DOE.
Against this backdrop, yesterday’s inventory report is bullish, theoretically exerting upward pressure on crude prices.
Yet, the current stability in prices may be attributed to reduced geopolitical risks, balanced against demand concerns. Markets are adopting a wait-and-see approach ahead of Q1 US GDP (today at 14:30) and the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, “core PCE prices” (tomorrow at 14:30). A stronger print could potentially dampen crude prices as market participants worry over the demand outlook.
Geopolitical “risk premiums” have decreased from last week, although concerns persist, highlighted by Ukraine’s strikes on two Russian oil depots in western Russia and Houthis’ claims of targeting shipping off the Yemeni coast yesterday.
With a relatively calmer geopolitical landscape, the market carefully evaluates data and fundamentals. While the supply picture appears clear, demand remains the predominant uncertainty that the market attempts to decode.
Analys
Also OPEC+ wants to get compensation for inflation

Brent crude has fallen USD 3/b since the peak of Iran-Israel concerns last week. Still lots of talk about significant Mid-East risk premium in the current oil price. But OPEC+ is in no way anywhere close to loosing control of the oil market. Thus what will really matter is what OPEC+ decides to do in June with respect to production in Q3-24 and the market knows this very well. Saudi Arabia’s social cost-break-even is estimated at USD 100/b today. Also Saudi Arabia’s purse is hurt by 21% US inflation since Jan 2020. Saudi needs more money to make ends meet. Why shouldn’t they get a higher nominal pay as everyone else. Saudi will ask for it

Brent is down USD 3/b vs. last week as the immediate risk for Iran-Israel has faded. But risk is far from over says experts. The Brent crude oil price has fallen 3% to now USD 87.3/b since it became clear that Israel was willing to restrain itself with only a muted counter attack versus Israel while Iran at the same time totally played down the counterattack by Israel. The hope now is of course that that was the end of it. The real fear has now receded for the scenario where Israeli and Iranian exchanges of rockets and drones would escalate to a point where also the US is dragged into it with Mid East oil supply being hurt in the end. Not everyone are as optimistic. Professor Meir Javedanfar who teaches Iranian-Israeli studies in Israel instead judges that ”this is just the beginning” and that they sooner or later will confront each other again according to NYT. While the the tension between Iran and Israel has faded significantly, the pain and anger spiraling out of destruction of Gaza will however close to guarantee that bombs and military strifes will take place left, right and center in the Middle East going forward.
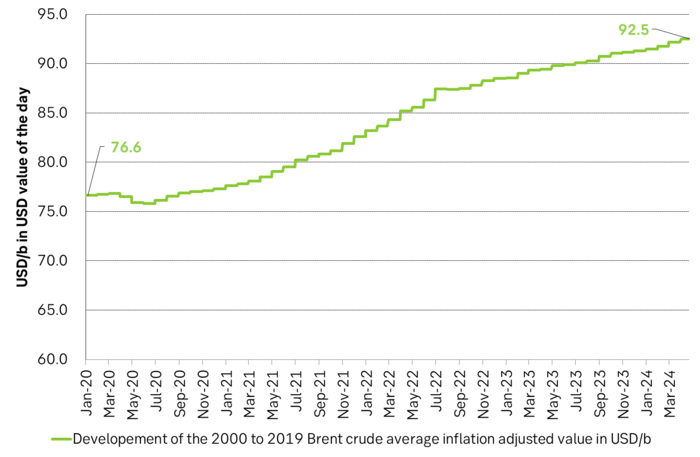
Also OPEC+ wants to get paid. At the start of 2020 the 20 year inflation adjusted average Brent crude price stood at USD 76.6/b. If we keep the averaging period fixed and move forward till today that inflation adjusted average has risen to USD 92.5/b. So when OPEC looks in its purse and income stream it today needs a 21% higher oil price than in January 2020 in order to make ends meet and OPEC(+) is working hard to get it.
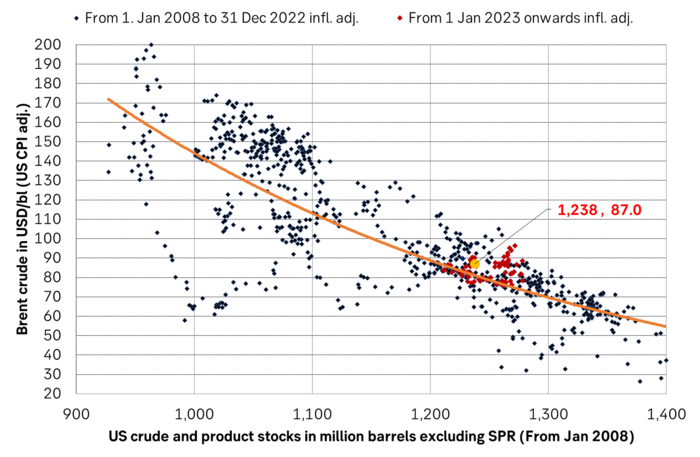
Much talk about Mid-East risk premium of USD 5-10-25/b. But OPEC+ is in control so why does it matter. There is much talk these days that there is a significant risk premium in Brent crude these days and that it could evaporate if the erratic state of the Middle East as well as Ukraine/Russia settles down. With the latest gains in US oil inventories one could maybe argue that there is a USD 5/b risk premium versus total US commercial crude and product inventories in the Brent crude oil price today. But what really matters for the oil price is what OPEC+ decides to do in June with respect to Q3-24 production. We are in no doubt that the group will steer this market to where they want it also in Q3-24. If there is a little bit too much oil in the market versus demand then they will trim supply accordingly.
Also OPEC+ wants to make ends meet. The 20-year real average Brent price from 2000 to 2019 stood at USD 76.6/b in Jan 2020. That same averaging period is today at USD 92.5/b in today’s money value. OPEC+ needs a higher nominal price to make ends meet and they will work hard to get it.
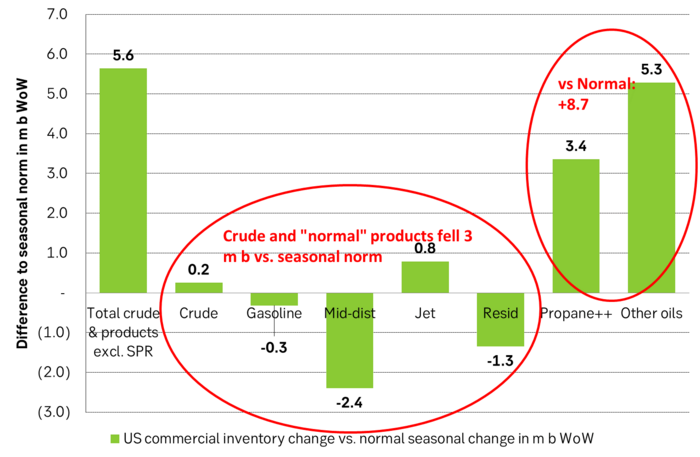
Inflation adjusted Brent crude price versus total US commercial crude and product stocks. A bit above the regression line. Maybe USD 5/b risk premium. But type of inventories matter. Latest big gains were in Propane and Other oils and not so much in crude and products
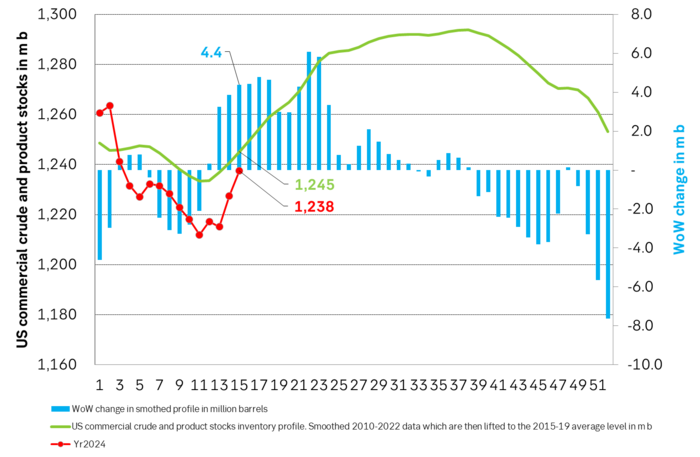
Total US commercial crude and product stocks usually rise by 4-5 m b per week this time of year. Gains have been very strong lately, but mostly in Propane and Other oils
Last week’s US inventory data. Big rise of 10 m b in commercial inventories. What really stands out is the big gains in Propane and Other oils
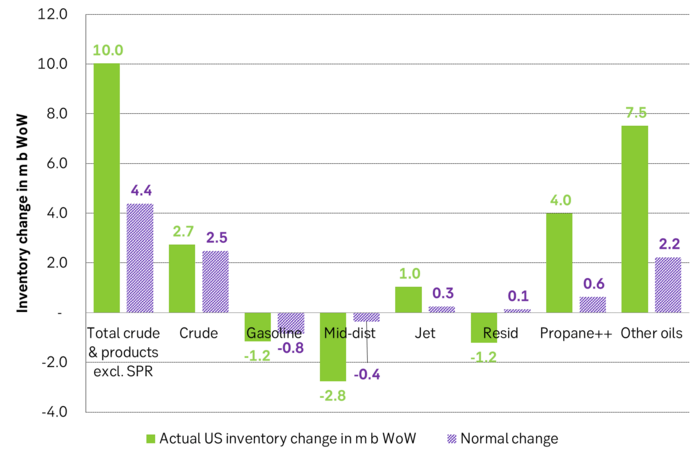
Take actual changes minus normal seasonal changes we find that US commercial crude and regular products like diesel, gasoline, jet and bunker oil actually fell 3 m b versus normal change.
Analys
Nat gas to EUA correlation will likely switch to negative in 2026/27 onward

Historically positive Nat gas to EUA correlation will likely switch to negative in 2026/27 onward

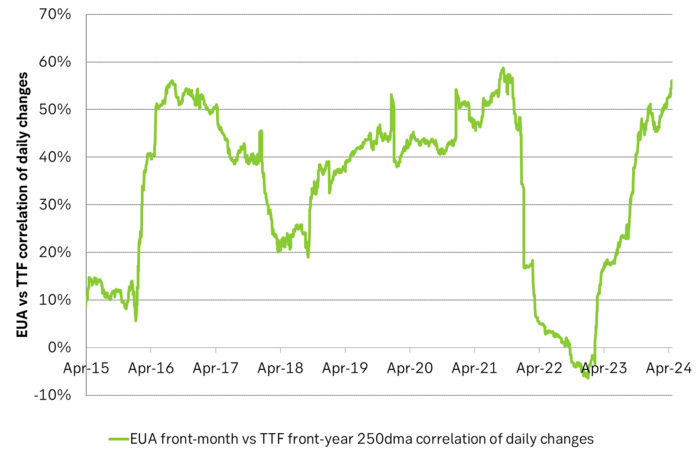
Historically there has been a strong, positive correlation between EUAs and nat gas prices. That correlation is still fully intact and possibly even stronger than ever as traders increasingly takes this correlation as a given with possible amplification through trading action.
The correlation broke down in 2022 as nat gas prices went ballistic but overall the relationship has been very strong for quite a few years.
The correlation between nat gas and EUAs should be positive as long as there is a dynamical mix of coal and gas in EU power sector and the EUA market is neither too tight nor too weak:
Nat gas price UP => ”you go black” by using more coal => higher emissions => EUA price UP
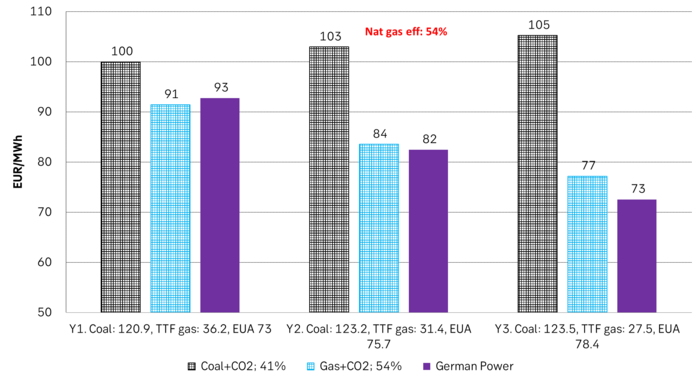
But in the future we’ll go beyond the dynamically capacity to flex between nat gas and coal. As the EUA price moves yet higher along with a tightening carbon market the dynamical coal to gas flex will max out. The EUA price will then trade significantly above where this flex technically will occur. There will still be quite a few coal fired power plants running since they are needed for grid stability and supply amid constrained local grids.
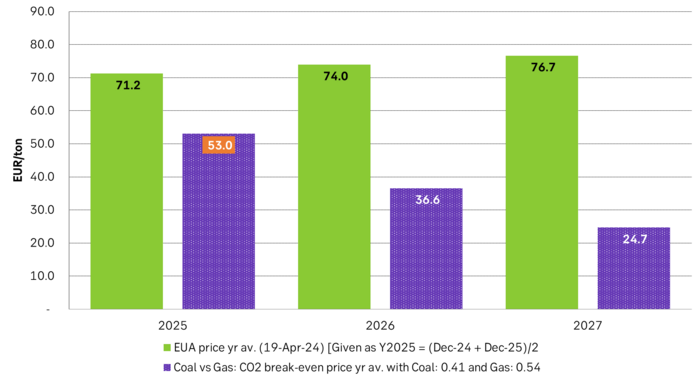
As it looks now we still have such overall coal to gas flex in 2024 and partially in 2025, but come 2026 it could be all maxed out. At least if we look at implied pricing on the forward curves where the forward EUA price for 2026 and 2027 are trading way above technical coal to gas differentials. The current forward pricing implications matches well with what we theoretically expect to see as the EUA market gets tighter and marginal abatement moves from the power sector to the industrial sector. The EUA price should then trade up and way above the technical coal to gas differentials. That is also what we see in current forward prices for 2026 and 2027.
The correlation between nat gas and EUAs should then (2026/27 onward) switch from positive to negative. What is left of coal in the power mix will then no longer be dynamically involved versus nat gas and EUAs. The overall power price will then be ruled by EUA prices, nat gas prices and renewable penetration. There will be pockets with high cost power in the geographical points where there are no other alternatives than coal.
The EUA price is an added cost of energy as long as we consume fossil energy. Thus both today and in future years we’ll have the following as long as we consume fossil energy:
EUA price UP => Pain for consumers of energy => lower energy consumption, faster implementation of energy efficiency and renewable energy => lower emissions
The whole idea with the EUA price is after all that emissions goes down when the EUA price goes up. Either due to reduced energy consumption directly, accelerated energy efficiency measures or faster switch to renewable energy etc.
Let’s say that the coal to gas flex is maxed out with an EUA price way above the technical coal to gas differentials in 2026/27 and later. If the nat gas price then goes up it will no longer be an option to ”go black” and use more coal as the distance to that is too far away price vise due to a tight carbon market and a high EUA price. We’ll then instead have that:
Nat gas higher => higher energy costs with pain for consumers => weaker nat gas / energy demand & stronger drive for energy efficiency implementation & stronger drive for more non-fossil energy => lower emissions => EUA price lower
And if nat gas prices goes down it will give an incentive to consume more nat gas and thus emit more CO2:
Cheaper nat gas => Cheaper energy costs altogether, higher energy and nat gas consumption, less energy efficiency implementations in the broader economy => emissions either goes up or falls slower than before => EUA price UP
Historical and current positive correlation between nat gas and EUA prices should thus not at all be taken for granted for ever and we do expect this correlation to switch to negative some time in 2026/27.
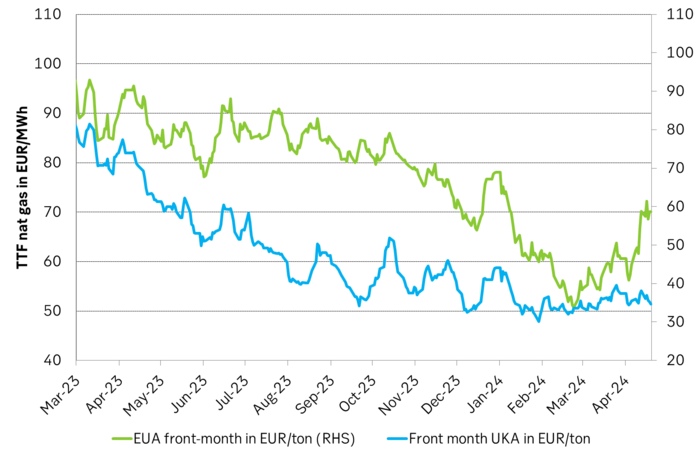
In the UK there is hardly any coal left at all in the power mix. There is thus no option to ”go black” and burn more coal if the nat gas price goes up. A higher nat gas price will instead inflict pain on consumers of energy and lead to lower energy consumption, lower nat gas consumption and lower emissions on the margin. There is still some positive correlation left between nat gas and UKAs but it is very weak and it could relate to correlations between power prices in the UK and the continent as well as some correlations between UKAs and EUAs.
Correlation of daily changes in front month EUA prices and front-year TTF nat gas prices, 250dma correlation.
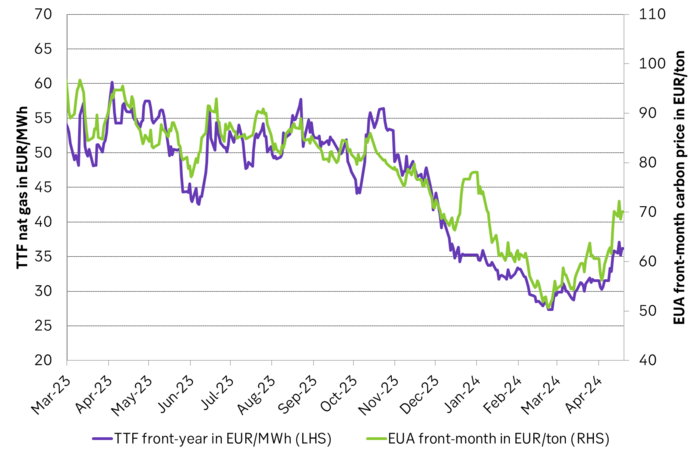
EUA price vs front-year TTF nat gas price since March 2023
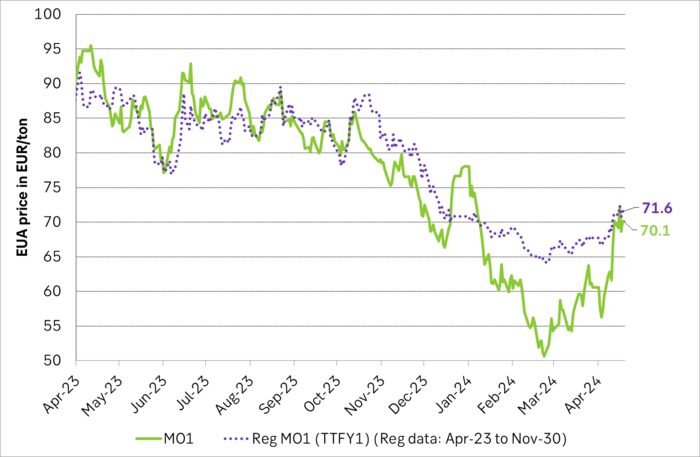
Front-month EUA price vs regression function of EUA price vs. nat gas derived from data from Apr to Nov last year.
The EUA price vs the UKA price. Correlations previously, but not much any more.
Forward German power prices versus clean cost of coal and clean cost of gas power. Coal is totally priced out vs power and nat gas on a forward 2026/27 basis.
Forward price of EUAs versus technical level where dynamical coal to gas flex typically takes place. EUA price for 2026/27 is at a level where there is no longer any price dynamical interaction or flex between coal and nat gas. The EUA price should/could then start to be negatively correlated to nat gas.
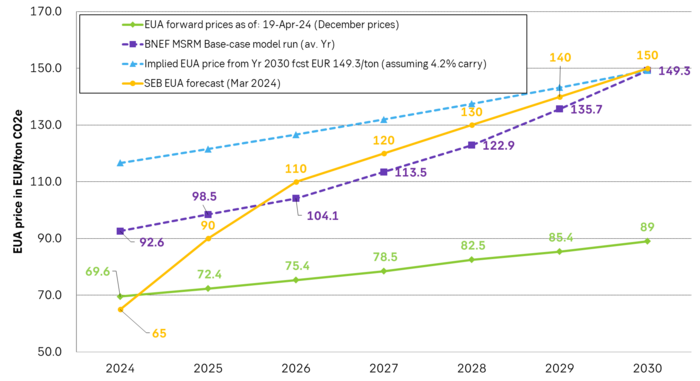
Forward EAU price vs. BNEF base model run (look for new update will come in late April), SEB’s EUA price forecast.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanGuldpriset når nytt all time high och bryter igenom 2300 USD
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanLundin Mining får köprekommendation av BMO
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanCentralbanker fortsatte att köpa guld under februari
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanUSAs stigande konsumtion av naturgas
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanKakaomarknaden är extrem för tillfället
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanHur mår den svenska skogsbraschen? Två favoritaktier
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBoliden på 20 minuter
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanBetydande underskott i utbudet av olja kan få priset att blossa upp