Analys
SEB – Jordbruksprodukter vecka 8, 2012
 Den senaste veckan har det varit små rörelser på marknaderna för jordbruksprodukter. Det betydande fallet i vetepriset efter den ”key reversal day” vi berättade om för två veckor sedan följdes av en liten rekyl uppåt i veckan som gått, men överlag står marknaderna för spannmål och väger, utan att vare sig köpare eller säljare har fått övertaget.
Den senaste veckan har det varit små rörelser på marknaderna för jordbruksprodukter. Det betydande fallet i vetepriset efter den ”key reversal day” vi berättade om för två veckor sedan följdes av en liten rekyl uppåt i veckan som gått, men överlag står marknaderna för spannmål och väger, utan att vare sig köpare eller säljare har fått övertaget.
USDA:s Outlook Forum går av stapeln idag torsdag och på fredag och det väntas komma ny information från USDA från denna på fredag. Konferensen sänds som ”webinar” och mer om detta kan läsas på: www.usda.gov/oce/forum .”Plantings” väntas uppgå till 94 miljoner acres för majs, 74 miljoner acres för sojabönor och 56.5 miljoner acres för vete.
Informationen väntas allmänt av marknaden att vara ”bearish” för spannmål. Enligt USDA väntas amerikanska bönder så mest majs sedan 1944. Mer finns att läsa på Bloomberg.
Detsamma gäller sojabönor, men minutiösa gissningar om arealen för USAs areal om 1-2 miljoner acres måste förstås ställas mot skördeestimaten för Argentina som ligger på mellan 43 och 48 mt. Den skillnaden motsvarar nästan 5 miljoner acres.
Vete
Vi har haft en negativ tro på vetets prisutveckling framöver, främst baserat på att La Niña väntas klinga av. En stor del av ”marknaden” tycks dela vår negativa syn. Till bilden av betydande lager hör Australiens lagernivå som i januari uppgick till 25.6 mt. Kanada som de senaste två åren drabbats av översvämningar väntas i år inte råka ut för detta, eftersom det tvärtom är torrt.
Algeriet har annonserat en tender för leverans i maj på 125,000 ton. Frankrike väntas ta hem denna, men det är sannolikt den sista för säsongen och vi är bara i februari månad. Algeriet väntas importera 6.1 mt under 2011/12-säsongen som slutar i juni. Inköpen görs av Algeriets statliga Office Algerien Interprofessionnel de Cereales (”OAIC”).
 Trots att det ännu är tidigt och därmed svårt att uttala sig om och bedöma konsekvenserna för grödor utsatta för den extrema kylan som drabbade Europa, med temperaturer under -30 grader i vissa delar, gör franska Strategie Grains ett försök och säger att köldknäppen inte kommer att orsaka någon allvarligare skada utan enligt deras första analys ”så kommer kylan inte att leda till större bortfall än vid ett normalår” men att en viss risk kvarstår. Där skador uppstått kommer dessa dock att ersättas med vårgrödor och de justerar upp sitt estimat för majsproduktion med 300 000 ton till 62.6 mt, vilket fortfarande är en minskning med 4 procent jämfört med 2011. Estimatet för korn ökades med 100 000 ton till 54.6 mt vilket återspeglar förhoppningar om en ökad sådd av vårgrödor i Tjeckien och Slovakien. Prognosen för EU’s ”mjuka” veteproduktion i år justeras ned med 600 000 ton till 132.7 mt vilket fortfarande är en ökning med 3 procent jämfört med förra året och lägger man till durumvete så estimeras den totala veteproduktion till 141.5 mt. Nedjusteringen beror huvudsakligen på förändringar i areal.
Trots att det ännu är tidigt och därmed svårt att uttala sig om och bedöma konsekvenserna för grödor utsatta för den extrema kylan som drabbade Europa, med temperaturer under -30 grader i vissa delar, gör franska Strategie Grains ett försök och säger att köldknäppen inte kommer att orsaka någon allvarligare skada utan enligt deras första analys ”så kommer kylan inte att leda till större bortfall än vid ett normalår” men att en viss risk kvarstår. Där skador uppstått kommer dessa dock att ersättas med vårgrödor och de justerar upp sitt estimat för majsproduktion med 300 000 ton till 62.6 mt, vilket fortfarande är en minskning med 4 procent jämfört med 2011. Estimatet för korn ökades med 100 000 ton till 54.6 mt vilket återspeglar förhoppningar om en ökad sådd av vårgrödor i Tjeckien och Slovakien. Prognosen för EU’s ”mjuka” veteproduktion i år justeras ned med 600 000 ton till 132.7 mt vilket fortfarande är en ökning med 3 procent jämfört med förra året och lägger man till durumvete så estimeras den totala veteproduktion till 141.5 mt. Nedjusteringen beror huvudsakligen på förändringar i areal.
Produktionen av spannmål och oljeväxter i Kanada 2012/13 förväntas bli något lägre än vad som estimerades för en månad sedan, men kommer att överstiga produktionen för 2011/12 enligt uppdaterad statistik från Ag Canada.
Produktionen avser de åtta huvudsakliga spannmålen och oljeväxterna och beräknas uppgå till 70.12 mt under 2012/13, en nedjustering från 70.32 mt i januari och en jämförelse med 65.85 mt 2011/12. I detta inkluderas canola, linfrö, sojabönor, vete, havre, korn, majs och råg.
Utgående lager för 2012/13 justeras ned till 11.70 mt (från 13.28 mt i januari) och den totala exporten för samma period estimeras till 33.27 mt, en liten ökning från förra månadens 33.04 mt.
Egyptens GASC har återigen köpt vete från USA, denna gång 180 000 ton. USA:s vete är just nu billigare än franskt, även med frakten beaktad.
Det amerikanska vetet har haft svårt att hävda sig under 2011/12 och förlorat marknadsandelar till i första hand Ryssland, eftersom ryskt vete flödat in på marknaden efter att exportförbudet hävdes förra sommaren, men har även haft svårt att konkurrera prismässigt med både Argentina och Frankrike.
I den senaste budgivningen fanns dock vare sig Ryssland eller Argentina med och det franska vetet som erbjöds var betydligt dyrare, trots högre fraktkostnad från USA till Egypten. Rysslands frånvaro denna gång kan troligtvis härledas till väderrelaterade logistik problem. Det är fruset i hamnarna och till och med lastade fartyg rapporteras ha svårt att segla ut.
Rysslands spannmålsexport har avtagit och uppgick endast till 250 000 ton under de två första veckorna i februari, en klar skillnad från en tidigare exporttakt på ungefär 2.8 mt per månad under 2011/12 fram till slutet på januari. Landet ska dock ha tillräckligt med spannmål för att täcka sitt eget behov och planerar därför att fortsätta med sin export som förväntas uppgå till 25 mt. Fram till idag har Ryssland exporterat ca 19.8 mt.
Ukraina har exporterat ca 600 000 ton spannmål, framförallt majs, de 15 första dagarna i februari till följd av den ovanligt stränga kylan och efter att regeringen bett handlare att vara restriktiva i sin export av vete. Det kan jämföras de 1.9 mt som exporterades under januari. Exporten av vete under första halvan av februari var lägre än 100 000 ton, jämfört med 540 000 ton under månaden innan.
Det sägs också att regeringen och landets spannmålshandlare nu har kommit överens om ett inofficiellt tak på 1.7 mt för export av vete under perioden februari till juli till följd av den svåra torkan i höstas. Med den begränsningen skulle den totala veteexporten komma att uppgå till 4.8 mt (jämfört med USDA’s prognos på 6.0 mt). Kazakstan räknar med en möjlig halvering av sin spannmålsskörd i år med en estimerad genomsnittlig nivå på 13-15 mt enligt landets jordbruksminister. Ett sådant resultat skulle ligga långt under de 27 mt spannmål som landet skördade förra året till följd av ett utmärkt väder under hela växtsäsongen, men det skulle fortfarande vara i linje med det 20-åriga genomsnittet. Vi har lite svårt att tolka detta påstående, eftersom Kazakstans jordbruksminister samtidigt påstår att arealen kommer att vara högre i år än förra året…. (Låter lite som ”Vremja” har återuppstått).
Pakistan kan komma att exportera upp till 1.5 mt vete i år, vilket matchar förra årets rekord, delvis tack vare en förväntad rekordskörd för tredje året i rad. Skörden förväntas uppgå till 24 mt ton i år, i stort sett oförändrad från förra året. Pakistan har en geografisk fördel i att exportera vete till Sydostasien och där kostnaderna för containerfrakt är försumbara. Landet var också en stor exportör förra året eftersom dess vete var bland det billigaste i världen under perioden maj-juli men exporten avtog efter att Ryssland hävde sitt exportförbud.
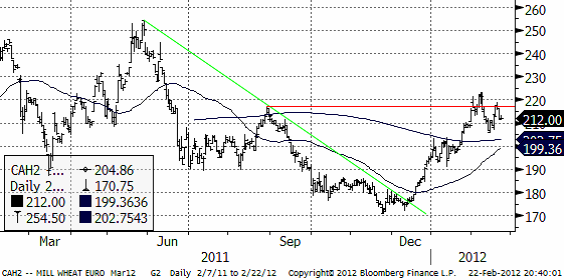
Nedan ser vi kursdiagrammet för marskontraktet på Matif. Uppgången den senaste veckan lyckades inte notera en ny toppnotering (över 225) och det får tolkas som ett svaghetstecken.
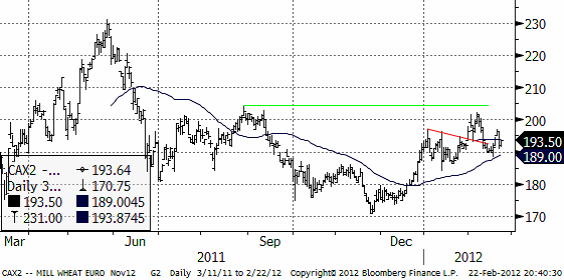
Nedan ser vi novemberkontraktet, som inte lyckats ta sig över huvudmotståndet på 205 euro per ton. Priset står och väger. 190 euro ser ut att utgöra ett förhållandevis starkt stöd och på ovansidan finns motståndet på 205. Just nu finns inga tecken på att marknaden på ett förestående utbrott från det här intervallet.
Maltkorn
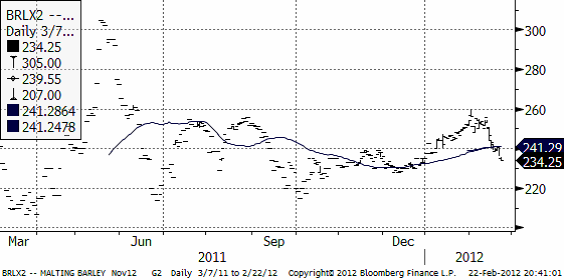
Maltkornet har handlats ner kraftigt. Tekniska stöd är brutna och nästa finns först nere på 220 euro för novemberleverans. Terminen handlas just nu i 234 euro.
Potatis
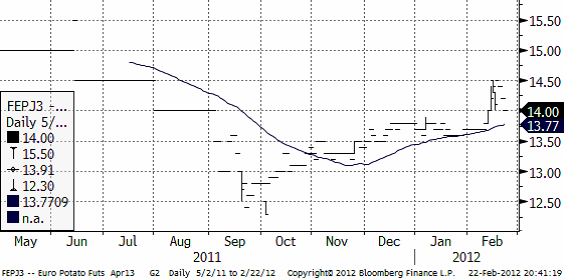
Priset på industripotatis steg upp till 14.50 euro för leverans i april 2013, men rekylerade sedan ner till 14 euro per deciton. Pristrenden är uppåtriktad.
Majs
Nederbörden i norra Argentina, Paraguay och södra Brasilien ligger på en normal nivå för den här årstiden. Torkan är historia och odlingsförhållandena har stabiliserats. Uruguay är dock fortfarande torrt.
Kina importerade 750 kt majs i januari och det är den högsta noteringen för månaden på 12 år. Spreaden mellan kinesiska priser och importpriser ligger på rekordnivåer. Det finns ett sug efter majs in mot Kina.
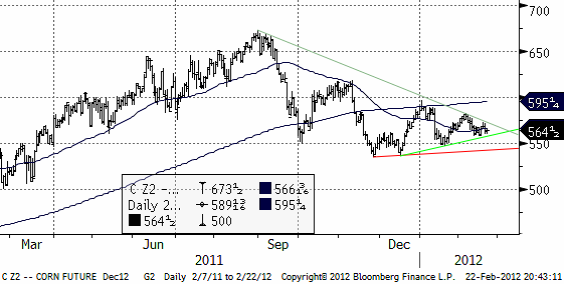
Nedan ser vi decemberkontraktet på majs på CBOT, där priserna bildat en klassisk ”triangelformation”. När priserna lämnar den, brukar detta vara starten på en större kursrörelse. Vi har trott och tror på fallande priser, men vill inte ta några positioner just nu, utan vill avvakta utbrottet ur triangeln. I synnerhet Kinas efterfrågan är ett stort frågetecken.
Sojabönor
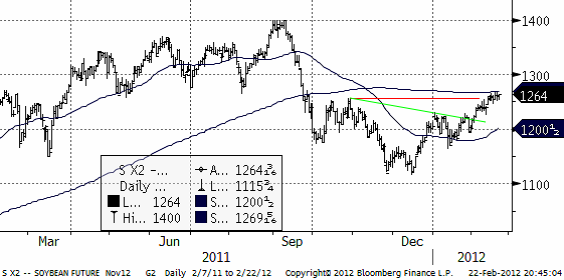
Sojabönorna gynnas av att vädret i Sydamerika har stabiliserats, eller rättare sagt, priset missgynnas. Priset har segat sig upp, efter att ha brutit en motståndslinje (den gröna i diagrammet nedan), men har inte på ett övertygande sätt gått över den röda motståndslinjen i diagrammet. Uppgången har förlorat momentum de senaste dagarna och det skulle kunna förebåda en kortsiktig rekyl nedåt.
Raps
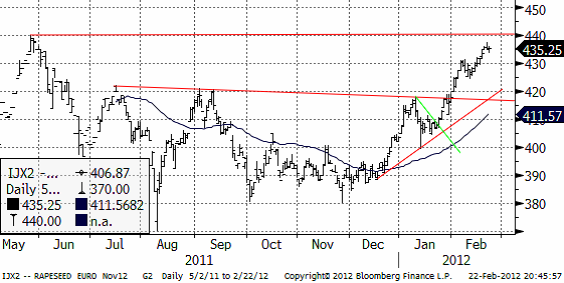
Novemberkontraktet har visat exceptionell styrka. Vi ser dock i diagrammet att priset nu ligger ganska nära 440 euro per ton. Detta är toppnoteringen från maj förra året och också en jämn siffra. Folk brukar hänga upp sina ”take profit” ordrar på jämna siffror. Av denna anledning tycker vi att det är ett utmärkt tillfälle att sälja terminer på novemberraps på dagens kursnivå om 435 euro.
Mjölk
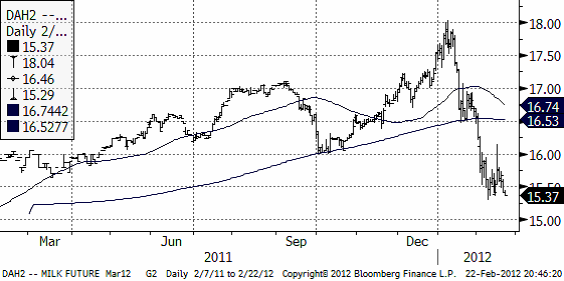
För två veckor sedan skrev vi att vi ansåg att prisfallet endast nått halvvägs och antog att fallet kunde nå 16. Det visade sig vara lite för försiktigt när vi nu ser att priset ligger på 15.37. Ser vi priset falla under februaris lägsta notering på marskontraktet finns potential att nå 15, men lejonparten av kursfallet bör vara över.
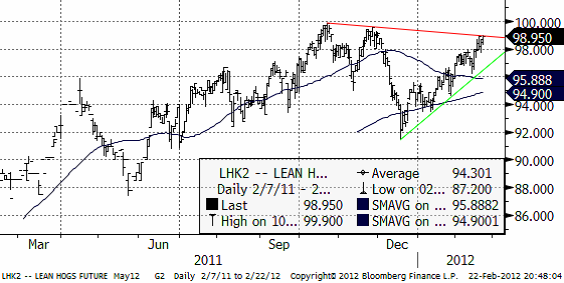
Gris
Priset på lean hogs som för majkontraktet nått 98.95 cent per pund, ligger precis under en motståndslinje (röd i diagrammet nedan). 100 cent borde vara ett hårt motstånd för priset att ta sig igenom. Det finns alltså gott om motstånd ansamlade precis ovanför dagens kurs. Om man måste välja, så väljer vi att vara sålda lean hogs här. Skulle priset bryta 100 måste vi omvärdera detta, naturligtvis.
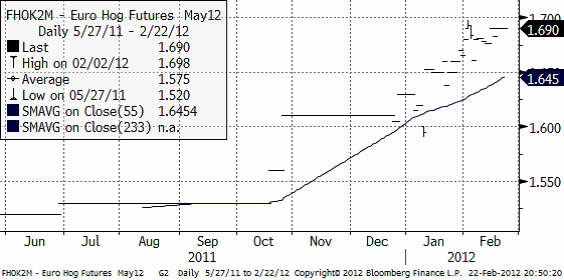
Priset i Europa har för majleverans stigit sedan i oktober och ligger nu på 1.69 euro per kilo. Bakom ligger bland annat eurons svaghet, men det förklarar inte allt. För ett år sedan var priserna så låga att bland annat svensk produktion inte bar sig. Med dagens priser är branschen vid vattenytan. Det fundamentala ”golvet” för priset ligger alltså bara precis under eller vid den här prisnivån, trots prisuppgången. Med det sagt, så är det ovanligt med en så lång prisuppgång utan rekyl och tyska priser ligger långt över amerikanska.
Valutor
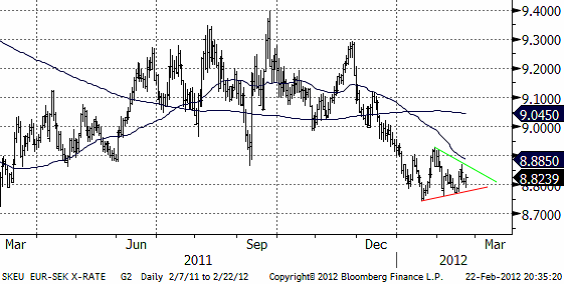
EURSEK
En ”triangelformation” har bildats sedan mitten av januari. Man bör invänta riktningen på utbrottet från den för att fatta beslut om att köpa eller sälja eursek.
8.70 har tidigare varit ett starkt ”golv” för växelkursen.
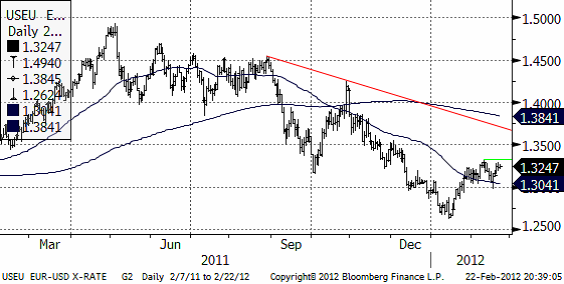
EURUSD
Kursen ligger inom ett intervall på 1.30 och 1.33.
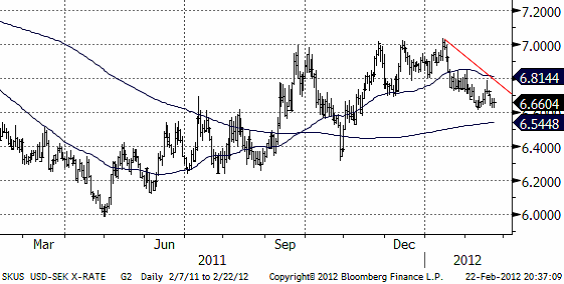
USDSEK
Dollarn ligger för närvarande i sjunkande trend.
[box]SEB Veckobrev Jordbruksprodukter är producerat av SEB Merchant Banking och publiceras i samarbete och med tillstånd på Råvarumarknaden.se[/box]
Disclaimer
The information in this document has been compiled by SEB Merchant Banking, a division within Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB (publ) (“SEB”).
Opinions contained in this report represent the bank’s present opinion only and are subject to change without notice. All information contained in this report has been compiled in good faith from sources believed to be reliable. However, no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is made with respect to the completeness or accuracy of its contents and the information is not to be relied upon as authoritative. Anyone considering taking actions based upon the content of this document is urged to base his or her investment decisions upon such investigations as he or she deems necessary. This document is being provided as information only, and no specific actions are being solicited as a result of it; to the extent permitted by law, no liability whatsoever is accepted for any direct or consequential loss arising from use of this document or its contents.
About SEB
SEB is a public company incorporated in Stockholm, Sweden, with limited liability. It is a participant at major Nordic and other European Regulated Markets and Multilateral Trading Facilities (as well as some non-European equivalent markets) for trading in financial instruments, such as markets operated by NASDAQ OMX, NYSE Euronext, London Stock Exchange, Deutsche Börse, Swiss Exchanges, Turquoise and Chi-X. SEB is authorized and regulated by Finansinspektionen in Sweden; it is authorized and subject to limited regulation by the Financial Services Authority for the conduct of designated investment business in the UK, and is subject to the provisions of relevant regulators in all other jurisdictions where SEB conducts operations. SEB Merchant Banking. All rights reserved.
Analys
Tightening fundamentals – bullish inventories from DOE

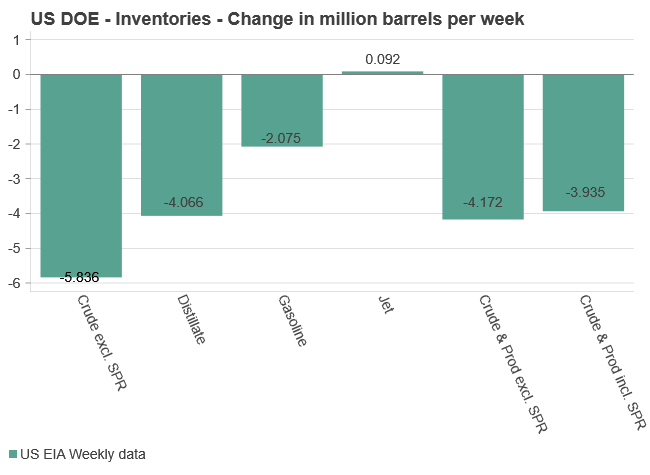
The latest weekly report from the US DOE showed a substantial drawdown across key petroleum categories, adding more upside potential to the fundamental picture.

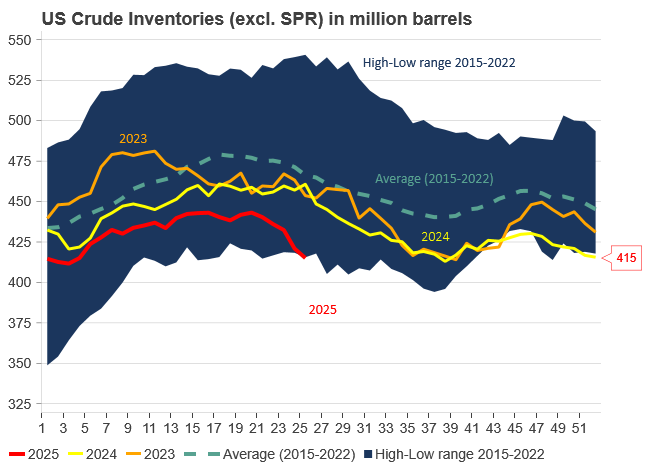
Commercial crude inventories (excl. SPR) fell by 5.8 million barrels, bringing total inventories down to 415.1 million barrels. Now sitting 11% below the five-year seasonal norm and placed in the lowest 2015-2022 range (see picture below).
Product inventories also tightened further last week. Gasoline inventories declined by 2.1 million barrels, with reductions seen in both finished gasoline and blending components. Current gasoline levels are about 3% below the five-year average for this time of year.
Among products, the most notable move came in diesel, where inventories dropped by almost 4.1 million barrels, deepening the deficit to around 20% below seasonal norms – continuing to underscore the persistent supply tightness in diesel markets.
The only area of inventory growth was in propane/propylene, which posted a significant 5.1-million-barrel build and now stands 9% above the five-year average.
Total commercial petroleum inventories (crude plus refined products) declined by 4.2 million barrels on the week, reinforcing the overall tightening of US crude and products.
Analys
Bombs to ”ceasefire” in hours – Brent below $70

A classic case of “buy the rumor, sell the news” played out in oil markets, as Brent crude has dropped sharply – down nearly USD 10 per barrel since yesterday evening – following Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. air base in Qatar. The immediate reaction was: “That was it?” The strike followed a carefully calibrated, non-escalatory playbook, avoiding direct threats to energy infrastructure or disruption of shipping through the Strait of Hormuz – thus calming worst-case fears.

After Monday morning’s sharp spike to USD 81.4 per barrel, triggered by the U.S. bombing of Iranian nuclear facilities, oil prices drifted sideways in anticipation of a potential Iranian response. That response came with advance warning and caused limited physical damage. Early this morning, both the U.S. President and Iranian state media announced a ceasefire, effectively placing a lid on the immediate conflict risk – at least for now.
As a result, Brent crude has now fallen by a total of USD 12 from Monday’s peak, currently trading around USD 69 per barrel.
Looking beyond geopolitics, the market will now shift its focus to the upcoming OPEC+ meeting in early July. Saudi Arabia’s decision to increase output earlier this year – despite falling prices – has drawn renewed attention considering recent developments. Some suggest this was a response to U.S. pressure to offset potential Iranian supply losses.
However, consensus is that the move was driven more by internal OPEC+ dynamics. After years of curbing production to support prices, Riyadh had grown frustrated with quota-busting by several members (notably Kazakhstan). With Saudi Arabia cutting up to 2 million barrels per day – roughly 2% of global supply – returns were diminishing, and the risk of losing market share was rising. The production increase is widely seen as an effort to reassert leadership and restore discipline within the group.
That said, the FT recently stated that, the Saudis remain wary of past missteps. In 2018, Riyadh ramped up output at Trump’s request ahead of Iran sanctions, only to see prices collapse when the U.S. granted broad waivers – triggering oversupply. Officials have reportedly made it clear they don’t intend to repeat that mistake.
The recent visit by President Trump to Saudi Arabia, which included agreements on AI, defense, and nuclear cooperation, suggests a broader strategic alignment. This has fueled speculation about a quiet “pump-for-politics” deal behind recent production moves.
Looking ahead, oil prices have now retraced the entire rally sparked by the June 13 Israel–Iran escalation. This retreat provides more political and policy space for both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia. Specifically, it makes it easier for Riyadh to scale back its three recent production hikes of 411,000 barrels each, potentially returning to more moderate increases of 137,000 barrels for August and September.
In short: with no major loss of Iranian supply to the market, OPEC+ – led by Saudi Arabia – no longer needs to compensate for a disruption that hasn’t materialized, especially not to please the U.S. at the cost of its own market strategy. As the Saudis themselves have signaled, they are unlikely to repeat previous mistakes.
Conclusion: With Brent now in the high USD 60s, buying oil looks fundamentally justified. The geopolitical premium has deflated, but tensions between Israel and Iran remain unresolved – and the risk of missteps and renewed escalation still lingers. In fact, even this morning, reports have emerged of renewed missile fire despite the declared “truce.” The path forward may be calmer – but it is far from stable.
Analys
A muted price reaction. Market looks relaxed, but it is still on edge waiting for what Iran will do

Brent crossed the 80-line this morning but quickly fell back assigning limited probability for Iran choosing to close the Strait of Hormuz. Brent traded in a range of USD 70.56 – 79.04/b last week as the market fluctuated between ”Iran wants a deal” and ”US is about to attack Iran”. At the end of the week though, Donald Trump managed to convince markets (and probably also Iran) that he would make a decision within two weeks. I.e. no imminent attack. Previously when when he has talked about ”making a decision within two weeks” he has often ended up doing nothing in the end. The oil market relaxed as a result and the week ended at USD 77.01/b which is just USD 6/b above the year to date average of USD 71/b.

Brent jumped to USD 81.4/b this morning, the highest since mid-January, but then quickly fell back to a current price of USD 78.2/b which is only up 1.5% versus the close on Friday. As such the market is pricing a fairly low probability that Iran will actually close the Strait of Hormuz. Probably because it will hurt Iranian oil exports as well as the global oil market.
It was however all smoke and mirrors. Deception. The US attacked Iran on Saturday. The attack involved 125 warplanes, submarines and surface warships and 14 bunker buster bombs were dropped on Iranian nuclear sites including Fordow, Natanz and Isfahan. In response the Iranian Parliament voted in support of closing the Strait of Hormuz where some 17 mb of crude and products is transported to the global market every day plus significant volumes of LNG. This is however merely an advise to the Supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and the Supreme National Security Council which sits with the final and actual decision.
No supply of oil is lost yet. It is about the risk of Iran closing the Strait of Hormuz or not. So far not a single drop of oil supply has been lost to the global market. The price at the moment is all about the assessed risk of loss of supply. Will Iran choose to choke of the Strait of Hormuz or not? That is the big question. It would be painful for US consumers, for Donald Trump’s voter base, for the global economy but also for Iran and its population which relies on oil exports and income from selling oil out of that Strait as well. As such it is not a no-brainer choice for Iran to close the Strait for oil exports. And looking at the il price this morning it is clear that the oil market doesn’t assign a very high probability of it happening. It is however probably well within the capability of Iran to close the Strait off with rockets, mines, air-drones and possibly sea-drones. Just look at how Ukraine has been able to control and damage the Russian Black Sea fleet.
What to do about the highly enriched uranium which has gone missing? While the US and Israel can celebrate their destruction of Iranian nuclear facilities they are also scratching their heads over what to do with the lost Iranian nuclear material. Iran had 408 kg of highly enriched uranium (IAEA). Almost weapons grade. Enough for some 10 nuclear warheads. It seems to have been transported out of Fordow before the attack this weekend.
The market is still on edge. USD 80-something/b seems sensible while we wait. The oil market reaction to this weekend’s events is very muted so far. The market is still on edge awaiting what Iran will do. Because Iran will do something. But what and when? An oil price of 80-something seems like a sensible level until something do happen.
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanStor uppsida i Lappland Guldprospekterings aktie enligt analys
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanBrookfield ska bygga ett AI-datacenter på hela 750 MW i Strängnäs
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanSommaren inleds med sol och varierande elpriser
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanOPEC+ ökar oljeproduktionen trots fallande priser
-

 Nyheter3 veckor sedan
Nyheter3 veckor sedanSilverpriset släpar efter guldets utveckling, har mer uppsida
-

 Analys4 veckor sedan
Analys4 veckor sedanBrent needs to fall to USD 58/b to make cheating unprofitable for Kazakhstan
-

 Nyheter4 veckor sedan
Nyheter4 veckor sedanTradingfirman XTX Markets bygger datacenter i finska Kajana för 1 miljard euro
-

 Nyheter2 veckor sedan
Nyheter2 veckor sedanUppgången i oljepriset planade ut under helgen